Flexible algorithm
A flexible algorithm is a customizable IGP routing method that:
-
enables operators to define path computation constraints based on specific metrics and link properties.
-
allows confining the path to a particular logical plane in networks with multiple planes.
-
supports user-defined meanings and intent for routing behaviors within a network.
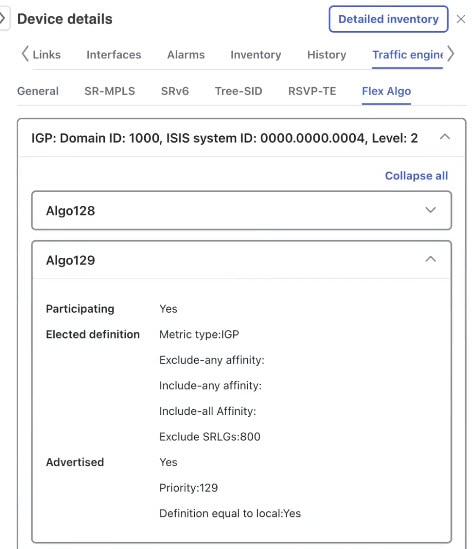
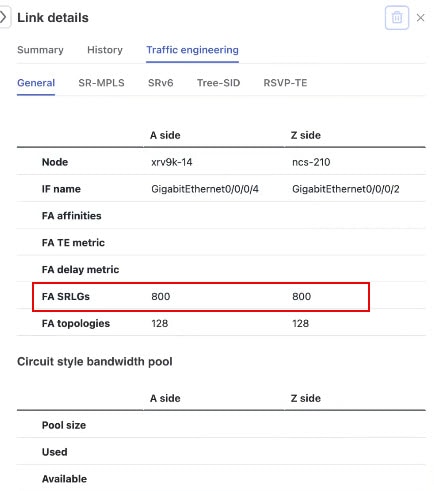
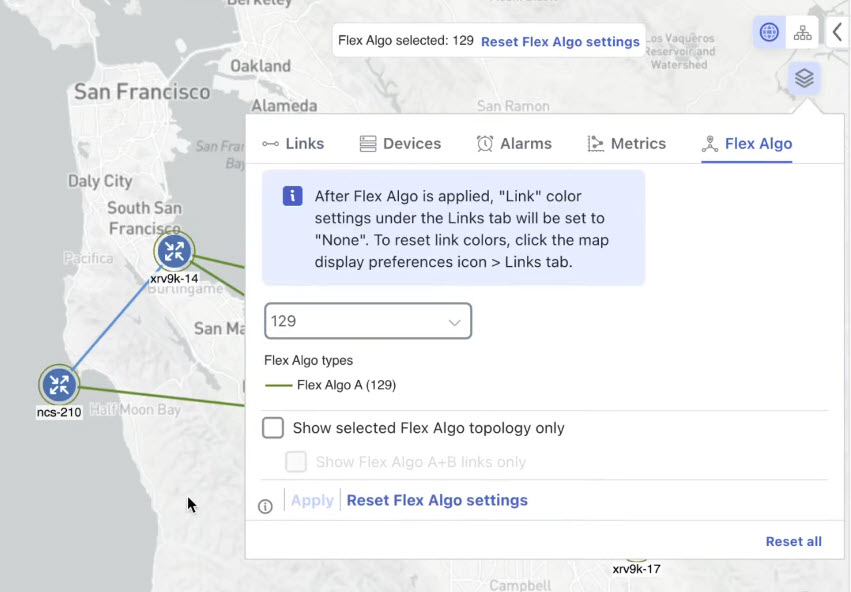
A flexible algorithm filters or confines the IGP topology to meet specific transport characteristics or policies, rather than just computing a default shortest path to all destinations. Crosswork Network Controller enables visualization of network subsets that provide a specific set of transport characteristics. This visualization helps you deploy, maintain, and verify that the flexible algorithm’s intended behavior is realized in your network.
For example:
-
You can use a flexible algorithm to improve service availability.
-
You can define disjoint logical topologies to enhance network resiliency against failures.
-
You can verify that two flexible algorithm topologies have no shared nodes or links, ensuring complete disjointness.
-
If common nodes or link exist, you can identify them and update configurations to better meet your network goals.




 Feedback
Feedback