- Preface
- Overview
- Using the Command-Line Interface
- Configuring the Switch Alarms
- Performing Switch Setup Configuration
- Configuring Cisco IOS Configuration Engine
- Configuring Switch Clusters
- Performing Switch Administration
- Configuring PTP
- Configuring PROFINET
- Configuring CIP
- Configuring SDM Templates
- Configuring Switch-Based Authentication
- Configuring IEEE 802.1x Port-Based Authentication
- Configuring Web-Based Authentication
- Configuring Interface Characteristics
- Configuring Smartports Macros
- Configuring VLANs
- Configuring VTP
- Configuring Voice VLAN
- Configuring STP
- Configuring MSTP
- Configuring Optional Spanning-Tree Features
- Configuring Resilient Ethernet Protocol
- Configuring Flex Links and the MAC Address-Table Move Update Feature
- Configuring DHCP
- Configuring Dynamic ARP Inspection
- Configuring IP Source Guard
- Configuring IGMP Snooping and MVR
- Configuring Port-Based Traffic Control
- Configuring SPAN and RSPAN
- Configuring LLDP, LLDP-MED, and Wired Location Service
- Configuring CDP
- Configuring UDLD
- Configuring RMON
- Configuring System Message Logging
- Configuring SNMP
- Configuring Network Security with ACLs
- Configuring QoS
- Configuring Auto-QoS
- Configuring EtherChannels
- Configuring Static IP Unicast Routing
- Configuring IPv6 Host Functions
- Configuring Link State Tracking
- Configuring IPv6 MLD Snooping
- Configuring Cisco IOS IP SLAs Operations
- Configuring Layer 2 Network Address Translation
- Troubleshooting the Cisco IOS Software
- Working with the Cisco IOS File System, Configuration Files, and Software Images
Cisco IE 2000 Switch Software Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS Release 15.0(2)EB
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
- Updated:
- January 7, 2016
Chapter: Configuring PROFINET
Configuring PROFINET
Finding Feature Information
Your software release may not support all the features documented in this chapter. For the latest feature information and caveats, see the release notes for your platform and software release.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to http://www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Restrictions for Configuring PROFINET
The switch does not support isochronous real-time communication channels.
Information About Configuring PROFINET
PROFINET is the PROFIBUS International (PI) open Industrial Ethernet Standard that uses TCP/IP and IT standards for automation control. PROFINET is particularly useful for industrial automation systems and process control networks, in which motion control and precision control of instrumentation and test equipment are important. It emphasizes data exchange and defines communication paths to meet speed requirements. PROFINET communication is scalable on three levels:
- Normal non-real-time communication uses TCP/IP and enables bus cycle times of approximately 100 ms.
- Real-time communication enables cycle times of approximately 10 ms.
- Isochronous real-time communication enables cycle times of approximately 1 ms.
PROFINET I/O is a modular communication framework for distributed automation applications. PROFINET I/O uses cyclic data transfer to exchange data, alarms, and diagnostic information with programmable controllers, input/output (I/O) devices, and other automation controllers (for example, motion controllers).
PROFINET I/O recognizes three classes of devices:
PROFINET Device Roles
Figure 9-1 PROFINET Device Roles
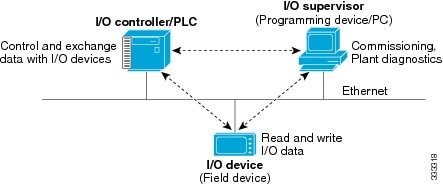
An I/O controller is a programmable logic controller (PLC) that controls I/O devices and exchanges data such as configuration, alarms, and I/O data through an automation program. The I/O controller and the I/O supervisor exchange diagnostic information. The I/O controller shares configuration and input/output information with the I/O device and receives alarms from the I/O device.
PROFINET is designed to be the sole or primary management system platform. Because the I/O controller detects the switch with the Discovery and Configuration Protocol (DCP), and sets the device name and IP address, you do not need to enter Cisco IOS commands for the basic configuration. For advanced configurations (for example, QoS, DHCP, and similar features) you must use Cisco IOS commands on the switch because these features cannot be configured by using PROFINET.
An I/O supervisor is an engineering station, such as a human machine interface (HMI) or PC, used for commissioning, monitoring, and diagnostic analysis. The I/O supervisor exchanges diagnostic, status, control, and parameter information with the I/O device.
An I/O device is a distributed input/output device such as a sensor, an actuator, or a motion controller.

Note![]() The switch acts as an I/O device, providing a PROFINET management connection to the I/O controllers.
The switch acts as an I/O device, providing a PROFINET management connection to the I/O controllers.
In a PROFINET I/O system, all the I/O devices communicate over an Ethernet communication network to meet the automation industry requirement for bus cycle times of less than 100 ms. The network uses switches and full-duplex data exchange to avoid data collisions.
PROFINET Device Data Exchange
After PROFINET uses DCP to discover devices, including the switch, they establish application relationships (ARs) and communication relationships (CRs). After a connection is established and information about device parameters is exchanged, input and output data is exchanged. The switch uses non-real-time CRs to exchange the data attributes listed in Table 9-1 and Table 9-2 .
|
|
|
|---|---|
Broadcast, unicast, multicast threshold exceeds configured levels. |
|
PROFINET devices are integrated by using a general station description (GSD) file that contains the data for engineering and data exchange between the I/O controller, the I/O supervisor, and the I/O devices, including the switch. Each PROFINET I/O field device must have an associated GSD file that describes the properties of the device and contains all this information required for configuration:
- Device identification information (device ID, vendor ID and name, product family, number of ports)
- Number and types of pluggable modules
- The Cisco IE 2000 8-port expander modules are not hot-swappable. Turn off the switch before connecting or disconnecting expander modules.
- Error text for diagnostic information
- Communication parameters for I/O devices, including the minimum cycle time, the reduction ratio, and the watch dog time

Note![]() Although the Cisco IE 2000 switch has a default reduction ratio of 128 ms, we recommend a reduction ratio of 256 ms or 512 ms to reduce the load on the switch CPU when the switch uses a complex configuration.
Although the Cisco IE 2000 switch has a default reduction ratio of 128 ms, we recommend a reduction ratio of 256 ms or 512 ms to reduce the load on the switch CPU when the switch uses a complex configuration.
- Configuration data for the I/O device modules, including speed, duplex, VLAN, port security information, alarms, and broadcast-rate-limiting thresholds
- Parameters configured for I/O device modules for the attributes listed in Table 9-2
The GSD file is on the switch, but the I/O supervisor uses this file.

Note![]() You must use the GSD file that is associated with the Cisco IOS release on the switch to manage your PROFINET network. Both the I/O supervisor and the Cisco IOS software alert you to a mismatch between the GSD file and the switch Cisco IOS software version.
You must use the GSD file that is associated with the Cisco IOS release on the switch to manage your PROFINET network. Both the I/O supervisor and the Cisco IOS software alert you to a mismatch between the GSD file and the switch Cisco IOS software version.
How to Configure PROFINET
Configuring PROFINET
You can use either the PROFINET software on the I/O supervisor or the Cisco IOS software for basic switch configuration.
Default Configuration
PROFINET is enabled by default on all the base switch module and expansion-unit Ethernet ports. If PROFINET has been disabled, follow the instructions in the “Enabling PROFINET” section.
Enabling PROFINET
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
(Optional) Sets the PROFINET device identifier (ID) by using the Cisco IOS software. The maximum length is 240 characters. The only special characters allowed are the period (.) and hyphen (-), and they are allowed only in specific positions within the ID string. It can have multiple labels within the string. Each label can be from 1 to 63 characters, and labels must be separated by a period (.). The final character in the string must not be zero (0). For more details about configuring the PROFINET ID, see the PROFINET specification, document number TC2-06-0007a, filename PN-AL-protocol_2722_V22_Oct07, available from PROFIBUS. |
||
(Optional) Changes the VLAN number. The default VLAN number is 1. The VLAN ID range is 1-4096. |
||
Monitoring and Maintaining PROFINET
|
|
|
|---|---|
Troubleshooting PROFINET
The PLC has LEDs that display red for alarms, and the I/O supervisor software monitors those alarms.
To troubleshoot PROFINET use the debug profinet privileged EXEC command with the keywords shown in Commands for Troubleshooting the PROFINET Configuration Table 9-4 . Be aware that the output of a debug command might cause a serial link to fail. You should use these commands only under the guidance of a Cisco Technical Support engineer. When you use this command, use Telnet to access the Cisco IOS command-line interface (CLI) by using Ethernet rather than a serial port.
Additional References
The following sections provide references related to switch administration:
Related Documents
|
|
|
|---|---|
Standards
|
|
|
|---|---|
No new or modified standards are supported by this feature, and support for existing standards has not been modified by this feature. |
MIBs
|
|
|
|---|---|
To locate and download MIBs using Cisco IOS XR software, use the Cisco MIB Locator found at the following URL and choose a platform under the Cisco Access Products menu: http://cisco.com/public/sw-center/netmgmt/cmtk/mibs.shtml |
RFCs
|
|
|
|---|---|
No new or modified RFCs are supported by this feature, and support for existing RFCs has not been modified by this feature. |
 Feedback
Feedback