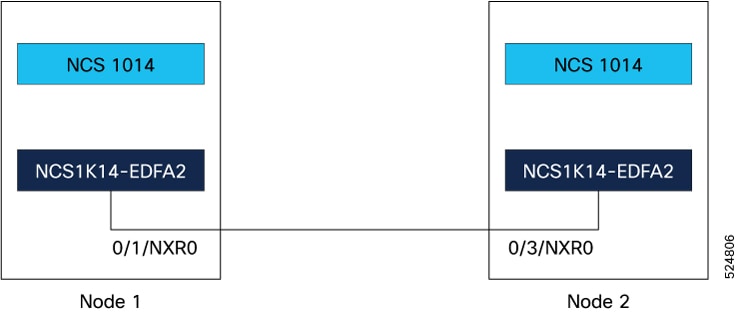
NCS 1014 link topology discovery
Automatic network topology discovery
Network topology discovery is automatic when you use an OSC channel created through the EDFA2 card. By connecting the NCS 1014 to Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) networks, NCS 1014 network information is automatically communicated across multiple LANs and WANs. In a network utilizing an OSC channel, all nodes can communicate with each other through this channel.
Understanding OSPF
OSPF is a link-state Internet routing protocol. Link-state protocols monitor their links with adjacent routers and assess the status of their connections to neighbors. These protocols advertise their directly connected networks and active links. Each link-state router compiles these link-state advertisements to form a topology of the entire network or area. From this database, the router calculates a routing table by constructing a shortest path tree. Routes are recalculated when topology changes occur. NCS 1014 supports only OSPFv2.
OSPF protocol in NCS networks
NCS 1014 uses the OSPFv2 protocol within internal NCS networks for node discovery, circuit routing, and node management. Enabling OSPFv2 on the NCS allows the NCS topology to be communicated to OSPF routers on a LAN. This eliminates the need to manually input static routes for NCS subnetworks. OSPF divides networks into smaller regions, called areas, each with a unique ID number, known as the area ID. Every OSPF network includes one backbone area called "area 0," and all other OSPF areas must connect to area 0.
 Feedback
Feedback