Precision Time Protocol
A Precision Time Protocol (PTP) is a time synchronization protocol that
-
achieves nanosecond-level synchronization of real-time clocks across networked devices
-
uses a master-client hierarchy to organize clock relationships, and
-
enables all devices in the network to continually synchronize to the most accurate clock through ongoing exchanges of timing messages.
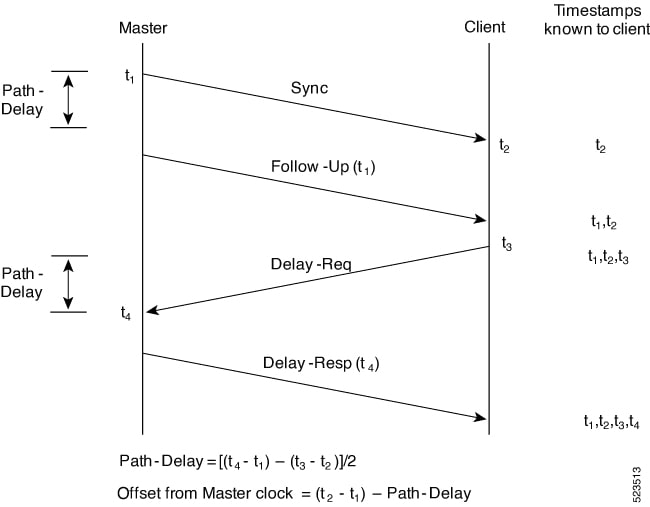
PTP is defined in the IEEE 1588 standard. The network selects the best available clock, known as the grandmaster clock, as the authoritative time source. All other network clocks, known as members, synchronize with this grandmaster clock. The protocol identifies the port connected to the most accurate device (the master clock), then synchronizes all other devices to it and maintains synchronization throughout the network.
Restrictions for PTP
Consider these restrictions when enabling PTP on Cisco 8000 series routers.
-
Do not configure PTP over IP on tagged interfaces of the 88-LC1-52Y8H-EM and 88-LC1-12TH24FH-E line cards.
-
The Sync2 interface is supported only when the 10 megahertz (MHz), one pulse per second (PPS), and time-of-day (ToD) ports are configured.
-
Configure PTP only on interfaces without global MACSec or MACSec enabled.
-
Enable PTP only when global MACSec-FIPS-Post is not configured, since MACSec-FIPS-Post is unavailable for individual interfaces.
-
Do not configure transparent Clock. Use one-step clock mode.
-
Configure the device to receive follow-up PTP packets to support a two-step peer primary. The device does not send follow-up PTP packets.
-
Avoid configuring PTP on bundle ethernet interfaces, bundle ethernet subinterfaces, loopback interfaces, and LAG ethernet subinterfaces.
-
Configure PTP only on individual bundle member links; do not configure it on bundle-ether interfaces.
Benefits of PTP
Use PTP to achieve accurate and stable timing in smart grid power automation applications, such as peak-hour billing, virtual power generators, and outage management. Accurate timing helps you monitor networks and troubleshoot issues more effectively. You can implement PTP, a message-based protocol, on packet-based networks such as ethernet.
PTP offers these benefits for your Ethernet network:
-
It has low cost and is easy to set up in existing Ethernet networks.
-
It requires minimal bandwidth for PTP data packets.
-
It is compatible with routers and different types of network delays.
Guidelines for PTP
The guidelines for PTP on Cisco 8000 Series routers are:
-
PTP is supported on Gigabit Ethernet interfaces (1G, 10G, 40G, and 100G).
-
If you use encapsulation default or untag on a subinterface, configure PTP on the subinterface—not on the main interface.

 Feedback
Feedback