Model-driven CLI features for data model visualization
A model-driven CLI feature is a programmability capability in Cisco IOS XR software that
-
enables users to display YANG data model structures and operational data directly via CLI commands,
-
provides configuration and operational output in both XML and JSON formats for easier parsing and automation, and
-
introduces specialized CLI commands that help transition between traditional CLI and model-driven approaches.
|
Feature Name |
Release Information |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Model-driven CLI to Show YANG Operational Data |
Release 7.3.2 |
This feature enables you to use a traditional CLI command to display YANG data model structures on the router console and also obtain operational data from the router in JSON or XML formats. The functionality helps you transition smoothly between CLI and YANG models, easing data retrieval from your router and network. This feature introduces the show yang operational command. |
|
Model-driven CLI to Show YANG Operational Data |
Release 25.2.1 |
This feature is deprecated. |
Cisco IOS XR Software provides a rich set of show commands and data models to access data from the router and network. Show commands present unstructured data, while data models provide structured data in XML or JSON formats; however, both methods can show different views. The model-driven CLI feature addresses adoption challenges by allowing operators to use the familiar CLI while accessing structured, model-driven output. This enables easier integration with parsing scripts and automation tools.
Structure of data model
The structure of a data model organizes configuration and operational data in a hierarchical format. Each data model consists of these primary components:
-
Model: The highest-level YANG file that defines a data schema e.g.,
ietf-interfaces.yang. -
Module: A logical collection of related definitions within the model e.g.,
ietf-interfaces. -
Container: A grouping node that organizes related nodes together e.g.,
interfaces,interfaces-state. -
List/Node: An array or list element within a container, often representing multiple items e.g.,
interface* [name]. -
Leaf: A single value node containing configuration or state data e.g.,
name,description,type,enabled,admin-status.
|
Component |
Description |
Example |
|---|---|---|
|
Model |
YANG file containing schema definitions |
ietf-interfaces.yang |
|
Module |
Group of related schema nodes |
ietf-interfaces |
|
Container |
Grouping node for related lists and leaves |
interfaces, interfaces-state |
|
List/Node |
Multiple entries identified by unique key |
interface* [name] |
|
Leaf |
Single data value node under a container or list |
name, type, enabled, etc.
|
CLI and navigation notes:
-
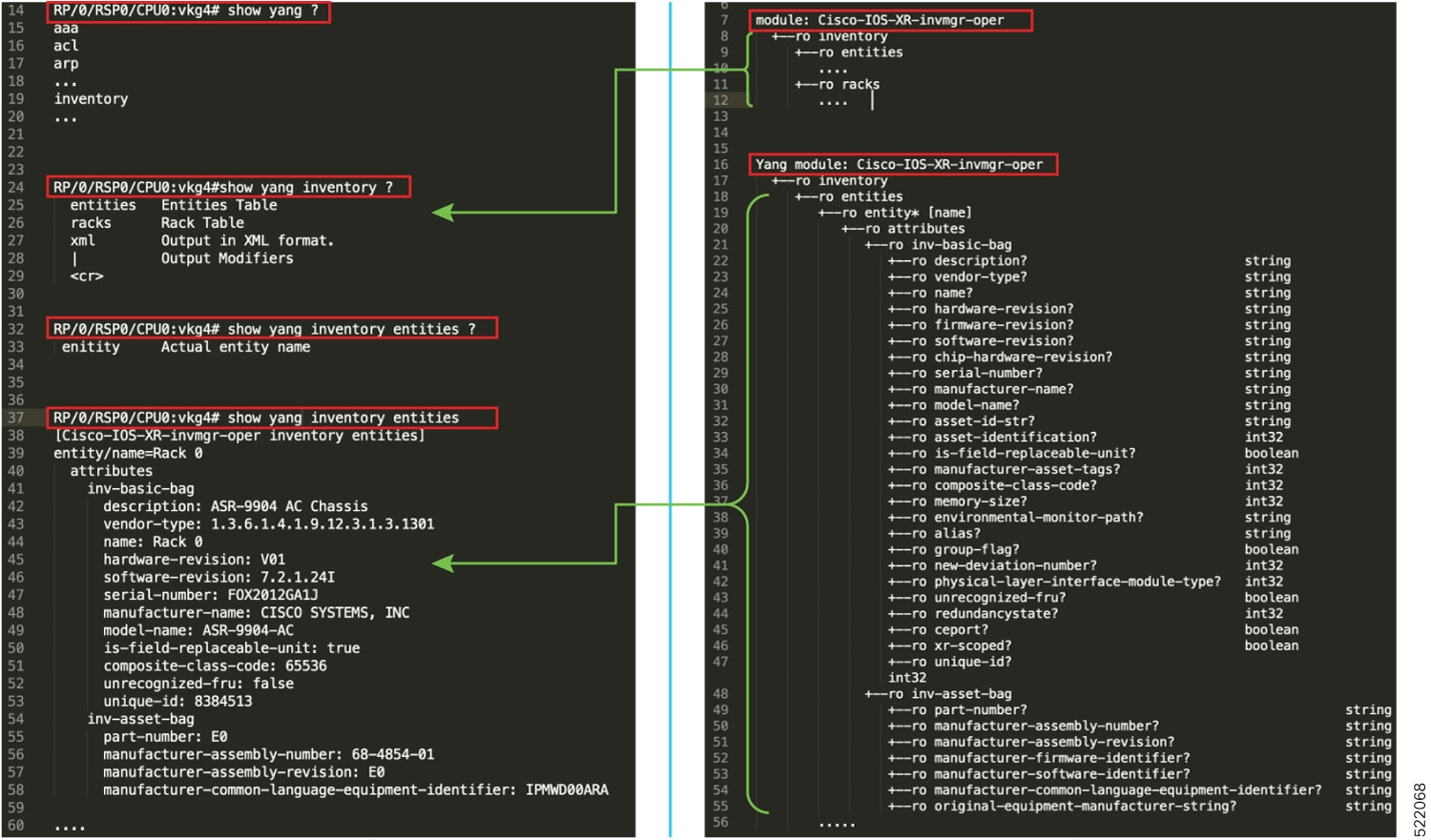
Use the show yang operational command to explore down to the leaf level in a data model, similar to navigating hierarchical data.
-
Data model structure guides how CLI outputs and configurations map to YANG-defined nodes.
The image show a mapping between CLI and data model, and how the structured data is displayed on the console.
 Feedback
Feedback