Cisco 8000 Series Routers Licensing Quick Reference
Licensing solutions for Cisco 8000 Series Routers
The available licensing solutions are:
- Smart Licensing: A flexible and convenient cloud-based software licensing model that simplifies the management of software licenses across your organization. It automatically creates a pool of licenses or entitlements for use throughout the organization. With Smart Licensing, you only pay for the features you currently need, with the option to upgrade as necessary, ensuring the security of your investment. For more information, see Smart Licensing.
- Smart Licensing Using Policy: An enhanced version of Smart Licensing that enables immediate use of devices right out of the box. This licensing solution streamlines the process, making it easier to manage your licenses. For more information, see Smart Licensing Using Policy.
- Specific License Reservation: A solution specifically designed for classified environments where electronic communication is restricted. In such environments, routers are unable to communicate directly with the Cisco Smart Software Manager (CSSM) or through SSM On-Prem. SLR enables the use of all entitlements on the router without the need for communication with Cisco. For more information, see Activate SLR licenses for air-gapped deployments.
- Traditional Licensing: A model that involves purchasing of a perpetual license for a specific feature set. The license is activated with a license key that is tied to the hardware device. You can activate all available software packages on your network devices and enable all the bundled features.
- Smart Licensing Perpetual mode: An operational mode of Smart Licensing Using Policy where compliance and enforcement actions are disabled. This mode applies to perpetual license customers who choose not to deploy Smart Licensing Using Policy registration or reporting workflows. For more information, see Smart Licensing Perpetual mode.
Comparison of licensing solutions
This table summarizes and contrasts the key attributes, supported deployments, communication modes, and reporting features of Cisco’s main licensing solutions. Use this guide to quickly determine which licensing method best meets your network requirements.
|
License Attributes |
Smart Licensing Using Policy |
Smart Licensing |
Specific License Reservation |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Activation of licenses |
Creates a trust relationship with CSSM |
Registers with CSSM |
Generates code from the device to reserve licenses in CSSM |
|
Supported deployments |
|
|
Offline deployment for air-gapped environments |
|
License communication transport mode |
|
|
Not applicable for SLR |
|
License reporting |
Generates RUM reports from the device and synchronizes with CSSM |
Generates Product Instance reports from CSSM or SSM On-Prem |
Not applicable for SLR |
|
Models supported |
Flexible Consumption Model 1, Flexible Consumption Model 2 |
Flexible Consumption Model 1 |
Not applicable |
Starting with Release 25.3.1, IOS XR software no longer supports Call Home transport mode. Configure CSLU or Smart Transport mode to ensure seamless operation of the licensing solution.
Flexible Consumption Models
A Flexible Consumption Model (FCM) is a licensing framework that
- allows organizations to tailor their software expenditures to actual, real-time usage requirements
- provides easy scalability based on changing business needs, and
- enables financial flexibility through subscription or usage-based payment structures.
Features of FCM
- Pay-as-you-grow: Enables you to lower initial costs and add more capacity over time.
- Simplify operations: FCM delivers the carrier-class IOS-XR software feature set with two software suites, Essentials and Advantage, that simplify license management.
- Utilize capital efficiently: License pooling enables an efficient way to share licenses across the network.
- Protect investment: Software portability provides investment protection by enabling porting of licenses to next-generation hardware.For more information, see Cisco IOS XR Software Flexible Consumption Model Data Sheet.
Enabling FCM
FCM is enabled by default on the Cisco 8000 Series routers.
Compliance requirements for FCM
Smart Licensing and Smart Licensing Using Policy solutions facilitate FCM by providing a centralized way to manage licenses with ease.
FCM lets you pay only for the software you use and quickly adjust subscriptions as your business grows or changes. These models typically require a low initial investment and support rapid increases in license consumption as needed. FCM requires specific actions and reporting by network devices to maintain compliance.
- Smart Licensing requirements: Devices must be registered to Smart Licensing and actively report usage to be considered compliant.
- Smart Licensing Using Policy requirements: Devices must have trust enablement and generate the first license usage report within 90 days.
- License usage reports: License usage is checked daily and reported to the Smart Licensing Manager at Cisco.com
In summary, FCM allows software costs to align with actual usage, while Smart Licensing or Smart Licensing Using Policy streamline the license management process.
Types of FCM
Cisco 8000 Series routers support 2 types of FCM. These models help customers optimize costs and efficiently scale network resources.
- FCM 1: Provides flexible billing and is suitable for standard enterprise and data center deployments.
- FCM 2: Pay-as-You-Grow licensing model that gives you the capability and flexibility to purchase software capacity as and when needed.
Comparison of FCM models and license suites
Cisco 8000 Series routers support two models of FCM licensing - FCM 1 and FCM 2. Each model offers distinct licensing suites to help organizations optimize costs and scale their networks efficiently.
|
Attributes |
FCM 1 |
FCM 2 |
|---|---|---|
|
Model description |
Provides flexible billing and is suitable for standard enterprise and data center deployments. |
Pay-as-You-Grow licensing model that gives you the capability and flexibility to purchase software capacity as and when needed. |
|
License suites |
Essentials, Advantage |
Essentials, Advantage, Premier |
|
License structure |
Hierarchical - higher tier includes lower |
Hierarchical - higher tier includes lower |
|
Premier suite |
Not available |
Available |
Components of FCM licensing
Both FCM 1 and FCM 2 comprise of these components:
- The hardware.
- The perpetual software component, known as Right To Use (RTU), which provides indefinite software licensing.
- The recurring software component, known as Software Innovation Access (SIA), which allows continuous software upgrades, license pooling, and faster access to new features for the subscription term.
For FCM 1, some product families may include, optional, a-la-carte software perpetual licenses for specialized platform-specific features.
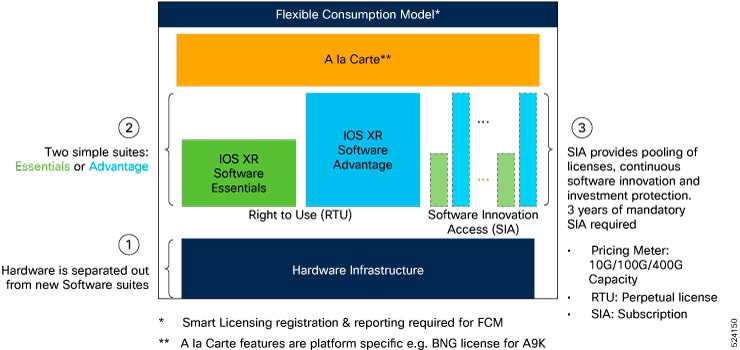
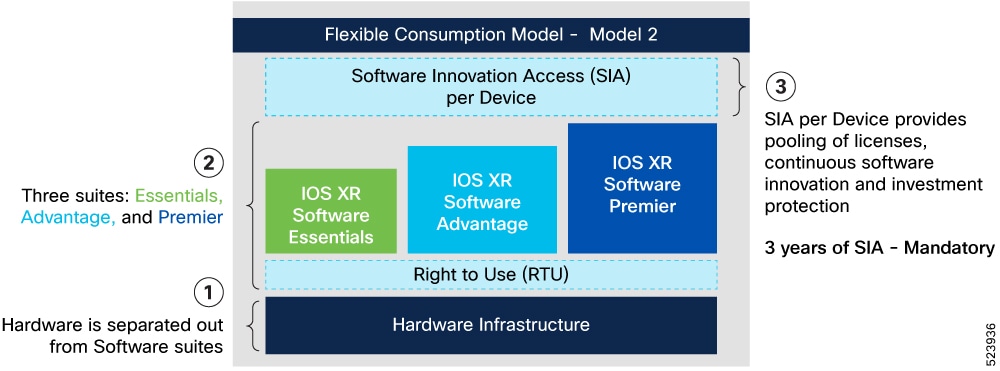
License suite tiers
Both FCM models follows a hierarchical structure where each higher-tier license encompasses the features and capabilities of the lower tiers.
- Essentials suite: The foundational tier, offering basic features and capabilities. The Essentials license suite serves fundamental transport needs. It includes the IOS XR comprehensive suite of routing and management services.
- Advantage suite: This tier includes everything in the Essentials tier, plus additional advanced features. The Advantage license suite enhances applications and network resilience. It includes all features of Essentials Software licenses with extra advanced routing and management services.
- Premier suite (FCM 2 only): The highest tier, which includes all features from both the Essentials and Advantage tiers, along with the most comprehensive set of functionalities. The Premier suite offers scalability for larger networks. It includes all features of Advantage Software licenses for highly advanced features.
Each license suite is nested, meaning Premier includes Advantage and Essentials, while Advantage includes Essentials.
All license suites use a nested structure, wherein each higher-tier suite includes the features and capabilities of the tiers below it.
FCM models and license suites
Cisco 8000 Series Routers and line cards support FCM Model 1 and FCM Model 2. The table shows the hardware, FCM model, and the available license suites.
|
When your router is... |
The supported FCM is... |
And the available licenses are... |
|---|---|---|
|
Cisco 8100 Series Cisco 8200 Series Cisco 8400 Series Cisco 8800 Series |
FCM1 |
Essential licenses that are necessary for every active port for operation. Example: ESS-CA-400G-RTU-2 |
|
Advantages without Essential licenses (earlier known as Advanced licenses) are Advantage licenses without the Essential licenses. Example: ADV-CA-400G-RTU-2 |
||
|
Advantages with Essential licenses are a combination of both Essential and Advantage licenses with a single PID. Example: ADN-CA-100G-SIA-3 |
||
|
Cisco 8608 Series Cisco 8700 Series Cisco 8200 Series and Cisco 8800 Series with P100-based ASIC |
FCM 2 |
Essential Licenses that are necessary for every active port for operation. Example: ESS-CA-400G-RTU-2 |
|
Advantages without Essential Licenses (earlier known as Advanced licenses) are Advantage licenses without the Essential licenses. Example: ADV-CA-400G-RTU-2 |
||
|
Advantages with Essential licenses are a combination of both Essential and Advantage licenses with a single PID. Example: ADN-CA-100G-SIA-3 |
||
|
Premier Licenses are additional licenses required on top of Advantage licenses for high scale services. Example: PRM-8KE-100G-RTU |
RTU licenses
Right-to-Use (RTU) licenses are software licenses that
- allows organizations to incrementally scale the functionality of their devices, and
- enables customers to pay for only what they use, especially when enabling features like advanced networking, higher bandwidth, or optical interfaces.
These are the various kinds of RTU licenses:
- Essential licenses: These are the base licenses that are required by every active port for its operation. For example, An example of Essential license is ESS-CA-400G-RTU-2.
- Advantage (earlier known as Advanced licenses) without essential licenses: These licenses are required on top of Essential Licenses for ports that use advanced features like L3VPN. An example of an Advantage license is ADV-CA-400G-RTU-2.
- Advantage with essential combination licenses: These licenses are packaged together as a combined entitlement. Example of an Advantage license with essentials is ESS-ADN-CA-100G-RTU.
- Tracking licenses: These licenses are required for hardware operation. An example of a Tracking license is 8201-TRK.
- Premier licenses: These additional licenses are required on top of Advantage licenses for large-scale VPN services. An example of a Premier license is PRM-8KE-100G-RTU.
SIA licenses
A Software Innovation Access (SIA) license is an FCM license that
- provides access to your network's latest software upgrades and features
- enables the consumption of Right-to-Use (RTU) licenses on for your devices , and
- ensures continuous software innovation and device support throughout the subscription period.
Benefits of SIA licenses
- Access to software innovation: Provides access to continuous software upgrades which contain latest features, security enhancements, and bug fixes for all your devices at a network level.
- Pooling of licenses: Allows RTU licenses to be shared across your FCM network from a common license pool through the virtual account.
- Protects your investment: Supports transfer of perpetual RTU licenses purchased for your current device to a next-generation router when you expand or upgrade your network.
Types of SIA licenses
The types of SIA licenses are
- Essential SIA license
- Advantage SIA license
- Premier SIA license
SIA license term
The initial term of a SIA subscription is for a term of three years. You can renew the subscription by contacting your Cisco account representative. An equal number of SIA licenses and corresponding RTU licenses are required to enjoy the benefits, and ensure that your network is in compliance.
If your device is in a state of SIA Out-of-Compliance (OOC) the benefits cease.
Guidelines and restrictions for SIA entitlement compliance
SIA entitlement compliance determines whether software upgrades are permitted for devices managed by FCM. Devices must remain in the In-Compliance state to allow software upgrades. Out-of-Compliance (OOC) devices face upgrade restrictions until compliance is restored.
-
The table shows the SIA compliance factors and its states.
SIA compliance and SIA states
Compliance
SIA In-Compliance State
SIA Out-of-Compliance State
License Usage Consumption
The device consumes fewer licenses than purchased.
The number of SIA licenses consumed exceeds the number of SIA licenses purchased. OOC can also occur when the RTU licenses consumed is higher than the number of SIA licenses purchased.
Reporting
The device reports regularly.
The term of the SIA license expires and you haven’t renewed the subscription.
Grace Period
NA
The SIA license grace period of 90 days expires.
License Authorization Status
NA
License Authorization Status is:
- Not Authorized: The license authorization code doesn’t contain sufficient counts for the request. This can occur when you attempt to use more licenses than the licenses available in your Virtual Account.
- Authorization Expired: The device hasn’t been able to connect to CSSM for an extended period, due to which the authorization status couldn’t be verified.
- When the device enters an OOC state, a grace period of 90 days, which is cumulative of all the previous occurrences, begins. During this period, SIA license benefits can still be availed. The system attempts to renew the authorization period by connecting with the CSSM during the grace period, or even after the grace period has expired. If an attempt isn’t successful, it remains in an OOC state. If the attempt is successful, a new authorization period begins and the device is In-Compliance.
Software upgrade restrictions based on compliance state
Software upgrades for a device are blocked under these circumstances:
- Software upgrades are blocked for all devices in the product family in the virtual account when the devices are Out-of-Compliance.
- Software upgrades are blocked when the device does not report within 90 days.
Manage SIA entitlement compliance
Step 1 | Verify the SIA Status field in the output of the show license platform summary command to check SIA device compliance status by checking. Example:Status: In-Compliance: Status: Out-of-Compliance (Grace Period Remaining): Status: Out-of-Compliance (Grace Period expired and upgrades are blocked): | ||||||||||
Step 2 | Perform these actions depending on the SIA status in step 1.
When you order SIA5 licenses in CSSM, your device may still display SIA3 in the output of the show license command on the device. However, CSSM enforces license compliance based on the SIA5 entitlement. You can validate your device against the SIA5 entitlement in CSSM, even if the device shows SIA3 locally. |
Licensing deployment guidelines
These are the guidelines for deploying licensing solutions.
- Starting with Release 24.3.1, tracking licenses are no longer supported.
- Starting with Release 25.3.1, IOS XR software no longer supports Call Home transport mode. Configure CSLU or Smart Transport mode to ensure seamless operation of the licensing solution.
-
License consumption for the interface varies depending on the releaase
If necessary, contact your Cisco Account Representative to convert SIA 400G license into four SIA 100G licenses.License consumption for interfacesIf your device is running a release...
Then the license consumption on the router is...
prior to Release 7.3.1
one 400G license per one 400G interface.
starting with Release 7.3.2 and later
four 100G licenses per one 400G interface.
License compliance requirements for the network
Network license compliance refers to the requirement that a product family within a virtual account must satisfy the following conditions:
- All devices are registered with the smart licensing server , either On-Prem or CSSM.
- The number of in-use SIA licenses does not exceed the number of available SIA licenses in your virtual account.
- The number of in-use RTU licenses does not exceed the number of available RTU licenses in your virtual account.
- Devices report license usage at least every 90 days.
Benefits of maintaining compliance:
- License pooling
- RTU portability
- Access to software upgrades
Consequences when out of compliance:
- Loss of license pooling and RTU portability.
- Software upgrade restrictions for the affected product family.
Enforcement scope
- Compliance is measured at the virtual account level and enforced based on the product family.
- Out-of-compliance status for one product family in a virtual account does not affect other families or the same family in a different virtual account.
Example:
If an ASR 9000 device exceeds its SIA license allocation, only ASR 9000s in that virtual account are affected—NCS 540 devices or ASR 9000s in other accounts are not.
FCM licenses
These tables provides the supported hardware for different FCM licenses for Cisco 8000 Series routers.
|
License Name |
Hardware Supported |
Consumption Pattern |
|---|---|---|
Essential and Advantage Licenses:
|
Fixed systems: Cisco 8201 Router Modular systems: Cisco 8812 Router |
The number of essential or advantage licenses that are consumed depends on the number of active ports and is reported on per chassis basis. |
Hardware Tracking Licenses: Fixed systems:
Line cards:
|
Tracking licenses are named based on the hardware supported. For example, 8201-TRK licenses support Cisco 8201 Router. |
The number of licenses that are consumed depends on the number of line cards in use. |
Some systems use tracking licenses such as XXX-TRK for hardware management in FCM 1.
Starting with Release 24.3.1, tracking licenses are no longer used.
|
License PID |
License Entitlement |
License Description |
|---|---|---|
|
ESS-CA-100G-RTU-2 |
Core and Agg Essentials Right-to-Use 100G |
Essentials 100G Right-to-Use License |
|
ESS-CA-400G-RTU-2 |
Core and Agg Advantage Right-to-Use 400G |
Essentials 400G Right-to-Use License |
|
ADN-CA-100G-RTU-2 |
Core and Agg Advantage Right-to-Use 100G |
Advantage 100G Right-to-Use License |
|
ADN-CA-400G-RTU-2 |
Core and Agg Advantage Right-to-Use 400G |
Advantage 400G Right-to-Use License |
|
ESS-ADN-CA-100G-RTU |
Core and Agg Essential and Advantage Right-to-Use / 100G |
Essential to Advantage 100G Right-to-Use License |
|
ESS-ADN-CA-400G-RTU |
Core and Agg Essential and Advantage Right-to-Use / 400G |
Essential to Advantage 400G Right-to-Use License |
|
License PID |
License Entitlement |
License Description |
|---|---|---|
|
ESS-CA-100G-SIA-3 |
Core/Aggr Essential SIA 3 yr term / 100G |
Essential 100G Software Innovation Access License |
|
ESS-CA-100G-SIA-5 |
Core/AggrEssential SIA 5 yr term / 100G |
Essential100G Software Innovation Access License |
|
ESS-CA-400G-SIA-3 |
Core/Agg Essential SIA 3 yr term / 400G |
Essential 400G Software Innovation Access License |
|
ESS-CA-400G-SIA-5 |
Core/Agg Essential SIA 5 yr term / 400G |
Essential 400G Software Innovation Access License |
|
ESS-ADN-CA-100GS3 |
Core and Agg Essentials - Advantage SIA per 400G 36- 59 months |
Essentials to Advantage 100G SIA Upgrade License |
|
ESS-ADN-CA-100GS5 |
Core and Agg Essentials - Advantage SIA per 100G 60- 120 months |
Essentials to Advantage 100G SIA Upgrade License |
|
ESS-ADN-CA-400GS3 |
Core and Agg Essentials - Advantage SIA per 400G 36- 59 months |
Essentials to Advantage 400G SIA Upgrade License |
|
ESS-ADN-CA-400GS5 |
Core and Agg Essentials - Advantage SIA per 400G 60- 120 months |
Essentials to Advantage 400G SIA Upgrade License |
|
License PID |
License Entitlement |
License Description |
|---|---|---|
|
ADN-CA-100G-SIA-3 |
Core/Agg Advantage SIA 3 yr term / 100G |
Advantage100G Software Innovation Access License |
|
ADN-CA-100G-SIA-5 |
Core/Agg Advantage SIA 5 yr term/ 100G |
Advantage100G Software Innovation Access License |
|
ADV-CA-100G-SIA-3 |
Core/Agg Advanced SIA 3 yr term / 100G |
Advantage 100G Software Innovation |
|
ADV-CA-100G-SIA-5 |
Core/Agg Advanced SIA 5 yr term / 100G |
Advantage 100G Software Innovation Access License |
|
ADN-CA-400G-SIA-3 |
Core/Agg Advantage SIA 3 yr term / 400G |
Advantage 400G Software Innovation Access License |
|
ADN-CA-400G-SIA-5 |
Core/Agg Advantage SIA 5 yr term / 400G |
Advantage 400G Software Innovation Access License |
|
ADV-CA-400G-SIA-3 |
Core/Agg Advanced SIA 3 yr term / 400G |
Advanced 400G Software Innovation Access License |
|
ADV-CA-400G-SIA-5 |
Core/Agg Advanced SIA 5 yr term / 400G |
Advanced 400G Software Innovation Access License |
|
License Name |
Hardware Supported |
Consumption Pattern |
|---|---|---|
|
Essentials: ESS-8KE-100G-RTU ESS-8KE-400G-RTU |
Fixed systems:
Modular systems:
Centralized systems:
|
Modular systems - Each line card requires a per system SIA for compliance. Fixed systems - One SIA per system |
|
Advantage: ADN-8KE-100G-RTU ADN-8KE-400G-RTU |
||
|
Premier: PRM-8KE-100G-RTU PRM-8KE-400G-RTU |
FCM 1 license consumption rules
Understanding the FCM 1 license consumption rules helps you calculate the number of licenses required for your device. Both SIA and RTU licenses follow the same calculation logic and so the number of SIA and RTU licenses required will be the same.
FCM 1 licensing includes these types of feature licenses:
- Per-system feature licenses: These licenses apply to the entire router and are consumed based on the total number of active interfaces for that feature. All active interfaces collectively consume these licenses.
- Per-port feature licenses: These licenses apply to specific interfaces on which the corresponding feature is configured and active.
Calculate per-system and per-port feature license consumption
The router calculates per-system and per-port feature license consumption based on feature priority and bandwidth. Follow this procedure to calculate the number of per-system and per-port licenses consumed by your device.
Step 1 | Obtain the total count of interfaces that consume per-system and per-port licenses from these tables listed by feature priority. When multiple features operate on the same interface, the router applies a priority order. Count only the highest priority feature for license consumption by that interface. These tables list the features in the priority order that the router follows, with per-system features having a higher priority over per-port features:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Step 2 | Calculate the total bandwidth for per-system and per-port features from the number of interfaces obtained in the previous step. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Step 3 | Apply these bandwidth rules to obtain the number of per-system and per-port feature licenses consumed by your device.
For example:
|
Revision history
|
Feature Name |
Release Information |
Feature Description |
|---|---|---|
| Release 25.4.1 |
Introduced in this release on: Fixed Systems (8200 [ASIC: Q200, P100], 8700 [ASIC: P100, K100], 8010 [ASIC: A100]); Centralized Systems (8600 [ASIC: Q200]); Modular Systems (8800 [LC ASIC: Q100, Q200, P100]) Smart Licensing Perpetual Mode simplifies licensing operations for customers with full-capacity perpetual licenses that cover the entire chassis or all line cards. These customers do not need to enable Smart Licensing Using Policy or report usage, which reduces administrative overhead across these deployments. |
|
| Release 25.4.1 |
Introduced in this release on: Fixed Systems (8010 [ASIC: A100])(select variants only*) *This feature is supported on:
|
|
| Release 25.4.1 |
Introduced in this release on: Fixed Systems (8010 [ASIC: A100], 8700 [ASIC: K100]) (select variants only*) *This feature is supported on:
|
|
| SIA licenses | Release 25.1.1 |
Introduced in this release on: Fixed Systems (8700 [ASIC: K100], 8010 [ASIC: A100])(select variants only*) *This feature is supported on:
|
| Support for Flexible Consumption Model 2 | Release 25.1.1 |
Introduced in this release on: Fixed Systems (8010 [ASIC: A100], 8700 [ASIC: K100]) (select variants only*) *This feature is supported on:
|
| Release 25.1.1 |
Introduced in this release on: Fixed Systems (8700 [ASIC: K100], 8010 [ASIC: A100])(select variants only*) *This feature is supported on:
|
|
Feature Name |
Release Information |
Feature Description |
|---|---|---|
| Support for Smart Licensing using Policy |
Release 24.3.1 |
Introduced in this release on: Fixed Systems (8200 [ASIC: P100], 8700 [ASIC: P100, K100])(select variants only*); Centralized Systems (8600 [ASIC:Q200])(select variants only*); Modular Systems (8800 [LC ASIC: P100])(select variants only*) Support for Smart Licensing using Policy is now extended to the hardware:
|
|
Release 24.3.1 |
Introduced in this release on: Fixed Systems (8200 [ASIC: P100], 8700 [ASIC: P100, K100])(select variants only*); Centralized Systems (8600 [ASIC:Q200])(select variants only*); Modular Systems (8800 [LC ASIC: P100])(select variants only*) The Flexible Consumption Model (FCM) provides the capability and flexibility to purchase software capacity as needed. This release introduces the FCM 2 that offers Essentials, Advantage, and Premier license suites. Premier license suite offers additional licenses that are required on top of Advantage licenses for high scale services. FCM 1 offers Essentials and Advantage license suites. These Cisco 8000 router variants and line cards support FCM Model 2.
|
|
|
Release 24.1.1 |
Cisco Smart Licensing Using Policy (SLP) is an enhancement to the existing Cisco Smart Licensing model. It streamlines the licensing process for Cisco IOS XR products by introducing a more flexible and automated approach. With SLP, you no longer need to register your device during installation, and there is no evaluation license state or period. This simplifies the licensing process and reduces complexity. To use SLP, your devices must establish trust and send the initial license usage report within 90 days. |
|
Feature Name |
Release Information |
Feature Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Support for Smart Licensing on the line cards, 8111_32EH and 8201_24H8FH |
Release 7.8.1 |
Support for Smart Licensing is now extended to the hardware:
|
| Release 7.5.4 |
Support for Smart Licensing is now extended to the 8202-32FH-M router. |
|
|
Support for Smart Licensing on the line cards, 8800-LC-48H-O, 88-LC0-36FH-MO and 88-LC0-36FH-O |
Release 7.3.16 |
Support for Smart Licensing is now extended to the hardware:
|
|
Release 7.3.1 |
Specific License Reservation is a solution designed for classified environments that don’t allow electronic communication in or out of the environment. |
|
|
Release 7.0.11 |
Smart Licensing is a cloud-based, flexible software licensing model that enables you to activate and manage Cisco software licenses across their organization. Smart Licensing solution allows you to track the status of your license and software usage trends. |