- Preface
- Overview
- Using the Command-Line Interface
- Configuring the Switch Alarms
- Performing Switch Setup Configuration
- Configuring Cisco IOS Configuration Engine
- Configuring Switch Clusters
- Performing Switch Administration
- Configuring PTP
- Configuring PROFINET
- Configuring CIP
- Configuring SDM Templates
- Configuring Switch-Based Authentication
- Configuring IEEE 802.1x Port-Based Authentication
- Configuring Web-Based Authentication
- Configuring Interface Characteristics
- Configuring Smartports Macros
- Configuring VLANs
- Configuring VTP
- Configuring Voice VLAN
- Configuring STP
- Configuring MSTP
- Configuring Optional Spanning-Tree Features
- Configuring Resilient Ethernet Protocol
- Configuring Flex Links and the MAC Address-Table Move Update Feature
- Configuring DHCP
- Configuring Dynamic ARP Inspection
- Configuring IP Source Guard
- Configuring IGMP Snooping and MVR
- Configuring Port-Based Traffic Control
- Configuring SPAN and RSPAN
- Configuring LLDP, LLDP-MED, and Wired Location Service
- Configuring CDP
- Configuring UDLD
- Configuring RMON
- Configuring System Message Logging
- Configuring SNMP
- Configuring Network Security with ACLs
- Configuring QoS
- Configuring Auto-QoS
- Configuring EtherChannels
- Configuring Static IP Unicast Routing
- Configuring IPv6 Host Functions
- Configuring Link State Tracking
- Configuring IPv6 MLD Snooping
- Configuring Cisco IOS IP SLAs Operations
- Configuring Layer 2 Network Address Translation
- Troubleshooting the Cisco IOS Software
- Working with the Cisco IOS File System, Configuration Files, and Software Images
Cisco IE 2000 Switch Software Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS Release 15.0(2)EB
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
- Updated:
- January 7, 2016
Chapter: Configuring DHCP
- Finding Feature Information
- Information About Configuring DHCP
- DHCP Snooping
- DHCP Server
- DHCP Relay Agent
- DHCP Snooping
- Option-82 Data Insertion
- Cisco IOS DHCP Server Database
- DHCP Snooping Binding Database
- Default DHCP Snooping Settings
- DHCP Snooping Configuration Guidelines
- DHCP Snooping Binding Database Guidelines
- Packet Forwarding Address
- DHCP Server Port-Based Address Allocation
- How to Configure DHCP
- Monitoring and Maintaining DHCP
- Configuration Examples for Configuring DHCP
- Additional References
Configuring DHCP
Finding Feature Information
Your software release may not support all the features documented in this chapter. For the latest feature information and caveats, see the release notes for your platform and software release.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to http://www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Information About Configuring DHCP
This chapter describes how to configure Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) snooping and option-82 data insertion, and the DHCP server port-based address allocation features on the switch. It also describes how to configure the IP source guard feature.
DHCP Snooping
DHCP is widely used in LAN environments to dynamically assign host IP addresses from a centralized server, which significantly reduces the overhead of administration of IP addresses. DHCP also helps conserve the limited IP address space because IP addresses no longer need to be permanently assigned to hosts; only those hosts that are connected to the network consume IP addresses.
DHCP Server
The DHCP server assigns IP addresses from specified address pools on a switch or router to DHCP clients and manages them. If the DHCP server cannot give the DHCP client the requested configuration parameters from its database, it forwards the request to one or more secondary DHCP servers defined by the network administrator.
DHCP Relay Agent
A DHCP relay agent is a Layer 3 device that forwards DHCP packets between clients and servers. Relay agents forward requests and replies between clients and servers when they are not on the same physical subnet. Relay agent forwarding is different from the normal Layer 2 forwarding, in which IP datagrams are switched transparently between networks. Relay agents receive DHCP messages and generate new DHCP messages to send on output interfaces.
DHCP Snooping
DHCP snooping is a DHCP security feature that provides network security by filtering untrusted DHCP messages and by building and maintaining a DHCP snooping binding database, also referred to as a DHCP snooping binding table.
DHCP snooping acts like a firewall between untrusted hosts and DHCP servers. You use DHCP snooping to differentiate between untrusted interfaces connected to the end user and trusted interfaces connected to the DHCP server or another switch.

Note![]() For DHCP snooping to function properly, all DHCP servers must be connected to the switch through trusted interfaces.
For DHCP snooping to function properly, all DHCP servers must be connected to the switch through trusted interfaces.
An untrusted DHCP message is a message that is received from outside the network or firewall. When you use DHCP snooping in a service-provider environment, an untrusted message is sent from a device that is not in the service-provider network, such as a customer’s switch. Messages from unknown devices are untrusted because they can be sources of traffic attacks.
The DHCP snooping binding database has the MAC address, the IP address, the lease time, the binding type, the VLAN number, and the interface information that corresponds to the local untrusted interfaces of a switch. It does not have information regarding hosts interconnected with a trusted interface.
In a service-provider network, a trusted interface is connected to a port on a device in the same network. An untrusted interface is connected to an untrusted interface in the network or to an interface on a device that is not in the network.
When a switch receives a packet on an untrusted interface and the interface belongs to a VLAN in which DHCP snooping is enabled, the switch compares the source MAC address and the DHCP client hardware address. If the addresses match (the default), the switch forwards the packet. If the addresses do not match, the switch drops the packet.
The switch drops a DHCP packet when one of these situations occurs:
- A packet from a DHCP server, such as a DHCPOFFER, DHCPACK, DHCPNAK, or DHCPLEASEQUERY packet, is received from outside the network or firewall.
- A packet is received on an untrusted interface, and the source MAC address and the DHCP client hardware address do not match.
- The switch receives a DHCPRELEASE or DHCPDECLINE broadcast message that has a MAC address in the DHCP snooping binding database, but the interface information in the binding database does not match the interface on which the message was received.
- A DHCP relay agent forwards a DHCP packet that includes a relay-agent IP address that is not 0.0.0.0, or the relay agent forwards a packet that includes option-82 information to an untrusted port.
If the switch is an aggregation switch supporting DHCP snooping and is connected to an edge switch that is inserting DHCP option-82 information, the switch drops packets with option-82 information when packets are received on an untrusted interface. If DHCP snooping is enabled and packets are received on a trusted port, the aggregation switch does not learn the DHCP snooping bindings for connected devices and cannot build a complete DHCP snooping binding database.
When an aggregation switch can be connected to an edge switch through an untrusted interface and you enter the ip dhcp snooping information option allow-untrusted global configuration command, the aggregation switch accepts packets with option-82 information from the edge switch. The aggregation switch learns the bindings for hosts connected through an untrusted switch interface. The DHCP security features, such as dynamic ARP inspection or IP source guard, can still be enabled on the aggregation switch while the switch receives packets with option-82 information on untrusted input interfaces to which hosts are connected. The port on the edge switch that connects to the aggregation switch must be configured as a trusted interface.
Option-82 Data Insertion
In residential, metropolitan Ethernet-access environments, DHCP can centrally manage the IP address assignments for a large number of subscribers. When the DHCP option-82 feature is enabled on the switch, a subscriber device is identified by the switch port through which it connects to the network (in addition to its MAC address). Multiple hosts on the subscriber LAN can be connected to the same port on the access switch and are uniquely identified.

Note![]() The DHCP option-82 feature is supported only when DHCP snooping is globally enabled and on the VLANs to which subscriber devices using this feature are assigned.
The DHCP option-82 feature is supported only when DHCP snooping is globally enabled and on the VLANs to which subscriber devices using this feature are assigned.
Figure 25-1 is an example of a metropolitan Ethernet network in which a centralized DHCP server assigns IP addresses to subscribers connected to the switch at the access layer. Because the DHCP clients and their associated DHCP server do not reside on the same IP network or subnet, a DHCP relay agent (the Catalyst switch) is configured with a helper address to enable broadcast forwarding and to transfer DHCP messages between the clients and the server.
Figure 25-1 DHCP Relay Agent in a Metropolitan Ethernet Network
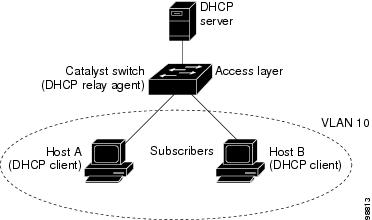
When you enable the DHCP snooping information option-82 on the switch, this sequence of events occurs:
- The host (DHCP client) generates a DHCP request and broadcasts it on the network.
- When the switch receives the DHCP request, it adds the option-82 information in the packet. By default, the remote-ID suboption is the switch MAC address, and the circuit-ID suboption is the port identifier, vlan-mod-port, from which the packet is received.
- If the IP address of the relay agent is configured, the switch adds this IP address in the DHCP packet.
- The switch forwards the DHCP request that includes the option-82 field to the DHCP server.
- The DHCP server receives the packet. If the server is option-82-capable, it can use the remote ID, the circuit ID, or both to assign IP addresses and implement policies, such as restricting the number of IP addresses that can be assigned to a single remote ID or circuit ID. The DHCP server then repeats the option-82 field in the DHCP reply.
- The DHCP server unicasts the reply to the switch if the request was relayed to the server by the switch. The switch verifies that it originally inserted the option-82 data by inspecting the remote ID and possibly the circuit ID fields. The switch removes the option-82 field and forwards the packet to the switch port that connects to the DHCP client that sent the DHCP request.
In the default suboption configuration, when the described sequence of events occurs, the values in these fields in Figure 25-2 do not change:
–![]() Length of the suboption type
Length of the suboption type
–![]() Length of the circuit-ID type
Length of the circuit-ID type
–![]() Length of the suboption type
Length of the suboption type
–![]() Length of the remote-ID type
Length of the remote-ID type
In the port field of the circuit-ID suboption, the port numbers start at 3. For example, on a switch with eight 10/100 ports and small form-factor pluggable (SFP) module slots, port 3 is the Fast Ethernet 1/1 port, port 4 is the Fast Ethernet 1/2 port, and so forth. Port 11 is the SFP module slot 1/1, and so forth.
Figure 25-2 shows the packet formats for the remote-ID suboption and the circuit-ID suboption when the default suboption configuration is used. The switch uses the packet formats when you globally enable DHCP snooping and enter the ip dhcp snooping information option global configuration command.
Figure 25-2 Suboption Packet Formats
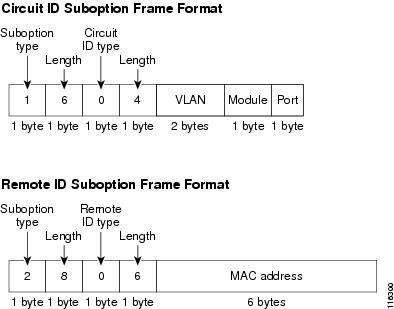
shows the packet formats for user-configured remote-ID and circuit-ID suboptions The switch uses these packet formats when DHCP snooping is globally enabled and when the ip dhcp snooping information option format remote-id global configuration command and the ip dhcp snooping vlan information option format-type circuit-id string interface configuration command are entered.
The values for these fields in the packets change from the default values when you configure the remote-ID and circuit-ID suboptions:
–![]() The length values are variable, depending on the length of the string that you configure.
The length values are variable, depending on the length of the string that you configure.
–![]() The length values are variable, depending on the length of the string that you configure.
The length values are variable, depending on the length of the string that you configure.
Figure 25-3 User-Configured Suboption Packet Formats
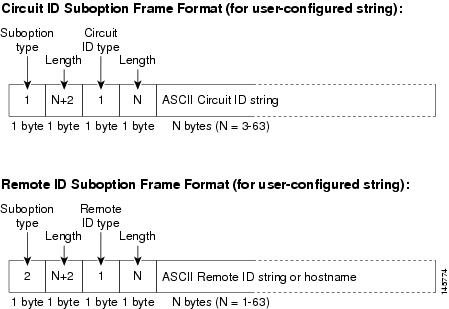
Cisco IOS DHCP Server Database
During the DHCP-based autoconfiguration process, the designated DHCP server uses the Cisco IOS DHCP server database. It has IP addresses, address bindings, and configuration parameters, such as the boot file.
An address binding is a mapping between an IP address and a MAC address of a host in the Cisco IOS DHCP server database. You can manually assign the client IP address, or the DHCP server can allocate an IP address from a DHCP address pool.
DHCP Snooping Binding Database
When DHCP snooping is enabled, the switch uses the DHCP snooping binding database to store information about untrusted interfaces. The database can have up to 8192 bindings.
Each database entry ( binding) has an IP address, an associated MAC address, the lease time (in hexadecimal format), the interface to which the binding applies, and the VLAN to which the interface belongs. The database agent stores the bindings in a file at a configured location. At the end of each entry is a checksum that accounts for all the bytes from the start of the file through all the bytes associated with the entry. Each entry is 72 bytes, followed by a space and then the checksum value.
To keep the bindings when the switch reloads, you must use the DHCP snooping database agent. If the agent is disabled, dynamic ARP inspection or IP source guard is enabled, and the DHCP snooping binding database has dynamic bindings, the switch loses its connectivity. If the agent is disabled and only DHCP snooping is enabled, the switch does not lose its connectivity, but DHCP snooping might not prevent DHCP spoofing attacks.
When reloading, the switch reads the binding file to build the DHCP snooping binding database. The switch updates the file when the database changes.
When a switch learns of new bindings or when it loses bindings, the switch immediately updates the entries in the database. The switch also updates the entries in the binding file. The frequency at which the file is updated is based on a configurable delay, and the updates are batched. If the file is not updated in a specified time (set by the write-delay and abort-timeout values), the update stops.
This is the format of the file with bindings:
Each entry in the file is tagged with a checksum value that the switch uses to verify the entries when it reads the file. The initial-checksum entry on the first line distinguishes entries associated with the latest file update from entries associated with a previous file update.
This is an example of a binding file:
When the switch starts and the calculated checksum value equals the stored checksum value, the switch reads entries from the binding file and adds the bindings to its DHCP snooping binding database. The switch ignores an entry when one of these situations occurs:
- The switch reads the entry and the calculated checksum value does not equal the stored checksum value. The entry and the ones following it are ignored.
- An entry has an expired lease time (the switch might not remove a binding entry when the lease time expires).
- The interface in the entry no longer exists on the system.
- The interface is a routed interface or a DHCP snooping-trusted interface.
Default DHCP Snooping Settings
|
|
|
|---|---|
Enabled in Cisco IOS software, requires configuration1 |
|
Enabled2 |
|
Enabled (invalid messages are dropped) 2 |
|
Replace the existing relay agent information 2 |
|
DHCP snooping option to accept packets on untrusted input interfaces3 |
|
Enabled in Cisco IOS software, requires configuration. Note The switch gets network addresses and configuration parameters only from a device configured as a DHCP server. |
|
Enabled in Cisco IOS software, requires configuration. This feature is operational only when a destination is configured. |
DHCP Snooping Configuration Guidelines
- You must globally enable DHCP snooping on the switch.
- DHCP snooping is not active until DHCP snooping is enabled on a VLAN.
- Before globally enabling DHCP snooping on the switch, make sure that the devices acting as the DHCP server and the DHCP relay agent are configured and enabled.
- Before configuring the DHCP snooping information option on your switch, be sure to configure the device that is acting as the DHCP server. For example, you must specify the IP addresses that the DHCP server can assign or exclude, or you must configure DHCP options for these devices.
- When configuring a large number of circuit IDs on a switch, consider the impact of lengthy character serstrings on the NVRAM or the flash memory. If the circuit-ID configurations, combined with other data, exceed the capacity of the NVRAM or the flash memory, an error message appears.
- Before configuring the DHCP relay agent on your switch, make sure to configure the device that is acting as the DHCP server. For example, you must specify the IP addresses that the DHCP server can assign or exclude, configure DHCP options for devices, or set up the DHCP database agent.
- If the DHCP relay agent is enabled but DHCP snooping is disabled, the DHCP option-82 data insertion feature is not supported.
- If a switch port is connected to a DHCP server, configure a port as trusted by entering the ip dhcp snooping trust interface configuration command.
- If a switch port is connected to a DHCP client, configure a port as untrusted by entering the no ip dhcp snooping trust interface configuration command.
- Do not enter the ip dhcp snooping information option allow-untrusted command on an aggregation switch to which an untrusted device is connected. If you enter this command, an untrusted device might spoof the option-82 information.
- You can display DHCP snooping statistics by entering the show ip dhcp snooping statistics user EXEC command, and you can clear the snooping statistics counters by entering the clear ip dhcp snooping statistics privileged EXEC command.

Note![]() Do not enable DHCP snooping on RSPAN VLANs. If DHCP snooping is enabled on RSPAN VLANs, DHCP packets might not reach the RSPAN destination port.
Do not enable DHCP snooping on RSPAN VLANs. If DHCP snooping is enabled on RSPAN VLANs, DHCP packets might not reach the RSPAN destination port.
DHCP Snooping Binding Database Guidelines
- Because both NVRAM and the flash memory have limited storage capacity, we recommend that you store the binding file on a TFTP server.
- For network-based URLs (such as TFTP and FTP), you must create an empty file at the configured URL before the switch can write bindings to the binding file at that URL. See the documentation for your TFTP server to determine whether you must first create an empty file on the server; some TFTP servers cannot be configured this way.
- To ensure that the lease time in the database is accurate, we recommend that you enable and configure NTP. For more information, see the “Configuring Time and Date Manually” section.
- If NTP is configured, the switch writes binding changes to the binding file only when the switch system clock is synchronized with NTP.
Packet Forwarding Address
If the DHCP server and the DHCP clients are on different networks or subnets, you must configure the switch with the ip helper-address address interface configuration command. The general rule is to configure the command on the Layer 3 interface closest to the client. The address used in the ip helper-address command can be a specific DHCP server IP address, or it can be the network address if other DHCP servers are on the destination network segment. Using the network address enables any DHCP server to respond to requests.
DHCP Server Port-Based Address Allocation
DHCP server port-based address allocation is a feature that enables DHCP to maintain the same IP address on an Ethernet switch port regardless of the attached device client identifier or client hardware address.
When Ethernet switches are deployed in the network, they offer connectivity to the directly connected devices. In some environments, such as on a factory floor, if a device fails, the replacement device must be working immediately in the existing network. With the current DHCP implementation, there is no guarantee that DHCP would offer the same IP address to the replacement device. Control, monitoring, and other software expect a stable IP address associated with each device. If a device is replaced, the address assignment should remain stable even though the DHCP client has changed.
When configured, the DHCP server port-based address allocation feature ensures that the same IP address is always offered to the same connected port even as the client identifier or client hardware address changes in the DHCP messages received on that port. The DHCP protocol recognizes DHCP clients by the client identifier option in the DHCP packet. Clients that do not include the client identifier option are identified by the client hardware address. When you configure this feature, the port name of the interface overrides the client identifier or hardware address and the actual point of connection, the switch port, becomes the client identifier.
In all cases, by connecting the Ethernet cable to the same port, the same IP address is allocated through DHCP to the attached device.
The DHCP server port-based address allocation feature is only supported on a Cisco IOS DHCP server and not a third-party server.
By default, DHCP server port-based address allocation is disabled.
How to Configure DHCP
Configuring the DHCP Relay Agent
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
Enables the DHCP server and relay agent on your switch. By default, this feature is enabled. |
||
Specifying the Packet Forwarding Address
Enabling DHCP Snooping and Option 82
Enabling the DHCP Snooping Binding Database Agent
Enabling DHCP Server Port-Based Address Allocation
Preassigning an IP Address
Monitoring and Maintaining DHCP
Configuration Examples for Configuring DHCP
Enabling DHCP Server Port-Based Address Allocation: Examples
In this example, a subscriber identifier is automatically generated, and the DHCP server ignores any client identifier fields in the DHCP messages and uses the subscriber identifier instead. The subscriber identifier is based on the short name of the interface and the client preassigned IP address 10.1.1.7.
This example shows that the preassigned address was correctly reserved in the DHCP pool:
Enabling DHCP Snooping: Example
This example shows how to enable DHCP snooping globally and on VLAN 10 and to configure a rate limit of 100 packets per second on a port:
Additional References
The following sections provide references related to switch administration:
Related Documents
Standards
|
|
|
|---|---|
No new or modified standards are supported by this feature, and support for existing standards has not been modified by this feature. |
MIBs
|
|
|
|---|---|
To locate and download MIBs using Cisco IOS XR software, use the Cisco MIB Locator found at the following URL and choose a platform under the Cisco Access Products menu: http://cisco.com/public/sw-center/netmgmt/cmtk/mibs.shtml |
RFCs
|
|
|
|---|---|
No new or modified RFCs are supported by this feature, and support for existing RFCs has not been modified by this feature. |
 Feedback
Feedback