Field Notice: FN74345 - Cisco On-Premises Calling Products: Impact on Secure Communication Due to Upcoming Changes to TLS certificates Issued by Public Certificate Authorities with Client Authentication EKU, Starting May 2026 - Workaround Provided
Available Languages
Notice
THIS FIELD NOTICE IS PROVIDED ON AN "AS IS" BASIS AND DOES NOT IMPLY ANY KIND OF GUARANTEE OR WARRANTY, INCLUDING THE WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY. YOUR USE OF THE INFORMATION ON THE FIELD NOTICE OR MATERIALS LINKED FROM THE FIELD NOTICE IS AT YOUR OWN RISK. CISCO RESERVES THE RIGHT TO CHANGE OR UPDATE THIS FIELD NOTICE AT ANY TIME.
Products Affected
| Affected Software Product | Affected Release | Affected Release Number | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| Emergency Responder | - | All releases are affected. | |
| Unified Communications Manager | - | All releases are affected including Session Management Edition | |
| Unified Communications Manager IM and Presence Service | - | All releases are affected. | |
| Unity Connection | - | All releases are affected. |
Defect Information
| Defect ID | Headline |
| CSCws03463 | Support for separate server and client Certificate for CUC |
| CSCws02424 | Support for Separate Server and Client Certificate Support for CUCM |
| CSCws03437 | Support for Separate Server and Client Certificate Support for IM&P |
| CSCws03022 | Support for separate server and client Certificate for CER |
Problem Description
Effective June 2026, the Chrome Root Program Policy will restrict Root certificate authority (CA) certificates that are included in the Chrome Root Store, phasing out multi-purpose roots to align all public-key infrastructure (PKI) hierarchies to serve only TLS server authentication use cases.
This constraint includes Root CAs that only assert an Extended Key Usage (EKU) for Server Authentication (id-kp-serverAuth). As a result, certificates issued by Public Root CA with only Server Authentication EKU will not be valid for client authentication in mutual TLS (mTLS) setups.
Background
To meet Chrome Root Program Policy requirements, effective June 2026, Public Root CAs that are part of the Google Chrome Root Store will be restricted to Server Authentication EKU only, sunsetting the Client Authentication EKU from it. As a response, public CA servers will stop issuing Client Authentication EKU certifications from May 2026.
Certificates must include ONLY Server Authentication EKU to maintain trust from the Google Chrome browser. Including the Client Authentication EKU in these certificates will be prohibited.
Although certain Public Root CAs continue to issue certificates containing the Client Authentication EKU, they will eventually be removed from the Chrome Root Store.
Certificates that are used for mTLS connections in Cisco Unified Communication devices are expected to include both Server and Client Authentication EKUs. Customers could choose to have these certificates from Public CA providers.
Server Authentication EKU-only certificates that are provided by Public Root CAs can "break" certificate validity, leading to potential authentication issues in Cisco Unified Communication devices and affecting proper functionality.
For more details, see Chrome Root Program Policy.
Problem Symptom
Cisco on-premises calling products can be affected by potential authentication issues and impacted functionality due to broken certificate validity that is caused by using Server Authentication-only certificates provided by Public Root CAs.
The following list shows examples of certificates that are used for mTLS connections in these Cisco on-premises calling products:
- Unified Communication Manager/Session Management Edition (Unified CM/Unified CM SME): Tomcat, TVS, Call Manager, IPSec
- Unified Communication Manager IM & Presence Service (Unified CM IM&P), formerly Cisco Unified Presence (CUP): cup-xmpp-s2s
- Emergency Responder: Tomcat
- Unity Connection: Tomcat
The following examples are of certificates that are used for different mTLS connections:
- Tomcat: Connections with external servers like Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP), filebeat, logslash server, and SIP Oauth over MRA
- Call Manager: SIP Trunk connections and internode / inter-cluster connections
- TVS: Online-CAPF (Certificate Authority Proxy Function) connection
- IPSec: IPSec connections with other Cisco Unified CM nodes and Gateways
- CUP: Secure SIP connections with Cisco Unified CM and third party clients
- CUP-XMPP-S2S: Extensible Messaging and Presence Protocol (XMPP) federation
Workaround/Solution
Before considering workaround and solution options, audit current certificates. Prepare an inventory of all public TLS certificates to identify which certificates contain the Client Authentication EKU.
Workaround
Administrators can choose from one of the following workaround options.
Option 1: Switch to Public Root CAs that provide combined EKU certificates
Some Public Root CAs, such as DigiCert and IdenTrust, issue certificates with combined EKU from an alternative root, which may not be included in the Chrome browser’s trust store. Coordinate with your CA provider to check the availability of such certificates, and, before deploying them, ensure that both the server presenting the certificate and the clients consuming it trust the corresponding Root CA.
This approach alleviates the need to upgrade server software to mitigate sunsetting of Client Authentication EKU enforced by the Google Chrome Root Program Policy.
The following table shows examples of Public Root CAs and EKU types:
CA Vendor EKU Type Root CA Issuing/Sub CA IdenTrust clientAuth + serverAuth IdenTrust Public Sector Root CA 1 IdenTrust Public Sector Server CA 1 IdenTrust clientAuth IdenTrust Public Sector Root CA 1 TrustID RSA ClientAuth CA 2 IdenTrust serverAuth (browser trusted) IdenTrust Commercial Root CA 1 HydrantID Server CA O1 DigiCert clientAuth + serverAuth DigiCert Assured ID Root G2 DigiCert Assured ID CA G2 DigiCert clientAuth DigiCert Assured ID Root G2 DigiCert Assured ID Client CA G2 DigiCert serverAuth (browser trusted) DigiCert Global Root G2 DigiCert Global G2 TLS RSA SHA256
Option 2: Renew current certificates to extend validity
Certificates that were issued by Public Root CAs before May 2026 that have both Server and Client Authentication EKU will continue to be honored until their term expires. However, it is best to renew combined EKU certificates before policy sunsetting occurs.
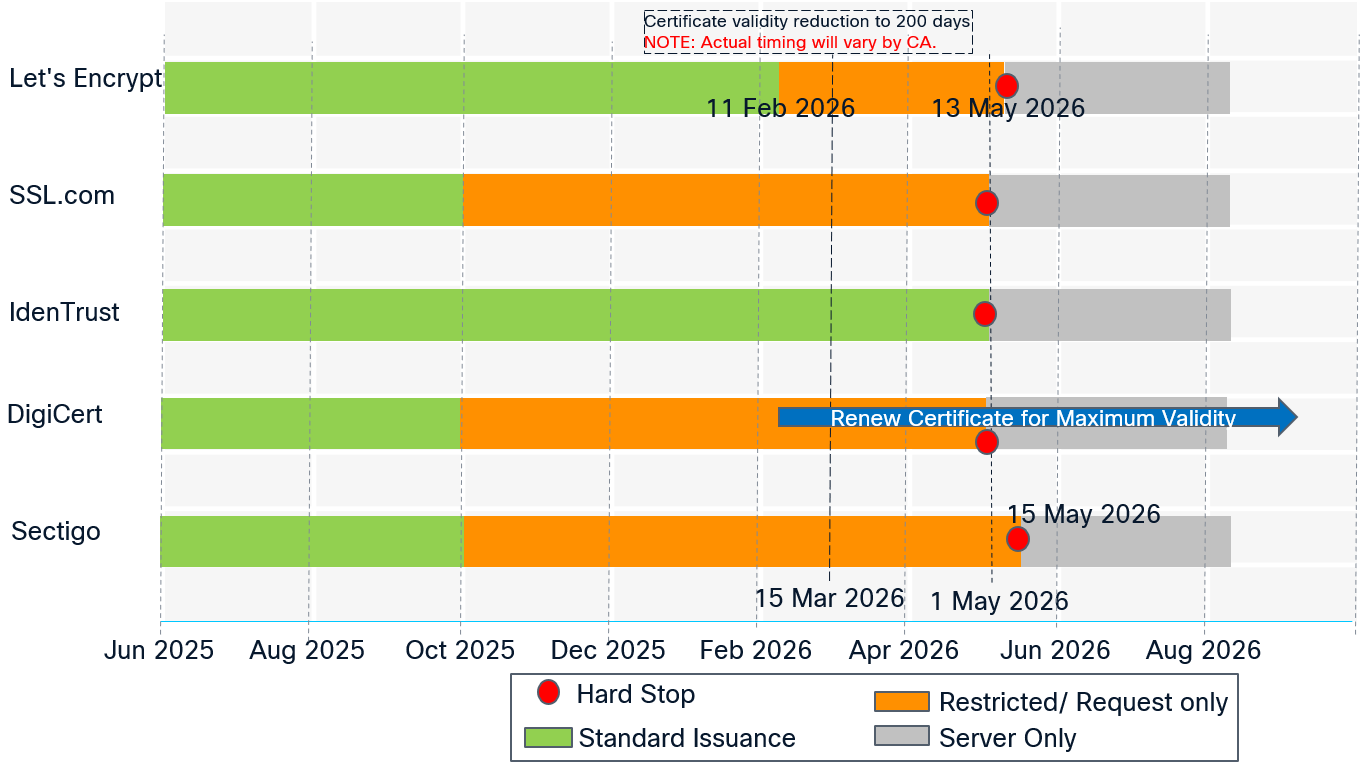
For maximum certificate validity, plan to renew certificates before March 15, 2026, after which Public CA-issued certificates will be valid only for 200 days. Public CA policy and implementation dates may vary. Check with your CA and plan your certificate renewal accordingly.
Note: Some Public CAs have stopped issuing combined EKU certificates and may not provide one by default. To generate a certificate with a combined EKU, work with Public CAs, which may provide special profiles.
Upgrade your servers after the solution mentioned below is available.
The following image shows the Client Authentication EKU depreciation timeline (subject to change):
To manage certificates for your Cisco Collaboration product, see the steps in the following admin guides:
Cisco Unified Communication Manager Certificate Regeneration
Cisco Emergency Responder 15 Certificate Management
Cisco Emergency Responder 14 Certificate Management
Cisco Unity Connection 15 Security Administration
Cisco Unity Connection 14 Security Administration
Option 3: Evaluate and Migrate to Alternatives
Evaluate feasibility of transition to a private PKI, and then set up a private CA to issue single certificates with combined EKU (Server and Client certificates with the required EKUs).
Before issuing or deploying a certificate, ensure that both the server presenting the certificate and all clients consuming it trust the corresponding Root CA. Using this approach will alleviate the need to upgrade server software to mitigate sunsetting of Client Authentication EKU enforced by the Google Chrome Root Policy.
Solution
The following product enhancements will be implemented in the fixed release that is described in the table in this section:
- Segregation of Client and Server certificates: This will enable support for two separate certificates on the same interface, such as Tomcat server certificates (with Server Authentication EKU) and Tomcat client certificate (with Client Authentication EKU) to facilitate mTLS connections. Customers must arrange for Client Authentication EKU certificates from either private PKI or alternate Root CAs.
- Options for administrators to disable Client Authentication EKU checks: This will allow on-premises calling products to ignore EKU from remote peers (client) that are requesting a connection with Server Authentication EKU-only certificate. This option will also allow on-premises calling products to (re)use the Server Authentication EKU-only certificate as a client certificate. Note: The remote peer will also have to support a similar “Ignore Client Authentication EKU” model.
To segregate Server and Client certificates or to use the Ignore EKU option, upgrade to the fixed release as shown in the following table:
| Product | Affected Release | Fixed Release |
|---|---|---|
| Emergency Responder Unified CM Unified CM IM&P Unified CM SME Unity Connection Unity Connection Survivable Remote Site Voicemail (SRSV) |
14 14 SU1 14 SU2 14 SU3 14 SU4 15 15 SU1 15 SU2 15 SU3a 15 SU4 |
15 SU5 (future release) |
Additional Information
This issue also affects Cisco Expressway and Cisco Unified Border Element (CUBE). For information, see the following field notices:
Revision History
| Version | Description | Section | Date |
| 1.1 | Updated information to explain that public CA servers will stop issuing Client Authentication EKU certifications from May 2026. | Background | 2026-FEB-03 |
| 1.0 | Initial Release | — | 2026-JAN-30 |
For More Information
For further assistance or for more information about this field notice, contact the Cisco Technical Assistance Center (TAC) using one of the following methods:
Receive Email Notification About New Field Notices
To receive email updates about Field Notices (reliability and safety issues), Security Advisories (network security issues), and end-of-life announcements for specific Cisco products, set up a profile in My Notifications.
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)
This Document Applies to These Products
- Emergency Responder 14
- Emergency Responder 15
- Unified Communications Manager (CallManager)
- Unified Communications Manager IM and Presence Service 15
- Unified Communications Manager IM and Presence Service Version 14
- Unified Communications Manager Version 14
- Unified Communications Manager Version 15
- Unity Connection Version 14
- Unity Connection Version 15
Unleash the Power of TAC's Virtual Assistance
 Feedback
Feedback