Release Notes for UCC SMF, Release 2026.01.0
Available Languages
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
- US/Canada 800-553-2447
- Worldwide Support Phone Numbers
- All Tools
 Feedback
Feedback
Ultra Cloud Core - Session Management Function, Release 2026.01.0
Ultra Cloud Core - Session Management Function, Release 2026.01.0
This Release Notes identifies changes and issues related to the software release of 5G Converged Core Session Management Function (SMF).
The key highlights of this release include:
· Comprehensive SGSN PDN modification and handover support: This enhancement ensures seamless and robust mobility for subscribers across various 2G/3G/4G network elements, improving service continuity during complex handover scenarios.
· Validated FQDN configuration and DNS resolution: Thorough validation of FQDN configuration and DNS resolution on the SMF for SCP and NRF interfaces enhances interoperability and reliability of network communication, simplifying integration and management.
· Enhanced service communication with SCP Model-C: This feature provides greater flexibility and efficiency in accessing network services by enabling intelligent routing based on location and capacity, leading to optimized communication, improved performance, and better resource utilization.
· Dynamic PCF-based CHF selection for SMF: SMF can now dynamically select the Charging Function (CHF) based on charging information from PCF, improving flexibility and accuracy in charging for both home and roaming subscribers.
· Key SMF enhancements for QoS and charging: Introduces support for default QoS flow indication to dynamically bind PCC rules and includes nFFQDN IE in charging messages, enhancing QoS management and subscriber charging accuracy.
· Robust mTLS support and validation on SMF: Thorough validation of Mutual TLS (mTLS) functionality ensures secure communication and enhanced data integrity for SMF operations, strengthening overall network security.
· Optimized 2G and 3G support on SBA interface: This feature allows network operators to suppress Network Requested Update PDP Context (NRUPC) for 2G/3G sessions over the SBA interface, optimizing signaling and resource usage.
· Dynamic QoS negotiation for GTPv1 SGSN: SMF now supports QoS negotiation during SGSN-initiated Update PDP Context procedures, enabling effective management and enforcement of QoS for 2G and 3G calls within the Converged Core architecture.
· Improved 2G and 3G procedure monitoring: New and enhanced metrics for 2G/3G mobility procedures over GTPv1 and GTPv2 interfaces, along with new EDR attributes to support session modify procedure across 2G, 3G, 4G, and 5G RAT types.
· Event exposure service for UE reachability: Enhances Reduced Capability (RedCap) functionality by allowing the SMF to subscribe to AMF notifications for UE reachability, optimizing resource usage for low-capability devices.
· Enhanced session management with 5G slice identifiers: Enables operators to collect and display session statistics and execute show/clear commands based on 5G network slice identifiers (SST and SD), offering greater flexibility and granularity in network operations.
· vSMF optimization for roaming PDU session modification: vSMF now suppresses location-only PDU session modification requests to the hSMF in roaming scenarios, optimizing N16 signaling.
· Immediate usage reporting on rulebase change: This enhancement enables the SMF to immediately report usage to the CHF upon rulebase changes during handovers or policy modifications, improving charging accuracy and compliance with dynamic policies.
· Granular session clearing enhancements: show subscriber, show subscriber count, and clear subscriber commands are enhanced with options for DNN-Profile and Subscriber-ID Prefixes, providing more flexible and granular control over subscriber session management.
· Real-time location reporting for voice call setup: SMF now supports fetching real-time user location from AMF (5G) or SGW/MME (4G) and notifying PCF before 5G SA or 4G voice call establishment, ensuring accurate location reporting and seamless call setup.
· Subscriber user-name format enhancement for RADIUS on SMF: SMF now supports sending the RADIUS User-Name AVP in the MSISDN@APN format via the new custom1 dictionary option in the RADIUS server-group configuration. The default behavior remains unchanged unless this option is explicitly set, providing greater flexibility for integration with external AAA systems.
For more information about Ultra Cloud Core - Session Management Function, see the Related resources section.
Release lifecycle milestones
The following table provides EoL milestones for Cisco UCC SMF software:
Table 1. EoL milestone information for UCC SMF, Release 2026.01.0
| Milestone |
Date |
| First Customer Ship (FCS) |
30-Jan-2026 |
| End of Life (EoL) |
30-Jan-2026 |
| End of Software Maintenance (EoSM) |
31-July-2027 |
| End of Vulnerability and Security Support (EoVSS) |
31-July-2027 |
| Last Date of Support (LDoS) |
31-July-2028 |
These milestones and the intervals between them are defined in the Cisco Ultra Cloud Core (UCC) Software Release Lifecycle Product Bulletin available on cisco.com.
This section provides a brief description of the new software features introduced in this release.
Table 2. New software features for UCC SMF, Release 2026.01.0
| Product impact |
Feature |
Description |
| Software Reliability |
This enhancement provides comprehensive SGSN PDN modification and handover support, including intra-SGSN and inter-SGSN, SGSN-to-S4-SGSN and MME handovers for complex back-to-back scenarios. |
|
| Ease of use |
The FQDN configuration and DNS resolution functionality on the SMF has been thoroughly validated and qualified in this release for SCP and NRF interfaces. |
|
| Upgrade |
Service Communication Proxy (SCP) model-C for peer node communication |
This feature provides enhanced flexibility and efficiency when accessing network services. By allowing consumers to select the most suitable network function instances, this approach supports optimized communication and service delivery. Additionally, SMF ensures requests are intelligently routed based on parameters like location and capacity, leading to improved performance, resource utilization, and overall network experience. Command introduced: nf-selection-model nf_model_priority [ nrf-query-scp ]— Used for selection of SCP model-C for NF peer communication. Default Setting: Disabled – Configuration required to enable |
| Upgrade |
You can now dynamically select the Charging Function (CHF) in SMF based on charging Information received from PCF, improving flexibility for both home and roaming subscribers. SMF uses CHF addresses or instance IDs sent by PCF during SM Policy association to choose the correct CHF. Commands introduced: nf-selection-model nf_model_priority [ nrf-query-peer-input | nrf-query-peer-input-scp | local-scp ] · nrf-query-peer-input and nrf-query-peer-input-scp —Support CHF selection using peer-input (ChargingInformation) received from PCF. · local-scp — Supports Model-C for locally configured CHF. This command also supports sending offline CHF requests via SCP. Default Setting: Disabled – Configuration required to enable. |
|
| Upgrade |
Enhancements in SMF:
|
This feature introduces these enhancements in SMF: · Default QoS flow indication support: This feature binds a dynamic PCC rule to the default bearer, when the SMF receives defQosFlowIndication IE as true from PCF. · nFFQDN IE in the nfConsumerIdentification message: This feature introduces nFFQDN IE in the nfConsumerIdentification message that SMF sends to the CHF for subscriber charging. · 2G and 3G support of dynamic ADC rules: This feature allows the 2G and 3G sessions to support dynamic ADC rule. |
| Ease of use |
The Mutual TLS (mTLS) functionality on the SMF has been thoroughly validated and qualified in this release. For comprehensive details, see the Interfaces Support chapter in the SMF Configuration and Administration Guide. |
|
| Upgrade |
This feature allows network operators to suppress Network Requested Update PDP Context (NRUPC) towards SGSN for 2G and 3G sessions over SBA interface. Command introduced: [ no ] deactivate-features 2g-3g-nrupc-This command is configured under the DNN profile. Default Settings: Disabled— Configuration required to enable. |
|
| Software Reliability |
This feature allows the network operator to manage and enforce QoS for 2G and 3G calls within the Converged Core architecture. |
|
| Upgrade |
This feature introduces these enhancements to support 2G and 3G mobility procedures in SMF: · Metrics to handle the events over GTPv1 and GTPv2 interfaces. · EDR attributes to support Session modify event for 2G, 3G, 4G, and 5G RAT types. · Extending the support of immediateReport indication in the N10 Subscription to Notification message to 2G and 3G. Commands introduced: subscription { local | notify-immediate } rat-type { nr | eutra | wlan | gera | utra } This CLI command is configured under the DNN profile. Default Setting: Disabled—Configuration required to enable. |
|
| Software Reliability |
This feature enhances the Reduced Capability functionality by allowing the SMF to subscribe to the event exposure notification from AMF. The event exposure notification informs the SMF when the RedCap UE is reachable. Commands enhanced: · service name type namf-evts-Subscribes to AMF's event exposure service. · message type AmfCreateEvtSubscription-Configures the failure handling action for AmfCreateEvtSubscription message type. · actiondef <actdef_name> priority <priority_val> action subscribe-ue-reachability-Enables UE reachability subscription. Default Settings: Disabled-Configuration required to enable. |
|
| Software Reliability |
Enhanced session management and statistics based on 5G network slice identifiers (SST/SD) |
This enhancement enables the SMF to collect and display session statistics, as well as execute show and clear commands, based on 5G network slice identifiers (SST and SD values). The CLI commands are updated to allow operators to manage sessions per slice, providing greater flexibility and granularity in network operations. Commands introduced: · show subscriber nf-service smf snssai starts-with <sstvalue> - Displays the subscriber sessions by matching the SST component with a specified <sstvalue> · clear subscriber nf-service smf snssai starts-with <sstvalue> - Clears the subscriber sessions by matching the SST component with a specified <sstvalue> Default Settings: Disabled-Configuration required to enable. |
| Software Reliability |
vSMF support for suppressing PDU session modification requests to hSMF |
This feature enables vSMF to suppress location-only PDU session modification requests to the hSMF in roaming scenarios, optimizing N16 signalling and aligning 5G with LTE networks. Command introduced: suppress-uli-only-reporting-on-n16 Default Settings: Disabled-Configuration required to enable. |
| Software Reliability |
SMF enhancement for immediate usage reporting on rulebase (RB) change |
This enhancement enables the SMF to immediately report usage to the CHF whenever a rulebase change occurs during handovers or policy modifications. A new configuration option is introduced to trigger usage reporting on rulebase changes, improving charging accuracy and compliance with dynamic policy changes. Commands introduced: · profile network-element chf nfprf-chf1 · report-trigger [management-intervention] condition [rb-change] exit Default Settings: Disabled-Configuration required to enable. |
| Ease of Use |
Session clearing enhancements |
With this release, the show subscriber, show subscriber count, and clear subscriber commands are enhanced and have additional configurable options for: · DNN-Profile: These options display subscriber session summary, number of subscriber sessions matched or clear the subscriber sessions based on dnn-profile. · Subscriber-ID Prefix: These options display subscriber session summary, number of subscriber sessions matched or clear the subscriber sessions based on subscriber-ID prefixes, which can be any one of the following options: IMSI, MSISDN, IMEI. |
| Software Reliability |
Real-time location reporting for 5G SA and 4G voice call setup |
SMF now supports fetching real-time user location and notifying the Policy Network Function (PCF) before a 5G SA or 4G voice call is established. The location is fetched from AMF in 5G and from SGW/MME in 4G. This feature allows the SMF to retrieve the latest user location from the AMF using the Namf_EventExposure service. It installs a new rule on the default bearer/flow for location fetching and then moves this rule to the voice bearer/flow for subsequent voice call setup, ensuring accurate location reporting and seamless voice call establishment. |
| Ease of Use |
SMF now supports sending the RADIUS User-Name AVP in the MSISDN@APN format through the new custom1 dictionary option under the RADIUS server-group configuration. Existing behavior remains unchanged unless this option is explicitly configured. |
This section provides a brief description of the behavior changes introduced in this release.
Table 3. Behavior changes for UCC SMF, Release 2026.01.0
| Description |
Behavior changes |
| PCF-initiated and UE-initiated modifications during 4G to 5G handover |
Previous Behavior: During a 4G to 5G handover, if both a PCF-initiated modification and a UE-initiated modification were received, the PCF-initiated modification was not handled. New Behavior: Now, when both PCF-initiated and UE-initiated modifications are received during a 4G to 5G handover, the system first responds to the UE-initiated modification and then processes the PCF-initiated modification. |
| Standardized Error Cause Values for vSMF Rejections During 4G to 5G Handover |
Previous Behavior: When the vSMF rejected a create request during a 4G home-routed to 5G roamer Handover (HO), it returned a non-standard cause value in the error response. The cause field contained a specific but non-standardized string detailing the rejection reason, rather than a 3GPP-compliant cause code. This behavior was prevalent across all vSMF/hSMF procedures, where non-standard cause values were consistently returned in failure responses. New Behavior: The vSMF now returns standardized 3GPP-compliant cause values in its failure responses, aligning SMF failure handling with 3GPP standards. Specifically, for rejections due to insufficient resources during a 4G to 5G roamer HO, the cause field will now explicitly reflect "INSUFFICIENT_RESOURCES". The detailed, specific reason for the rejection will be provided in the detail field. This change ensures adherence to 3GPP specifications and improves interoperability, clarity for troubleshooting, and overall system compliance. |
| EPSFB - DLDR collision - invalid_rat_type for DLDR getting pegged. |
Previous behavior: In the 2025.03.0 build, DLDR (Downlink Data Report) handling during EPS-FB (EPS Fallback) led to an increase in the Invalid-RAT-Type KPI. This was a change from the 2024.03.0 build's behavior. New Behavior: The system's behavior for DLDR during EPS-FB has been reverted to that of the 2025.03.0 build. DLDR will now be ignored if EPS-FB is in progress, resolving the Invalid-RAT-Type KPI increase. |
| Change in Timing for PDU Session Type Comparison in SMF |
Previous Behavior: When processing a PDU session setup, the SMF compared the UE-requested PDU session type with the DNN-configured PDU session type after receiving the UDM subscription. If the types did not match, the PDU session setup was rejected at this stage. New Behavior: The SMF now performs the comparison between the UE-requested PDU session type and the DNN-configured PDU session type before interacting with the UDM. If there is a mismatch, the PDU session setup is rejected immediately, eliminating the need for further UDM interaction. This change streamlines the setup process, reduces resource usage, and prevents avoidable signaling with the UDM when the session types are incompatible. |
| Prevention of ghost calls through clearing buffered packets when the UE Is not responding
|
Previous Behavior: During an MT voice call, SMF attempted to transition the UE from Idle to Active. If the transition failed with a UE_NOT_RESPONDING error, the call was rejected; however, SIP INVITE packets buffered at the UPF were not cleared. When the UE later transitioned to the Active state, these buffered packets were forwarded, resulting in a ghost call being delivered to the UE. New Behavior: If the Idle-to-Active transition fails with UE_NOT_RESPONDING or UE_NOT_REACHABLE, SMF now instructs the UPF to clear all buffered packets by setting the DroBuf flag. This prevents stale SIP INVITE packets from being forwarded when the UE becomes Active, thereby eliminating ghost calls. |
| Enhancement in the extended buffering time for RedCap support |
SMF receives Estimated Maximum Wait Time from the AMF, determines the Extended Buffering Time, and sends it to the UPF. The Extended Buffering Time should be equal to or greater than the Estimated Maximum Wait Time. UPF buffers the packets for the received Estimated Maximum Wait Time. When the buffering time is over, it drops the subsequent packets. Previous behavior: If the Estimated Maximum Wait Time was not the exact multiple of the timer unit in DBD (Downlink Buffer Duration), which is encoded within the N4 message, SMF was considering the nearest lower multiple value. This reduced the buffer time and caused the UPF to drop the subsequent packets earlier. This caused packet loss. New behavior: As part of this behavior changes, if the received Estimated Maximum Wait Time is not the exact multiple of the timer unit in DBD in the N4 message, SMF considers the nearest higher multiple value. It increases the buffer time and does not cause packet loss. |
| Changes in smf_service_node_mgr_stats for DHCP sessions |
Previous Behavior: For DHCP sessions, the ip_req_type label was set to ip-dhcp-id-alloc, ip-dhcp-id-dealloc, or ip-dhcp-id-realloc. New Behavior: · id-only-alloc · id-only-dealloc · id-only-realloc These statistics are reported when the SMF service performs ID allocation, deallocation, or reallocation for DHCP sessions. |
| 3GPP SBI correlation and peer information headers |
Previous Behavior: The SMF did not send the HTTP headers 3gpp-Sbi-Correlation-Info and 3gpp-Sbi-NF-Peer-Info in HTTP request messages originating from it. |
| Enhanced preferred-server locality discovery behavior |
Previous Behavior: When the preferred-server locality configuration was changed, new call attempts would not trigger discovery using the updated value if already discovered profiles were still considered valid. The system relied on the existing profiles' validity and did not initiate a fresh discovery process to reflect configuration changes. |
| Upgrades in RedCap compliance profiles |
Previous behavior: SMF was sending RedCap Rat type NR_REDCAP over the N7 interface from the 3GPP specification 17.3.0 and over the N40 interface from the specification version 17.0.0. New behavior: In order to comply with the specification, SMF is enhanced to send the Rat type NR_REDCAP over the N7 interface from the 3GPP specification 17.5.0 and over the N40 interface from specification version 17.1.0. |
| Configurable UUID support for SMF registration with NRF
|
Previous Behavior: SMF always generated a new Universally Unique Identifier (UUID) for its NF instance ID, which was used in the NRF registration request. New Behavior: A new optional configuration has been added, allowing the UUID to be specified at the instance level in the SMF profile. When the UUID is configured, the SMF uses this value as the NF instance ID for the NRF registration request. If the UUID is not configured, the SMF continues to generate a new UUID as before. Customer Impact: Customers who require a specific or consistent UUID for the SMF NF instance in NRF registration can now configure it directly. Existing deployments that do not specify a UUID remain unaffected and will continue using auto-generated values. |
| Change in allowed range for upper threshold in IPAM configuration |
Previous Behavior: The upper threshold value in the IPAM configuration was configurable within the range of 1 to 100. New Behavior: The upper threshold value can now be set only within the range of 10 to 100. Attempts to configure a value below 10 will result in a CLI validation error. The default value of 80 remains unchanged. |
| BGP router ID selection prioritizes the loopback interface |
Previous Behavior: Legacy - In releases prior to 2026.01.0i11, if you deploy IPv6-only environments, BGP router IDs may not work because they are derived from the IPv4 address assigned to the BGP server’s interface. Prior to this enhancement (after initial IPv6-only support), for IPv6-only BGP servers, the Router ID is taken from a new IPv4 address configured on the loopback interface. For IPv4-only or dual-stack BGP servers, the Router ID is still derived from the interface's IPv4 address. This could still lead to inconsistent Router ID sources depending on the BGP server's IP version. New Behavior: The BGP Router ID selection now prioritizes the loopback interface. If an IPv4 address is configured on the loopback (lo) interface, that address will be used as the BGP Router ID. This applies universally, regardless of whether the BGP server is IPv4-only, IPv6-only, or dual-stack. If no IPv4 address is present on the loopback interface, the system will fall back to the previous Router ID selection logic (for example, using an IPv4 address from a BGP server's interface). Customer Impact: · Centralized Configuration: Allows for a centralized and predictable Router ID assignment across all BGP Speaker pods, eliminating the issue of multiple Router IDs per pod. · Enhanced IPv6 Support: Ensures that IPv6-only BGP server deployments can reliably obtain a Router ID by prioritizing the loopback IPv4 address, removing a previous limitation. · Simplified Operations: Reduces complexity in BGP configuration and troubleshooting by standardizing the Router ID source. · Backward Compatibility: Maintains existing functionality for deployments that do not configure an IPv4 address on the loopback interface. |
| Missing FQDN port in authority header and incorrect nf_type in stats for SCP |
Case 1: When both the FQDN and FQDN port are configured, SMF does not send port information to the peer NF (such as UDM, PCF, or SCP) in the authority header. Ideally, SMF should include the port with the FQDN in the authority header if the port is not the scheme's default port. Previous Behavior: SMF is not sending port information with FQDN in authority header when the port is not the scheme's default port. New Behavior: SMF is sending port information with FQDN in authority header when the port is not the scheme's default port. Case 2: The nf_req_received_messages_total and nf_resp_sent_messages_total stats have different nf_type for SCP Model D. In case of SCP Model D, nf_req_received_messages_total stats populate nf_type with Peer NF (UDM, PCF, CHF, AMF), while nf_resp_sent_messages_total populate nf_type as SCP. Ideally, the nf_type value should be consistent across request and response stats. Previous Behavior: nf_req_recieved_messages_total stats populate nf_type with Peer NF(UDM/PCF/CHF/AMF) string. nf_req_recieved_messages_total{app_name="SMF",cluster="SMF",data_center="DC",gr_instance_id="1",instance_id="0",message_type="UdmSdmGetUESMSubscriptionData",nf_type="UDM",service_name="rest-ep",svc_name="nudm-sdm"} 1 nf_resp_sent_messages_total{app_name="SMF",cluster="SMF",data_center="DC",gr_instance_id="1",instance_id="0",message_type="UdmSdmGetUESMSubscriptionData",nf_type="SCP",result="SendSuccess",service_name="rest-ep",status_code="200",svc_name="nudm-sdm"} 1 New Behavior: nf_req_recieved_messages_total stats populate nf_type with SCP string. nf_resp_sent_messages_total{app_name="SMF",cluster="SMF",data_center="DC",gr_instance_id="1",instance_id="0",message_type="UdmSdmGetUESMSubscriptionData",nf_type="SCP",result="SendSuccess",service_name="rest-ep",status_code="200",svc_name="nudm-sdm"} 1 |
| N16 Enhancement: N1 SM Information Included to vSMF |
Previous Behavior: During UE-initiated and Network-initiated PDU session release, the n1SmInfoToUE IE was not included in N16 messages sent by the hSMF to the vSMF, and the N1 Release Command was not sent. During PDU session establishment, the N1 Establishment Accept was not consistently included in the n1SmInfoToUE IE when EPS interworking was disabled. New Behavior: During UE-initiated and Network-initiated PDU session release, the n1SmInfoToUE IE is included in N16 messages sent by the hSMF to the vSMF and carries the N1 Release Command. During PDU session establishment, the N1 Establishment Accept is consistently included in the n1SmInfoToUE IE, even when EPS interworking is disabled. |
| AMF 504 (UE_NOT_REACHABLE) handling for N11 N1N2 message transfer |
Previous Behavior: When the AMF returned an HTTP 504 (UE_NOT_REACHABLE) response for an N11 N1N2MessageTransfer request, the SMF evaluated the configured FHT and retransmitted or retried the request accordingly. In AMF Set deployments, this could result in retries to alternate AMFs. New Behavior: When the AMF returns an HTTP 504 (UE_NOT_REACHABLE) response for an N11 N1N2MessageTransfer request, the SMF treats the response as final and does not apply the FHT. No re-transmission or retry is attempted to the same or alternate AMFs. |
| Updated APN string validation for 4G attach requests |
Previous Behavior: For 4G attach requests received at cnSGW/SMF/cnPGW, APN string validation permitted only printable ASCII characters, excluding the space character. This corresponds to ASCII decimal values 33 through 126 (inclusive). If the APN string contained any character outside this range, the attach request was rejected with the cause: "Missing or unknown APN (78)". New Behavior: For 4G attach requests received at cnSGW/SMF/cnPGW, APN string validation now permits all UTF-8 characters within the ASCII range, corresponding to ASCII decimal values 0 through 127 (inclusive). If the APN string contains any character outside this range (that is, non-UTF-8 characters), the attach request is rejected with the cause: "Missing or unknown APN (78)". Customer Impact: If a 4G attach request received at cnSGW/SMF/cnPGW contains an APN string with any non-UTF-8 character, the request will be rejected with the cause: "Missing or unknown APN (78)". This behavior may impact 5G-to-4G handover scenarios, including SOS APN, where the APN is incorrectly encoded or malformed during session creation, potentially resulting in attach or service establishment failure. |
| Graceful error handling for invalid NGAP content |
Previous Behavior: SMF used to restart unexpectedly during ASN decoding when invalid NGAP content was received (such as an invalid IE length). This behavior resulted in call loss and service interruption. New Behavior: SMF now gracefully handles invalid NGAP content. Instead of restarting, the software rejects malformed messages by sending a "400 Bad Request" response and terminates only the affected procedure. Customer Impact: With this update, the SMF remains stable, and only the impacted procedure is terminated, resulting in improved service continuity and reliability. |
| Inclusion of locality in PCF and CHF group IDs |
Previous Behavior: pcfGroupId and chfGroupId did not include the locality filter value. New Behavior: Starting from SMF 2026.01.0i11 release, pcfGroupId and chfGroupId will now include the locality filter value whenever locality is part of the discovery filter. Locality is included in the discovery filter when both of the following conditions are met: · locality preferred-server is configured under profile nf-pair. · The locality client of profile nf-pair matches the locality specified in SMF Profile Configuration. Customer Impact: For customers using the locality preferred-server feature, the system will now generate more specific Group IDs for the PCF and CHF. |
| User-name AVP format change in RADIUS authentication and accounting |
Previous Behavior: The SMF sent only the MSISDN in the user-name AVP for RADIUS authentication and accounting requests. New Behavior: The SMF can now send the user-name AVP in the format MSISDN@APN for RADIUS authentication and accounting requests. This behavior is controlled by a new "custom1" dictionary option available at both the radius-profile and server-group levels. Customer Impact: For customers requiring the MSISDN@APN format for RADIUS user-name AVP, the system now supports this via the "custom1" dictionary. Existing configurations using the 3GPP or ISE dictionaries are not affected. |
| Inclusion of HomeProvidedChargingID in hSMF Create Response |
Previous Behavior: The HomeProvidedChargingID Information Element (IE) was not included in the hSMF create response during a roaming 4G to 5G handover. New Behavior: Starting from the 2026.01.0i11 release, the HomeProvidedChargingID IE is now included in the hSMF create response during a roaming 4G to 5G handover. This IE carries the charging ID that was originally generated during the 4G attach. Customer Impact: Customers will now see the HomeProvidedChargingID IE in N16 create response messages during 4G to 5G handovers. |
| Accurate reporting of node and location information in charging requests |
Previous Behavior: During handover transitions, node and location information were immediately overwritten with the updated session context. Consequently, the system fetched these values from data that already contained the new AMF PLMN and node information. This resulted in charging requests reflecting the current session's data instead of the preceding session's data. New Behavior: The AMF PLMN is now updated only after the charging request is processed, preserving the old session information for charging workflows. This ensures that the system continues to read the correct session data during charging, allowing both servingNodeID and userLocationInformation to accurately reflect the previous location during the charging request. Customer Impact: This change ensures that charging reports contain accurate location and node information during handovers, preventing potential billing discrepancies. |
| Direct forwarding capability for 5G to 4G handover |
Support for direct forwarding (DFT) during 5G to 4G handover has been added, improving handover options and error handling. Previous Behavior: · Only indirect data forwarding (IDFT) was allowed when handing over from 5G to 4G. · Direct forwarding (DFT) was introduced in Release 16 but not supported by SMF. · If idft was not configured, a 500 error was returned to AMF. New Behavior: · DFT is now fully supported for 5G to 4G handovers. · SMF handles and maps eNB F-TEID for direct forwarding and includes it in handover messages. · If indirect forwarding is not possible due to missing configuration, a 403 error is now sent with the cause "NO_DATA_FORWARDING?. Customer Impact: · Enables direct forwarding during 5G to 4G handover, improving flexibility and performance. · Failure cause codes are now clearer if neither method is supported. |
| GnGp handover support and mobility procedures handling for 2G/3G |
Case 1: Enhanced serving node and time zone trigger support Previous Behavior: Time-zone triggers were unsupported and serving node changes were detected solely by Bearer TEID changes. New Behavior: Time-zone triggers are now supported, and serving node changes are identified by IP address changes. Case 2: EDR support for session modify procedure Previous Behavior: The SMF did not support EDR for Session Modify procedure for 4G. New Behavior: This release enhances the SMF's capabilities of EDR support for Session Modify procedure for 4G, aligned with the existing 2G and 3G capabilities. Case 3: UDM subscribe and notification for 2G and 3G Previous Behavior: The SMF did not support UDM subscription and notification functionalities for 2G and 3G networks. New Behavior: With this release, SMF supports the UDM subscription and notification functionalities for 2G and 3G RAT types, enabling improved subscriber management. Case 4. Updated show/clear and db_total metrics for GTPV1 and GTPV2 Previous Behavior: ratType values for 2G/3G in show/clear CLIs and db_records_total metrics were generic ("geran", "utran", "GERA", "UTRA"). New Behavior: ratType values now include V1/V2 specifics (e.g., "geran-v1", "GERA-V2") for 2G/3G in both show/clear commands and db_records_total metrics. Case 5. smf_service_stats_2g_3g metrics update Previous Behavior: smf_current_procedure metrics included procedure_type, status, reason, rat_type, dnn, and roaming_status. New Behavior: The smf_current_procedure attributes have been updated to include direct_tunnel, serv_node_change, and location_change, replacing older attributes. Case 6. Empty bearer list support for 2G/3G handover Previous Behavior: During a 4G to 2G/3G handover, if a ModifyBearerRequest lacked a bearer context list, dedicated bearers were not cleared by the SMF. New Behavior: The SMF now invokes an internal clear subscriber request to properly clear dedicated bearers during such 4G to 2G/3G handovers. |
| CHF usage reporting post 5G/4G handover |
Previous Behavior: During handovers, concurrent or out-of-order processing of N1N2 and N11 SMContext signalling could cause incomplete state transitions in the SMF. This prevented the expected N4 update and resulted in missing charging/usage reports to CHF. New Behavior: The SMF now manages concurrent signalling collisions, ensuring correct session state transitions and triggering of N4/N40 signalling after handover. This enables accurate and consistent usage reporting to CHF. |
| N4 update now sent on CHF response during 5G roaming handover |
Previous Behavior: During a 5G homer-to-roamer handover, if no new flow was created and an N4 update was required due to a CHF response, hSMF did not send the N4 update. This resulted in the QBC URR not being modified as expected, particularly when an N7 update response was not received and SMF proceeded with the CHF update. New Behavior: During a 5G homer-to-roamer handover, if no new flow is created and an N4 update is required due to a CHF response, hSMF now sends the N4 update as expected. This ensures the QBC URR is properly modified, even when an N7 response is not received and SMF continues with the CHF update. |
| Corrected handling of empty N7 Update Response messages |
Previous Behavior: When the SMF received an empty N7 Update Response (N7UpdateRsp) message (200 OK without smPolicyDecision), it incorrectly detected a change in the flowInformation attribute. This resulted in the SMF triggering either an unnecessary AssignEbi message (leading to unintended new flow creation) or a UBR with a redundant TFT change. New Behavior: The SMF no longer performs any action when the smPolicyDecision is missing in the N7UpdateRsp. The system correctly identifies that no flow information has changed, thereby preventing unnecessary signaling and unintended flow creation. Customer Impact: This change eliminates redundant signaling and prevents the creation of unintended flows, ensuring more stable and efficient session management. |
This table lists the resolved issues in this specific software release.
Note: This software release may contain bug fixes first introduced in other releases. To see additional information, click the bug ID to access the Cisco Bug Search Tool. To search for a documented Cisco product issue, type in the browser: <bug_number> site:cisco.com.
Table 4. Resolved issues for UCC SMF, Release 2026.01.0
| Description |
|
| Slice SST matching for three digits not working. |
|
| For half attach scenarios for 2g/3g over 5g, SmContextCreateReq is treated as HO request. |
|
| SMF does not handle DFT flow related n11smContextUpdate carrying eNB-FTEID for 5G to 4G CM HO. |
|
| AMF-SET-SMF sending requests to deregistered AMF. |
|
| N4 wrong ULI format error logs-when the session/bearer is without ULI. |
|
| SMF-service pod restart "panic: runtime error: index out of range [0] with length 0". |
|
| vSMF sending EBI 0, resulting in Handover failure. |
|
| vSMF not sending mapped slice information to UE. |
|
| vSMF is not sending hoPreparationIndication during 4G to 5G HO. |
|
| smf-service restart or Recovered from Panic (if Resiliency Handling feature) when AMF incorrectly sends SmContextCreate with the message: Message Type: PDU Session Modification Complete. |
|
| SMF-REDCAP-Lower-compliance-RATTYPE sent empty in 4G to 5G for REDCAP. |
|
| EPSFB-DLDR collision-invalid_rat_type for DLDR getting pegged. |
|
| SMF sending 404-Retrieve and N1N2failurenotification collision. |
|
| SMF fails to process the addition of PCC rule belonging to default flow with packetFilterUsage true post N2 failure. |
|
| SMF-Service restarts when 5qI missing in policy create response. |
|
| SMF does not do NRF discovery when locality attribute is changed and looks up expired cached data. |
|
| AMF-SET- SMF sending NRF discovery request with nf-instance-ID in ebi failure. |
|
| SMF sends 5qi=0 in epco IE in UBReq triggered in response of MBC post 5g to 4G HO. |
|
| Collision - SMF-Discovery for wifi-NR hO in collision scenario sending empty target instanceID. |
|
| PDU session establishment getting failed because of EBI assignment failure with NF-Set based subscription feature enabled. |
|
| Setting DROBU required to avoid ghost calling. |
|
| SMF-NR, when receiving 504, need not retry another AMF in set. |
|
| SMF node-monitor PODs discover false unreachable node events due to ICMP echo ID collision in parallel pings. |
|
| SMF-ASN.1 vulnerability impact. |
|
| SMF-Roaming-hSMF not including N1 release command. |
|
| Addition of an IPAM pool on P/P rack is not taking effect on S/S rack. |
|
| HO issues: 504 retry not working during ebi assignment. |
|
| Extended Buffering Time to be on the higher side. |
|
| SMF does not handle quotaHoldingTime/ValidityTime=0 use case for preEmptive quota functionality. |
|
| SMF is not cleaning up IP pool details from SMF when a pool is made offline and unconfigured. |
|
| SOS APN rejection during Handover. |
|
| SMF configuration to send username as msisdn and apn to Radius. |
|
| pcf_req_ded_brr_mod/del failure - upf_failure - Outgoing_Message_Processing_Failure |
|
| Roaming - Missing charging ID in hSMF and vSMF in 4G to 5G HO. |
|
| WLAN to 5G Handoff: Delete Session Response with "System Failure" cause sent before Delete Bearer Request/Response exchange. |
|
| Single entry in etcd pod for host n/w pods s11-gtpc,gtpc,proto when hostname does not include hyphen. |
|
| SMF sends UNK_RULE_ID for one of voice rule from 2nd volte call when voice rule installed on default & moved to dedicated bearer. |
|
| VONR- SMF does flow creation for N7 notify for default-flow-indication true. |
This table lists the open issues in this specific software release.
Note: This software release may contain open bugs first identified in other releases. To see additional information, click the bug ID to access the Cisco Bug Search Tool.
Table 5. Open issues for Ultra Cloud Core - Session Management Function, Release 2026.01.0
| Bug ID |
Description |
| IoT |
|
| ATT UDM is not able to process supportedfeatures sent by SMF. |
|
| Rest Ep pod go routine and memory spike observed during SCP C call model run with mTLS enabled. |
|
This section lists compatibility information of the Cisco UCC software products that are verified to work with this version of the UCC SMF software.
Table 6. Compatibility information for UCC SMF, Release 2026.01.0
| Product |
Supported Release |
| Ultra Cloud Core SMI |
2026.01.1.08 |
| Ultra Cloud CDL |
2.1 |
| Ultra Cloud Core UPF |
2026.01.0 |
| Ultra Cloud cnSGWc |
2026.01.0 |
This section provides information about the release packages associated with UCC SMF software.
Table 7. Software packages for UCC SMF, Release 2026.01.0
| Software Package |
Description |
Release |
| ccg-2026.01.0.SPA.tgz |
The SMF offline release signature package. This package contains the SMF deployment software, NED package, as well as the release signature, certificate, and verification information. |
2026.01.0 |
| ncs-6.4.8.2-ccg-nc-1.1. 2026.01.0.tar.SPA.tgz |
The NETCONF NED package. This package includes all the yang files that are used for NF configuration. Note that NSO is used for the NED file creation. |
6.4.8.2 |
| ncs-6.1.14-ccg-nc-1.1. 2026.01.0.tar.SPA.tgz |
|
6.1.14 |
Cloud native product version numbering system
The show helm list command displays detailed information about the version of the cloud native product currently deployed.
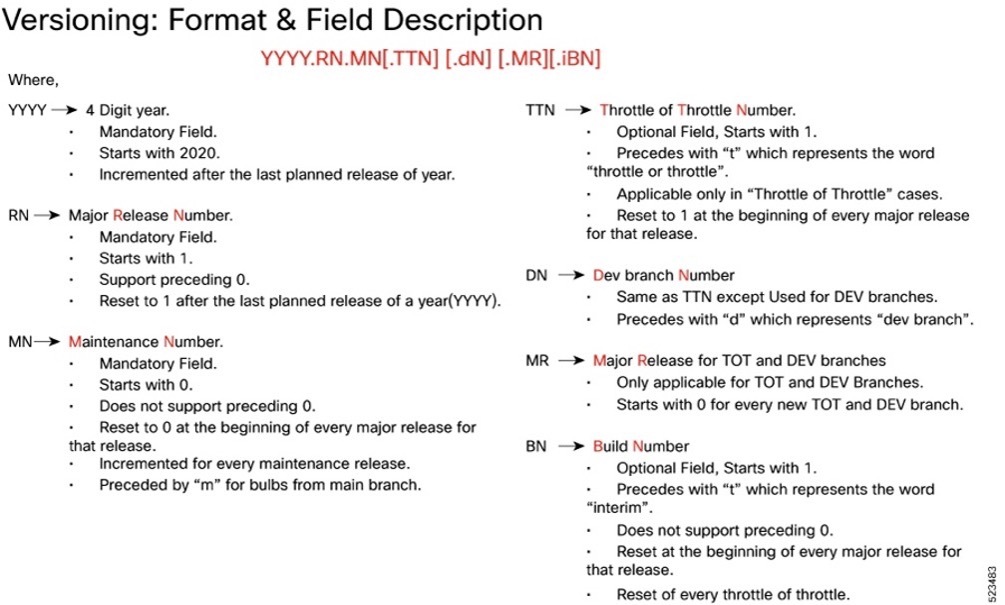
Image checksum information is available through Cisco.com Software Download Details. To find the checksum, hover the mouse pointer over the software image you have downloaded.
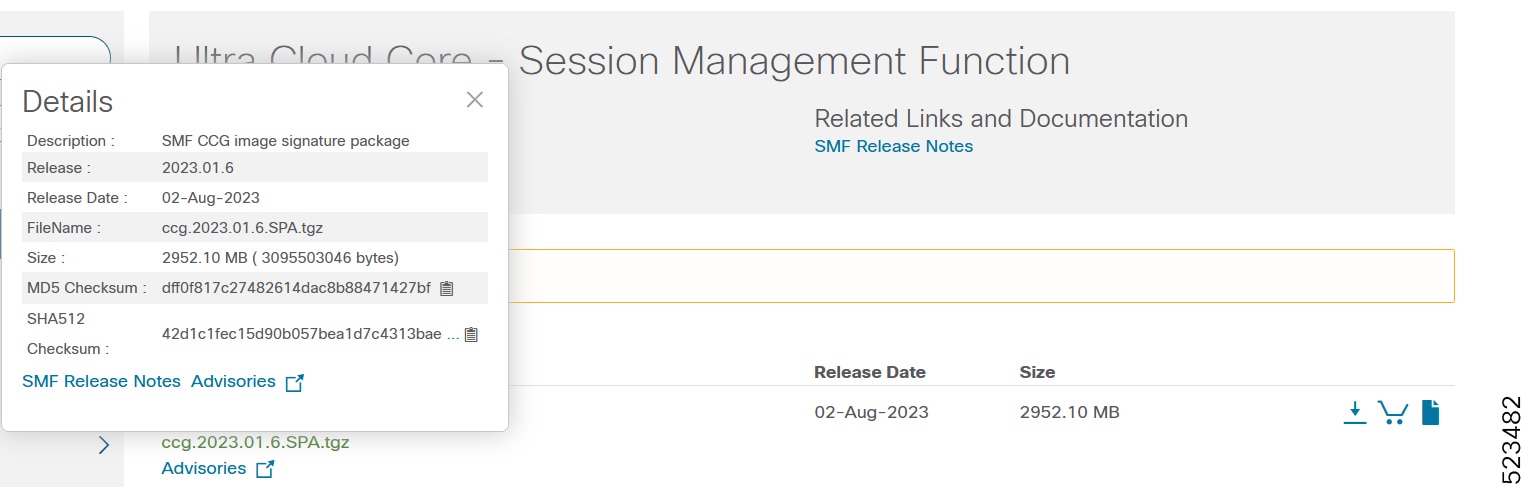
To validate the information, calculate a SHA512 checksum using the information in the following table and verify that it matches the one provided on the software download page.
To calculate a SHA512 checksum on your local desktop, see this table.
Table 8. Checksum calculations per operating system
| Operating System |
SHA512 checksum calculation command examples |
| Microsoft Windows |
Open a command line window and type the following command: > certutil.exe -hashfile <filename.extension> SHA512 |
| Apple MAC |
Open a terminal window and type the following command: $ shasum -a 512 <filename.extension> |
| Linux |
Open a terminal window and type the following command: $ sha512sum <filename.extension> OR $ shasum -a 512 <filename.extension> |
| Note: <filename> is the name of the file. <extension> is the file type extension (for example, .zip or .tgz). |
|
If the SHA512 checksum does not match, we advise you not to attempt upgrading any systems with the corrupted software image. Download the software again and verify the SHA512 checksum again. If there is a constant mismatch, please open a case with the Cisco Technical Assistance Center.
This table provides key resources and links to the support information and essential documentation for cnSGWc and other Ultra Cloud Core (UCC) products.
Table 9. Related resources and additional information
| Resource |
Link |
| SMF documentation |
|
| cnSGWc documentation |
|
| SMI documentation |
|
| UPF documentation |
|
| Service request and additional information |
Cisco and the Cisco logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Cisco and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and other countries. To view a list of Cisco trademarks, go to this URL: www.cisco.com/go/trademarks. Third-party trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (1110R)
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses and phone numbers used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses and phone numbers. Any examples, command display output, network topology diagrams, and other figures included in the document are shown for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses or phone numbers in illustrative content is unintentional and coincidental.
© 2026 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Feedback
Feedback