Overview
CAPWAP is an IEEE standard protocol that enables a wireless LAN controller to manage multiple APs. It also allows Wireless LAN Controllers (WLCs) to exchange control and data plane information over a secure communication tunnel.
-
Operates at Layer 3 and requires IP addresses on both APs and WLCs.
-
Establishes tunnels on UDP ports 5246 (control) and 5247 (data) for IPv4 and IPv6, with DTLS encryption for security.
-
Allows centralized management of the wireless network and supports secure communication between APs and controllers.
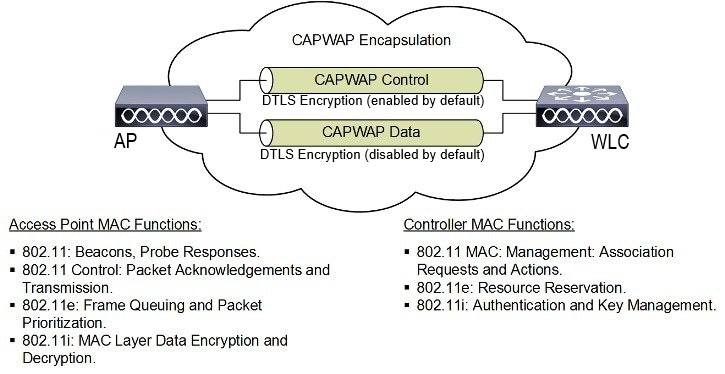
CAPWAP Protocol
CAPWAP uses DTLS to secure the control channel, encrypting all management and control traffic between the AP and WLC. The data channel is disabled by default. To enable CAPWAP data encryption, a DTLS license is required on the WLC and additional configuration is necessary on the AP.
-
DTLS ensures encrypted communication to prevent eavesdropping or tampering.
-
If an AP does not support DTLS data encryption, only the control plane is secured.
-
If an AP supports Data DTLS, it enables data DTLS after receiving configuration from the controller and performs a DTLS handshake on port 5247.
-
All data traffic between the AP and controller is encrypted after successful DTLS session establishment.
-
The IW9165E uses the IETF standard CAPWAP to communicate between the controller and other APs on the network.
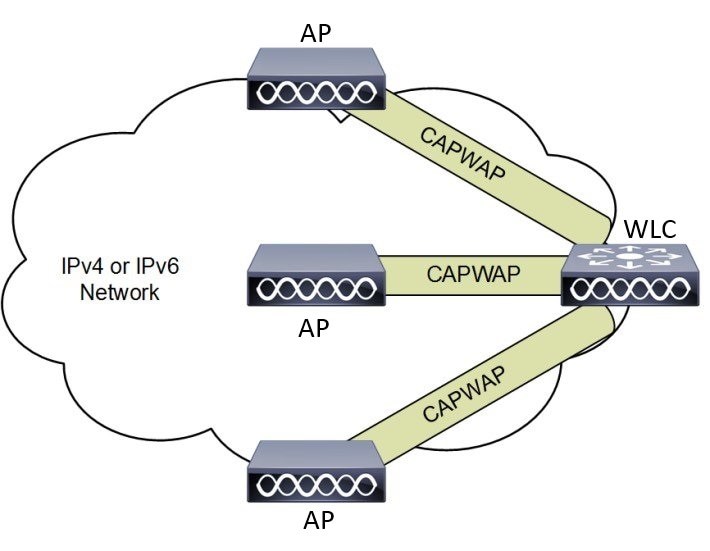
CAPWAP APs Connected to a WLC
This figure shows CAPWAP APs connected to a wireless LAN controller, illustrating the secure communication tunnel established between the APs and the WLC using CAPWAP and DTLS encryption.
Provisioning certificates on Lightweight Access Points
Certificate provisioning on a Lightweight Access Point (LAP) consists of several coordinated steps involving the LAP, controller, and certificate authority (CA).
Summary
The following actors and components participate in the certificate provisioning process:
-
LAP: Initiates the certificate request and installs the signed certificate.
-
Controller: Acts as a CA proxy and validates certificates during the JOIN process.
-
CA: Signs the certificate request forwarded by the controller.
This process ensures secure communication by provisioning and validating device certificates on the LAP.
Workflow
These stages describe the certificate provisioning workflow on a Lightweight Access Point (LAP):
- Certificate Request : The LAP sends a certificate request to the controller to get a signed X.509 certificate.
- CA Proxy : The controller acts as a CA proxy to facilitate the signing of the certificate request by the CA.
- Certificate Installation and Reboot : Both the LSC CA and the LAP device certificates are installed in the LAP, and the system reboots automatically.
- JOIN Request : After the reboot, the LAP sends the LSC device certificate to the controller as part of the JOIN request.
- JOIN Response and Validation : The controller sends the new device certificate and validates the inbound LAP certificate with the new CA root certificate as part of the JOIN response.
What’s next
Use LSC provisioning functionality to configure, authorize, and manage certificate enrollment with the existing PKI infrastructure for the controller and AP.
Understanding CAPWAP connectivity On AP
CAPWAP (Control and Provisioning of Wireless Access Points) is a protocol that enables APs to discover, join, and communicate securely with wireless controllers, supporting both split and local MAC operation modes.
-
Facilitates secure discovery and connection between APs and controllers using DTLS.
-
Supports two operational modes: Split MAC and Local MAC .
-
Enables centralized management of configuration, firmware, and user data traffic through control and data channels.
CAPWAP connectivity and operation details
CAPWAP connectivity involves a discovery phase, secure connection establishment, and management of AP configuration and data through dedicated channels.
-
APs initiate a discovery phase by sending discovery request messages to locate a controller.
-
Controllers respond with discovery responses, after which a secure DTLS connection is established.
-
APs send CAPWAP join requests and receive join responses to complete the joining process.
-
Controllers manage AP configuration, firmware, and control/data transactions post-join.
CAPWAP join process
This section describes the CAPWAP join process between an access point and a wireless LAN controller.
-
Enable CAPWAP on the AP.
-
AP sends discovery request to controller.
-
Controller replies with discovery response.
-
AP sends join request; controller sends join response.
-
Secure DTLS connection is established for CAPWAP control and data messages.
CAPWAP communication between the access point and the wireless LAN controller is established over two logical channels, each serving a distinct function:
-
Control Channel: Used for configuration messages, image downloads, and client key exchanges. APs must acknowledge each message before sending the next.
-
Data Channel: Used for encapsulation and tunneling of user data traffic between APs and WLCs, enabling centralized policy enforcement and QoS.
|
Attributes |
Split MAC |
Local MAC |
|---|---|---|
|
MAC Function Distribution |
802.11 protocol split between AP and WLC |
All MAC functions performed at AP |
|
Data Frame Handling |
Encapsulated and exchanged between WLC and AP |
Locally bridged or tunneled as Ethernet frames |
|
Management Frame Processing |
Partially at AP, partially at WLC |
Entirely at AP |
 Tip |
In either mode, the AP processes Layer 2 wireless management frames locally before forwarding them to the controller. |
Example: CAPWAP Join and Data Flow
For example, when a new AP is powered on, it sends a CAPWAP discovery request to locate a controller. After receiving a discovery response, the AP establishes a secure DTLS connection, sends a join request, and upon acceptance, the controller manages the AP’s configuration and data traffic through CAPWAP channels.
Reset button settings
The reset button on the IW9165E device allows users to perform different reset actions based on how long the button is pressed.
-
Pressing the reset button for less than 20 seconds performs a full reset.
-
Pressing the reset button for more than 20 seconds and less than 60 seconds performs a full factory reset (clears the FIPS flag).
-
The LED turns blinking red after the boot loader receives the reset signal.
Reset button operation details
To perform a reset, ensure you press the device's reset button before powering on the device. The LED will indicate the reset status by turning blinking red after the boot loader receives the reset signal.
Ethernet port usage on CAPWAP mode
The Catalyst IW9165E supports up to a 3.6 Gbps PHY data rate with two 2x2 multiple input and multiple output (MIMO) and two ethernet ports (2.5G mGig and 1G).
Catalyst IW9165E have below internal port mapping rules:
-
Wired0 – One mGig (2.5 Gbps) ethernet ports with 802.3af, 802.3at, 802.3bt PoE support.

Note
The wired0 port is used as CAPWAP uplink port in the AP local/Flexconnect mode.
-
Wired1 – 1Gig ethernet Lan Port.

Note
Starting from 17.14.1 release, RLAN feature is not supported in the wired1 port.
 Feedback
Feedback