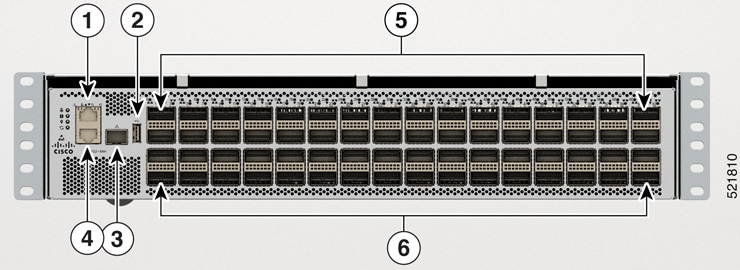
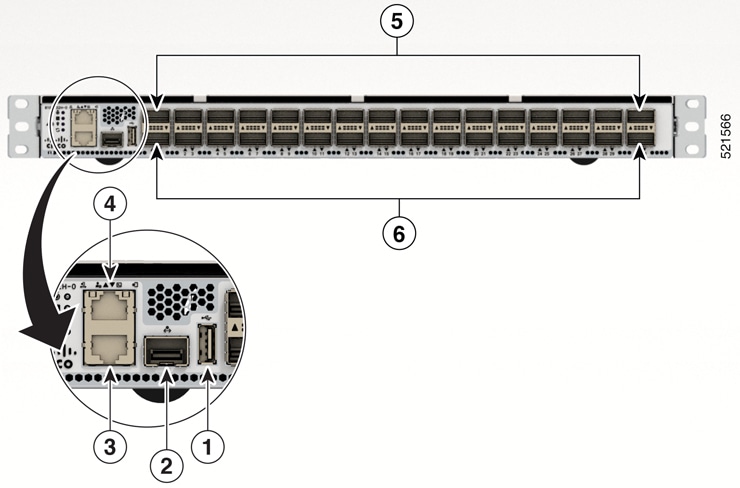
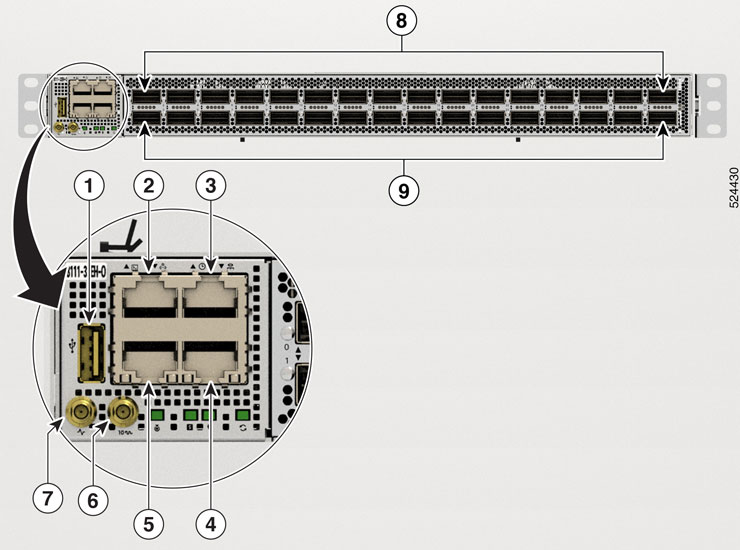
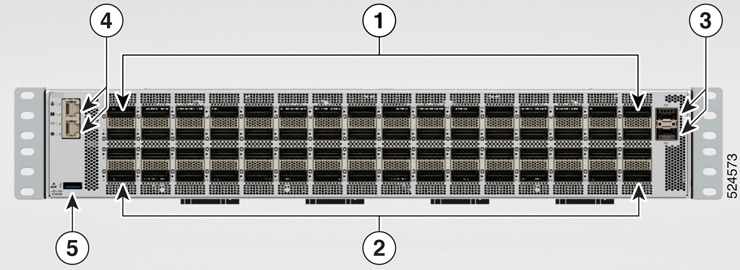
Port Connection Guidelines
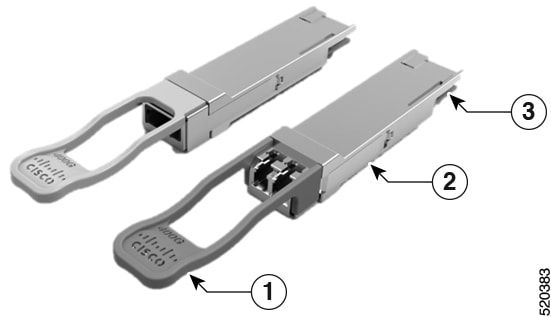
Depending on the chassis , you can use optical modules and RJ-45 connectors to connect the ports to other network devices.
To prevent damage to the fiber-optic cables, we recommend that you keep the transceivers disconnected from their fiber-optic cables when installing the transceiver in the line card. Before removing a transceiver from the router, remove the cable from the transceiver.
To maximize the effectiveness and life of your transceivers and optical cables, ensure the following:
-
Wear an ESD-preventative wrist strap that is connected to an earth ground whenever you handle transceivers.
-
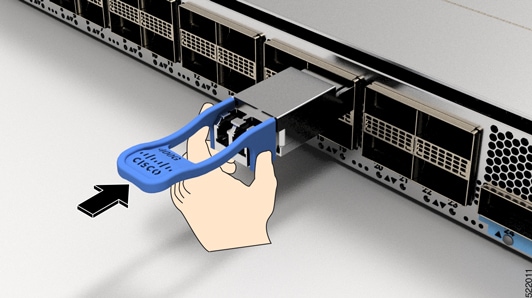
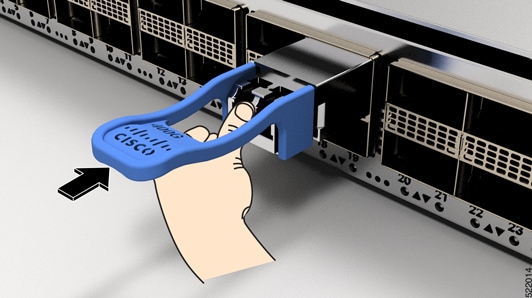
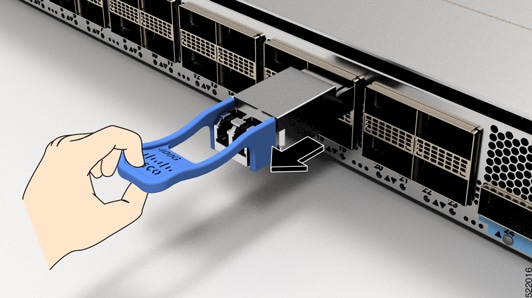
Do not remove and insert a transceiver more often than is necessary. Repeated removals and insertions can shorten its useful life.
-
Keep the transceivers and fiber-optic cables clean and dust free to maintain high signal accuracy and to prevent damage to the connectors. Attenuation (loss of light) is increased by contamination. Connector loss should be kept below 0.35 dB.
-
Clean these parts before installation to prevent dust from scratching the fiber-optic cable ends.
-
Clean the connectors regularly; the required frequency of cleaning depends upon the environment. In addition, clean connectors when they are exposed to dust or accidentally touched. Both wet and dry cleaning techniques can be effective; refer to your site's fiber-optic connection cleaning procedures.
-
Do not touch the ends of connectors. Touching the ends can leave fingerprints and cause other contamination.
-
-
Inspect routinely for dust and damage. If you suspect damage, clean and then inspect fiber ends under a microscope to determine if damage has occurred.








 Feedback
Feedback