NF Registration and Deregistration Service Operations
Feature Summary and Revision History
Summary Data
|
Applicable Product(s) or Functional Area |
5G-NRF |
|
Applicable Platform(s) |
SMI |
|
Feature Default Setting |
Enabled – Always-on |
|
Related Changes in this Release |
Not Applicable |
|
Related Documentation |
Not Applicable |
Revision History
|
Revision Details |
Release |
|---|---|
|
First introduced. |
2026.01 |
Feature Description
The NF Register and Deregister service operations enable NRF to process the NF registration or deregistration request from any of the NF and store it in, or remove it from, the database.
How it Works
This section describes how NF Registration and Deregistration feature works.
NF Registration
NRF REST Endpoint
-
The NRF REST endpoint receives the NFRegister request over HTTP2/JSON. The HTTP method is PUT, and the URL is /root/nnrf-nfm/v1/nf-instances. The body contains the NFProfile in JSON format.
Note: The default value, /root, is a configurable parameter.
-
On receiving the request, the request is validated to check if the mandatory fields are present in the request. If not, then the response is sent back with status 400 (BAD REQUEST).
-
If the validation succeeds, then the NFRegister request is transformed into protobuf format and sent towards the Service Pod for processing.
-
The worker, after processing the request, sends a response toward the endpoint. The response is then transformed from protobuf-based format to JSON-based format.
-
The response is then checked for the response code; if it’s a new node success response, then the updated NFProfile is sent back in the response body with the status code as 201 (CREATED). Else, if it’s an error code, the error code is sent back to the client.
NRF Service Engine
-
The NRF Engine receives the protobuf-based request from the REST endpoint through the IPC system.
-
The NRF Engine gets the nfInstanceId from the message and creates an entry in CDL, with nfInstanceId as Primary key and few other required fields as Unique and non-Unique keys.
-
The entire NFProfile is set into the data of the DBRecord request.
-
If the create is successful, the response code 201 is sent back to the REST endpoint.
-
In case of error while storing the response, error code is sent back as 500.
NF Deregistration
NRF REST Endpoint
-
The NRF REST endpoint receives the NFDeregister request over HTTP2/JSON. The HTTP method is DELETE, and the URL is /root/nnrf-nfm/v1/nf-instances/{nfInstanceId} with no request body.
Note: The default value, /root, is a configurable parameter.
-
The NFDeregister request is transformed into protobuf format and sent toward the Service Pod for processing.
-
The messages are routed from REST endpoint to Service Pod based on Affinity. The nfInstanceId is the Primary key for Affinity.
-
The Service Pod, after processing the request, sends a response toward the endpoint. The response is transformed from protobuf-based format to JSON-based format.
-
The response is then checked for the response code; if it’s a success response, then the status code 204 (NO CONTENT) is sent back to the client with no response body. If the response code is 404, then the status code 404 (NOT FOUND) is sent back to the client with no response body. In other error cases, response code 500 is sent back.
NRF Service Engine
-
The NRF Engine receives the protobuf-based request from the REST endpoint through the IPC system.
-
The NRF Engine gets the nfInstanceId and attempts to load the profile from the CDL DB.
-
If the profile is not present, the response is sent back to the rest-ep with response code as 404.
-
If the profile is present, the profile is deleted by sending a delete request to the Datastore service.
-
If the request is successful, the response is sent back to the rest-ep with response code as 200.
-
For errors while deleting, response code is sent back as 500.
Call Flows
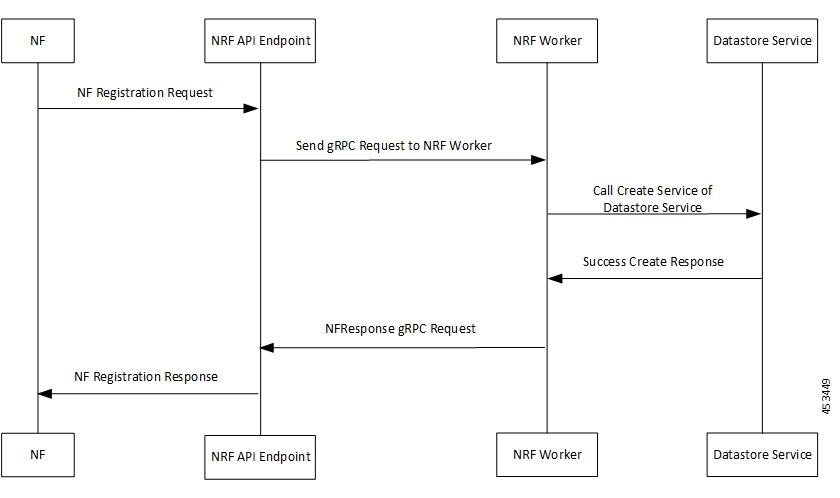
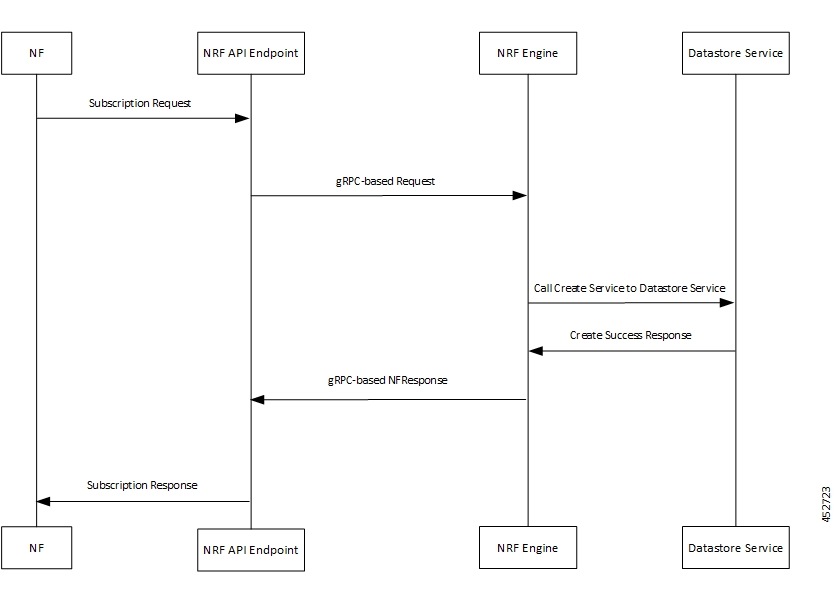
NFRegister Success Call Flow
This section describes the successful NF Registration call flow.
|
Step |
Description |
|---|---|
|
1 |
The NF sends NF Registration Request to NRF API endpoint. The NRF API endpoint transforms the REST request to gRPC. |
|
2 |
The NRF API endpoint sends gRPC request to the NRF worker. The NRF worker decodes gRPC request and prepares DBRecord message to be sent to the Datastore service. |
|
3 |
The NRF worker sends call create service to Datastore service. |
|
4 |
The Datastore service responds to NRF worker with SUCCESS Create Response. |
|
5 |
The NRF worker builds NFResponse gRPC Request and sends it to NRF API endpoint. The NRF API endpoint transforms the gRPC NFResponse message to REST-based response message. |
|
6 |
The NRF API endpoint sends NF Registration Response to the NF. |
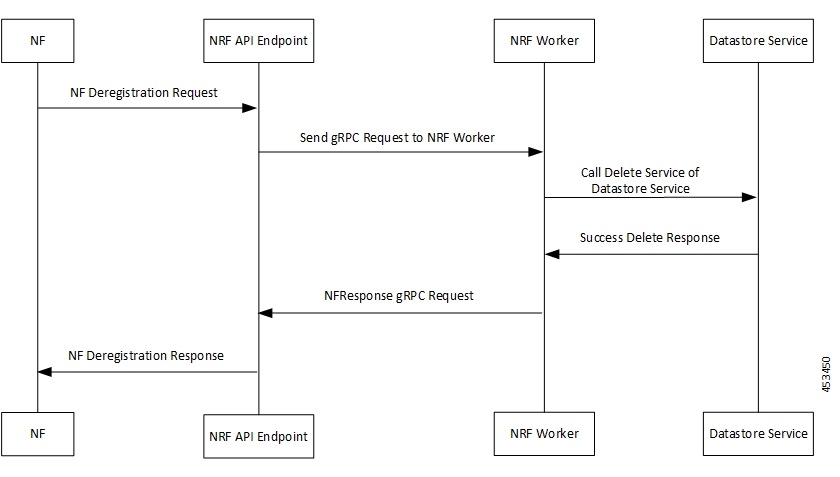
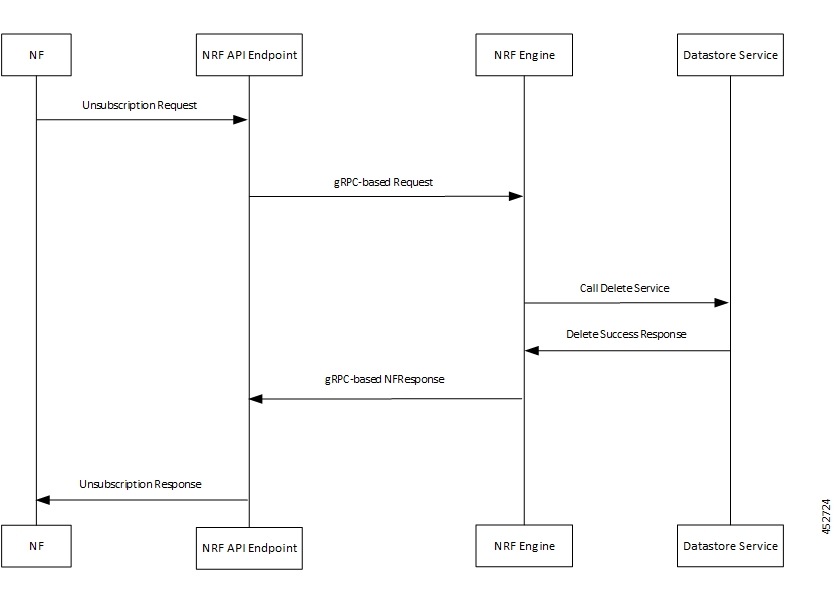
NFDeregister Success Call Flow
This section describes the successful NF Deregistration call flow.
|
Step |
Description |
|---|---|
|
1 |
The NF sends NF Deregistration Request to NRF API endpoint. The NRF API endpoint transforms the REST request to gRPC. |
|
2 |
The NRF API endpoint sends gRPC request to the NRF worker. The NRF worker decodes gRPC request and prepares DBRecordFilter message to be sent to the Datastore service. |
|
3 |
The NRF worker sends call delete service to Datastore service. |
|
4 |
The Datastore service responds to NRF worker with SUCCESS Delete Response. |
|
5 |
The NRF worker builds NFResponse gRPC Request and sends it to NRF API endpoint. The NRF API endpoint transforms the gRPC NFResponse message to REST-based response message. |
|
6 |
The NRF API endpoint sends NF Deregistration Response to the NF. |

 Feedback
Feedback