Feature History for IP SLAs - ICMP Path Echo Operation
This table provides release and platform support information for the features explained in this module.
These features are available in all the releases subsequent to the one they were introduced in, unless noted otherwise.
|
Release |
Feature Name and Description |
Supported Platform |
|---|---|---|
| Cisco IOS XE 17.18.1 |
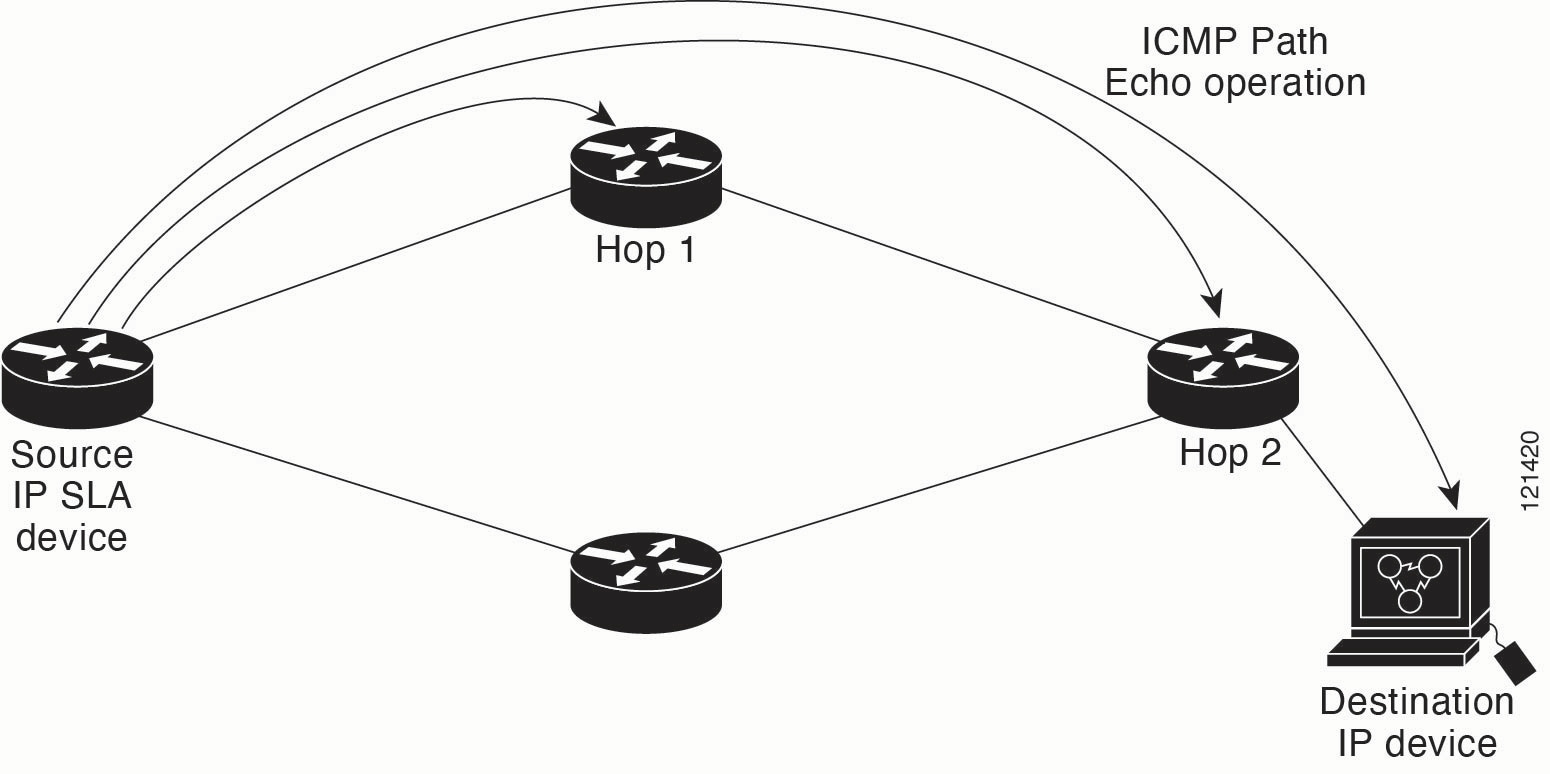
IP SLAs - ICMP Path Echo Operation: This operation monitors both end-to-end and hop-by-hop response times between a Cisco device and other IP-enabled devices. |
Cisco C9350 Series Smart Switches Cisco C9610 Series Smart Switches |
 Feedback
Feedback