- Preface
- Overview
- Using the Command-Line Interface
- Configuring the Switch Alarms
- Performing Switch Setup Configuration
- Configuring Cisco IOS Configuration Engine
- Configuring Switch Clusters
- Performing Switch Administration
- Configuring PTP
- Configuring PROFINET
- Configuring CIP
- Configuring SDM Templates
- Configuring Switch-Based Authentication
- Configuring IEEE 802.1x Port-Based Authentication
- Configuring Web-Based Authentication
- Configuring Interface Characteristics
- Configuring Smartports Macros
- Configuring VLANs
- Configuring VTP
- Configuring Voice VLAN
- Configuring STP
- Configuring MSTP
- Configuring Optional Spanning-Tree Features
- Configuring Resilient Ethernet Protocol
- Configuring Flex Links and the MAC Address-Table Move Update Feature
- Configuring DHCP
- Configuring Dynamic ARP Inspection
- Configuring IP Source Guard
- Configuring IGMP Snooping and MVR
- Configuring Port-Based Traffic Control
- Configuring SPAN and RSPAN
- Configuring LLDP, LLDP-MED, and Wired Location Service
- Configuring CDP
- Configuring UDLD
- Configuring RMON
- Configuring System Message Logging
- Configuring SNMP
- Configuring Network Security with ACLs
- Configuring QoS
- Configuring Auto-QoS
- Configuring EtherChannels
- Configuring Static IP Unicast Routing
- Configuring IPv6 Host Functions
- Configuring Link State Tracking
- Configuring IPv6 MLD Snooping
- Configuring Cisco IOS IP SLAs Operations
- Configuring Layer 2 Network Address Translation
- Troubleshooting the Cisco IOS Software
- Working with the Cisco IOS File System, Configuration Files, and Software Images
Configuring Resilient Ethernet Protocol
Finding Feature Information
Your software release may not support all the features documented in this chapter. For the latest feature information and caveats, see the release notes for your platform and software release.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to http://www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Prerequisites for REP
You can configure all of these features when your switch is running the Per VLAN Spanning-Tree Plus (PVST+). You can configure only the noted features when your switch is running the Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP) or the Rapid PVST+(RPVST+) protocol.
Restrictions for REP
You can configure the UplinkFast or the BackboneFast feature for Rapid PVST+ or for the MSTP, but the feature remains disabled (inactive) until you change the spanning-tree mode to PVST+.
Information About Configuring REP
REP
Resilient Ethernet Protocol (REP) is a Cisco proprietary protocol that provides an alternative to Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) to control network loops, handle link failures, and improve convergence time. REP controls a group of ports connected in a segment, ensures that the segment does not create any bridging loops, and responds to link failures within the segment. REP provides a basis for constructing more complex networks and supports VLAN load balancing.
One REP segment is a chain of ports connected to each other and configured with a segment ID. Each segment consists of standard (non-edge) segment ports and two user-configured edge ports. A switch can have no more than two ports that belong to the same segment, and each segment port can have only one external neighbor. A segment can go through a shared medium, but on any link only two ports can belong to the same segment. REP is supported only on Layer 2 trunk interfaces.
Figure 23-1 shows an example of a segment consisting of six ports spread across four switches. Ports E1 and E2 are configured as edge ports. When all ports are operational (as in the segment on the left), a single port is blocked, shown by the diagonal line. When there is a failure in the network, as shown in the diagram on the right, the blocked port returns to the forwarding state to minimize network disruption.
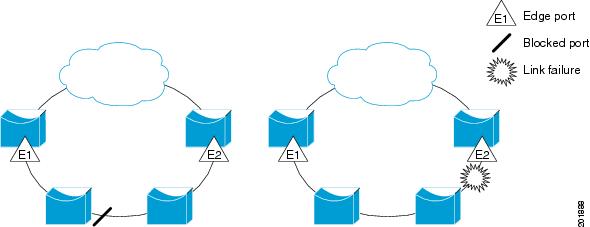
The segment shown in Figure 23-1 is an open segment; there is no connectivity between the two edge ports. The REP segment cannot cause a bridging loop and it is safe to connect the segment edges to any network. All hosts connected to switches inside the segment have two possible connections to the rest of the network through the edge ports, but only one connection is accessible at any time. If a failure causes a host to be unable to access its usual gateway, REP unblocks all ports to ensure that connectivity is available through the other gateway.
The segment shown in Figure 23-2, with both edge ports located on the same switch, is a ring segment. In this configuration, there is connectivity between the edge ports through the segment. With this configuration, you can create a redundant connection between any two switches in the segment.
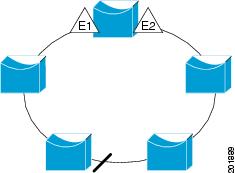
REP segments have these characteristics:
- If all ports in the segment are operational, one port (referred to as the alternate port) is in the blocked state for each VLAN. If VLAN load balancing is configured, two ports in the segment control the blocked state of VLANs.
- If one or more ports in a segment is not operational, causing a link failure, all ports forward traffic on all VLANs to ensure connectivity.
- In case of a link failure, the alternate ports are unblocked as quickly as possible. When the failed link comes back up, a logically blocked port per VLAN is selected with minimal disruption to the network.
You can construct almost any type of network based on REP segments. REP also supports VLAN load-balancing, controlled by the primary edge port but occurring at any port in the segment.
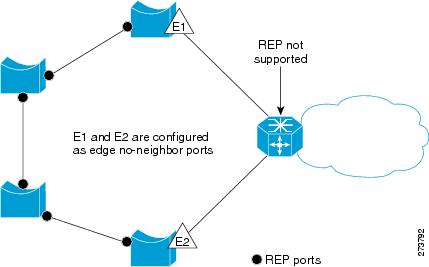
In access ring topologies, the neighboring switch might not support REP, as shown in Figure 23-3. In this case, you can configure the non-REP facing ports (E1 and E2) as edge no-neighbor ports. These ports inherit all properties of edge ports, and you can configure them the same as any edge port, including configuring them to send STP or REP topology change notices to the aggregation switch. In this case the STP topology change notice (TCN) that is sent is a multiple spanning-tree (MST) STP message.
Figure 23-3 Edge No-Neighbor Ports
- You must configure each segment port; an incorrect configuration can cause forwarding loops in the networks.
- REP can manage only a single failed port within the segment; multiple port failures within the REP segment cause loss of network connectivity.
- You should configure REP only in networks with redundancy. Configuring REP in a network without redundancy causes loss of connectivity.
Link Integrity
REP does not use an end-to-end polling mechanism between edge ports to verify link integrity. It implements local link failure detection. The REP Link Status Layer (LSL) detects its REP-aware neighbor and establishes connectivity within the segment. All VLANs are blocked on an interface until it detects the neighbor. After the neighbor is identified, REP determines which neighbor port should become the alternate port and which ports should forward traffic.
Each port in a segment has a unique port ID. The port ID format is similar to that used by the spanning tree algorithm: a port number (unique on the bridge), associated to a MAC address (unique in the network). When a segment port is coming up, its LSL starts sending packets that include the segment ID and the port ID. The port is declared as operational after it performs a three-way handshake with a neighbor in the same segment.
A segment port does not become operational if:
- No neighbor has the same segment ID.
- More than one neighbor has the same segment ID.
- The neighbor does not acknowledge the local port as a peer.
Each port creates an adjacency with its immediate neighbor. Once the neighbor adjacencies are created, the ports negotiate to determine one blocked port for the segment, the alternate port. All other ports become unblocked. By default, REP packets are sent to a BPDU class MAC address. The packets can also be sent to the Cisco multicast address, which is used only to send blocked port advertisement (BPA) messages when there is a failure in the segment. The packets are dropped by devices not running REP.
Fast Convergence
Because REP runs on a physical link basis and not a per-VLAN basis, only one hello message is required for all VLANs, reducing the load on the protocol. We recommend that you create VLANs consistently on all switches in a given segment and configure the same allowed VLANs on the REP trunk ports. To avoid the delay introduced by relaying messages in software, REP also allows some packets to be flooded to a regular multicast address. These messages operate at the hardware flood layer (HFL) and are flooded to the whole network, not just the REP segment. Switches that do not belong to the segment treat them as data traffic. You can control flooding of these messages by configuring a dedicated administrative VLAN for the whole domain.
The estimated convergence recovery time on fiber interfaces is less than 200 ms for the local segment with 200 VLANs configured. Convergence for VLAN load balancing is 300 ms or less.
VLAN Load Balancing
One edge port in the REP segment acts as the primary edge port; the other as the secondary edge port. It is the primary edge port that always participates in VLAN load balancing in the segment. REP VLAN balancing is achieved by blocking some VLANs at a configured alternate port and all other VLANs at the primary edge port. When you configure VLAN load balancing, you can specify the alternate port in one of three ways:
- By entering the port ID of the interface. To identify the port ID of a port in the segment, enter the show interface rep detail interface configuration command for the port.
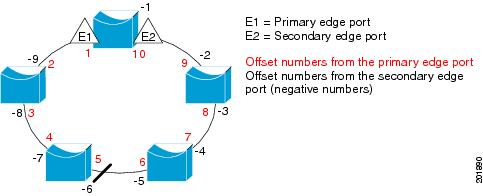
- By entering the neighbor offset number of a port in the segment, which identifies the downstream neighbor port of an edge port. The neighbor offset number range is –256 to +256; a value of 0 is invalid. The primary edge port has an offset number of 1; positive numbers above 1 identify downstream neighbors of the primary edge port. Negative numbers indicate the secondary edge port (offset number -1) and its downstream neighbors.

Note![]() You configure offset numbers on the primary edge port by identifying a port’s downstream position from the primary (or secondary) edge port. You would never enter an offset value of 1 because that is the offset number of the primary edge port itself.
You configure offset numbers on the primary edge port by identifying a port’s downstream position from the primary (or secondary) edge port. You would never enter an offset value of 1 because that is the offset number of the primary edge port itself.
Figure 23-4 shows neighbor offset numbers for a segment where E1 is the primary edge port and E2 is the secondary edge port. The red numbers inside the ring are numbers offset from the primary edge port; the black numbers outside of the ring show the offset numbers from the secondary edge port. Note that you can identify all ports (except the primary edge port) by either a positive offset number (downstream position from the primary edge port) or a negative offset number (downstream position from the secondary edge port). If E2 became the primary edge port, its offset number would then be 1 and E1 would be -1.
- By entering the preferred keyword to select the port that you previously configured as the preferred alternate port with the rep segment segment-id preferred interface configuration command.
Figure 23-4 Neighbor Offset Numbers in a Segment
When the REP segment is complete, all VLANs are blocked. When you configure VLAN load balancing, you must also configure triggers in one of two ways:
- Manually trigger VLAN load balancing at any time by entering the rep preempt segment segment-id privileged EXEC command on the switch that has the primary edge port.
- Configure a preempt delay time by entering the rep preempt delay seconds interface configuration command. After a link failure and recovery, VLAN load balancing begins after the configured preemption time period elapses. Note that the delay timer restarts if another port fails before the time has elapsed.

Note![]() When VLAN load balancing is configured, it does not start working until triggered by either manual intervention or a link failure and recovery.
When VLAN load balancing is configured, it does not start working until triggered by either manual intervention or a link failure and recovery.
When VLAN load balancing is triggered, the primary edge port sends out a message to alert all interfaces in the segment about the preemption. When the secondary port receives the message, it is reflected into the network to notify the alternate port to block the set of VLANs specified in the message and to notify the primary edge port to block the remaining VLANs.
You can also configure a particular port in the segment to block all VLANs. Only the primary edge port initiates VLAN load balancing, which is not possible if the segment is not terminated by an edge port on each end. The primary edge port determines the local VLAN load balancing configuration.
Reconfigure the primary edge port to reconfigure load balancing. When you change the load balancing configuration, the primary edge port again waits for the rep preempt segment command or for the configured preempt delay period after a port failure and recovery before executing the new configuration. If you change an edge port to a regular segment port, the existing VLAN load balancing status does not change. Configuring a new edge port might cause a new topology configuration.
Spanning Tree Interaction
REP does not interact with STP or with the FlexLink feature, but can coexist with both. A port that belongs to a segment is removed from spanning tree control and STP BPDUs are not accepted or sent from segment ports. Therefore, STP cannot run on a segment.
To migrate from an STP ring configuration to REP segment configuration, begin by configuring a single port in the ring as part of the segment and continue by configuring contiguous ports to minimize the number of segments. Each segment always contains a blocked port, so multiple segments means multiple blocked ports and a potential loss of connectivity. When the segment has been configured in both directions up to the location of the edge ports, you then configure the edge ports.
REP Ports
Ports in REP segments are Failed, Open, or Alternate.
- A port configured as a regular segment port starts as a failed port.
- After the neighbor adjacencies are determined, the port transitions to alternate port state, blocking all VLANs on the interface. Blocked port negotiations occur and when the segment settles, one blocked port remains in the alternate role and all other ports become open ports.
- When a failure occurs in a link, all ports move to the failed state. When the alternate port receives the failure notification, it changes to the open state, forwarding all VLANs.
A regular segment port converted to an edge port, or an edge port converted to a regular segment port, does not always result in a topology change. If you convert an edge port into a regular segment port, VLAN load balancing is not implemented unless it has been configured. For VLAN load balancing, you must configure two edge ports in the segment.
A segment port that is reconfigured as a spanning tree port restarts according the spanning tree configuration. By default, this is a designated blocking port. If PortFast is configured or if STP is disabled, the port goes into the forwarding state.
REP Segments
A segment is a collection of ports connected one to the other in a chain and configured with a segment ID. To configure REP segments, you configure the REP administrative VLAN (or use the default VLAN 1) and then add the ports to the segment using interface configuration mode. You should configure two edge ports in the segment, with one of them the primary edge port and the other by default the secondary edge port. A segment has only one primary edge port. If you configure two ports in a segment as the primary edge port, for example, ports on different switches, the REP selects one of them to serve as the segment primary edge port. You can also optionally configure where to send segment topology change notices (STCNs) and VLAN load balancing.
Default REP Configuration
REP is disabled on all interfaces. When enabled, the interface is a regular segment port unless it is configured as an edge port.
When REP is enabled, the sending of segment topology change notices (STCNs) is disabled, all VLANs are blocked, and the administrative VLAN is VLAN 1.
When VLAN load balancing is enabled, the default is manual preemption with the delay timer disabled. If VLAN load balancing is not configured, the default after manual preemption is to block all VLANs at the primary edge port.
REP Configuration Guidelines
Follow these guidelines when configuring REP:
- We recommend that you begin by configuring one port and then configure the contiguous ports to minimize the number of segments and the number of blocked ports.
- If more than two ports in a segment fail when no external neighbors are configured, one port changes to a forwarding state for the data path to help maintain connectivity during configuration. In the show rep interface privileged EXEC command output, the Port Role for this port shows as Fail Logical Open ; the Port Role for the other failed port shows as Fail No Ext Neighbor. When the external neighbors for the failed ports are configured, the ports go through the alternate port state transitions and eventually go to an open state or remain as the alternate port, based on the alternate port election mechanism.
- REP ports must be Layer 2 trunk ports.
- Be careful when configuring REP through a Telnet connection. Because REP blocks all VLANs until another REP interface sends a message to unblock it, you might lose connectivity to the switch if you enable REP in a Telnet session that accesses the switch through the same interface.
- You cannot run REP and STP or REP and Flex Links on the same segment or interface.
- If you connect an STP network to the REP segment, be sure that the connection is at the segment edge. An STP connection that is not at the edge could cause a bridging loop because STP does not run on REP segments. All STP BPDUs are dropped at REP interfaces.
- You must configure all trunk ports in the segment with the same set of allowed VLANs, or a misconfiguration occurs.
- REP ports follow these rules:
–![]() There is no limit to the number of REP ports on a switch; however, only two ports on a switch can belong to the same REP segment.
There is no limit to the number of REP ports on a switch; however, only two ports on a switch can belong to the same REP segment.
–![]() If only one port on a switch is configured in a segment, the port should be an edge port.
If only one port on a switch is configured in a segment, the port should be an edge port.
–![]() If two ports on a switch belong to the same segment, they must be both edge ports, both regular segment ports, or one regular port and one edge no-neighbor port. An edge port and regular segment port on a switch cannot belong to the same segment.
If two ports on a switch belong to the same segment, they must be both edge ports, both regular segment ports, or one regular port and one edge no-neighbor port. An edge port and regular segment port on a switch cannot belong to the same segment.
–![]() If two ports on a switch belong to the same segment and one is configured as an edge port and one as a regular segment port (a misconfiguration), the edge port is treated as a regular segment port.
If two ports on a switch belong to the same segment and one is configured as an edge port and one as a regular segment port (a misconfiguration), the edge port is treated as a regular segment port.
- REP interfaces come up in a blocked state and remains in a blocked state until notified that it is safe to unblock. You need to be aware of this to avoid sudden connection losses.
- REP sends all LSL PDUs in untagged frames on the native VLAN. The BPA message sent to the Cisco multicast address is sent on the administration VLAN, which is VLAN 1 by default.
- You can configure how long a REP interface remains up without receiving a hello from a neighbor. You can use the rep lsl-age-timer value interface configuration command to set the time from 120 ms to 10000 ms. The LSL hello timer is then set to the age-timer value divided by 3. In normal operation, three LSL hellos are sent before the age timer on the peer switch expires and checks for hello messages.
–![]() In Cisco IOS Release 12.2(52)SE, the LSL age-timer range changed from 3000 to 10000 ms in 500-ms increments to 120 to 10000 ms in 40-ms increments. If the REP neighbor device is not running Cisco IOS release 12.2(52)SE or later, do not configure a timer value less than 3000 ms. Configuring a value less than 3000 ms causes the port to shut down because the neighbor switch does not respond within the requested time period.
In Cisco IOS Release 12.2(52)SE, the LSL age-timer range changed from 3000 to 10000 ms in 500-ms increments to 120 to 10000 ms in 40-ms increments. If the REP neighbor device is not running Cisco IOS release 12.2(52)SE or later, do not configure a timer value less than 3000 ms. Configuring a value less than 3000 ms causes the port to shut down because the neighbor switch does not respond within the requested time period.
–![]() EtherChannel port channel interfaces do not support LSL age-timer values less than 1000 ms. If you try to configure a value less than 1000 ms on a port channel, you receive an error message and the command is rejected.
EtherChannel port channel interfaces do not support LSL age-timer values less than 1000 ms. If you try to configure a value less than 1000 ms on a port channel, you receive an error message and the command is rejected.
REP Administrative VLAN
To avoid the delay introduced by relaying messages in software for link-failure or VLAN-blocking notification during load balancing, REP floods packets at the hardware flood layer (HFL) to a regular multicast address. These messages are flooded to the whole network, not just the REP segment. You can control flooding of these messages by configuring an administrative VLAN for the whole domain.
Follow these guidelines when configuring the REP administrative VLAN:
How to Configure REP
Configuring the REP Administrative VLAN
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
Specifies the administrative VLAN. The range is 2 to 4096. The default is VLAN 1. To set the admin VLAN to 1, enter the no rep admin vlan global configuration command. |
||
Configuring REP Interfaces
For REP operation, you need to enable it on each segment interface and identify the segment ID. This step is required and must be done before other REP configuration. You must also configure a primary and secondary edge port on each segment. All other steps are optional.
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
Specifies the interface, and enters interface configuration mode. The interface can be a physical Layer 2 interface or a port channel (logical interface). The port-channel range is 1 to 48. |
||
rep segment segment-id [ edge [ no-neighbor ] [ primary ]] [ preferred ] |
Enables REP on the interface, and identifies a segment number. The segment ID range is from 1 to 1024. These optional keywords are available: Note You must configure two edge ports, including one primary edge port for each segment.
Note Although each segment can have only one primary edge port, if you configure edge ports on two different switches and enter the primary keyword on both switches, the configuration is allowed. However, REP selects only one of these ports as the segment primary edge port. You can identify the primary edge port for a segment by entering the show rep topology privileged EXEC command.
Note Configuring a port as preferred does not guarantee that it becomes the alternate port; it merely gives it a slight edge among equal contenders. The alternate port is usually a previously failed port. |
|
(Optional) Configures the edge port to send segment topology change notices (STCNs). |
||
rep block port { id port-id | neighbor_offset | preferred } vlan { vlan-list | all } |
(Optional) Configures VLAN load balancing on the primary edge port, identify the REP alternate port in one of three ways, and configure the VLANs to be blocked on the alternate port.
Note Because you enter this command at the primary edge port (offset number 1), you would never enter an offset value of 1 to identify an alternate port. |
|
(Optional) You must enter this command and configure a preempt time delay if you want VLAN load balancing to automatically trigger after a link failure and recovery. The time delay range is 15 to 300 seconds. The default is manual preemption with no time delay. |
||
(Optional) Configures a time (in milliseconds) for which the REP interface remains up without receiving a hello from a neighbor. The range is from 120 to 10000 ms in 40-ms increments. The default is 5000 ms (5 seconds). Note If the neighbor device is not running Cisco IOS Release 12.2(52)SE or later, it only accepts values from 3000 to 10000 ms in 500-ms intervals. EtherChannel port channel interfaces do not support LSL age-timer values less than 1000 ms. |
||
Setting Manual Preemption for VLAN Load Balancing
If you do not enter the rep preempt delay seconds interface configuration command on the primary edge port to configure a preemption time delay, the default is to manually trigger VLAN load balancing on the segment. Be sure that all other segment configuration has been completed before manually preempting VLAN load balancing. When you enter the rep preempt segment segment-id command, a confirmation message appears before the command is executed because preemption can cause network disruption.
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
Configuring SNMP Traps for REP
You can configure the switch to send REP-specific traps to notify the SNMP server of link operational status changes and port role changes.
Monitoring and Maintaining REP
Configuration Examples for Configuring REP
Configuring the Administrative VLAN: Example
This example shows how to configure the administrative VLAN as VLAN 100 and verify the configuration by entering the show interface rep detail command on one of the REP interfaces:
Segment-id: 2 (Edge)
PortID: 00010019E7144680
Preferred flag: No
Operational Link Status: TWO_WAY
Current Key: 0002001121A2D5800E4D
Port Role: Open
Blocked Vlan: <empty>
Admin-vlan: 100
Preempt Delay Timer: disabled
LSL Ageout Timer: 5000 ms
LSL PDU rx: 3322, tx: 1722
HFL PDU rx: 32, tx: 5
BPA TLV rx: 16849, tx: 508
BPA (STCN, LSL) TLV rx: 0, tx: 0
BPA (STCN, HFL) TLV rx: 0, tx: 0
EPA-ELECTION TLV rx: 118, tx: 118
EPA-COMMAND TLV rx: 0, tx: 0
EPA-INFO TLV rx: 4214, tx: 4190
Configuring a Primary Edge Port: Examples
This example shows how to configure an interface as the primary edge port for segment 1, to send STCNs to segments 2 through 5, and to configure the alternate port as the port with port ID 0009001818D68700 to block all VLANs after a preemption delay of 60 seconds after a segment port failure and recovery. The interface is configured to remain up for 6000 milliseconds without receiving a hello from a neighbor.
This example shows how to configure an interface as the primary edge port when the interface has no external REP neighbor:
Configuring VLAN Blocking: Example
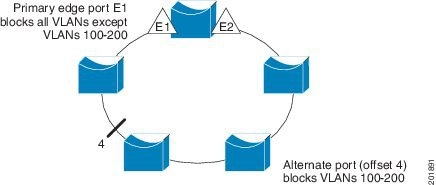
This example shows how to configure the VLAN blocking configuration shown in Figure 23-5. The alternate port is the neighbor with neighbor offset number 4. After manual preemption, VLANs 100 to 200 are blocked at this port, and all other VLANs are blocked at the primary edge port E1 (Gigabit Ethernet port 1/0/1).
Figure 23-5 Example of VLAN Blocking
Additional References
The following sections provide references related to switch administration:
Related Documents
|
|
|
|---|---|
Standards
|
|
|
|---|---|
No new or modified standards are supported by this feature, and support for existing standards has not been modified by this feature. |
MIBs
|
|
|
|---|---|
To locate and download MIBs using Cisco IOS XR software, use the Cisco MIB Locator found at the following URL and choose a platform under the Cisco Access Products menu: http://cisco.com/public/sw-center/netmgmt/cmtk/mibs.shtml |
RFCs
|
|
|
|---|---|
No new or modified RFCs are supported by this feature, and support for existing RFCs has not been modified by this feature. |
 Feedback
Feedback