Exec scripts
Exec scripts are on-box scripts that
-
automate device configurations throughout the network,
-
are written in Python using libraries provided by Cisco with the base package, and
-
execute within the Cisco IOS XR operating system.
-
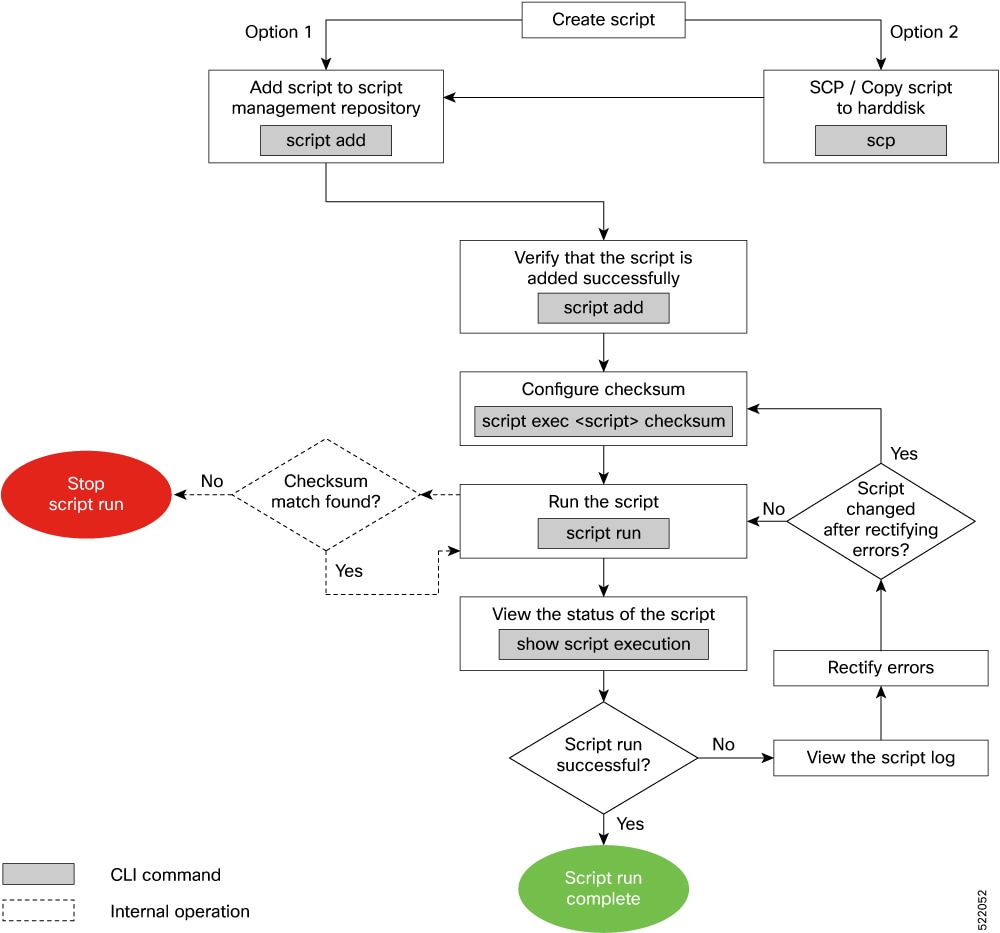
A script management repository on the router manages exec scripts and is replicated on both route processors (RPs).
-
In IOS XR, AAA authorization determines user permissions required to run exec scripts; root privileges are necessary.
 Note |
This chapter does not delve into creating Python scripts, but assumes that you have basic understanding of Python programming language. This section will walk you through the process involved in deploying and using the scripts on the router. |
 Feedback
Feedback