Configuring SNMP using CLI
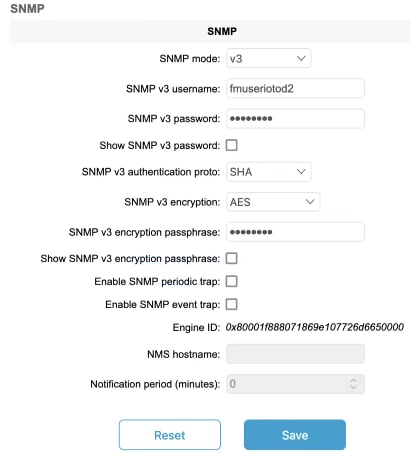
URWB software for network management functionalities uses SNMP applications. The SNMP implementation supports queries (solicited) and traps (unsolicited). If you enable SNMP traps, specify the server address to which the monitoring information is sent.
 Note |
The same SNMP configuration must be set for all gateways in the network. |
To configure SNMP, use the following CLI commands:
 Note |
|
|
Purpose |
Command or Action |
||
|---|---|---|---|
|
To enable or disable SNMP functionality |
|
||
|
To specify the SNMP protocol version |
|
||
|
To specify the SNMP v2c community ID number (SNMP v2c) |
|
||
|
To specify the SNMP v3 username (SNMP v3) |
|
||
|
To specify the SNMP v3 user password (SNMP v3) |
|
||
|
To specify the SNMP v3 authentication protocol (SNMP v3) |
|
||
|
To specify the SNMP v3 encryption protocol (SNMP v3) |
|
||
|
To specify the SNMP v3 encryption passphrase (SNMP v3) |
|
||
|
To specify the SNMP periodic trap settings |
|
||
|
To specify the notification trap period for periodic SNMP traps |
|
||
|
To enable or disable SNMP event traps |
|
||
|
To specify the SNMP NMS hostname or IP address |
|
||
|
To disable SNMP configuration |
|
|
Purpose |
Command or Action |
|---|---|
|
To configure SNMP v2 |
|
|
To configure SNMP v3 |
|




 Feedback
Feedback