About Access Control Lists
ACL implementation for VXLAN is the same as regular IP traffic. The host traffic is not encapsulated in the ingress direction at the encapsulation switch. The implementation is a bit different for the VXLAN encapsulated traffic at the decapsulation switch as the ACL classification is based on the inner payload. The supported ACL scenarios for VXLAN are explained in the following topics and the unsupported cases are also covered for both encapsulation and decapsulation switches.
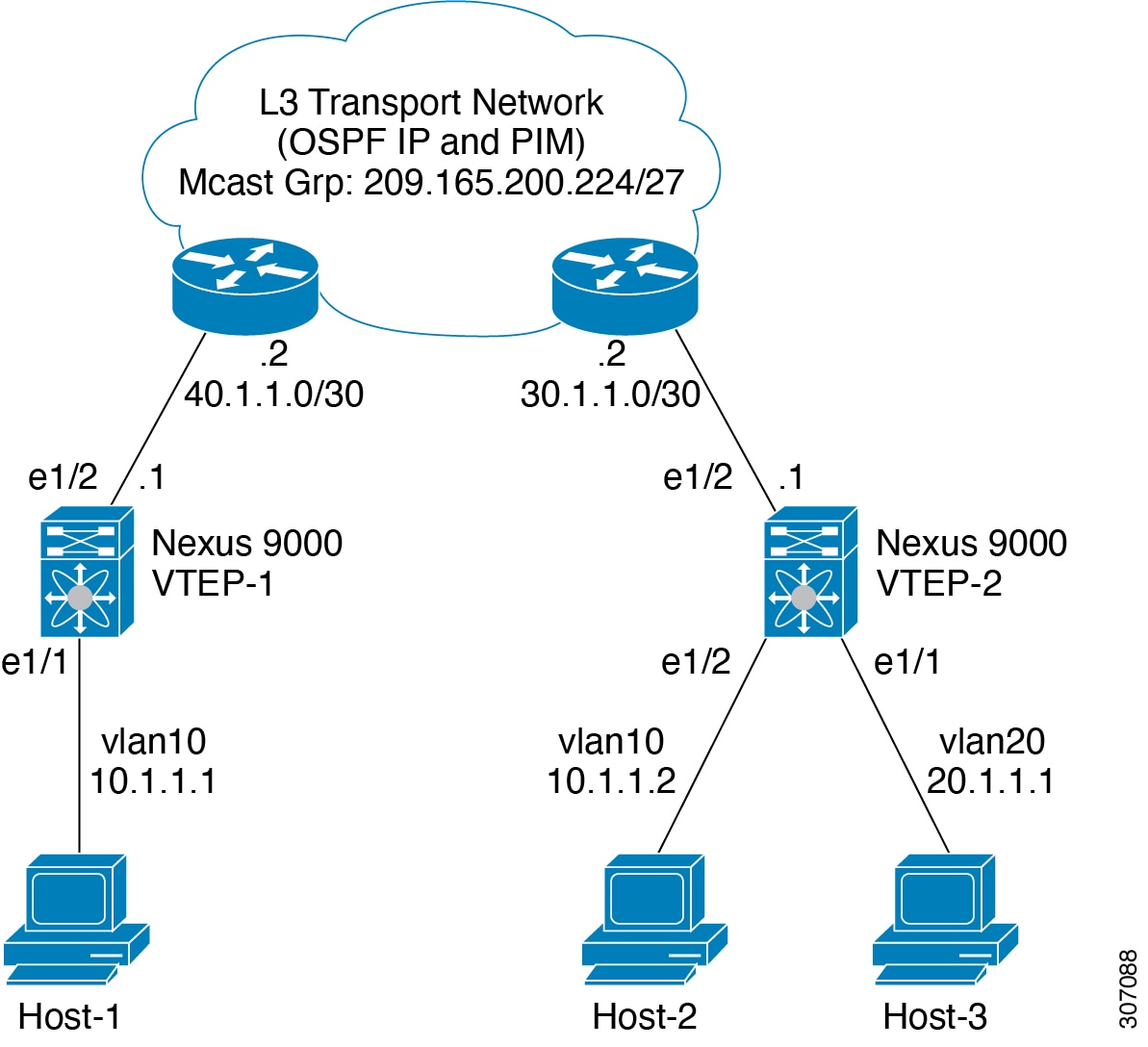
All scenarios that are mentioned in the previous table are explained with the following host details:
-
Host-1: 10.1.1.1/24 VLAN-10
-
Host-2: 10.1.1.2/24 VLAN-10
-
Host-3: 20.1.1.1/24 VLAN-20
-
Case 1: Layer 2 traffic/L2 VNI that flows between Host-1 and Host-2 on VLAN-10.
-
Case 2: Layer 3 traffic/L3 VNI that flows between Host-1 and Host-3 on VLAN-10 and VLAN-20.
 Feedback
Feedback