Cisco DNA Center Release 2.3.3.0 Announcement
Available Languages
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
We are pleased to announce the general availability of Cisco DNA Center 2.3.3. This release continues our ongoing commitment to innovation and simplicity and delivers compelling business value to help you deploy, maintain, and troubleshoot your network at scale.
Some of the key highlights in this release include:
● Improved network and client performance
◦ Identify and correlate issues using the new global assurance event viewer
◦ Get deeper insights into wireless client behavior with Intel® Connectivity Analytics
◦ View client location in 3D maps for improved visual troubleshooting
● Reduced network operations costs
◦ Improve visibility into software image upgrades and minimize maintenance window time.
◦ Enable self-service BYOD workflows with Cisco UDN, now available in EU and APAC
● Endpoints classified based on MAC address and IP address to target MAC address spoofers
● New FIPS 140-2 certification
AI-enhanced radio resource management simulator
Recent advancements in Cisco DNA Center’s AI-enhanced Radio Resource Management (RRM) have leveraged AI/ML to create a deep understanding of unique wireless environments and make configuration recommendations that improve the performance, coverage, and capacity of the Wi-Fi network.
In this release, we have added a new AI RRM simulator that enables the network operator to get a preview of the impact of RRM changes. When Cisco DNA Center recommends RRM-setting changes, or when the network administrator plans changes to settings such as channel, channel width, or power, the network administrator will be able to:
● Simulate how the RF environment will respond to recommended changes
● Analyze the impact of potential changes during a particular time interval
● View the proposed changes measured in quantified stats, including RRM health, co-channel interference, and utilization
Planned for version 2.3.3.2.
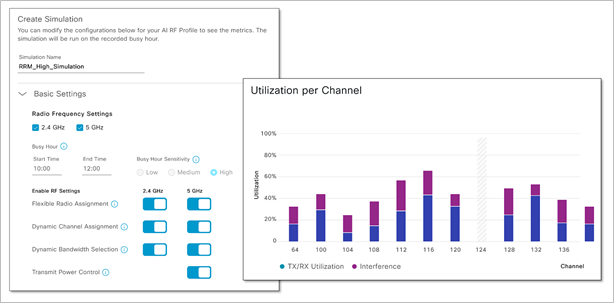
Enhanced RRM simulator
Global assurance event viewer
Network devices can generate huge volumes of data from events related to the network infrastructure and the users on the network. Because of the amount of data, it can be a challenge for network administrators to correlate all the events to understand which ones are relevant.
The new global assurance event viewer gives the network administrator a consolidated view of events from all connected devices, where they can search and filter on the events that are most important to address. The event view allows the user to:
● Troubleshoot network issues and quickly get to the root cause
● Identify the most important range of time to focus on
● Correlate events that happen across multiple devices or users
● Isolate events on specific devices and users
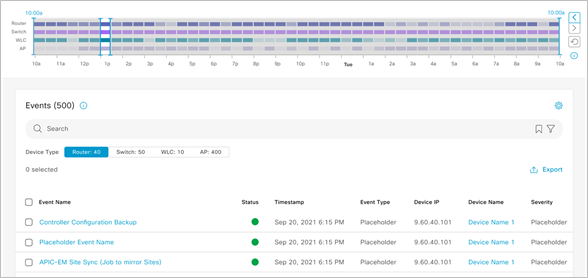
Global assurance event viewer
Intel Connectivity Analytics
When troubleshooting wireless client problems, IT engineers have long faced challenges because different devices have different hardware, software, and drivers. This variability can lead to devices making different roaming decisions in various RF scenarios. Troubleshooting a user’s device and attempting to reproduce a problem has been time-consuming, inefficient, and sometimes not possible.
Cisco continues to expand its partnership with Intel to exclusively provide granular, driver-level insights from wireless clients using the latest Intel chipsets and drivers without the need for installing client-side agents. So now network administrators can easily see important troubleshooting data from the client’s point of view, including device details such as OS and driver versions and RF stats such as the numbers of radios seen and their signals.
Using device behavior insights on issues such as roaming and disconnect reasons and errors, the network administrator can now get to the bottom of wireless client issues, making them more efficient and enabling them to close tickets faster.
To provide insights into the security and performance impacts of unauthorized access points, this new feature set also provides visibility into a device’s attempts to connect to rogue and neighbor BSSIDs.****
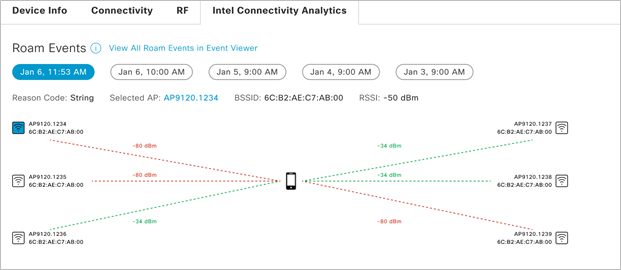
Intel Connectivity Analytics
Cisco Spaces client location in 3D maps
Cisco Wireless 3D Analyzer has revolutionized how wireless network administrators view and interact with the wireless network in their physical spaces. 3D views have redefined wireless network planning and deployment and have given users a new level of coverage validation, ensuring that the actual coverage meets the designed specifications and enhances user experiences.
Starting with this release, Cisco DNA Center is expanding on its 3D troubleshooting capabilities, using connectivity with Cisco Spaces to provide client location on 3D map views. Granular visibility into the wireless coverage where users are helps administrators correlate user location and experience. Workflows to the Client 360 page provide a deeper level of wireless client troubleshooting capabilities.
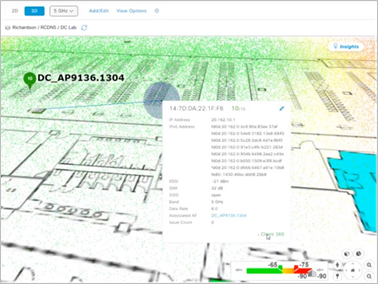
Client location in 3D maps
RF penetration from two floors away in 3D maps
The signal from an access point covers more than just the floor that the access point is deployed on. Sometimes the closest access point to a user is on a floor above or below. In this version of Cisco DNA Center, 3D maps can show the wireless coverage from access points on adjacent floors above and below, extending up to two levels, giving the administrator a better understanding of coverage.
Cisco DNA Center Insights
Cisco DNA Center can now send monthly emails to all users of the system, presenting users with personalized information about their network and curated content from Cisco. Users can opt in to:
● Monitor deployment progress with information about newly onboarded devices
● Track operational efficiency with a summary of issues resolved
● Check security compliance with Software Image Management updates
● Keep informed of upcoming Cisco events
● Stay on top of new Cisco® product releases
● Improve IT success with insights into new product capabilities
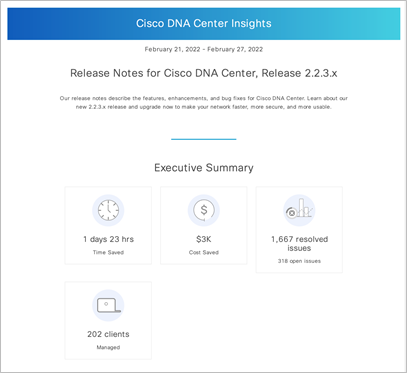
Cisco DNA Center Insights
Intelligent capture enhancements
When a Cisco DNA Center user wants to take an intelligent packet capture, they want the data to be available as quickly as possible, and without unnecessary burden on the network. In this version, when the network administrator runs a full, partial, or scheduled capture, they will be able to choose which wireless LAN controllers (WLCs) to run a capture on. The capture will be run just on the specified WLCs, reducing load on the network and generating the capture much more quickly than was previously possible.
NetOps with Cisco DNA automation
Access point provisioning enhancements
Network administrators who need to broadcast separate SSIDs on different sections of a floor can now easily do it without breaking the AP group into multiple floors. To do this, they can add access points to AP zones, which are logical groups comprising device tags, SSIDs, and RF profiles in a wireless network profile.
Additionally, customers can now create custom policy tag names to be used during AP provisioning instead of Cisco DNA Center auto-generating them. Combining custom policy tags with AP zones allows customers to broadcast different SSIDs on the same floor, removing the complexity of creating multiple floors.
6Ghz manual radio configuration override
For cases when users want to override radio resource management (RRM) configuration on 6Ghz radios, users can now manually configure those settings, which include administrative status, channel, and power.
Reduced maintenance window for software image upgrades
When IT does upgrades of network infrastructure at scale, they want the network downtime to be minimal. Cisco DNA Center 2.3.3 helps by separating the parts of the upgrade process that impact the network from the parts that don’t. So now the user can distribute the files to all the target devices while they are still running and perform the image activation later.
Additionally, this version makes managing and troubleshooting upgrades faster and easier, with step-by-step details of both distribution and activation phases as they happen. Now the user has detailed information on the entire upgrade process as it happens.
Enhanced UDN administration and troubleshooting
With Cisco DNA Center 2.3.3, we are now expanding the reach of Cisco’s User Defined Network (UDN) solution by launching UDN Cloud in Germany and Singapore. This offers customers in EMEA and APJC increased flexibility and scale, along with improved data resiliency, compliance, and security.
Additionally, we have added new capabilities to the UDN Cloud portal such as:
● Endpoint management: Allowing network administrators to add, remove, or move end- user devices to UDN rooms as required
● Summary page view: Allowing network administrators to have a bird’s-eye view where UDN is deployed, including a summary of UDN-enabled SSIDs, endpoint counts, and UDN-enabled RLAN ports
● UDN room limit: Allowing network administrators to restrict the number of devices in a UDN room and limit the devices a user can register within a UDN room, thus reducing unwanted costs of deploying unlimited devices
This helps network administrators to improve UDN administration and troubleshooting.
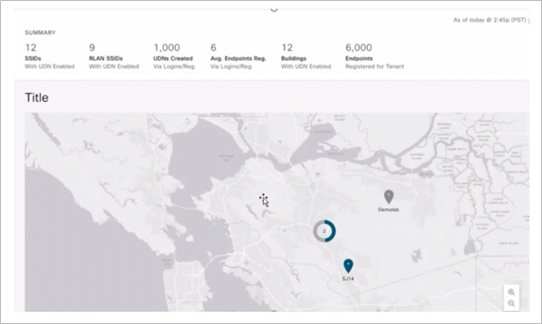
UDN summary page
Enhanced “learn device configuration” workflow
This release makes it easier than ever to onboard wireless network devices without risking changes to the device’s existing configuration. A new guided workflow learns the intent of the configuration from wireless LAN controllers (WLCs) and access points, and creates reusable wireless design elements such as SSIDs, RF profiles, advanced model configuration templates, and CLI templates. It also learns policy tags, AAA-override VLAN details, remote teleworker details, and mesh settings.
As the network scales to support more sites and users, the network operator can reuse the learned configuration policies to provision new wireless devices with speed and consistency.
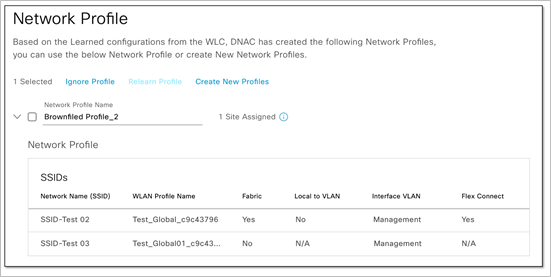
Network profile
Flexible AP refresh workflow
A refresh of a large-scale wireless network can be time-consuming and labor intensive. Cisco DNA Center’s AP refresh workflow is designed to guide customers through the process and is adding two new features to further improve IT’s operational efficiency during a wireless network refresh.
First, the user can now refresh access points even if they hadn’t been provisioned by Cisco DNA Center. This expands the scope of the devices that are eligible to be refreshed.
Additionally, the new access points can now join any WLC, rather than having the restriction of needing to join the same WLC as the previous access points.
Detect connections to low-reputation sites via Talos
Endpoints that attempt to access weak, compromised, or malicious sites pose a significant security risk. Now, Cisco DNA Center connects with the Talos® IP and Domain Reputation Center to detect when endpoints attempt to access sites with an untrusted reputation. When these threats are detected, the network administrator can then remediate manually or automatically, reducing the risk.
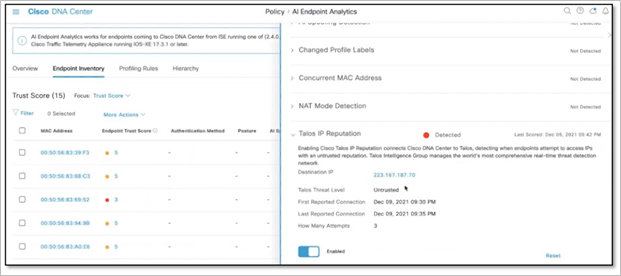
Endpoints remediation
IP-based endpoint classification
Malicious actors who spoof MAC addresses to avoid detection are a dangerous threat. Taking action against them without also affecting the spoofed devices can be especially challenging. Now, the network operator can define policy based on both the MAC address and the NAD IP, enhancing security and keeping IT-sanctioned devices operating normally.
Extended node onboarding with Cisco DNA Essentials license
Customers want to migrate their access layer to a fabric without additional licensing expenses. In previous versions, it was not possible to integrate existing Layer-2 switching networks into a fabric with Cisco DNA Essentials licenses. Now customers can onboard new or existing Layer-2 switches with Cisco DNA Essentials licenses into an SD-Access fabric, maintaining their existing network blueprint at the access layer.
DevOps: Innovation and integration
Cisco DNA Center Dashboard for Splunk Enterprise
The Cisco DNA Center Dashboard application for Splunk Enterprise integrates with Cisco DNA Center to offer a single view of network status, client health, application visibility, and more. This offers customers an easy way to get started integrating Cisco DNA Center and Splunk. It also gives users a way to view long-term network trends.
The Cisco DNA Center Dashboard application will be available soon for download on Splunkbase.
Cisco DNA Center Dashboard for Splunk Enterprise
SD-Access APIs
Customers can now use custom and third-party solutions to automate SDA orchestration through SD-Access APIs. This will reduce the overall time it takes to create, change, and delete fabrics while delivering consistent outcomes at each fabric configuration step.
Enhancements to rogue access point APIs
Developers can now use APIs to edit MAC addresses on the allowed list so they can control which nearby access points are considered friendly. Also, a new API allows applications to get threat types and threat levels defined by aWIPS, Cisco’s Adaptive Wireless Intrusion Prevention System.
Deployment-ready with Cisco DNA Platform
FIPS support
When data is shared using weak or deprecated ciphers, that data is at risk of being decrypted by malicious actors. This version of Cisco DNA Center introduces support for FIPS 140-2-compliant cryptography modules, ensuring that only strong NIST-approved ciphers are used, and enabling deployment in security-conscious verticals such as the public sector, finance, and healthcare.
During installation, the administrator can choose to enable FIPS, which will ensure only NIST-approved ciphers are used for data encryption.
For more details, see the Cisco DNA Center FIPS Compliance Letter.
Scale increase for sites and devices
Cisco DNA Center now supports up to 6000 sites.
Additionally, in a 3-node cluster, the system can still support up to 18,000 access points (plus 6000 network devices) or up to 10,000 network devices (plus 14,000 access points) for a total of 24,000 devices.
● Release notes for Cisco DNA Center 2.3.3.0
● Cisco DNA Center compatibility matrix