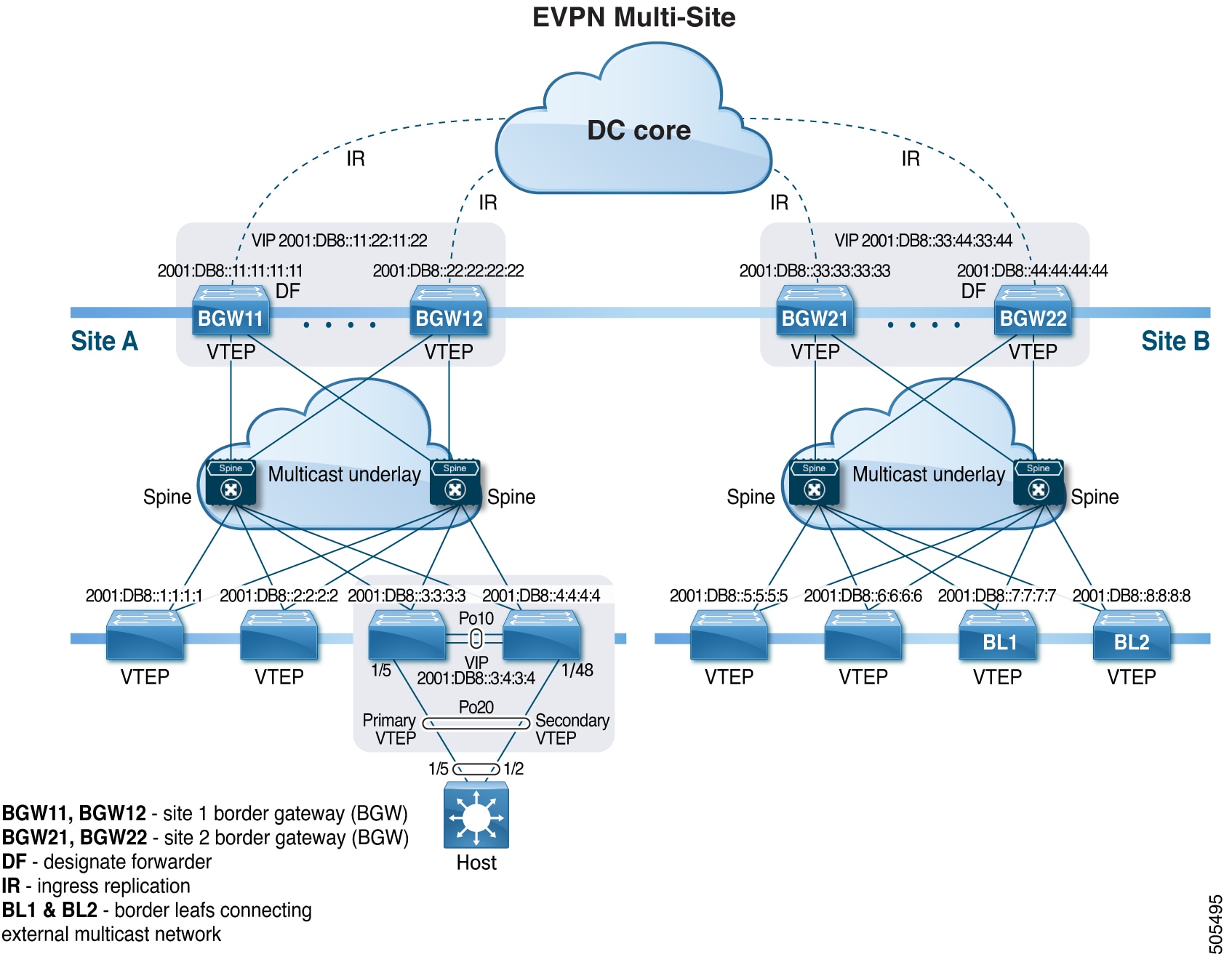
About VXLAN EVPN Multi-Site
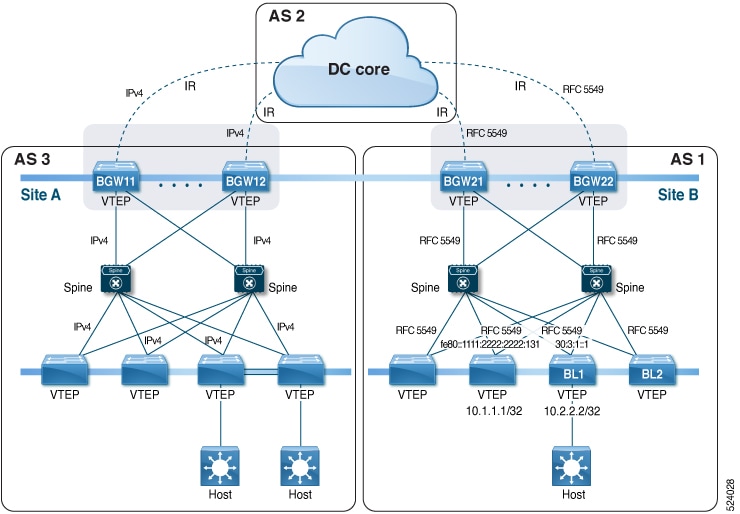
The VXLAN EVPN Multi-Site solution interconnects two or more BGP-based Ethernet VPN (EVPN) sites/fabrics (overlay domains) in a scalable fashion over an IP-only network. This solution uses border gateways (BGWs) in anycast or vPC mode to terminate and interconnect two sites. The BGWs provide the network control boundary that is necessary for traffic enforcement and failure containment functionality.
In the BGP control plane for releases prior to Cisco NX-OS Release 9.3(5), BGP sessions between the BGWs rewrite the next hop information of EVPN routes and reoriginate them. Beginning with Cisco NX-OS Release 9.3(5), reorigination is always enabled (with either single or dual route distinguishers), and rewrite is not performed. For more information, see Dual RD Support for Multi-Site.
VXLAN Tunnel Endpoints (VTEPs) are only aware of their overlay domain internal neighbors, including the BGWs. All routes external to the fabric have a next hop on the BGWs for Layer 2 and Layer 3 traffic.
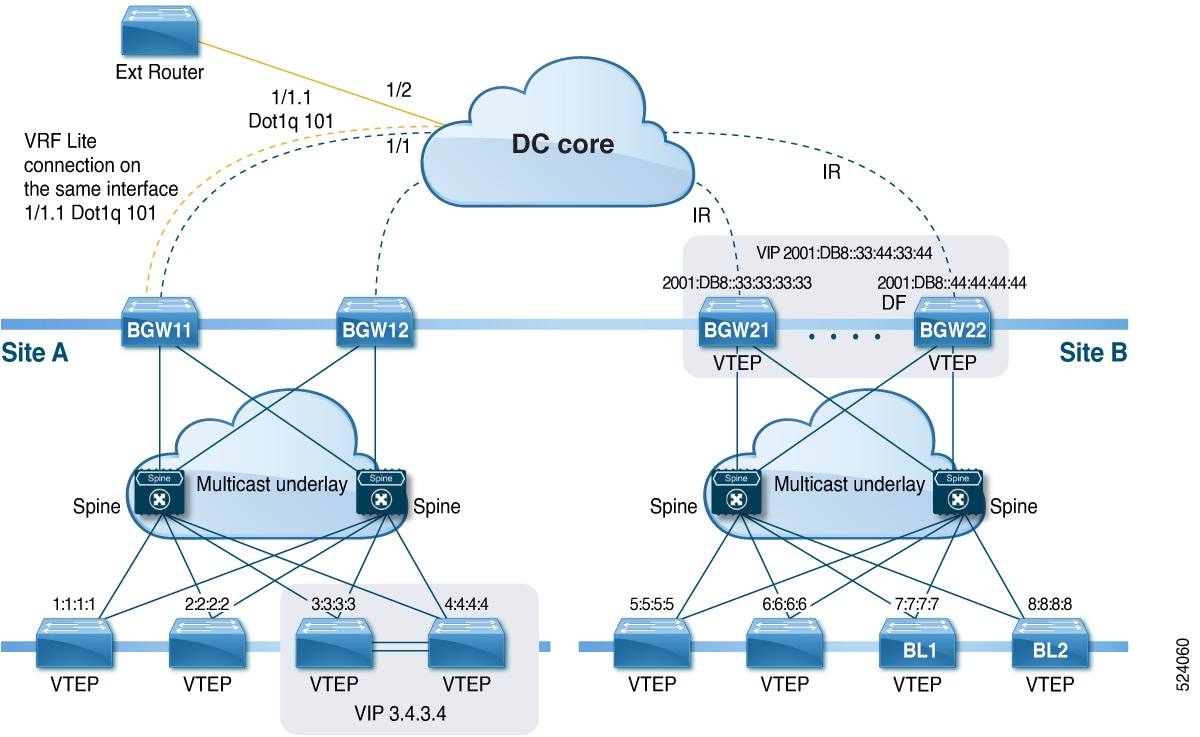
The BGW is the node that interacts with nodes within a site and with nodes that are external to the site. For example, in a leaf-spine data center fabric, it can be a leaf, a spine, or a separate device acting as a gateway to interconnect the sites.
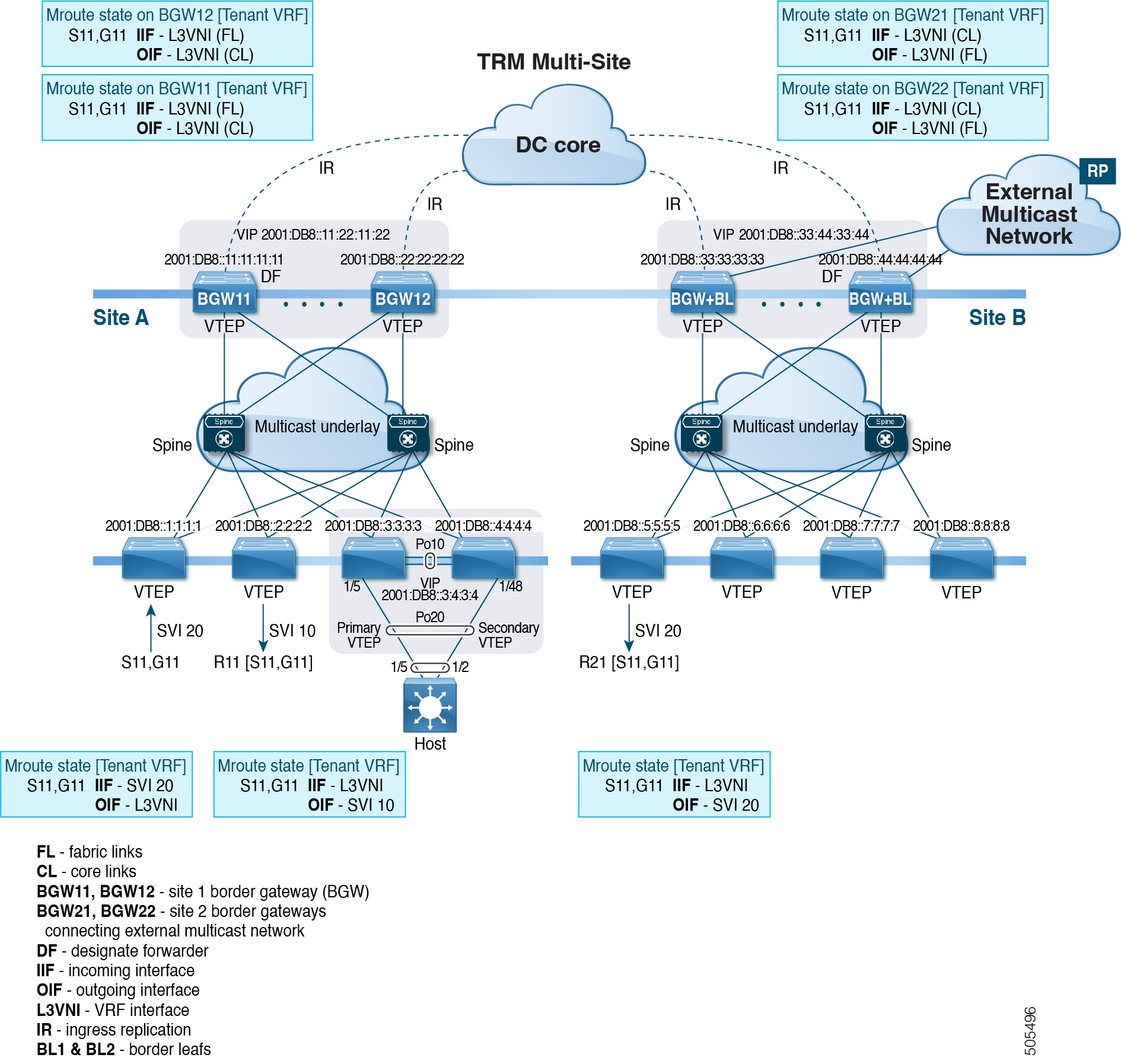
The VXLAN EVPN Multi-Site feature can be conceptualized as multiple site-local EVPN control planes and IP forwarding domains interconnected via a single common EVPN control and IP forwarding domain. Every EVPN node is identified with a unique site-scope identifier. A site-local EVPN domain consists of EVPN nodes with the same site identifier. BGWs on one hand are also part of the site-specific EVPN domain and on the other hand a part of a common EVPN domain to interconnect with BGWs from other sites. For a given site, these BGWs facilitate site-specific nodes to visualize all other sites to be reachable only via them. This means:
-
Site-local bridging domains are interconnected only via BGWs with bridging domains from other sites.
-
Site-local routing domains are interconnected only via BGWs with routing domains from other sites.
-
Site-local flood domains are interconnected only via BGWs with flood domains from other sites.
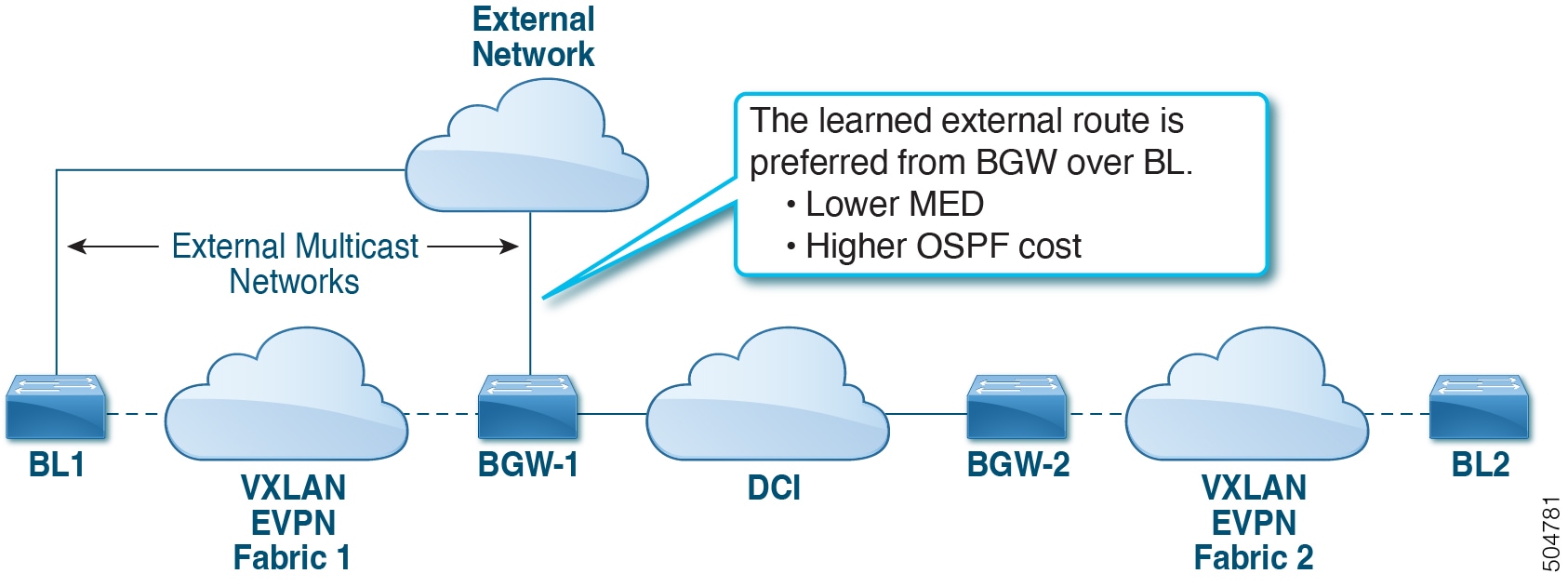
Selective Advertisement is defined as the configuration of the per-tenant information on the BGW. Specifically, this means IP VRF or MAC VRF (EVPN instance). In cases where external connectivity (VRF-lite) and EVPN Multi-Site coexist on the same BGW, the advertisements are always enabled.
 Note |
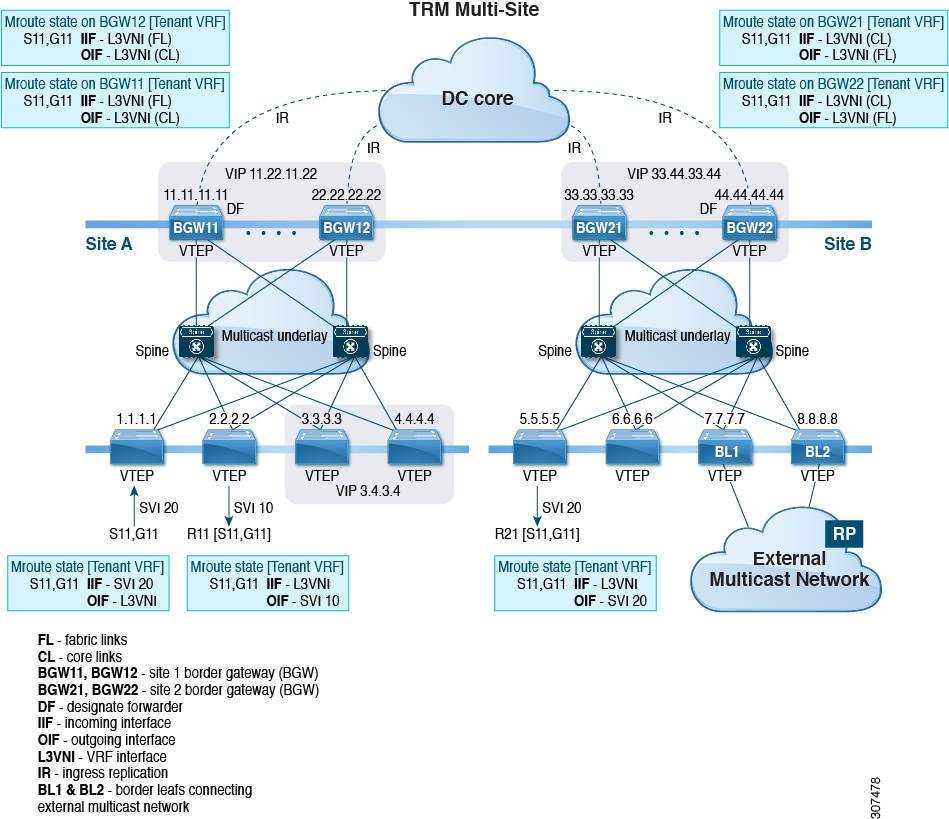
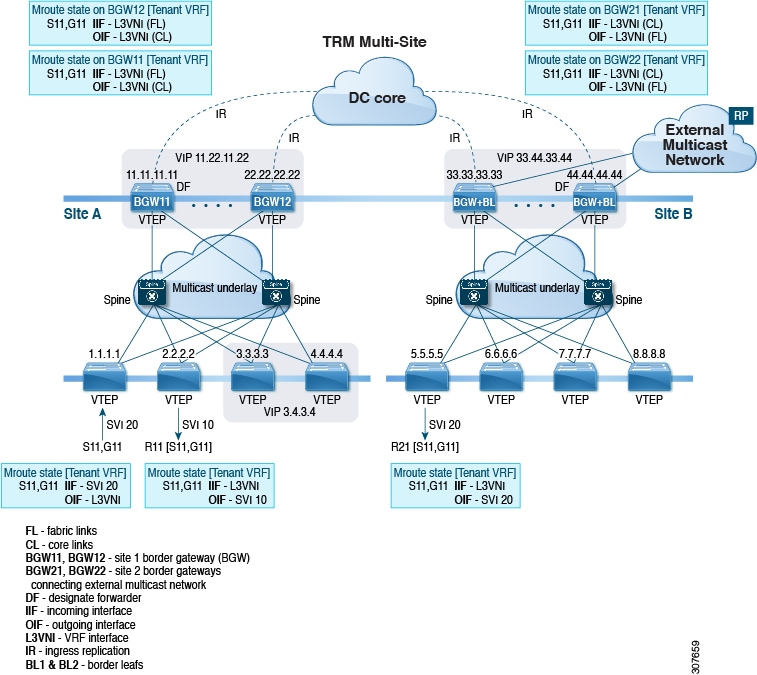
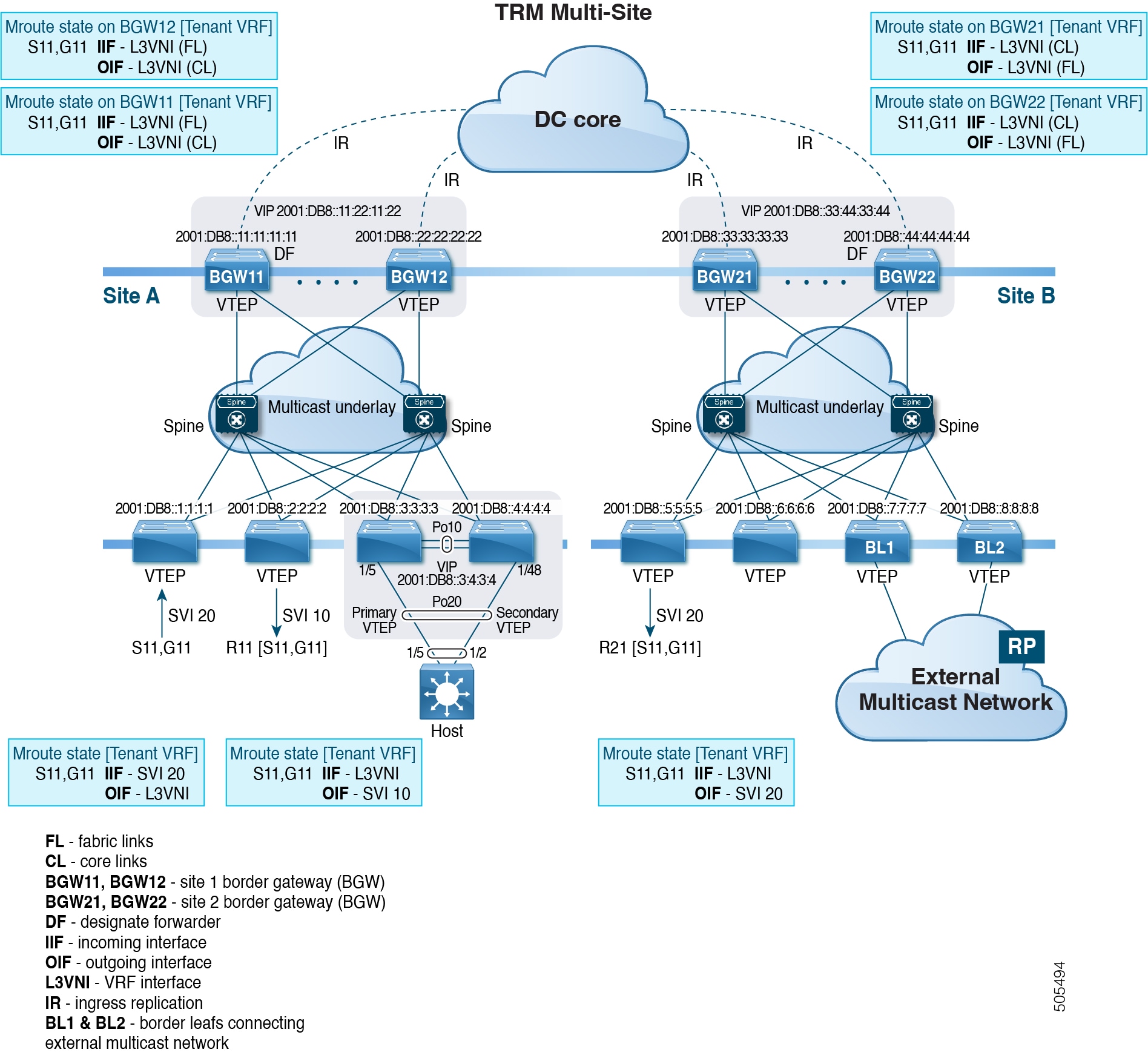
The MVPN VRI ID must be configured for TRM on anycast BGW if the site ID is greater than two bytes. The same VRI ID needs to be configured in all anycast BGWs that are part of the same site. However, the VRI ID must be unique within the network. That is, other anycast BGWs or vPC leaves must use different VRI IDs. |
 Feedback
Feedback