Limitations
-
gRPC is not supported over the GCC interface. Therefore, Open Config and streaming telemetry are not supported over the GCC interface.
-
Only the Tx and Rx packet count information are available in GCC statistics.
-
The devices can be remotely managed over the GCC interface only when they are connected to the management network through GCC. Therefore, initial provisioning and bringing up of the GCC interface must be performed either through the console or management Ethernet interface.
-
These headless or high availability events at the intermediate nodes may affect remote node management of subsequent nodes:
-
Reload of the route processor
-
Reload of IOS XR
-
Restart of the driver process
-
-
IP fragmentation is not supported on GCC interface for the SCP protocol. As a workaround, you can apply any of the following configurations to limit the maximum packet size below the fragmentation limit (1454 bytes):
-
Use the tcp mss <maximum segment size> command (for example, tcp mss 1200 ) in the global configuration mode. The maximum segment limit is applied to all interfaces.
-
Use the ipv4 mtu <MTU size> command in the interface configuration mode. The MTU size is applied only to the specified interface.
-
-
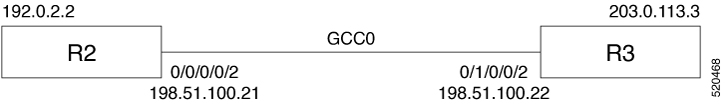
The Coherent DSP controller supports the GCC0 interface on the QXP card.
-
The GCC0 speed on the QXP card is 7.7 Mbps.


 Feedback
Feedback