Wireless device provisioning overview
These sections provide information about how to provision various Cisco wireless devices.
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
These sections provide information about how to provision various Cisco wireless devices.
Controllers and access points are designed for use in many countries with varying regulatory requirements. The radios within the access points are assigned to a specific regulatory domain at the factory (such as -E for Europe), but the country code enables you to specify a particular country of operation within that regulatory domain (such as FR for France or ES for Spain). Configuring a country code ensures that each radio’s broadcast frequency bands, interfaces, channels, and transmit power levels are compliant with country-specific regulations.
Catalyst Center provisions controllers with country codes according to the site they are assigned. In the case of controllers, they can be assigned to more than one site. So, they can be assigned more than one country code. During provisioning, Catalyst Center assigns sites to the controller along with the sites’ country codes. For example, a controller that manages both India and US sites is assigned the IN and US country codes.
When access points are provisioned, they are assigned to a floor. If the access point is a ROW AP, Catalyst Center gets the country code for the site and assigns it to the AP. Any additional APs on the same floor are assigned the same country code.
During AP provisioning with an RF profile selected, out of all the DCA Channels configured on the RF profile, only the supported channels as per the country code are considered for Dynamic Channel Assignment (DCA). You can see the list of unsupported DCA channels in the AP preprovision summary step of the AP provision workflow on Catalyst Center.
The country code information is displayed on the Device 360 window for controllers and access points.
For a complete list of country codes supported per product, see https://www.cisco.com/c/dam/assets/prod/wireless/wireless-compliance-tool/index.html.
Make sure that you have defined the global network settings before provisioning a Cisco Wireless Controller, including:
Network servers, such as AAA, DHCP, and DNS.
For more information, see Configure global network servers.
Device credentials, such as CLI, SNMP, HTTP, and HTTPS.
For more information, see Add global CLI credentials, Add global SNMPv2c credentials, Add global SNMPv3 credentials, and Add global HTTPS credentials.
IP address pools.
For more information, see Configure IP address pools.
Wireless settings, such as SSIDs, wireless interfaces, and wireless radio frequency profiles.
 Note |
When you upgrade from an earlier release:
This configuration might change the intended configuration for the Cisco AireOS Wireless Controllers and wireless controllers running Cisco IOS XE Release 17.6 or earlier. You can update the Auth Key Management settings for the SSIDs before reprovisioning the wireless controllers. |
For more information, see Configure global wireless settings.
Make sure that you have the wireless controller in your inventory. If not, use the Discovery feature to discover the controller.
Make sure that the wireless controller is added to a site. For more information, see Assign an unprovisioned device to a site.
You cannot reuse any pre-existing VLANs on devices. Provisioning fails if Catalyst Center pushes the same VLAN that already exists on the device.
You cannot make any configuration changes to the wireless controller that is being managed by the Catalyst Center manually. You must perform all configurations from the Catalyst Center GUI.
Ensure that the prerequisite is met. For more information, see Prerequisites for provisioning a Cisco AireOS Controller.
|
Step 1 |
From the main menu, choose . The Inventory window display with the discovered devices listed. |
||
|
Step 2 |
Expand the Global site in the left pane, and select the site, building, or floor that you’re interested in. The available devices in the chosen site display in the Inventory window. |
||
|
Step 3 |
In the Devices table, click the Search field. In the Quick Filters tab, do these steps:
|
||
|
Step 4 |
Check the check box next to the device name that you want to provision. |
||
|
Step 5 |
From the Actions drop-down list, choose . The Assign Site window displays. |
||
|
Step 6 |
Click Choose a site to assign a site for the wireless controller. |
||
|
Step 7 |
In the Add Sites window, check the check box next to the site name to associate the wireless controller, and click Save. |
||
|
Step 8 |
Click Apply. |
||
|
Step 9 |
Click Next. The Configuration window displays. |
||
|
Step 10 |
Select a role for the wireless controller: Active Main WLC or Guest Anchor WLC. |
||
|
Step 11 |
Click Select Primary Managed AP Locations to select the managed AP location for the wireless controller. |
||
|
Step 12 |
In the Managed AP Location window, check the check box next to the site name. You can either select a parent site or the individual sites. If you select a parent site, the children under that parent site are automatically selected.
|
||
|
Step 13 |
Click Save. |
||
|
Step 14 |
(Optional) Check the AP Authorization List check box to choose the authorization list for AP authorization, and do these tasks:
|
||
|
Step 15 |
Under Interface and VLAN Configuration, click + Add and configure the interface and VLAN details for an active main wireless controller. Interface and VLAN configuration is applicable for nonfabric wireless controller provisioning only. The Configure Interface and VLAN window displays. |
||
|
Step 16 |
From the Interface Name drop-down list, choose the interface name.
|
||
|
Step 17 |
In the VLAN ID field, enter a value for the VLAN. |
||
|
Step 18 |
In the Interface IP Address field, enter a value for the interface IP address. |
||
|
Step 19 |
In the Interface Net Mask (in bits) field, enter the subnet mask for the interface. |
||
|
Step 20 |
In the Gateway IP Address field, enter the gateway IP address. |
||
|
Step 21 |
From the LAG/Port Number drop-down list, choose the link aggregation or the port number. |
||
|
Step 22 |
Click OK. |
||
|
Step 23 |
(Optional) For a guest anchor wireless controller, change the VLAN ID configuration by changing the VLAN ID under Assign Guest SSIDs to DMZ site. |
||
|
Step 24 |
Under Mobility Group, click Configure to configure the wireless controller as the mobility peer. |
||
|
Step 25 |
In the Configure Mobility Group slide-in pane, from the Mobility Group Name drop-down list, you can either add a new mobility group by clicking +, or choose a mobility group from the existing mobility groups. Information about the existing mobility peers is loaded from the intent available in the Catalyst Center.
|
||
|
Step 26 |
In the RF Group Name text box, enter a name for the RF group. |
||
|
Step 27 |
Under Mobility Peers, click Add to configure the wireless controller as a mobility peer. |
||
|
Step 28 |
In the Add Mobility Peer slide-in pane, configure accordingly: |
||
|
Step 29 |
Click Configure Mobility. |
||
|
Step 30 |
To reset the mobility group name and the RF group name, you can do one of these tasks:
This action automatically sets the RF Group Name to default and removes all peers. After provisioning, the mobility on the device is set and the device is removed from all other peers. |
||
|
Step 31 |
Click Next. The Feature Templates window displays. |
||
|
Step 32 |
In the Devices pane, you can either search for a feature template by entering its name in the Find field, or expand the device and select a feature template. The selected feature template displays in the right pane. |
||
|
Step 33 |
Check the check box next to the Design Name that you want to provision, and click Configure to edit the feature template. You can’t edit all the configurations at this step. |
||
|
Step 34 |
After making the necessary changes, click Apply. |
||
|
Step 35 |
Click Next. The Advanced Configuration window displays, which is where you can enter the values for predefined template variables. |
||
|
Step 36 |
Search for the device or the template in the Devices panel. |
||
|
Step 37 |
Enter a value for the predefined template variable in the wlanid field. |
||
|
Step 38 |
Click Next. |
||
|
Step 39 |
In the Summary step, review the device details, and click Next to provision the device. |
||
|
Step 40 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||
|
Step 41 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
||
|
Step 42 |
Provision the secondary controller. |
||
|
Step 43 |
The Status column in the Device Inventory window shows SUCCESS after a successful deployment. After provisioning, if you want to make any changes, click Design, change the site profile, and provision the wireless controller again. |
||
|
Step 44 |
After the devices are deployed successfully, the Provision Status changes from Configuring to Success. |
||
|
Step 45 |
In the Device Inventory window, click See Details in the Provision Status column to get more information about the network intent or to view a list of actions that you need to take. |
||
|
Step 46 |
Click See Details under Device Provisioning. |
||
|
Step 47 |
Click View Details under Deployment of network intent, and click the device name. |
||
|
Step 48 |
Expand the Configuration Summary area to view the operation details, feature name, and the management capability. The configuration summary also displays any errors that occurred while provisioning the device. |
||
|
Step 49 |
Expand the Provision Summary area to view details of the exact configuration that is sent to the device. |
Cisco Wireless Controller high availability (HA) can be configured through Catalyst Center. Currently, both the formation and breaking of wireless controller HA is supported; switchover options are not supported.
The Discovery and Inventory features of wireless controller 1 and wireless controller 2 must be successful. The devices must be managed.
The service ports and the management ports of wireless controller 1 and wireless controller 2 must be configured.
The redundancy ports of wireless controller 1 and wireless controller 2 must be physically connected.
The management address of wireless controller 1 and wireless controller 2 must be in the same subnet. The redundancy management address of wireless controller 1 and wireless controller 2 must also be in the same subnet.
Manually configure this boot variables on the wireless controller:
config t
boot system bootflash::<device_iosxe_image_filename>
config-register 0x2102
show boot. (IOSXE cli)
BOOT variable = bootflash:<device_iosxe_image_filename>,12;
Configuration register is 0x2102
|
Step 1 |
From the main menu, choose . The window displays with the discovered devices listed. |
||
|
Step 2 |
Check the check box next to the wireless controller name that you want to configure as the primary controller. |
||
|
Step 3 |
From the Actions drop-down list, choose . The High Availability slide-in pane displays.
By default, the chosen wireless controller becomes the primary controller and the Primary WLC field is disabled. |
||
|
Step 4 |
Enter the Redundancy Management IP and the Peer Redundancy Management IP address in the respective text boxes. The IP addresses used for redundancy management IP and peer redundancy management IP should be configured in the same subnet as the management interface of the wireless controller. Ensure that these IP addresses are unused IP addresses within that subnet range. |
||
|
Step 5 |
From the Select Secondary WLC drop-down list, choose the secondary controller.
|
||
|
Step 6 |
Click Configure HA. |
||
|
Step 7 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||
|
Step 8 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
||
|
Step 9 |
When the task is deployed, the HA configuration is initiated in the background using the CLI commands. First, the primary wireless controller is configured. On success, the secondary wireless controller is configured. After the configuration is completed, both wireless controllers reboot. This process may take up to 2.5 minutes to complete. |
||
|
Step 10 |
To verify the HA configuration: |
Cisco wireless controller 1 and wireless controller 2 are configured with redundancy management, redundancy units, and SSO. The wireless controllers reboot in order to negotiate their role as active or standby. Configuration is synced from active to standby.
On the Show Redundancy Summary window, you can see these configurations:
SSO is enabled.
The wireless controller is active.
The wireless controller is in hot standby.
The management port of the active wireless controller is shared by both the controllers and will be pointing to the active controller. The user interface, Telnet, and SSH on the standby wireless controller will not work. You can use the console and service port interface to control the standby wireless controller.
Catalyst Center sends commands to configure Cisco Wireless Controller HA.
Catalyst Center sends the commands to wireless controller 1, including:
config interface address redundancy-management 198.51.100.xx peer-redundancy-management 198.51.100.yy
config redundancy unit primary
config redundancy mode sso
Catalyst Center sends the commands to wireless controller 2, including:
config interface address redundancy-management 198.51.100.yy peer-redundancy-management 198.51.100.xx
config redundancy unit secondary
config port adminmode all enable
config redundancy mode sso
Enter these commands to verify the HA configuration from the wireless controller:
To check HA-related details: config redundancy mode sso
To check the configured interfaces: show redundancy summary
The Catalyst Center Disable HA feature is supported on Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controllers and Cisco AireOS Wireless Controllers.
Ensure that the HA device in the existing deployment is configured outside of Catalyst Center.
|
Step 1 |
From the main menu, choose . The Inventory window is displayed with the discovered devices listed. |
|
Step 2 |
Check the check box next to the name of the wireless controller that has the HA feature that you want to disable. |
|
Step 3 |
From the Actions drop-down list, choose . The High Availability slide-in pane display. High Availability slide-in pane shows the Redundancy Summary of selected wireless controller configured from outside Catalyst Center. |
|
Step 4 |
Click Disable HA. |
|
Step 5 |
In the Warning dialog box, click OK. |
|
Step 6 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
|
Step 7 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
|
Step 8 |
After the task deploys, a success message displays at the bottom of the window indicating that the HA feature has been successfully disabled for the selected wireless controller. |
Use the procedure to provision APs.
Make sure that you have Cisco APs in your inventory. If not, use the Discovery feature to discover APs. For more information, see Discover Your Network.
Make sure that you enable the required licenses for the APs on the License Manager window. For more information, see "Manage Licenses" in the Cisco Catalyst Center Administrator Guide.
If you add new AP zones or SSIDs, you must reprovision the wireless controller. For more information, see Provision a Cisco AireOS Controller and Provision a Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller.
If you update the AP zone configurations, you must reprovision the wireless controller. For more information, see Provision a Cisco AireOS Controller and Provision a Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller.
If you’re using N+1 HA and modify any nonflex SSIDs that are already provisioned on the primary and secondary controllers to flex SSIDs (or conversely), make sure that the states of WLANs are consistent across both the primary and secondary controllers on the corresponding site.
For example, SSID1 is configured on a network profile as flex SSID, provisioned on both the primary and secondary controllers, and later modified as nonflex SSID. If you reprovision only the primary controller without reprovisioning the secondary controller, SSID1 becomes nonflex SSID on the primary controller but remains flex SSID on the secondary controller. If you provision an AP on a site shared by both the primary and secondary controllers, the provisioning fails. To ensure consistency, you must reprovision the secondary controller. When you reprovision the secondary controller, SSID1 changes to nonflex SSID on the secondary controller too and both controllers have the same state for SSID1 before provisioning the AP.
For ROW APs, we recommend that you create an AP profile with the necessary country code and configure custom site tags. For more information, see Configure additional settings for an AP profile for Cisco IOS XE devices and Add AP groups, flex groups, site tags, and policy tags to a network profile.
|
Step 1 |
From the main menu, choose . |
||||||||||
|
Step 2 |
Check the check box next to the APs that you want to provision. You can choose up to 300 APs simultaneously. |
||||||||||
|
Step 3 |
From the Actions drop-down list, choose . |
||||||||||
|
Step 4 |
If you chose APs that don't meet the license requirements, Catalyst Center displays a dialog box with the details. In the dialog box, choose the required option.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 5 |
In the Assign Site step, configure the required parameters.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 6 |
In the Configuration step, configure the required parameters. |
||||||||||
|
Step 7 |
In the Summary step, review the device details, and click Next to provision the AP. |
||||||||||
|
Step 8 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||||||
|
Step 9 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
||||||||||
|
Step 10 |
You’re prompted with a message that the creation or modification of an AP group is in progress and then a message that APs will reboot after provisioning. Click OK. The Last Sync Status column in the Inventory window shows SUCCESS for a successful deployment. |
Use this procedure to migrate APs from one wireless controller to another wireless controller with the same floors in the network hierarchy.
Ensure that the old wireless controller (for example, WC1) is provisioned with the required sites (for example, Building-1 with Floor-1, Floor-2, and Floor-3) as the primary-managed AP location.
Ensure that the APs that need to be migrated are provisioned on the floors managed by the old wireless controller (for example, Building-1/Floor-1, Building-1/Floor-2, Building-1/Floor-3 managed by WC1).
|
Step 1 |
Add a new building and floor to the network hierarchy (for example, Building-New with Floor-New). For more information, see Add, edit, and delete a building and Add, edit, and delete a floor. |
|
Step 2 |
Create a wireless network profile and assign it to the newly added floor (Floor-New). For more information, see Create network profiles for wireless. |
|
Step 3 |
Reprovision the old wireless controller with the newly added floor (Floor-New) as the primary-managed AP location and remove the old sites (Floor-1, Floor-2, and Floor-3). For more information, see Provision a Cisco AireOS Controller and Provision a Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller. |
|
Step 4 |
Provision the new wireless controller (for example, WC2) with the old sites (Floor-1, Floor-2, and Floor-3) as the primary-managed AP locations. For more information, see Provision a Cisco AireOS Controller and Provision a Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller. |
|
Step 5 |
Use the Configure Access Points workflow to change the primary wireless controller name and IP address. In the Configure AP Parameters window of this workflow, do these steps:
For more information, see Configure APs. |
|
Step 6 |
Do these steps to ensure that the APs have joined the new wireless controller (WC2): |
|
Step 7 |
Reprovision the APs to deploy the latest configuration. For more information, see Provision Cisco APs on day 1. |
Using the Factory Reset feature, you can clear the configurations on the APs and reset them to the default configuration. After the AP configurations are cleared, the APs reboot.
 Important |
Resetting an AP disrupts the network connectivity for all the associated clients. |
Ensure that the APs are reachable.
|
Step 1 |
From the main menu, choose . |
|
Step 2 |
In the Devices table, click the Access Points device family button to display the list of available APs. |
|
Step 3 |
Check the check box next to the APs that you want to reset. You can select up to 100 APs for factory reset. |
|
Step 4 |
From the Actions drop-down list, choose . |
|
Step 5 |
Under Factory Reset, choose one of these options:
|
|
Step 6 |
Under Schedule Task, do these steps: |
|
Step 7 |
To view the APs selected for reset, expand the Selected Devices drop-down list. |
|
Step 8 |
Click Apply. To view the status of AP reset, go to the window and open the relevant work item. |
You can enable Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) ping on APs that are in FlexConnect mode and in an unreachable state. Catalyst Center uses the ICMP to ping FlexConnect APs that are in unreachable state every 5 minutes to enhance reachability and then updates the reachability status in the Inventory window.
|
Step 1 |
From the main menu, choose . |
|
Step 2 |
Check the Enable ICMP ping for unreachable access points in FlexConnect mode check box to enable the ICMP ping. |
|
Step 3 |
Click Save. This success message displays: ICMP Ping status updated successfully. Catalyst Center starts pinging FlexConnect APs that are disassociated from Cisco Wireless Controllers but are reachable. You can view the reachability status in the Inventory window. |
|
Step 4 |
To view the reachability status, choose . |
|
Step 5 |
The Reachability column shows Ping Reachable when the device is reachable by the ICMP ping. |
The Cisco Mobility Express wireless network solution comprises at least one 802.11ac Wave 2 Cisco Aironet Series access point with an in-built, software-based wireless controller managing other APs in the network. The AP acting as the wireless controller is referred to as the primary AP. The other APs in the Cisco Mobility Express network, which are managed by this primary AP, are referred to as subordinate APs.
Design your network hierarchy with sites, buildings, floors, and so on. For more information, see Create, edit, and delete a site, Add, edit, and delete a building, and Add, edit, and delete a floor.
Define the device credentials, such as CLI, SNMP, HTTP, and HTTPS at the global level. The credentials that are defined at the global level are inherited by the sites. For more information, see Add global CLI credentials, Add global SNMPv2c credentials, and Add global SNMPv3 credentials.
Create WLANs, interfaces, and RF profiles.
Configure the DHCP server with Option #43 or Option #60. This is the IP address of the Catalyst Center Plug and Play server. Using this IP address, the APs contact the PnP server and download the configuration.
Make sure that you have Mobility Express APs in the inventory. If not, discover them using the Discovery feature. For more information, see Discover your network using CDP, Discover your network using an IP address range or CIDR, and About Inventory.
The APs should be in the factory reset state without any Cisco Wireless Controller configurations.
|
Step 1 |
The Cisco Mobility Express contacts the DHCP server and connects to the Catalyst Center Plug and Play server. |
||
|
Step 2 |
The DHCP server allocates the IP address with Option #43, which is the IP address of the Catalyst Center Plug and Play server. |
||
|
Step 3 |
The Mobility Express AP starts the PnP agent and contacts the PnP server.
|
||
|
Step 4 |
Find the unclaimed AP in the tab. The table lists all the unclaimed devices. The State column shows as Unclaimed. Use the Filter or Find option to find specific devices. You must wait for the Onboarding Status to become Initialized. |
||
|
Step 5 |
To claim the AP, check the check box next to the AP device name. |
||
|
Step 6 |
Choose in the menu bar above the device table. The Claim Devices window displays. |
||
|
Step 7 |
In the Site Assignment window, choose a site from the Site drop-down list. Claiming the selected AP to this particular site also applies the associated configurations. |
||
|
Step 8 |
Click Next. |
||
|
Step 9 |
To configure a device, click the device name in the Configuration window. |
||
|
Step 10 |
In the Configuration for device name window, assign the static IP details for the device:
|
||
|
Step 11 |
Click Save. |
||
|
Step 12 |
Click Next. The Summary window is displayed. |
||
|
Step 13 |
Click Claim in the Summary window. After the Mobility Express AP is claimed, the configured IP address is assigned to the Mobility Express AP. |
||
|
Step 14 |
(Optional) Add devices in bulk from a CSV file. For more information, see Add devices in bulk. When you bulk import Mobility Express APs through a CSV file, all the Mobility Express APs appear on the window. Based on the VRRP protocol, only one Mobility Express AP among the imported ME APs becomes the primary AP. The remaining APs become subordinate APs. After claiming the primary AP, you don't need to claim the subordinate APs. Catalyst Center does not clear the subordinate APs from the Plug and Play window. You must delete those subordinate APs manually from the window. |
||
|
Step 15 |
To provision the Cisco Wireless Controller, see Provision a Cisco AireOS Controller. |
With Catalyst Center, you can add and provision the Cisco Wireless Controller, which belongs to existing sites with pre-existing infrastructure.
 Note |
This workflow is being deprecated. |
Start by running a Discovery job on the device. All your devices are displayed on the Inventory window. For more information, see Discover Your Network and About Inventory.
The wireless controller should be reachable and in the Managed state on the Inventory window. For more information, see About Inventory.
|
Step 1 |
From the main menu, choose . The window displays with the discovered devices listed. |
||
|
Step 2 |
Click Filter and enter the appropriate values in the selected filter field. For example, for the Device Name filter, enter the name of the device. The data that is displayed in the Devices table is automatically updated according to your filter selection. |
||
|
Step 3 |
Check the check box next to the wireless controller device name that you want to provision. |
||
|
Step 4 |
From the Actions drop-down list, choose . The Site Assignment window opens and the Learn Device Configuration workflow begins.
|
||
|
Step 5 |
Associate a site to the controller in the Assign Site step:
|
||
|
Step 6 |
The Resolve Conflict step shows any conflicting configurations in Catalyst Center that you need to resolve. |
||
|
Step 7 |
Click Next. |
||
|
Step 8 |
The Design Object window lists all the learned configurations. |
||
|
Step 9 |
Choose to assign a site to the network profile. |
||
|
Step 10 |
In the Network Profiles window, do this configuration:
|
||
|
Step 11 |
From the main menu, choose . |
||
|
Step 12 |
In the Summary window, review the configuration settings. |
||
|
Step 13 |
Click Deploy. |
||
|
Step 14 |
In the Provision Devices slide-in pane, do these steps to preview the CLI configuration: |
The Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller is the next generation of wireless controllers built for intent-based networking. The Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller is Cisco IOS XE based and integrates the RF excellence from Aironet with the intent-based networking capabilities of Cisco IOS XE to create the best-in-class wireless experience for your organization.
The Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller is built on a modular operating system and uses open, programmable APIs that enable automation of day-zero and day-n network operations.
The Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller is available in multiple form factors:
Catalyst 9800-40 Wireless Controller.
Catalyst 9800-80 Wireless Controller.
Catalyst 9800-CL Cloud Wireless Controller: Deployable on private cloud (ESXi, KVM, Cisco ENCS, and Hyper-V) and manageable by Catalyst Center.
Catalyst 9800 Embedded Wireless Controller for Catalyst 9300 Series Switches, Catalyst 9400 Series Switches, and Catalyst 9500H Series Switches.
Cisco Catalyst 9800-L Wireless Controller: Provides seamless software updates for small- to mid-size enterprises. The Cisco Catalyst 9800-L Wireless Controller is available in two variations. You can choose between copper and fiber uplinks, which gives you flexibility in your network.
This table lists the supported virtual and hardware platforms for the Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller:
| Platform | Description |
|---|---|
|
Cisco Catalyst 9800-80 Wireless Controller |
Supports up to 6000 access points and 64,000 clients. Supports up to 80 Gbps throughput and occupies a 2-rack unit space. Modular wireless controller with up to 100-GE uplinks and seamless software updates. |
|
Cisco Catalyst 9800-40 Wireless Controller |
A fixed wireless controller with seamless software updates for mid-sized organizations and campus deployments. Supports up to 2000 access points and 32,000 clients. Supports up to 40 Gbps throughput and occupies a 1-rack unit space. Provides four 1-GE or 10-GE uplink ports. |
|
Cisco Catalyst 9800-CL Cloud Wireless Controller |
Cisco Catalyst 9800-CL Cloud Wireless Controller can be deployed in a private cloud or a public cloud as Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS). Cisco Catalyst 9800-CL Cloud Wireless Controller is the next generation of enterprise-class virtual wireless controllers built for high availability and security. A virtual form factor of Cisco Catalyst 9800-CL Cloud Wireless Controller for private cloud supports ESXi, KVM, Cisco ENCS, and Hyper-V hypervisors. |
|
Cisco Catalyst 9800 Embedded Wireless Controller for Catalyst 9000 Series Switches |
Cisco Catalyst 9800 Embedded Wireless Controller for Catalyst 9000 Series Switches bring the wired and wireless infrastructure together with consistent policy and management. This deployment model supports only Cisco SD-Access, which is a highly secure solution for small campuses and distributed branches. The embedded controller supports access points (APs) only in Fabric mode. |
|
Cisco Catalyst 9800-L Wireless Controller |
Cisco Catalyst 9800-L Wireless Controller provides seamless software updates for small to mid-size enterprises. The Cisco Catalyst 9800-L Wireless Controller is available in two variations. You can choose between copper and fiber uplinks, which gives you flexibility in your network.
|
This table lists the host environments supported by the Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller:
| Host Environment | Software Version |
|---|---|
|
VMware ESXi |
|
|
KVM |
|
|
NFVIS |
Cisco ENCS 3.8.1 and 3.9.1 |
This table lists the Cisco Enterprise Network Function Virtualization Infrastructure Software (NFVIS) versions supported in Catalyst Center:
 Note |
Cisco Enterprise NFVIS devices support the N-1 to N upgrade path only. For example, upgrade from Cisco Enterprise NFVIS 3.11.x to Cisco Enterprise NFVIS 3.12.x only is supported. Upgrade from Cisco Enterprise NFVIS 3.11.x to Cisco Enterprise NFVIS 4.1.x is not supported. |
| Cisco Enterprise NFVIS version | Enterprise network compute system device platform | Notes |
|---|---|---|
|
4.1.2 4.1.1 3.12.3 3.11.3 3.11.2 3.11.1 |
ENCS 5400 UCS-E UCS-C |
Catalyst Center supports these NFVIS upgrade paths: NFVIS v3.11.1 > 3.11.2 > 3.11.3 > 3.12.3 > 4.1.1 > 4.1.2. Cisco Enterprise NFVIS 3.12.1 is not supported on any versions of Catalyst Center. Upgrade to Cisco Enterprise NFVIS 3.12.1 from Cisco Enterprise NFVIS 3.11.x using Catalyst Center is not supported. Upgrade to Cisco Enterprise NFVIS 3.12.2 from Cisco Enterprise NFVIS 3.12.1 using Catalyst Center is not supported. Upgrade to Cisco Enterprise NFVIS 3.12.2 from 3.11.2 is supported using Catalyst Center. Cisco Enterprise NFVIS 3.12.2 is supported on Catalyst Center. |
|
3.12.2 3.11.3 3.11.2 3.11.1 |
ENCS 5100 |
Cisco 5100 ENCS does not support Cisco Enterprise NFVIS 3.10.x. |
Install Catalyst Center.
For more information, see the Cisco Catalyst Center Installation Guide.
For information on software image upgrade, see Software image upgrade support for Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller.
Log in to the Catalyst Center GUI and verify that the applications you need are in the Running state.
From the main menu, choose .
Integrate Cisco Identity Services Engine with Catalyst Center. After integration, any devices that Catalyst Center discovers along with relevant configurations and data are pushed to Cisco ISE.
Discover the Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller.
You must enable NETCONF and set the port to 830 to discover the Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller. NETCONF provides a mechanism to install, manipulate, and delete configurations of network devices.
For more information, see Discover your network using CDP or Discover your network using an IP address range or CIDR.
You must add the wireless management IP address manually.
 Note |
On the Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller, you must configure a static IP address for the wireless management interface to prevent provisioning failure. |
While performing discovery using the Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) or an IP address range in the Discovery window, choose Use Loopback from the Preferred Management IP drop-down list to specify the device's loopback interface IP address.
Make sure that the discovered devices appear in the Device Inventory window and are in the Managed state.
For more information, see About Inventory and Display information about your inventory.
You must wait for the devices to move to a Managed state.
To verify the Assurance connection with the Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller, use these commands:
Trustpoint DNAC-CA
Subject Name:
cn=kube-ca
Serial Number (hex): 00E***************
Certificate configured.
Trustpoint sdn-network-infra-iwan:
Subject Name:
cn=sdn-network-infra-ca
Serial Number (hex): 378***************
Certificate configured.Telemetry subscription brief
ID Type State Filter type
-----------------------------------------------------
1011 Configured Valid tdl-uri
1012 Configured Valid tdl-uri
1013 Configured Valid tdl-uri #show telemetry internal connection
Telemetry connection
Address Port Transport State Profile
---------------------------------------------------------
IP address 25103 tls-native Active sdn-network-infra-iwanNetwork-Assurance : True
Server Url : https://10.***.***.***
ICap Server Port Number : 3***
Sensor Backhaul SSID :
Authentication : UnknownConfigure a TACACS server while configuring authentication and policy servers.
Configuring TACACS is not mandatory if you have configured the username locally on the Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller.
Design your network hierarchy by adding sites, buildings, and floors so that later you can easily identify where to apply design settings or configurations.
You can either create a new network hierarchy, or if you have an existing network hierarchy on Cisco Prime Infrastructure, you can import it into Catalyst Center.
To import and upload an existing network hierarchy, see Import your site hierarchy to Catalyst Center.
To create a new network hierarchy, see Create, edit, and delete a site and Add, edit, and delete a building.
Add the location information of APs, and position them on the floor map to visualize the heatmap coverage.
For more information, see Work with APs on a floor map.
Define network settings, such as AAA (Cisco ISE is configured for Network and Client Endpoint), NetFlow Collector, NTP, DHCP, DNS, syslog, and SNMP traps. These network servers become the default for your entire network. You can add a TACACS server while adding a AAA server.
For more information, see Network settings overview, Configure global network servers, and Add AAA server.
Create a wireless radio frequency profile with the parent profile as custom.
For more information, see Create a wireless radio frequency profile.
Create IP address pools at the global level.
Catalyst Center uses IP address pools to automate the configuration and deployment of SD-Access networks.
To create an IP address pool, see Configure IP address pools.
You must reserve an IP address pool for the building that you are provisioning. For more information, see Reserve IP Address Pools.
Create enterprise and guest wireless networks. Define the global wireless settings once; Catalyst Center then pushes the configurations to various devices across geographical locations.
Designing a wireless network is a two-step process. First, you must create SSIDs, and then associate the created SSID to a wireless network profile. This profile helps you to construct a topology, which is used to deploy devices on a site.
 Note |
When you upgrade from an earlier release:
This configuration might change the intended configuration for the Cisco AireOS Wireless Controllers and wireless controllers running Cisco IOS XE Release 17.6 or earlier. You can update the Auth Key Management settings for the SSIDs before reprovisioning the wireless controllers. |
For more information, see Create SSIDs for an enterprise wireless network and Create SSIDs for a guest wireless network. For information about other wireless settings, see Configure global wireless settings.
Configure the backhaul settings. For more information, see Manage backhaul settings.
In the Policy window for the Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller, do this configuration:
Create a virtual network. The virtual network segments your physical network into multiple logical networks.
Create a group-based access control policy and add a contract. For more information, see Create group-based access control policy.
Configure high availability.
For more information, see Configure high availability for the Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller.
Provision the Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller with the configurations added during the design phase.
For more information, see Provision a Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller.
Configure and deploy application policies on the Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller.
For more information, see Create an application policy, Deploy an application policy, and Edit an application policy.
 Note |
You must provision Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller devices before deploying an application policy. |
For Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller devices, two different policies with different business relevance for two different SSIDs do not work. The last deployed policy always takes precedence when you are setting up relevance.
For Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller devices, changing the default business relevance for an application does not work in FlexConnect mode.
You can apply an application policy only on a nonfabric SSID.
Discover the Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller.
Enable NETCONF and set the port to 830 to discover Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller. NETCONF enables wireless services on the controller and provides a mechanism to install, manipulate, and delete the configuration of network devices.
For more information, see Discover your network using CDP, or Discover your network using an IP address range or CIDR.
Make sure that the devices appear in the device inventory and are in the Managed state.
For more information, see About Inventory and Display information about your inventory.
|
Step 1 |
From the main menu, choose . The window displays with the discovered devices listed. |
|
Step 2 |
Import the Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller software image from your local computer or from a URL. For more information, see Import a software image. |
|
Step 3 |
Assign the software image to a device family. For more information, see Manage software image assignment for a device family. |
|
Step 4 |
You can mark a software image as Golden by clicking the star for a device family or a particular device role. For more information, see Mark a software image as golden. |
|
Step 5 |
Provision the software image. From the main menu, choose . |
|
Step 6 |
In the Inventory window, check the check box next to the Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller whose image you want to upgrade. |
|
Step 7 |
From the Actions drop-down list, choose . For more information, see Provision a software image. |
Configuring high availability (HA) on the Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller involves these prerequisites:
Both the Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controllers are running the same software version and have the active software image on the primary wireless controller.
The service ports and management ports of Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller 1 and Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller 2 are configured.
The redundancy ports of Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller 1 and Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller 2 are physically connected.
Preconfigurations such as interface configurations, route addition, ssh line configurations, and NETCONF-YANG configurations are completed on the Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller appliance.
The management interface of Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller 1 and Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller 2 are in the same subnet.
The discovery and inventory of Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller 1 and Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller 2 devices are successful from Catalyst Center.
The devices are reachable and in the Managed state.
|
Step 1 |
From the main menu, choose . The Inventory window displays with the discovered devices listed. |
||
|
Step 2 |
To view devices available in a particular site, expand the Global site in the left pane, and choose the site, building, or floor that you’re interested in. All the devices available in that chosen site display in the Inventory window. |
||
|
Step 3 |
In the Devices table, click the Search field. In the Quick Filters tab, do these steps:
|
||
|
Step 4 |
In the Inventory window, check the check box next to the required Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller name to configure it as a primary controller. |
||
|
Step 5 |
Hover your cursor over Actions and choose . The High Availability slide-in pane displays.
By default, the selected Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller becomes the primary controller and the Primary C9800 field is disabled. |
||
|
Step 6 |
From the Select Primary Interface and Select Secondary Interface drop-down lists, choose the interface that is used for HA connectivity. The HA interface serves these purposes:
|
||
|
Step 7 |
From the Select Secondary C9800 drop-down list, choose the secondary controller to create an HA pair.
|
||
|
Step 8 |
Enter the Redundancy Management IP and Peer Redundancy Management IP addresses in the respective fields.
|
||
|
Step 9 |
From the Netmask drop-down list, choose the netmask address. |
||
|
Step 10 |
Click Configure HA. |
||
|
Step 11 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||
|
Step 12 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. When the task is deployed, the HA configuration is initiated in the background using the CLI commands. First, the primary controller is configured. On success, the secondary controller is configured. Both the devices reboot once the HA is enabled. This process may take up to 2.5 minutes to complete. |
||
|
Step 13 |
To verify the HA configuration: |
||
|
Step 14 |
To manually resynchronize the controller:
|
These actions occur after the HA process completes:
Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller 1 and Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller 2 are configured with redundancy management, redundancy units, and Single sign-on (SSO). The devices reboot to negotiate their role as an active controller or a standby controller. The configuration is synchronized from active to standby.
 Note |
If you've configured a AAA server or Cisco ISE server for client and endpoint authentication in Catalyst Center then in a HA setup, the CTS credentials for active and standby controllers are synchronized and hence, during a HA switchover, Catalyst Center doesn’t update the CTS credentials for the wireless controllers on Cisco ISE. |
On the Show Redundancy Summary window, you can see these configurations:
SSO is enabled.
The Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller 1 is in the active state.
The Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller 2 is in the standby state.
High availability (HA) allows you to reduce the downtime of wireless networks that occurs because of the failover of controllers. You can configure HA on Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller through Catalyst Center.
|
Step 1 |
Use these commands to configure HA on the primary controller for Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller:
|
||
|
Step 2 |
Use these commands to configure HA on the secondary controller for Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller:
|
||
|
Step 3 |
Run the chassis clear command to clear or delete all the HA-related parameters, such as the local IP, remote IP, HA interface, mask, timeout, and priority.
|
||
|
Step 4 |
Use these commands to configure HA on the primary controller for Cisco Catalyst 9800-40 Wireless Controller and Cisco Catalyst 9800-80 Wireless Controller devices:
|
||
|
Step 5 |
Use these commands to configure HA on the secondary controller for Cisco Catalyst 9800-40 Wireless Controller and Cisco Catalyst 9800-80 Wireless Controller devices:
|
||
|
Step 6 |
Run the chassis clear command to clear or delete all the HA-related parameters, such as the local IP, remote IP, HA interface, mask, timeout, and priority.
|
Use these commands to verify the high availability configurations from Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller:
Run the config redundancy mode sso command to check the HA-related details.
Run the show chassis command to view chassis configurations about the HA pair, including the MAC address, role, switch priority, and current state of each controller device in the redundant HA pair.
Run the show ip interface brief command to view the actual operating redundancy mode running on the device, and not the configured mode as set by the platform.
Run the show redundancy states command to view the redundancy states of the active and standby controllers.
Run the show redundancy summary command to check the configured interfaces.
Run the show romvar command to verify high availability configuration details.
N+1 high availability
Catalyst Center supports N+1 high availability (HA) on Cisco AireOS wireless controllers and Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controllers.
Cisco AireOS wireless controllers have a dedicated stock-keeping unit (SKU) for their N+1 controllers. Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controllers don't have a dedicated SKU; the same model must be used for HA.
The N+1 HA architecture provides redundancy for controllers across geographically separated data centers with low-cost deployments.
N+1 HA allows Cisco Wireless Controllers to be used as backup controllers for multiple primary controllers. These wireless controllers are independent of each other and do not share configuration or IP addresses on any of their interfaces. When a primary wireless controller resumes operation, the APs fall back automatically from the backup wireless controller to the primary wireless controller if the AP fallback option is enabled.
Catalyst Center supports primary and secondary controller configurations for N+1 HA.
N+1 HA is configured at the AP level, not at the global level. Configurations are pushed directly to the AP.
 Note |
The primary and secondary controllers must be of the same device type. For example, if the primary device is a Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller, the secondary device must also be a Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller. |
APs with higher priority on the primary controller always connect first to the backup controller, even if they have to push out the lower priority APs.
The N+1 HA configuration has these limitations:
Auto provisioning of a secondary controller is not supported because of the VLAN ID configuration.
You must reprovision the secondary controller manually with the latest design configuration if you made any changes to the primary controller.
Catalyst Center does not support fault tolerance.
Access Point Stateful Switch Over (AP SSO) functionality is not supported for N+1 HA. The AP Control and Provisioning of Wireless Access Points (CAPWAP) state machine is restarted when the primary controller fails.
Discover primary and the secondary controller by running the Discovery feature.
For more information, see Discover your network using CDP, or Discover your network using an IP address range or CIDR.
Make sure that the wireless controllers are reachable and in the Managed state.
For more information, see About Inventory and Display information about your inventory.
Verify the network connectivity between devices. If the primary controller goes down, the AP should be able to join the secondary controller through the N+1 configuration.
Create two buildings to manage the primary and secondary locations for both devices. For example, create two buildings, Building A and Building B, where Building A is the primary managed location for controller-1 and also the secondary managed location for controller-2, and Building B is configured only as a primary managed location for controller-2.
For more information, see Create, edit, and delete a site and Add, edit, and delete a building.
Add and position APs on a floor map to get a coverage heatmap visualization during the design phase.
For more information, see Work with APs on a floor map.
Create two SSIDs and associate them as the backhaul SSIDs.
For more information, see Create SSIDs for an enterprise wireless network and Create SSIDs for a guest wireless network.
This procedure shows how to configure N+1 high availability (HA) on Cisco Wireless Controller and Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller.
|
Step 1 |
From the main menu, choose . The Inventory window displays with the discovered devices listed. |
|
Step 2 |
Check the check box next to the desired controller to provision it as a primary controller. |
|
Step 3 |
From the Actions drop-down list, choose . The Assign Site window displays. |
|
Step 4 |
Click Choose a site to assign a primary-managed AP location for the primary controller. |
|
Step 5 |
In the Choose a site window, select a site and click Save. |
|
Step 6 |
Click Next. The Configuration window displays, which shows the primary-managed AP location for the primary device. |
|
Step 7 |
Add or update the managed AP locations for the primary controller by clicking Select Primary Managed AP Locations. |
|
Step 8 |
In the Managed AP Location window, check the check box next to the site name, and click Save. You can either select a parent site or the individual sites. |
|
Step 9 |
Configure the interface and VLAN details. |
|
Step 10 |
Under the Configure Interface and VLAN area, configure the IP address and subnet mask details, and click Next. |
|
Step 11 |
In the Advanced Configuration window, configure the values for the predefined template variables, and click Next. |
|
Step 12 |
In the Summary window, verify the managed AP locations for the primary controller and other configuration details, and click Next. |
|
Step 13 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
|
Step 14 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
|
Step 15 |
To provision the secondary controller, in the Inventory window, check the check box next to the desired controller to provision it as a secondary controller. |
|
Step 16 |
From the Actions drop-down list, choose . The Assign Site window displays. |
|
Step 17 |
Click Choose a site to assign the managed AP location for the secondary controller. The managed AP location for the secondary controller should be the same as the managed AP location of the primary controller. |
|
Step 18 |
In the Choose a site window, check the check box next to the site name to associate the secondary controller, and click Save. |
|
Step 19 |
Click Next. The Configuration window displays, which shows the primary AP managed and secondary-managed AP locations for the secondary device. |
|
Step 20 |
Add or update the managed AP locations for the secondary controller by clicking Select Secondary Managed AP Locations. |
|
Step 21 |
In the Managed AP Location window, check the check box next to the site name, and click Save. You can either select a parent site or the individual sites. |
|
Step 22 |
Configure the interface and VLAN details for the secondary controller. |
|
Step 23 |
Under the Configure Interface and VLAN area, configure the IP address and subnet mask details for the secondary controller, and click Next. |
|
Step 24 |
In the Advanced Configuration window, configure the values for the predefined template variables, and click Next. |
|
Step 25 |
In the Summary window, verify the managed AP locations for the secondary controller and other configuration details, and click Next. |
|
Step 26 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
|
Step 27 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
|
Step 28 |
To verify the managed locations of the primary and secondary controllers, click the device name of the controllers that you provisioned on the window. |
|
Step 29 |
In the dialog box, click View Device Details. |
|
Step 30 |
In the device details window, click the Wireless Info tab to view the primary and secondary managed location details. |
|
Step 31 |
Provision the AP for the primary controller. For more information, see Provision Cisco APs on day 1. |
The mobility configuration in Catalyst Center allows you to group a set of Cisco Wireless Controllers into a mobility group for a seamless roaming experience of wireless clients.
By creating a mobility group, you can enable multiple wireless controllers in a network to dynamically share information and forward traffic when inter-controller or inter-subnet roaming occurs. Mobility groups enable you to limit roaming between different floors, buildings, or campuses in the same enterprise by assigning different mobility group names to different wireless controllers within the same wireless network.
Catalyst Center allows you to create mobility groups between various platforms, such as Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller and Cisco AireOS Controllers.
The mobility configuration has these guidelines and limitations:
You cannot select multiple controllers for configuring mobility on the Provision window.
You cannot create mobility groups with the group name as default. This resets the mobility and RF group names as default and deletes all the peers.
You cannot configure a mobility group name on the anchor controller.
You must reboot the wireless controller manually if there is a change to the virtual IP address when configuring mobility groups on Cisco AireOS Controllers.
Wireless controllers with the same mobility group name are automatically grouped into a single mobility group and added as peers to each other.
When configuring mobility groups on Cisco AireOS Controllers, if the wireless controllers do not have the IP address 192.0.2.1, Catalyst Center pushes the virtual IP address 192.0.2.1 to all the wireless controllers.
Do not explicitly add guest anchor controllers to the mobility group. The provisioned guest anchor controllers do not appear in the drop-down list while adding peers in the mobility configuration window.
If you provision a wireless controller as a guest anchor, ensure that it is not added to the mobility group.
Here is the workflow that you can follow to configure mobility on Cisco Wireless Controller:
To configure mobility, you must provision a wireless controller with the mobility group name, RF group name, and mobility peers.
The configuration that is applied during the wireless controller provisioning is automatically replicated to all the mobility peers configured in that group.
Resynchronize the wireless controllers to get the latest tunnel status.
These use cases explain the steps to configure mobility between controllers.
This use case assumes that wireless controller 1, wireless controller 2, and wireless controller 3 are newly added to Catalyst Center with the mobility group name, "Default." These wireless controllers aren't yet provisioned.
Provision wireless controller 1 by configuring the mobility group name, RF group name, and adding wireless controller 2 and wireless controller 3 as peers.
Provision wireless controller 2.
In the Provision window, the mobility configuration is automatically populated for wireless controller 2 with the group name and peers.
Provision wireless controller 3.
After provisioning all the wireless controllers, resynchronize the wireless controllers to receive the latest tunnel status.
This use case assumes that wireless controller 1, wireless controller 2, and wireless controller 3 have already been added to Catalyst Center with different mobility group names. These wireless controllers are provisioned.
Provision wireless controller 1 by configuring the mobility group name, RF group name, and adding wireless controller 2 and wireless controller 3 as peers.
The mobility configuration is automatically replicated across other peers, such as wireless controller 2 and wireless controller 3.
After the successful provisioning of wireless controller 1, wireless controller 2 and wireless controller 3 are added as peers on the wireless controller 1.
On wireless controller 2, wireless controller 1 and wireless controller 3 are added as peers.
On wireless controller 3, wireless controller 1 and wireless controller 2 are added as peers.
|
Step 1 |
From the main menu, choose . The Inventory window displays, which lists all the discovered devices. |
||
|
Step 2 |
Check the check box next to the Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller name for which you want to configure mobility. |
||
|
Step 3 |
From the Actions drop-down list, choose . The Configure Mobility Group slide-in pane displays. For more information, see Mobility configuration overview. |
||
|
Step 4 |
From the Mobility Group Name drop-down list, you can either add a new mobility group by clicking +, or choose from the existing mobility groups. Information about the existing mobility peers is loaded from the intent available in Catalyst Center.
|
||
|
Step 5 |
In the RF Group Name field, enter a name for the RF group. |
||
|
Step 6 |
To enable Datagram Transport Layer Security (DTLS) data encryption, click the Data Link Encryption button on. |
||
|
Step 7 |
To enable or disable Cipher configuration for mobility, use the DTLS High Cipher Only toggle button. Cipher configuration is applicable for Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller Release 17.5 or later. You must manually reboot the device for changes to take effect. |
||
|
Step 8 |
To manually reboot the device after making changes in the DTLS cipher configuration to take effect after provision, enable the Restart for DTLS Ciphers to take effect toggle button. |
||
|
Step 9 |
Under Mobility Peers, click Add to configure a mobility peer. You can add a maximum of 24 peer devices to a mobility group. |
||
|
Step 10 |
In the Add Mobility Peer slide-in pane, do this configuration: |
||
|
Step 11 |
Click Configure Mobility. |
||
|
Step 12 |
(Optional) You can reset the mobility group name and the RF group name using one of these methods:
This step automatically sets the RF Group Name to default and removes all peers. After you provision, the mobility on the device is set and the device is removed from all other peers. |
||
|
Step 13 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||
|
Step 14 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Catalyst Center allows you to enable or disable AP Impersonation. AP Impersonation is a global setting that provides a quick and effective means to detect and report phishing incidents. AP Impersonation is supported for Catalyst 9800 Controllers.
|
Step 1 |
From the main menu, choose . |
||
|
Step 2 |
Click . |
||
|
Step 3 |
In the left hierarchy tree, Global is selected by default. Expand the Global site and select the desired site, building, or floor.
|
||
|
Step 4 |
Click the AP Impersonation tab. |
||
|
Step 5 |
Check the Enable AP Impersonation check box to enable AP Impersonation. |
||
|
Step 6 |
Select the type: Auth IE or Infra MFP.
|
||
|
Step 7 |
Click Save. |
||
|
Step 8 |
(Optional) To disable the AP Impersonation, uncheck the Enable AP Impersonation check box. |
Ciphersuites are a set of encryption and integrity algorithms designed to protect radio communication on your wireless LAN.
You can configure multiple DTLS (Data Datagram Transport Layer Security) Ciphersuites on Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller, Cisco Catalyst 9800 Embedded Wireless Controller for Catalyst 9000 Series Switches, and Cisco Embedded Wireless Controller on Catalyst Access Points platforms running Release 17.5 or later.
You can configure DTLS Ciphersuites either at the global level or site level.
Make sure that the Device Controllability feature is enabled on the window.
Discover Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controllers in your network using the Discovery functionality so that the discovered devices are listed in the Inventory window.
|
Step 1 |
From the main menu, choose . |
|
Step 2 |
From the left hierarchy tree, select Global to configure all sites with the same DTLS Ciphersuite configuration. From the left hierarchy tree, select a site to configure DTLS Ciphersuites at the site level. The DTLS Ciphersuite configuration will be pushed to the controller available on that particular site. |
|
Step 3 |
Click Security Settings. |
|
Step 4 |
Click the Configure DTLS Ciphersuites tab. |
|
Step 5 |
Uncheck the Skip DTLS Ciphersuite Config check box to configure Ciphersuites as part of Device Controllability. |
|
Step 6 |
Configure either default Ciphersuites or custom Ciphersuites. By default, the Default Ciphersuite is selected. The Default Ciphersuite box shows the list of default Ciphersuites and these Ciphersuites are configured as default on the device. You cannot change the priority of these default ciphersuites. |
|
Step 7 |
To configure custom Ciphersuites, click the Custom button. Custom Ciphersuite overrides the default Ciphersuites with priority. |
|
Step 8 |
From the Version drop-down list, choose the DTLS version. Based on the DTLS version, Catalyst Center shows the available Ciphersuites. |
|
Step 9 |
Click the blue toggle button next to the Ciphersuite if you do not want to apply any of the Ciphersuites. |
|
Step 10 |
To change the priority of Ciphersuites, drag each Ciphersuite. |
|
Step 11 |
Click Save. The message DTLS Ciphersuite Config Saved successfully is displayed. |
|
Step 12 |
To apply the Ciphersuite configuration, you must provision the device. For more information, see Provision a Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller. |
The Rolling AP Upgrade feature is supported on the Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller in an N+1 HA setup. This feature helps you upgrade software images on the APs associated with the Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller in your wireless LAN network. To achieve the zero downtime, it is possible to upgrade APs in a staggered way using the N+1 Rolling AP Upgrade feature.
The primary controller identifies the candidate APs through the radio resource management neighbor AP map. The upgrade process starts with the software image downloading to the primary controller while the image is predownloaded to the candidate APs. After the candidate APs have been upgraded and rebooted, they join the secondary controller in a staggered manner. After all the APs have joined the secondary controller, the primary controller reboots. The APs rejoin the primary controller in a staggered manner after it is rebooted.
Here are the prerequisites for configuring the Rolling AP Upgrade feature:
An N+1 HA setup with two wireless controllers, one as the primary controller and the other one as the secondary.
The primary and the N+1 controllers have the same configuration and manage the same location in the network.
The N+1 controller is already running the Golden image so that Rolling AP Upgrade works with zero downtime.
Golden images are standardized images for network devices and Catalyst Center automatically downloads the images from cisco.com. Image standardization helps in device security and optimal device performance.
The N+1 controller is reachable and in Managed state in Catalyst Center.
Both the controllers are part of the same mobility group, and a mobility tunnel is established between the primary and N+1 controller. The upgrade information between the primary and N+1 controllers are exchanged through the mobility tunnel.
 Note |
If you have a cyclic N+1 HA deployment, where wireless controller 1 is N+1 for wireless controller 2 and wireless controller 2 is N+1 for wireless controller 1, you cannot run Rolling AP Upgrade on both devices. Instead, one controller must go through a normal upgrade. You can run Rolling AP Upgrade on the other controller after the first controller is upgraded without the rolling AP upgrade. |
This procedure shows how to configure a Rolling AP Upgrade on Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controllers.
 Note |
N+1 Rolling AP Upgrade is supported on fabric and nonfabric deployments. |
|
Step 1 |
Install Catalyst Center. For more information, see the Cisco Catalyst Center Installation Guide. |
|
Step 2 |
Log in to the Catalyst Center GUI and verify that the applications you need are in the Running state. From the main menu, choose . |
|
Step 3 |
Discover the wireless controller using the Discovery feature. You must enable NETCONF and set the port to 830 to discover the Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller. NETCONF provides a mechanism to install, manipulate, and delete the configurations on network devices. For more information, see Discover your network using CDP or Discover your network using an IP address range or CIDR. |
|
Step 4 |
Make sure that the discovered devices appear in the Device Inventory window and are in the Managed state. For more information, see About Inventory and Display information about your inventory. You must wait for devices to move to a Managed state. |
|
Step 5 |
Design your network hierarchy by adding sites, buildings, and floors so that later you can easily identify where to apply design settings or configurations. You can either create a new network hierarchy, or if you have an existing network hierarchy on Cisco Prime Infrastructure, you can import it into Catalyst Center. To import and upload an existing network hierarchy, see Import your site hierarchy to Catalyst Center. To create a new network hierarchy, see Create, edit, and delete a site and Add, edit, and delete a building. |
|
Step 6 |
Add the location information of APs, and position them on the floor map to visualize the heatmap coverage. For more information, see Work with APs on a floor map. |
|
Step 7 |
Provision the primary controller with the primary managed AP location, Rolling AP Upgrade enabled, and mobility group configured with the secondary controller as its peer. To do this, choose , and check the check box next to the primary controller name. |
|
Step 8 |
Configure the N+1 controller as the mobility peer in the Mobility Group configuration. For more information, see Mobility configuration overview. |
|
Step 9 |
Provision the N+1 HA controller by configuring the primary controller's primary managed AP location as the N+1 controller's secondary managed AP location. This configures the secondary controller as the N+1 controller. For more information, see Provision a Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller. |
|
Step 10 |
Provision the APs that are associated with the primary controller. |
|
Step 11 |
Import the software images to the repository. For more information, see Import a software image. |
|
Step 12 |
Assign the software image to a device family. For more information, see Manage software image assignment for a device family. |
|
Step 13 |
Mark the software image as Golden by clicking the star for a device family or a device role. For more information, see Mark a software image as golden. |
|
Step 14 |
Before upgrading the image, make sure that the image readiness checks are successful for both devices. Also make sure that the status of the N+1 Device Check and the Mobility Tunnel Check has a green tick mark.
|
|
Step 15 |
Initiate the upgrade on primary controller. |
|
Step 16 |
On the Software Images window, check the check box next to the primary controller. |
|
Step 17 |
From the Actions drop-down list, choose . For more information, see Provision a software image. |
|
Step 18 |
To monitor the progress of the image upgrade, click In Progress in the Software Image column. The Device Status window displays this information:
|
Use this procedure to provision a Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller.
Ensure that you have completed the steps in Configure a Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller in Catalyst Center.
|
Step 1 |
From the main menu, choose . |
||||||||||
|
Step 2 |
In the Devices table, check the check box next to the wireless controller name that you want to provision. |
||||||||||
|
Step 3 |
From the Actions drop-down list, choose . |
||||||||||
|
Step 4 |
If the wireless controller manages APs that don't meet the license requirements, Catalyst Center displays a dialog box with the details. In the dialog box, click the required option.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 5 |
In the Assign Site window, assign a site to the wireless controller.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 6 |
In the Configuration window, select a role for the Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller: Active Main WLC or Anchor. |
||||||||||
|
Step 7 |
Select the managed AP location.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 8 |
Select either a parent site or individual sites for the managed AP locations, and click Save. If you select a parent site, all the children under the parent site are also chosen. You can uncheck the check box to deselect a child site.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 9 |
(Optional) Check the AP Authorization List check box to select the authorization list for AP authorization, and then configure the AP authorization settings.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 10 |
For an active main wireless controller, configure the interface and VLAN details. |
||||||||||
|
Step 11 |
In the Assign Interface area, configure the interface settings.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 12 |
(Optional) Check the Skip AP Provision check box to skip configuring the AP-related commands while provisioning the Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller. For more information, see Skip AP provision during wireless controller provisioning. |
||||||||||
|
Step 13 |
(Optional) Check the Rolling AP Upgrade check box to enable the Rolling AP Upgrade feature in an N+1 HA setup. (Optional) If you check this check box, from the AP Reboot % drop-down list, select the percentage of APs that can be rebooted with minimal client disruptions. For more information, see Workflow to Configure a Rolling AP Upgrade. |
||||||||||
|
Step 14 |
Click Next. |
||||||||||
|
Step 15 |
In the Devices pane of the Feature Templates window, select a feature template. You can either search for a feature template by entering its name in the Find field, or expand the device and select a feature template. The chosen feature template is displayed in the right pane. |
||||||||||
|
Step 16 |
Check the check box next to the Design Name that you want to provision, and click Configure to edit the feature template. You can’t edit all the configurations in this step. |
||||||||||
|
Step 17 |
After making the necessary changes, click Apply. |
||||||||||
|
Step 18 |
Click Next. |
||||||||||
|
Step 19 |
In the Devices pane of the Advanced Configuration window, search for the device or template. |
||||||||||
|
Step 20 |
In the wlanid field, enter a value for the predefined template variable, and click Next. |
||||||||||
|
Step 21 |
In the Summary window, review the configuration settings, and click Next. |
||||||||||
|
Step 22 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||||||
|
Step 23 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 24 |
Verify the configurations that are pushed from Catalyst Center to the device using the show commands on the wireless controller.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 25 |
After the devices are deployed successfully, the Provision Status changes from Configuring to Success. |
||||||||||
|
Step 26 |
In the Inventory window, from the Focus drop-down list, select Provision. |
||||||||||
|
Step 27 |
Under the Provisioning Status column, click the See Details link of a corresponding device to view information about network intent or a list of actions. |
||||||||||
|
Step 28 |
In the device slide-in pane, click See Details under Device Provisioning. |
||||||||||
|
Step 29 |
Click View Details under Deployment of network intent, and click the device name. |
||||||||||
|
Step 30 |
Click and expand the device name. |
||||||||||
|
Step 31 |
Expand the Configuration Summary area to view the operation details, feature name, and management capability. The configuration summary also displays any error (with failure reasons) that occurred while provisioning the device. |
||||||||||
|
Step 32 |
Expand the Provision Summary area to view details of the configuration that is sent to the device. |
||||||||||
|
Step 33 |
Provision the AP. |
With Catalyst Center, you can add and provision devices such as Cisco Wireless Controllers and Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controllers in the existing deployment.
 Note |
The Learn Device Configuration workflow is being deprecated. To manage Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controllers with existing configurations, you can use the per-device configurations. For more information, see Configure per-device features for a Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller. |
Start by running a Discovery job on the device. All your devices are displayed on the Inventory window. For more information, see Discover Your Network and About Inventory.
The wireless controller should be reachable and in the Managed state on the Inventory window. For more information, see About Inventory.
To discover Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller, you must enable NETCONF and set the port to 830. For more information, see Discovery overview.
Design your network hierarchy by adding sites, buildings, and floors so that later you can easily identify where to apply design settings or configurations. You can either create a new network hierarchy or, if you have an existing network hierarchy on Cisco Prime Infrastructure, import it into Catalyst Center.
For more information about importing and uploading an existing network hierarchy, see Import your site hierarchy to Catalyst Center.
For more information about creating a new network hierarchy, see Create, edit, and delete a site and Add, edit, and delete a building.
|
Step 1 |
From the main menu, choose . The window displays with the discovered devices listed. |
||
|
Step 2 |
Click Filter and enter the appropriate values in the selected filter field. For example, for the Device Name filter, enter the name of the device. The data that displays in the Devices table automatically updates according to your filter selection. |
||
|
Step 3 |
Check the check box next to the wireless controller device name that you want to provision. |
||
|
Step 4 |
From the Actions drop-down list, choose . The Site Assignment window opens and the Learn Device Configuration workflow begins.
|
||
|
Step 5 |
Follow Step 3 through Step 13 in Learn device configurations from devices with pre-existing infrastructure. |
||
|
Step 6 |
From the main menu, choose . |
||
|
Step 7 |
Click Filter to locate the device that you want to provision. The data that displays in the Devices table is automatically updated according to your filter selection. |
||
|
Step 8 |
Check the check box next to the wireless controller that you want to provision. |
||
|
Step 9 |
From the Actions drop-down list, choose . |
||
|
Step 10 |
Review the details in the Assign Site step, and click Next. |
||
|
Step 11 |
In the Configuration step, do this configuration:
|
||
|
Step 12 |
In the Model Configuration step, do this configuration:
|
||
|
Step 13 |
In the Advanced Configuration window, you can enter values for the predefined template variables.
|
||
|
Step 14 |
In the Summary window, review the configuration settings. (To make any changes, click Edit.) |
||
|
Step 15 |
To proceed, click Deploy. |
||
|
Step 16 |
In the Schedule window, click Now or Later to indicate when you want to start the configuration, and click Apply. |
||
|
Step 17 |
(Optional) After deploying the configuration on the devices, the Task Progress bar displays the progress of the ongoing provisioning task under (which you can view by clicking the task name). |
||
|
Step 18 |
Provision the AP. For more information, see Provision Cisco APs on day 1. |
The Cisco Embedded Wireless Controller on Catalyst Access Points (EWC-APs) is the next-generation Wi-Fi solution, which combines the Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller with Cisco Catalyst 9100 Series Access Points, creating the best-in-class wireless experience for the evolving and growing organization.
Design your network hierarchy with sites, buildings, floors, and so on.
For more information, see Create, edit, and delete a site and Add, edit, and delete a building.
Define the device credentials, such as CLI, SNMP, HTTP, and HTTPS for the site where you want to claim the device.
For more information, see Add global CLI credentials, Add global SNMPv2c credentials, and Add global SNMPv3 credentials.
Create wireless SSIDs, wireless interfaces, and wireless Radio Frequency profiles.
For more information, see Create SSIDs for an enterprise wireless network, Create SSIDs for a guest wireless network, Create a wireless interface, and Create a wireless radio frequency profile.
 Note |
For Cisco Embedded Wireless Controller on Catalyst Access Points, only Flex-based SSID creation is supported. |
Configure the DHCP server with Option #43 on the switch where the Cisco Embedded Wireless Controller on Catalyst Access Points is connected. This IP address is IP address of the Catalyst Center Plug and Play (PnP) server. Using this IP address, the APs contact the PnP server, but remain in the Unclaimed state.
Make sure that you have the Cisco Embedded Wireless Controller on Catalyst Access Points in the inventory. If not, discover them using the Discovery feature. For more information, see Discover your network using CDP, Discover your network using an IP address range or CIDR, and About Inventory.
The APs should be in the factory reset state without any Cisco Wireless Controller configurations.
The Cisco Embedded Wireless Controller on Catalyst Access Points is available in multiple form factors:
Cisco Embedded Wireless Controller on Catalyst 9115AX Access Points
Cisco Embedded Wireless Controller on Catalyst 9117AX Access Points
Cisco Embedded Wireless Controller on Catalyst 9120AX Access Points
Cisco Embedded Wireless Controller on Catalyst 9130AX Access Points
|
Step 1 |
The Cisco Embedded Wireless Controller on Catalyst Access Points contacts the DHCP server. In response, the DHCP server provides the IP address along with Option #43, which contains the IP address of the Cisco Plug and Play server. |
||
|
Step 2 |
Based on Option #43, the Cisco Embedded Wireless Controller on Catalyst Access Points turns on the Plug and Play agent and contacts the Catalyst Center Plug and Play server.
|
||
|
Step 3 |
Find the unclaimed Cisco Embedded Wireless Controller on Catalyst Access Points in the tab. The table lists all the unclaimed devices. The State column shows as Unclaimed. Use the Filter or Find option to find specific devices. You must wait for the onboarding status to become Initialized under the Onboarding State column. |
||
|
Step 4 |
To claim the Cisco Embedded Wireless Controller on Catalyst Access Points, check the check box next to the AP device name. |
||
|
Step 5 |
Choose in the menu bar above the device table. The Claim Devices window displays. |
||
|
Step 6 |
In the Assign Site window, choose a site from the Site drop-down list. Claiming the selected AP to this particular site also applies the associated configurations. |
||
|
Step 7 |
Click Next. |
||
|
Step 8 |
In the Assign Configuration window, to configure a device, click the corresponding Assign option. |
||
|
Step 9 |
In the Configuration for device name slide-in pane, do these tasks:
|
||
|
Step 10 |
Click Save. |
||
|
Step 11 |
Click Next. The Summary window displays. |
||
|
Step 12 |
Click Claim. After the Cisco Embedded Wireless Controller on Catalyst Access Points claim is successful, the configured wireless management address, subnet mask, and gateway are assigned to the Cisco Embedded Wireless Controller. The claimed device is now listed on the window and moved to the Managed state. The device is automatically provisioned. After the provisioning is complete, you can view the device on the Provisioned tab of the window. |
With Catalyst Center, you can migrate from Cisco AireOS Controller to Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller using the workflow to learn the device configurations.
 Note |
This workflow is being deprecated. |
Design your network hierarchy by adding sites, buildings, and floors.
Discover the Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller by running the Discovery feature and add it to the Inventory. Make sure that the device status is reachable and in the Managed state.
You must enable NETCONF and set the port to 830 to discover the Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller. NETCONF provides a mechanism to install, manipulate, and delete the configurations of network devices.
Discover the Cisco AireOS Controllers and add it to the Inventory. Make sure that the device status is reachable and in the Managed state.
|
Step 1 |
From the main menu, choose . The Inventory window displays, which lists the discovered devices. |
||
|
Step 2 |
Check the check box next to the Cisco AireOS Controller. |
||
|
Step 3 |
From the Actions drop-down list, choose . |
||
|
Step 4 |
In the Assign Device to Site window, click Choose a Site. |
||
|
Step 5 |
In the Add Sites window, check the check box next to the site name to associate a Cisco AireOS Controller. |
||
|
Step 6 |
Click Save. |
||
|
Step 7 |
From the Actions drop-down list, choose . The Site Assignment window opens and the Learn Device Configuration workflow begins.
|
||
|
Step 8 |
In the Assign Site window, click Next. |
||
|
Step 9 |
The Resolve Conflict window shows any conflicting configurations in Catalyst Center that you need to resolve. Click Next. |
||
|
Step 10 |
In the Design Object window, click Next. |
||
|
Step 11 |
In the left pane, click Network. The right pane displays network configurations that were learned as part of the device configuration learning process, and shows information, including:
|
||
|
Step 12 |
Click Next. |
||
|
Step 13 |
In the left pane, click Wireless. The Wireless window displays the enterprise SSIDs, guest SSIDs, wireless interfaces, and RF profiles that are present on the device. |
||
|
Step 14 |
For an SSID with a preshared key (PSK), enter the passphrase key. |
||
|
Step 15 |
In the left pane, click Discarded Config. This displays the conflicting and the existing configurations on Catalyst Center. The discarded configuration entries are available under these categories:
|
||
|
Step 16 |
Click Next. |
||
|
Step 17 |
The Network Profile window lists the network profile or site profile that is created based on the AP and WLAN combination. |
||
|
Step 18 |
Click Save. A success message displays. |
||
|
Step 19 |
Choose to view the SSID and interface configurations that Catalyst Center has learned from the Cisco AireOS Controller. |
||
|
Step 20 |
Choose to assign a site to the network profile. |
||
|
Step 21 |
In the Network Profiles window, click Assign Site to add sites to the selected profile. |
||
|
Step 22 |
In the Add Sites to Profile window, choose a site from the drop-down list, and click Save. |
||
|
Step 23 |
Click the Provision tab. |
||
|
Step 24 |
Check the check box next to the Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller that you want to provision. |
||
|
Step 25 |
From the Actions drop-down list, choose Provision. |
||
|
Step 26 |
Click Choose a site to assign a site for the Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller. |
||
|
Step 27 |
In the Choose a site window, check the check box next to the site name to associate a Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller. |
||
|
Step 28 |
Click Next. The Configuration window displays. |
||
|
Step 29 |
Select a role for the Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller as Active Main WLC. |
||
|
Step 30 |
Click Select Primary Managed AP Locations to configure a managed AP location for the primary controller. |
||
|
Step 31 |
In the Managed AP Location window, check the check box next to the site name. You can either select a parent site or the individual sites. If you select a parent site, the children under that parent site are automatically selected. |
||
|
Step 32 |
Click Save. |
||
|
Step 33 |
Click Next. |
||
|
Step 34 |
The Summary window shows the configurations that will be pushed to the Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller from the Cisco AireOS Controller. |
||
|
Step 35 |
Click Deploy to provision the Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller. |
||
|
Step 36 |
Click Now to deploy the device immediately. Click Later to schedule deployment for a later time and click Apply. |
||
|
Step 37 |
After the devices are deployed successfully, the Provision Status changes from Configuring to Success. |
||
|
Step 38 |
In the Device Inventory window, click See Details in the Provision Status column to get more information about the network intent or to view a list of actions that you need to take. |
||
|
Step 39 |
To manually resynchronize the Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller, on the window, choose the controller that you want to manually synchronize. |
||
|
Step 40 |
From the Actions drop-down list, choose Resync. |
||
|
Step 41 |
Provision the AP. |
Configure and provision a Cisco Catalyst 9800 Embedded Wireless Controller for Catalyst 9000 Series Switches
|
Device role |
Platforms |
|---|---|
|
Embedded Wireless Controller |
Cisco Catalyst 9300 Series Switches Cisco Catalyst 9400 Series Switches Cisco Catalyst 9500H Series Switches |
|
Fabric Edge |
Cisco Catalyst 9300 Series Switches Cisco Catalyst 9400 Series Switches Cisco Catalyst 9500H Series Switches Cisco Catalyst 3600 Series Switches Cisco Catalyst 3850 Series Switches |
|
APs |
Cisco 802.11ac Wave 2 APs:
Cisco 802.11ac Wave 1 APs
Cisco Catalyst 9105 Series Wi-Fi 6 Access Points Cisco Catalyst 9115 Series Wi-Fi 6 Access Points Cisco Catalyst 9117 Series Wi-Fi 6 Access Points Cisco Catalyst 9120 Series Wi-Fi 6 Access Points Cisco Catalyst 9124 Series Wi-Fi 6 Access Points Cisco Catalyst 9130 Series Wi-Fi 6 Access Points Cisco Catalyst 9136 Series Wi-Fi 6 Access Points Cisco Catalyst Wireless 9136I Wi-Fi 6 Access Point Cisco Catalyst Wireless 9163E Wi-Fi 6 Access Point Cisco Catalyst Wireless 9166D Wi-Fi 6 Access Point Cisco Catalyst Wireless 9166I Wi-Fi 6 Access Point Cisco Catalyst Wireless 9162I Wi-Fi 6 Access Point Cisco Catalyst Wireless 9164I Wi-Fi 6 Access Point Cisco Catalyst Wireless 9167 Series Wi-Fi 6 Access Point Cisco Catalyst 9172H Series Wi-Fi 7 Access Points Cisco Catalyst 9172I Series Wi-Fi 7 Access Points Cisco Catalyst Wireless 9176 Series Wi-Fi 6 Access Point Cisco Catalyst 9176D1 Series Wi-Fi 7 Access Points Cisco Catalyst 9176I Series Wi-Fi 7 Access Points Cisco Catalyst Wireless 9178 Series Wi-Fi 6 Access Point Cisco Catalyst 9178I Series Wi-Fi 7 Access Points |
On Cisco Catalyst 9800 Embedded Wireless Controller for Catalyst 9300 Series Switches, make sure that these commands are present if the switch is already configured with aaa new-model:
aaa new-modelaaa authentication login default localaaa authorization exec default localaaa session-id commonThis is required for NETCONF configuration. These configurations are not required if you are using automated underlay for provisioning.
Install Catalyst Center.
For more information, see the Cisco Catalyst Center Installation Guide.
Log in to the Catalyst Center GUI and verify that the applications you need are in the Running state.
From the main menu, choose .
Integrate Cisco Identity Services Engine with Catalyst Center. After Cisco ISE is registered with Catalyst Center, any device that Catalyst Center discovers, along with relevant configurations and other data, is pushed to Cisco ISE.
Discover Cisco Catalyst 9000 Series Switches and the edge switches.
You must enable NETCONF and set the port to 830 to discover Cisco Catalyst 9800 Embedded Wireless Controller for Catalyst 9000 Series Switches.
Do not enable NETCONF to discover the edge switches.
For more information, see Discover your network using CDP and Discover your network using an IP address range or CIDR.
Change the Preferred Management IP to Use Loopback.
Make sure that the devices appear in the device inventory and are in Managed state.
For more information, see About Inventory and Display information about your inventory.
Ensure that the devices are in the Managed state.
Design your network hierarchy, which represents your network's geographical location. You can create sites, buildings, and floors so that later you can easily identify where to apply the design settings or configurations.
You can either create a new network hierarchy, or if you have an existing network hierarchy on Cisco Prime Infrastructure, you can import it into Catalyst Center.
To import and upload an existing network hierarchy, see the Import your site hierarchy to Catalyst Center.
To create a new network hierarchy, see the Create, edit, and delete a site and Add, edit, and delete a building.
For a nonfabric network, add and position APs on a floor map to get heatmap visualization during the design phase.
For a fabric network, you cannot place APs on a floor map during the design time. The APs are onboarded after adding devices to a fabric network.
For more information, see Work with APs on a floor map.
Define network settings, such as AAA (Cisco ISE is configured for Network and Client Endpoint), NetFlow Collector, NTP, DHCP, DNS, syslog, and SNMP traps. These network servers become the default for your entire network.
You can configure up to six AAA servers on the Wireless window during the SSID creation.
For more information, see Network settings overview, Configure global network servers, and Add AAA server.
Configure device credentials, such as CLI, SNMP, and HTTPs.
For more information, see Configure global device credentials, Add global CLI credentials, Add global SNMPv2c credentials, Add global SNMPv3 credentials, and Add global HTTPS credentials.
Configure IP address pools at the global level.
To configure an IP address pool, see Configure IP address pools.
To reserve an IP address pool for the building that you are provisioning, see Reserve IP Address Pools.
Create enterprise and guest wireless networks. Define the global wireless settings once, and then Catalyst Center pushes the configurations to various devices across geographical locations.
Designing a wireless network is a two-step process. First, you must create SSIDs on the Wireless window. Then, associate the created SSID to a wireless network profile. This profile helps you to construct a topology, which is used to deploy devices on a site.
For more information, see Create SSIDs for an enterprise wireless network and Create SSIDs for a guest wireless network.
Configure the backhaul settings.
On the Policy window, do this configuration:
Create a virtual network. The virtual network segments your physical network into multiple logical networks.
Create a group-based access control policy, and add a contract. For more information, see Create group-based access control policy.
Provision Cisco Catalyst 9000 Series Switches and the edge node switches with the configurations added during the design phase.
Create a fabric site.
Add devices to the fabric network by creating a CP+Border+Edge or CP+Border.
Enable embedded wireless capabilities on the Cisco Catalyst 9800 Embedded Wireless Controller for Catalyst 9000 Series Switches.
Onboard APs in the fabric site.
For more information, see Provision SD-Access LISP Fabric Network.
After the devices are deployed successfully, the deploy status changes from Configuring to Success.
Before provisioning a Cisco Catalyst 9800 Embedded Wireless Controller on Catalyst 9000 Series Switches, ensure that you have completed the steps in Configure Cisco Catalyst 9800 Embedded Wireless Controller for Catalyst 9000 Switches.
This procedure explains how to provision embedded wireless on Cisco Catalyst 9300 Series Switches, Cisco Catalyst 9400 Series Switches, and Cisco Catalyst 9500H Series Switches.
|
Step 1 |
From the main menu, choose . The Inventory window display with the discovered devices listed. |
|
Step 2 |
Check the check box next to the Catalyst 9000 Series Switch device and the edge switch that you want to associate to a site. |
|
Step 3 |
From the Actions drop-down list, choose . Assign the devices to a site. For more information, see Assign an unprovisioned device to a site. |
|
Step 4 |
In the window, check the check box next to the device name that you want to provision. |
|
Step 5 |
To provision the edge switch, check the check box next to the edge switch that you want to provision. |
|
Step 6 |
To add devices to a fabric site, click the menu icon and choose . |
|
Step 7 |
Create a fabric site. For more information, see Add a fabric site. |
|
Step 8 |
Add an IP transit network. |
|
Step 9 |
Add devices and associate virtual networks to a fabric site. |
|
Step 10 |
Add the Cisco Catalyst 9000 Series Switch as a control plane, a border node, and an edge node or a control plane and a border node.
|
|
Step 11 |
To enable embedded wireless on the device, click the device that is added as a Edge, CP+Border+Edge or CP+Border, and click the Embedded Wireless LAN Controller toggle button. |
|
Step 12 |
On the Manage Scope window, do these tasks:
You can select either a parent site or individual sites. If you select a parent site, all the children under the parent site are also selected. You can uncheck the check box to deselect an individual site. You can also use the Search Hierarchy search field or the filter icon to find a site. |
|
Step 13 |
Click Next. |
|
Step 14 |
On the Advanced window, configure the required settings. To enable the Rolling AP Upgrade feature, check the Enable check box. (Optional) If you check this check box, from the AP Reboot Percentage drop-down list, select a percentage. |
|
Step 15 |
Click Next. |
|
Step 16 |
On the Summary window, review the configuration settings, and click Save. |
|
Step 17 |
On the Modify Fabric step, click Now to commit the changes, and click Apply to apply the configurations. |
|
Step 18 |
In the Catalyst Center GUI, click the menu icon and choose . A list of fabric sites displays. |
|
Step 19 |
Select the fabric site that was created, and click the Host Onboarding tab to enable IP pool for APs. |
|
Step 20 |
Select the authentication template that is applied for devices in the fabric site. Then, click Save. |
|
Step 21 |
Under Virtual Networks, click INFRA_VN to associate one or more IP pools with the selected virtual network. |
|
Step 22 |
Under Virtual Network, click the guest virtual networks to associate IP pools for the selected guest virtual network. |
|
Step 23 |
Check the IP Pool Name check box that was created for APs during the design phase. |
|
Step 24 |
Click Update to save the setting. The AP gets the IP address from the specified pool, which is associated with the AP VLAN and registers with the wireless controller through one of the discovery methods. |
|
Step 25 |
Specify wireless SSIDs within the network that hosts can access. Under the Wireless SSID section, select the guest or enterprise SSIDs and assign address pools, and click Save. |
|
Step 26 |
Manually trigger resynchronization by choosing to see the APs on Catalyst Center for embedded wireless. |
|
Step 27 |
Provision the AP. For more information, see Provision Cisco APs on day 1. |
|
Step 28 |
Configure and deploy application policies. For more information, see Create an application policy, Deploy an application policy, and Edit an application policy. Provision the Catalyst 9300 Series Switches and Cisco Catalyst 9500H Series Switches before deploying an application policy. Two different policies with different business relevance for two different SSIDs don’t work. The last deployed policy takes precedence when you’re setting up the relevance. Changing the default business relevance for an application doesn’t work in FlexConnect mode. You can apply an application policy only on a nonfabric SSID. |
Catalyst Center allows you to customize individual features or parameters on Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controllers using the Per-Device Configuration feature. Using Per-Device Configuration, you can create, edit, clone, and delete the device-level configurations for a wireless controller.
You can use these configurations to onboard new wireless controllers to Catalyst Center and manage their configurations. You can also manage the APs associated with these wireless controllers.
By default, the Per-Device Configuration feature is disabled on Catalyst Center. To enable the configurations, see Enable Per-Device Configuration for a Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller.
Per-Device Configuration isn’t supported for
wireless controllers that were previously added to Catalyst Center and are using intent-based wireless network configurations with site-based network profiles (for these wireless controllers, Per-Device Configuration is available in read-only mode), and
SD-Access wireless configurations.
For AI-Enhanced RRM configurations, Per-Device Configuration is supported for only the Assurance use case with the Enable Without Device Provisioning deployment type.
Ensure that the wireless controller is running Cisco IOS XE Release 17.12 or later.
Add the wireless controller to Catalyst Center.
You can add a single device manually and add multiple devices using discovery or by importing a CSV file on the Inventory window. For more information, see Add devices to the Catalyst Center Inventory.
You can migrate the devices from Cisco Prime Infrastructure using the Prime Data Migration Tool (PDMT). For more information, see Cisco Prime Infrastructure to Cisco Catalyst Center Prime Data Migration Guide.
Ensure that the devices are displayed on the Inventory window and are in the Managed state.
For more information, see About Inventory and Display information about your inventory.
Design your network hierarchy by adding areas, buildings, and floors. This structure makes it easier to identify sites for applying configurations later.
You can either
create a network hierarchy (see Create, edit, and delete a site and Add, edit, and delete a building), or
import an existing network hierarchy into Catalyst Center if you have it on Cisco Prime Infrastructure (see Import your site hierarchy to Catalyst Center).
Add the location information of APs, and position them on the floor map to visualize the heatmap coverage.
For more information, see Work with APs on a floor map.
Ensure that the country codes are configured.
For more information, see About wireless devices and country codes.
Use this procedure to enable the Per-Device Configuration feature for a Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller.
 Note |
If the wireless controller is managed using intent-based wireless network configurations with site-based network profiles, Per-Device Configuration can be used in read-only mode for the wireless controllers. |
Ensure that the prerequisites are met. See Prerequisites for Per-Device Configuration for a Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
|
Step 3 |
From the top-left corner of the device details window, click Enable Per-Device Configuration. |
|
Step 4 |
In the Per-device configuration dialog box, view the details and click Enable. |
Ensure that the wireless controller is resynchronized before performing other operations. For more information on manually resynchronizing the wireless controller, see Resynchronize device information.
Use this procedure to configure and provision individual features using Per-Device Configuration for a wireless controller.
Ensure that
the prerequisites are met (see Prerequisites for Per-Device Configuration for a Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller) and
Per-Device Configuration is enabled on the wireless controller (see Enable Per-Device Configuration for a Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller).
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||
|
Step 3 |
(Optional) From the top-left corner of the device details window, click Manage APs to modify the AP configuration for the APs associated with the wireless controller. For more information, see Manage APs associated with a Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller. |
||
|
Step 4 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, configure and provision the required features for the wireless controller.
To search for a configuration, in the left pane of the device details window, click the Search Features field, and enter the name of the configuration.
|
Use this procedure to manage the APs associated with a wireless controller through Per-Device Configuration. You can configure the tags (site tag, policy tag, and RF tag) and tag-mapping profiles for APs associated with a wireless controller.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 3 |
From the top-left corner of the device details window, click Manage APs. |
||||||||||
|
Step 4 |
(Optional) In the Access Points slide-in pane, edit the AP configuration set under Operational Access Points.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 5 |
(Optional) Assign APs to a site.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 6 |
(Optional) Click Configure AP and Radio Parameters to configure the AP and radio parameters. For more information, see Configure APs. |
||||||||||
|
Step 7 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||||||||||
|
Step 8 |
If the wireless controller manages APs that don't meet the license requirements, Catalyst Center displays a dialog box with the details. In the dialog box, choose the required option.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 9 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||||||
|
Step 10 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to customize the Per-Device Configuration table settings for a feature if the device details window displays a table.
 Note |
This procedure isn’t applicable if the window doesn't display a table for the feature, such as Airtime Fairness. |
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, click the required settings. |
|
Step 4 |
In the corresponding configuration table, click the gear icon at the top-right corner. |
|
Step 5 |
Click Table Appearance to adjust the table density and table striping.
|
|
Step 6 |
(Optional) To reset the table settings, click Reset All Settings. |
Use this procedure to edit the Per-Device Configuration for a feature if the device details window displays a table.
 Note |
This procedure isn’t applicable if the window doesn't display a table for the feature, such as Airtime Fairness. |
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, click the required per-device feature. |
|
Step 4 |
Check the check box next to the configuration that you want to edit. |
|
Step 5 |
Hover your cursor over Actions and click Edit. |
|
Step 6 |
In the slide-in pane, edit the required configurations. |
|
Step 7 |
Click Review and Provision. |
|
Step 8 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
|
Step 9 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to clone the Per-Device Configuration for a feature if the device details window displays a table.
 Note |
This procedure isn’t applicable if the window doesn't display a table for the feature, such as Airtime Fairness. |
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, click the required per-device feature. |
|
Step 4 |
Check the check box next to the configuration that you want to clone. |
|
Step 5 |
Hover your cursor over Actions and click Clone. |
|
Step 6 |
In the slide-in pane, complete the required configurations. |
|
Step 7 |
(Optional) Edit the other necessary configurations. |
|
Step 8 |
Click Review and Provision. |
|
Step 9 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
|
Step 10 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to delete the Per-Device Configuration for a feature if the device details window displays a table.
 Note |
This procedure isn’t applicable if the window doesn't display a table for the feature, such as Airtime Fairness. |
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, click the required per-device feature. |
|
Step 4 |
Check the check box next to the configurations that you want to delete. |
|
Step 5 |
Hover your cursor over Actions and click Delete. |
|
Step 6 |
In the dialog box, click Yes. |
|
Step 7 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
|
Step 8 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
This section provides information about the per-device WLAN configurations for a wireless controller.
Use this procedure to create a WLAN profile for a wireless controller and provision it. WLAN profiles configure the Wi-Fi settings, enabling users to connect to a wireless network.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand WLAN and click WLAN Profiles. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Step 4 |
Click Add. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Step 5 |
In the General tab of the Create WLAN Profile slide-in pane, complete these configurations. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Step 6 |
Under Security, click Layer 2 and configure a security policy.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Step 7 |
(Optional) Under Security, click Layer 3 and complete these configurations. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Step 8 |
(Optional) Under Security, click AAA and complete these configurations. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Step 9 |
(Optional) Under Advanced, click 11ax and complete these configurations. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Step 10 |
(Optional) Under Advanced, click 11k and complete these configurations. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Step 11 |
(Optional) Under Advanced, click 11v BSS and complete these configurations. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Step 12 |
(Optional) Under Advanced, click Device Analytics and check the required check boxes to enable the corresponding configurations.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Step 13 |
(Optional) Under Advanced, click Max Clients and enter data in these fields.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Step 14 |
Under Advanced, click Off Channel Scan and complete these configurations. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Step 15 |
Under Advanced, click Miscellaneous and complete these configurations. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Step 16 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Step 17 |
If the wireless controller manages APs that don't meet the license requirements, Catalyst Center displays a dialog box with the details. In the dialog box, choose the required option.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Step 18 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Step 19 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to create a policy profile for a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand WLAN and click Policy Profiles. |
||||||||||
|
Step 4 |
Click Add. |
||||||||||
|
Step 5 |
In the General tab of the Create Policy Profile slide-in pane, complete the required configurations. |
||||||||||
|
Step 6 |
(Optional) Click Access Policies and configure the required access policies. |
||||||||||
|
Step 7 |
Click QoS and AVC and complete the required configurations. |
||||||||||
|
Step 8 |
Under SIP-CAC, check the required check boxes to enable the corresponding configurations.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 9 |
(Optional) Click Mobility and configure mobility anchors. |
||||||||||
|
Step 10 |
Under Advanced, click WLAN Timeout and configure the client WLAN timeout. |
||||||||||
|
Step 11 |
(Optional) Under Advanced, click WLAN Flex Policy and configure a WLAN flex policy. |
||||||||||
|
Step 12 |
(Optional) Under Advanced, click AAA Policy and configure the AAA policy. |
||||||||||
|
Step 13 |
(Optional) Under Advanced, click DHCP and configure DHCP for wireless clients.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 14 |
(Optional) Under Advanced, click DNS Layer Security and configure DNS layer security. |
||||||||||
|
Step 15 |
(Optional) Under Advanced, click Miscellaneous and configure miscellaneous wireless profile configurations such as user-defined (private) network, air time fairness, and so on. |
||||||||||
|
Step 16 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||||||||||
|
Step 17 |
If the wireless controller manages APs that don't meet the license requirements, Catalyst Center displays a dialog box with the details. In the dialog box, choose the required option.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 18 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||||||
|
Step 19 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to create a remote LAN (RLAN) profile for a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand WLAN and click Remote LAN Profiles. |
||||||||||
|
Step 4 |
Click Add. |
||||||||||
|
Step 5 |
In the General tab of the Create Remote LAN Profile slide-in pane, complete these configurations. |
||||||||||
|
Step 6 |
Under Security, click Layer 2 and configure Layer 2 security policies for the RLAN. |
||||||||||
|
Step 7 |
(Optional) Under Security, click Layer 3 and configure the Layer 3 policies and ACL for the RLAN. |
||||||||||
|
Step 8 |
(Optional) Under Security, click AAA and check the Local EAP Authentication check box to enable an EAP profile on an RLAN. If you check this check box, from the EAP Profile Name drop-down list, choose an EAP profile name. Associating an RLAN profile with local EAP enhances security, access control, compliance, network performance, user management, troubleshooting, and scalability in a wireless network environment. |
||||||||||
|
Step 9 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||||||||||
|
Step 10 |
If the wireless controller manages APs that don't meet the license requirements, Catalyst Center displays a dialog box with the details. In the dialog box, choose the required option.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 11 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||||||
|
Step 12 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to create a remote LAN (RLAN) policy for a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand WLAN and click Remote LAN Policies. |
||||||||||
|
Step 4 |
Click Add. |
||||||||||
|
Step 5 |
In the General tab of the Create Remote LAN Policy slide-in pane, complete the required configurations. |
||||||||||
|
Step 6 |
Click Access Policies and complete the required configurations. |
||||||||||
|
Step 7 |
Click Advanced and complete the required configurations. |
||||||||||
|
Step 8 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||||||||||
|
Step 9 |
If the wireless controller manages APs that don't meet the license requirements, Catalyst Center displays a dialog box with the details. In the dialog box, choose the required option.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 10 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||||||
|
Step 11 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to edit the parameters in the default 802.11be profile for a wireless controller and provision it. 802.11be profile is applicable for wireless controllers that are running Cisco IOS XE Release 17.15.1 or later.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand WLAN and click 802.11be Profiles. |
||||||||||
|
Step 4 |
Click the radio button next to the default 802.11be profile. |
||||||||||
|
Step 5 |
Hover your cursor over Actions and click Edit. |
||||||||||
|
Step 6 |
(Optional) In the Description field of the Edit 802.11be Profiles slide-in pane, update the description. |
||||||||||
|
Step 7 |
(Optional) Use the required check boxes to enable or disable the corresponding parameters. |
||||||||||
|
Step 8 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||||||||||
|
Step 9 |
If the wireless controller manages APs that don't meet the license requirements, Catalyst Center displays a dialog box with the details. In the dialog box, choose the required option.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 10 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||||||
|
Step 11 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
This section provides information about the per-device RF configurations for a Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller.
Use this procedure to create an RF profile for a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand RF and click RF Profiles. |
||||||||||
|
Step 4 |
Click Add. |
||||||||||
|
Step 5 |
In the General tab of the Create RF Profiles slide-in pane, configure the required parameters. |
||||||||||
|
Step 6 |
Click 802.11 and do these steps:
|
||||||||||
|
Step 7 |
Under RRM, click Trap Thresholds and complete the required configurations. |
||||||||||
|
Step 8 |
Under RRM, click Coverage and complete the required configurations. |
||||||||||
|
Step 9 |
Under RRM, click TPC and complete the required configurations. |
||||||||||
|
Step 10 |
Under RRM, click DCA and complete the required configurations. |
||||||||||
|
Step 11 |
If you chose the 2.4-GHz band, under RRM, click Band Select and complete these configurations. |
||||||||||
|
Step 12 |
Click 802.11ax and complete the required configurations. |
||||||||||
|
Step 13 |
Click Advanced and complete the required configurations. |
||||||||||
|
Step 14 |
Click 802.11be and use the Preamble Puncture toggle button to enable or disable preamble puncturing. |
||||||||||
|
Step 15 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||||||||||
|
Step 16 |
If the wireless controller manages APs that don't meet the license requirements, Catalyst Center displays a dialog box with the details. In the dialog box, choose the required option.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 17 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||||||
|
Step 18 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to create a radio antenna profile for a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand RF and click Radio Antenna Profiles. |
||||||||||
|
Step 4 |
Click Add. |
||||||||||
|
Step 5 |
In the Radio Antenna Profile Name field of the Create Radio Antenna Profile slide-in pane, enter a name for the radio antenna profile. The profile name can contain up to 32 characters. |
||||||||||
|
Step 6 |
(Optional) In the Description field, enter a description. |
||||||||||
|
Step 7 |
From the Antenna Beam drop-down list, choose a beam steering mode for the AP slot. |
||||||||||
|
Step 8 |
(Optional) In the Number of Antennas to be Enabled field, enter the number of antennas to be enabled for the AP slot. The valid range is from 0 to 8. |
||||||||||
|
Step 9 |
(Optional) Check the required check boxes to enable the corresponding configurations.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 10 |
Under DTIM Period, in the 6 GHz Band field, enter a Delivery Traffic Indication Map (DTIM) interval for the 6-GHz band. The valid range is from 1 to 255. The default value is 1. |
||||||||||
|
Step 11 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||||||||||
|
Step 12 |
If the wireless controller manages APs that don't meet the license requirements, Catalyst Center displays a dialog box with the details. In the dialog box, choose the required option.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 13 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||||||
|
Step 14 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to create a multi-basic service set identifier (BSSID) profile for a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand RF and click Multi BSSID Profiles. |
||||||||||
|
Step 4 |
Click Add. |
||||||||||
|
Step 5 |
In the Multi BSSID Profile Name field of the Create Multi BSSID Profile slide-in pane, enter a name for the multi-BSSID profile. |
||||||||||
|
Step 6 |
(Optional) In the Description field, enter a description. |
||||||||||
|
Step 7 |
(Optional) Under 802.11ax, check the corresponding check boxes to enable the corresponding parameters. |
||||||||||
|
Step 8 |
(Optional) Under 802.11be, check the corresponding check boxes to enable the corresponding parameters. |
||||||||||
|
Step 9 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||||||||||
|
Step 10 |
If the wireless controller manages APs that don't meet the license requirements, Catalyst Center displays a dialog box with the details. In the dialog box, choose the required option.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 11 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||||||
|
Step 12 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
This section provides information about the per-device AP join configurations for a Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller.
Use this procedure to create an AP join profile for a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand AP Join and click AP Join Profiles. |
||||||||||
|
Step 4 |
Click Add. |
||||||||||
|
Step 5 |
In the General tab of the Create AP Join Profile slide-in pane, complete these configurations. |
||||||||||
|
Step 6 |
Click Client and complete these configurations. |
||||||||||
|
Step 7 |
Under CAPWAP, click High Availability and complete these configurations. |
||||||||||
|
Step 8 |
Under CAPWAP, click Advanced and complete these configurations. |
||||||||||
|
Step 9 |
Under AP, click General and complete these configurations. |
||||||||||
|
Step 10 |
(Optional) Under AP, click Power Management and complete these configurations. |
||||||||||
|
Step 11 |
Under AP, click Hyperlocation and complete these configurations. |
||||||||||
|
Step 12 |
Under AP, click AP Statistics and complete these configurations. |
||||||||||
|
Step 13 |
Under Management, click Device and complete these configurations. |
||||||||||
|
Step 14 |
Under Management, click User and complete these configurations.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 15 |
Under Management, click Credentials and complete these configurations.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 16 |
(Optional) Under Management, click CDP and check the CDP State check box to enable CDP for the AP. |
||||||||||
|
Step 17 |
Click Security and complete these configurations. |
||||||||||
|
Step 18 |
(Optional) Under iCAP Client Telemetry, click Full Packet Trace and complete these configurations. |
||||||||||
|
Step 19 |
(Optional) Under iCAP Client Telemetry, click Partial Packet Trace and complete the configurations. |
||||||||||
|
Step 20 |
Under iCAP Client Telemetry, click Anomaly Detection and complete these configurations. |
||||||||||
|
Step 21 |
Under iCAP Client Telemetry, click Statistics and complete these configurations. |
||||||||||
|
Step 22 |
Click iCAP AP Telemetry Subscriptions and complete these configurations. |
||||||||||
|
Step 23 |
(Optional) Click QoS and complete these configurations. |
||||||||||
|
Step 24 |
Click Miscellaneous and complete these configurations.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 25 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||||||||||
|
Step 26 |
If the wireless controller manages APs that don't meet the license requirements, Catalyst Center displays a dialog box with the details. In the dialog box, choose the required option.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 27 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||||||
|
Step 28 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to configure the global mesh parameters for a wireless controller and provision them.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand AP Join and click Mesh. |
||||||||||
|
Step 4 |
Click the Global tab. |
||||||||||
|
Step 5 |
(Optional) Under General, use the check boxes to enable or disable the corresponding configurations.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 6 |
(Optional) Under Backhaul, use the check boxes to enable or disable the corresponding configurations.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 7 |
(Optional) Under Security, check the PSK Provisioning check box to enable PSK provisioning for the MAP.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 8 |
Under Alarm, enter data in these fields.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 9 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||||||||||
|
Step 10 |
If the wireless controller manages APs that don't meet the license requirements, Catalyst Center displays a dialog box with the details. In the dialog box, choose the required option.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 11 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||||||
|
Step 12 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to create a mesh preshared key (PSK) for a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand AP Join and click Mesh. |
||||||||||
|
Step 4 |
Click the PSK Keys tab. |
||||||||||
|
Step 5 |
Click Add.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 6 |
From the Index drop-down list of the Create Mesh Profile Key slide-in pane, choose an index for the PSK. |
||||||||||
|
Step 7 |
In the Psk Key field, enter the PSK. The PSK can contain from 3 to 32 characters. |
||||||||||
|
Step 8 |
From the Psk Key Type drop-down list, choose a PSK type. |
||||||||||
|
Step 9 |
(Optional) In the Description field, enter a description for the PSK. |
||||||||||
|
Step 10 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||||||||||
|
Step 11 |
If the wireless controller manages APs that don't meet the license requirements, Catalyst Center displays a dialog box with the details. In the dialog box, choose the required option.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 12 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||||||
|
Step 13 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to create a mesh profile for a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand AP Join and click Mesh. |
||||||||||
|
Step 4 |
Click the Mesh Profiles tab. |
||||||||||
|
Step 5 |
Click Add. |
||||||||||
|
Step 6 |
In the General tab of the Create Mesh Profile slide-in pane, complete these configurations. |
||||||||||
|
Step 7 |
Click Advanced and complete these configurations. |
||||||||||
|
Step 8 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||||||||||
|
Step 9 |
If the wireless controller manages APs that don't meet the license requirements, Catalyst Center displays a dialog box with the details. In the dialog box, choose the required option.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 10 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||||||
|
Step 11 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to create a power profile for a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand AP Join and click Power Profiles. |
||||||||||
|
Step 4 |
Click Add. |
||||||||||
|
Step 5 |
In the Profile Name field of the Create Power Profile slide-in pane, enter a name for the power profile. |
||||||||||
|
Step 6 |
(Optional) In the Description field, enter a description. |
||||||||||
|
Step 7 |
(Optional) In the Power Save Client Threshold field, enter the threshold up to which the AP can stay on the power save mode. The valid range is from 1 to 32. The default value is 1. |
||||||||||
|
Step 8 |
(Optional) Under Rules, click Add to add a rule.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 9 |
(Optional) To delete the rules, complete these steps.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 10 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||||||||||
|
Step 11 |
If the wireless controller manages APs that don't meet the license requirements, Catalyst Center displays a dialog box with the details. In the dialog box, choose the required option.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 12 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||||||
|
Step 13 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
You can set up daily, weekly, or monthly recurrence schedules for calendar profiles. When associated with a power policy, this configuration automates the powering down of interfaces connected to APs. Use this procedure to create a calendar profile for a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand AP Join and click Calendar Profiles. |
||||||||||
|
Step 4 |
Click Add. |
||||||||||
|
Step 5 |
In the Profile Name field of the Create Calendar Profile slide-in pane, enter a name for the calendar profile. |
||||||||||
|
Step 6 |
Under Recurrence, choose the recurrence frequency for the calendar profile.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 7 |
Under Start Time and End Time, enter the start time and end time for the recurrence schedule. |
||||||||||
|
Step 8 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||||||||||
|
Step 9 |
If the wireless controller manages APs that don't meet the license requirements, Catalyst Center displays a dialog box with the details. In the dialog box, choose the required option.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 10 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||||||
|
Step 11 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
This section provides information about the per-device flex profile configurations for a Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller.
Use this procedure to create a flex profile for a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, click Flex Profiles. |
||||||||||
|
Step 4 |
Click Add. |
||||||||||
|
Step 5 |
In the General tab of the Create Flex Profile slide-in pane, complete these configurations. |
||||||||||
|
Step 6 |
(Optional) Click Local Authentication and complete these configurations. |
||||||||||
|
Step 7 |
(Optional) Click Policy ACL and configure the ACLs.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 8 |
(Optional) Click VLAN and configure VLANs.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 9 |
(Optional) Click DNS Layer Security and configure parameter maps.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 10 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||||||||||
|
Step 11 |
If the wireless controller manages APs that don't meet the license requirements, Catalyst Center displays a dialog box with the details. In the dialog box, choose the required option.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 12 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||||||
|
Step 13 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
This section provides information about the per-device tag configurations for a Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller.
Use this procedure to create a site tag for the APs associated with a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Tags and click Site Tags. |
||||||||||
|
Step 4 |
Click Add. |
||||||||||
|
Step 5 |
In the Site Tag Name field of the Create Site Tag slide-in pane, enter a name for the site tag. |
||||||||||
|
Step 6 |
(Optional) In the Description field, enter a description. |
||||||||||
|
Step 7 |
From the AP Join Profile drop-down list, choose an AP join profile. To create an AP join profile, see Create an AP join profile for a Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller. |
||||||||||
|
Step 8 |
Use the Local Site check box to enable or disable the local site. If this check box is unchecked, from the Flex Profile drop-down list, choose a flex profile. To create a flex profile, see Create a flex profile for a Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller. |
||||||||||
|
Step 9 |
In the Load field, enter an estimate of the relative load contributed by the site. The valid range is from 0 to 1000. The default value is 0. You can use the AP count for an approximate value. |
||||||||||
|
Step 10 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||||||||||
|
Step 11 |
If the wireless controller manages APs that don't meet the license requirements, Catalyst Center displays a dialog box with the details. In the dialog box, choose the required option.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 12 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||||||
|
Step 13 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to create a policy tag for the APs associated with a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Tags, and click Policy Tags. |
||||||||||
|
Step 4 |
Click Add. |
||||||||||
|
Step 5 |
In the Tag Name field of the Create Policy Tags slide-in pane, enter a name for the policy tag. |
||||||||||
|
Step 6 |
(Optional) In the Description field, enter a description. |
||||||||||
|
Step 7 |
(Optional) Under WLAN Profile - Policy Profile Mapping, configure the WLAN profile to policy profile mapping.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 8 |
(Optional) Under RLAN Profile - RLAN Policy Mapping, configure RLAN profile to RLAN policy mapping.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 9 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||||||||||
|
Step 10 |
If the wireless controller manages APs that don't meet the license requirements, Catalyst Center displays a dialog box with the details. In the dialog box, choose the required option.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 11 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||||||
|
Step 12 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to create an RF tag for the APs associated with a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Tags and click RF Tags. |
||||||||||
|
Step 4 |
Click Add. |
||||||||||
|
Step 5 |
In the Tag Name field of the Create RF Tag slide-in pane, enter a name for the RF tag. |
||||||||||
|
Step 6 |
(Optional) In the Description field, enter a description. |
||||||||||
|
Step 7 |
(Optional) From these drop-down lists, choose the required RF profile for the corresponding band.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 8 |
(Optional) Click Show Slot Configuration to view and update the slot configurations. From these drop-down lists, choose the required radio antenna profile for the corresponding band and slot.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 9 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||||||||||
|
Step 10 |
If the wireless controller manages APs that don't meet the license requirements, Catalyst Center displays a dialog box with the details. In the dialog box, choose the required option.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 11 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||||||
|
Step 12 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to configure the tag priority for a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Tags and click Tag Mapping. |
||||||||||
|
Step 4 |
(Optional) In the Tag Priority tab, use the toggle buttons to enable or disable the required configurations.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 5 |
(Optional) Check the AP Tag Persistency check box to enable persistent AP tags. |
||||||||||
|
Step 6 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||||||||||
|
Step 7 |
If the wireless controller manages APs that don't meet the license requirements, Catalyst Center displays a dialog box with the details. In the dialog box, choose the required option.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 8 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||||||
|
Step 9 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to create static tag mapping for APs associated with a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Tags and click Tag Mapping. |
||||||||||
|
Step 4 |
Click the Static tab. |
||||||||||
|
Step 5 |
Click Add. The opens. |
||||||||||
|
Step 6 |
In the AP Ethernet MAC Address field of the Add Access Point slide-in pane, enter the Ethernet MAC address of the AP. |
||||||||||
|
Step 7 |
From these drop-down lists, choose the required tags.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 8 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||||||||||
|
Step 9 |
If the wireless controller manages APs that don't meet the license requirements, Catalyst Center displays a dialog box with the details. In the dialog box, choose the required option.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 10 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||||||
|
Step 11 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to create a location-based tag-mapping rule for APs associated with a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Tags and click Tag Mapping. |
||||||||||
|
Step 4 |
Click the Location tab. |
||||||||||
|
Step 5 |
Click Add. |
||||||||||
|
Step 6 |
In the General tab of the Create Location Rule slide-in pane, complete these configurations. |
||||||||||
|
Step 7 |
(Optional) Click AP Provisioning and complete these configurations.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 8 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||||||||||
|
Step 9 |
If the wireless controller manages APs that don't meet the license requirements, Catalyst Center displays a dialog box with the details. In the dialog box, choose the required option.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 10 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||||||
|
Step 11 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to create a rule-based tag-mapping profile for APs associated with a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Tags and click Tag Mapping. |
||||||||||
|
Step 4 |
Click the Rule-Based tab. |
||||||||||
|
Step 5 |
Click Add. |
||||||||||
|
Step 6 |
In the Rule Name field of the Add Regex Rule Profile slide-in pane, enter a name for the rule. |
||||||||||
|
Step 7 |
In the AP Name Regex field, enter a regular expression for filtering the AP name. For example, if you have an AP ap-lab-12, you can configure the filter with a regular expression, such as ap-lab, to match the AP name. |
||||||||||
|
Step 8 |
(Optional) In the Priority field, enter a priority for the rule. If you enter 0, the rule becomes inactive. You must enter a valid priority value for an active rule. |
||||||||||
|
Step 9 |
(Optional) From these drop-down lists, choose the required tags.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 10 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||||||||||
|
Step 11 |
If the wireless controller manages APs that don't meet the license requirements, Catalyst Center displays a dialog box with the details. In the dialog box, choose the required option.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 12 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||||||
|
Step 13 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
This section provides information about the per-device security configurations for a Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller.
Use this procedure to create a RADIUS server for a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||||||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||||||
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Security and click AAA. |
||||||
|
Step 4 |
Hover your cursor over Servers/Groups, under RADIUS, click Servers. |
||||||
|
Step 5 |
Click Add. |
||||||
|
Step 6 |
In the Server Name field of the Create RADIUS Server slide-in pane, enter a unique name for the RADIUS server. |
||||||
|
Step 7 |
From the Type drop-down list, choose the required type. |
||||||
|
Step 8 |
Based on the type of the RADIUS server, enter data in the corresponding field.
|
||||||
|
Step 9 |
(Optional) Check the PAC Key check box to transition from key to Proxy Auto Configuration (PAC) key. |
||||||
|
Step 10 |
Complete these configurations.
|
||||||
|
Step 11 |
(Optional) Enter data in these fields.
|
||||||
|
Step 12 |
(Optional) To enable a change of authorization (CoA) key for dynamic updates to user sessions, check the Support for CoA check box.
(Optional) If you check this check box, from the CoA Server Key Type drop-down list, choose a key type. If you chose a CoA server key type, enter data in these fields.
|
||||||
|
Step 13 |
(Optional) Check the Automate Tester check box to set up automated network testing. If you check this check box, complete these configurations.
|
||||||
|
Step 14 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||||||
|
Step 15 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||
|
Step 16 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to create a RADIUS server group for a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Security and click AAA. |
|
Step 4 |
Hover your cursor over Servers/Groups, under RADIUS, click Server Groups. |
|
Step 5 |
Click Add. |
|
Step 6 |
In the Server Group Name field of the Create RADIUS Server Group slide-in pane, enter a name for the RADIUS server group. |
|
Step 7 |
From the Source Interface VLAN ID drop-down list, choose a VLAN ID. Associating a VLAN with a RADIUS server group allows you to control network access and policies based on user authentication and authorization. |
|
Step 8 |
From the MAC Delimiter drop-down list, choose the character for RADIUS compatibility mode. |
|
Step 9 |
From the MAC Filtering drop-down list, choose a MAC filtering option. |
|
Step 10 |
(Optional) In the Dead Time (min) field, enter the time, in minutes, to stop using an unresponsive server. The valid range is from 0 to 1440. |
|
Step 11 |
(Optional) Check the Load Balance check box to enable load balancing in the RADIUS server group. |
|
Step 12 |
Under Servers, add servers using one of these options.
|
|
Step 13 |
Click Review and Provision. |
|
Step 14 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
|
Step 15 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to create a TACACS+ server for a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Security and click AAA. |
|
Step 4 |
Hover your cursor over Servers/Groups, under TACACS+, click Servers. |
|
Step 5 |
Click Add. |
|
Step 6 |
In the Server Name field of the Create TACACS+ Server slide-in pane, enter a name for the TACACS+ server. |
|
Step 7 |
From the Type drop-down list, choose the required type. |
|
Step 8 |
Based on the type of the TACACS+ server, enter data in the corresponding field.
|
|
Step 9 |
From the Key Type drop-down list, choose a key type. |
|
Step 10 |
In the Key field, enter the key for the TACACS+ server for secure authentication. |
|
Step 11 |
In the Confirm Key field, confirm the key for the TACACS+ server. |
|
Step 12 |
(Optional) In the Port field, enter the port number to listen for the incoming requests. The valid range is from 0 to 65535. The default value is 49. |
|
Step 13 |
(Optional) In the Server Timeout (sec) field, enter the time in seconds to wait for a response from the TACACS+ server. The valid range is from 1 to 1000. |
|
Step 14 |
Click Review and Provision. |
|
Step 15 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
|
Step 16 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to create a TACACS+ server group for a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Security and click AAA. |
|
Step 4 |
Hover your cursor over Servers/Groups, under TACACS+, click Server Groups. |
|
Step 5 |
Click Add. |
|
Step 6 |
In the Server Group Name field of the Create TACACS+ Server Group slide-in pane, enter a name for the server group. |
|
Step 7 |
Under Servers, add servers using one of these options.
|
|
Step 8 |
Click Review and Provision. |
|
Step 9 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
|
Step 10 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to create an LDAP server for a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||||||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||||||
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Security and click AAA. |
||||||
|
Step 4 |
Hover your cursor over Servers/Groups, under LDAP, click Servers. |
||||||
|
Step 5 |
Click Add. |
||||||
|
Step 6 |
In the Server Name field of the Create LDAP Server slide-in pane, enter a name for the LDAP server. |
||||||
|
Step 7 |
From the Type drop-down list, choose the required type. |
||||||
|
Step 8 |
Based on the type of the LDAP server, enter data in the corresponding field.
|
||||||
|
Step 9 |
(Optional) Check the Authenticate check box to enable a secure and compliant connection between the wireless controller and the LDAP server. If you check this check box, enter data in these fields.
|
||||||
|
Step 10 |
In the Port field, enter the server listening port number. The valid range is from 1 to 65535. The default value is 389. |
||||||
|
Step 11 |
In the User Based DN field, enter the base Distinguished Name (DN). |
||||||
|
Step 12 |
(Optional) In the Server Timeout (sec) field, enter the time, in seconds, to wait for a response from the LDAP server before retransmission. The valid range is from 1 to 65535. The default value is 30. |
||||||
|
Step 13 |
(Optional) Check the Secure Mode check box to ensure that the communication between the wireless controller and LDAP server is encrypted. (Optional) If you check this check box, from the Trustpoint Name drop-down list, choose a trustpoint. |
||||||
|
Step 14 |
(Optional) Under User Object Types, configure user object types.
|
||||||
|
Step 15 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||||||
|
Step 16 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||
|
Step 17 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to create an LDAP server group for a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Security and click AAA. |
|
Step 4 |
Hover your cursor over Servers/Groups, under LDAP, click Server Groups. |
|
Step 5 |
Click Add. |
|
Step 6 |
In the Server Group Name field of the Create LDAP Server Group slide-in pane, enter a name for the server group. |
|
Step 7 |
Under Servers, add servers using one of these options.
|
|
Step 8 |
Click Review and Provision. |
|
Step 9 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
|
Step 10 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to create an authentication method list for a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Security and click AAA. |
|
Step 4 |
Hover your cursor over AAA Method List and click Authentication. |
|
Step 5 |
Hover your cursor over Add and choose an authentication type.
|
|
Step 6 |
In the Method List Name field of the Create Authentication Method List Profile slide-in pane, enter a name for the authentication method list profile. |
|
Step 7 |
From the Group Type drop-down list, choose an option.
|
|
Step 8 |
(Optional) If you chose Group, check the Fallback to Local check box to use the fallback to the local username authentication. |
|
Step 9 |
(Optional) From the Server Groups drop-down list, choose a server group. To create a server group, see Create a RADIUS server group for a Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller and Create a TACACS+ server for a Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller. |
|
Step 10 |
Click Review and Provision. |
|
Step 11 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
|
Step 12 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to create an authorization method list for a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Security and click AAA. |
|
Step 4 |
Hover your cursor over AAA Method List and click Authorization. |
|
Step 5 |
Hover your cursor over Add and choose an authorization type. For MAC filter authorization, choose Type - Network. |
|
Step 6 |
In the Method List Name field of the Create Authorization Method List Profile slide-in pane, enter a name for the authorization method list profile. |
|
Step 7 |
From the Group Type drop-down list, choose an option.
|
|
Step 8 |
(Optional) If you chose Group, check the Fallback to Local check box to use the fallback to the local username authentication. |
|
Step 9 |
(Optional) Check the Authenticated check box to indicate success when the authentication is completed. |
|
Step 10 |
(Optional) From the Server Groups drop-down list, choose a server group. For information about how to create a server group, see Create a RADIUS server group for a Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller and Create a TACACS+ server for a Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller. |
|
Step 11 |
Click Review and Provision. |
|
Step 12 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
|
Step 13 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to create an accounting method list for a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Security and click AAA. |
|
Step 4 |
Hover your cursor over AAA Method List and choose Accounting. |
|
Step 5 |
Hover your cursor over Add and choose an AAA accounting type. For AAA-based accounting, choose Type - Identity. |
|
Step 6 |
In the Method List Name field of the Create Accounting Method List Profile slide-in pane, enter a name for the accounting method list profile. |
|
Step 7 |
From the Server Groups drop-down list, choose a server group for accounting. To create a server group, see Create a RADIUS server group for a Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller and Create a TACACS+ server for a Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller. |
|
Step 8 |
Click Review and Provision. |
|
Step 9 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
|
Step 10 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to configure the global AAA parameters for a wireless controller and provision them.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||||||||||||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||||||||||||
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Security and click AAA. |
||||||||||||
|
Step 4 |
Hover your cursor over AAA Advanced and choose Global Configuration. |
||||||||||||
|
Step 5 |
Under Global Configurations, complete these configurations.
|
||||||||||||
|
Step 6 |
Under RADIUS Attributes - Accounting, complete these configurations.
|
||||||||||||
|
Step 7 |
Under RADIUS Attributes - Authentication, complete these configurations.
|
||||||||||||
|
Step 8 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||||||||||||
|
Step 9 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||||||||
|
Step 10 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to configure the AP policy for a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Security and click AAA. |
|
Step 4 |
Hover your cursor over AAA Advanced and choose AP Policy. |
|
Step 5 |
(Optional) Check the required check boxes to configure the corresponding policies.
|
|
Step 6 |
From the Authorization Method List drop-down list, choose an authorization method list. To create an authorization method list for Type - Credential-download, see Create an authorization method list for a Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller. |
|
Step 7 |
Click Review and Provision. |
|
Step 8 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
|
Step 9 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to create a password policy for a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Security and click AAA. |
|
Step 4 |
Hover your cursor over AAA Advanced and choose Password Policy. |
|
Step 5 |
Click Add. |
|
Step 6 |
Enter data in these fields of the Create Password Policy slide-in pane.
|
|
Step 7 |
(Optional) Check the Prohibit Consecutive Four Keyboard Letters check box to prohibit the use of consecutive characters or numbers on the keyboard in the password. If you check this check box, the password can't contain four consecutive letters or numbers on the keyboard in both directions. |
|
Step 8 |
(Optional) Enter data in these fields.
|
|
Step 9 |
Click Review and Provision. |
|
Step 10 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
|
Step 11 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to configure RADIUS fallback for a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Security and click AAA. |
|
Step 4 |
Hover your cursor over AAA Advanced and choose RADIUS Fallback. |
|
Step 5 |
(Optional) Enter data in these fields.
|
|
Step 6 |
Click Review and Provision. |
|
Step 7 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
|
Step 8 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to create an attribute list for a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||||||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||||||
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Security and click AAA. |
||||||
|
Step 4 |
Hover your cursor over AAA Advanced and choose Attribute Lists. |
||||||
|
Step 5 |
Click Add. |
||||||
|
Step 6 |
In the Attribute List Name field of the Create Attribute List slide-in pane, enter a name for the attribute list. |
||||||
|
Step 7 |
(Optional) Under Attributes, configure the required attributes.
|
||||||
|
Step 8 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||||||
|
Step 9 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||
|
Step 10 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to create a device authentication serial number for a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Security and click AAA. |
|
Step 4 |
Hover your cursor over AAA Advanced and choose Serial Numbers. |
|
Step 5 |
Click Add. |
|
Step 6 |
In the Serial Number field of the Create Device Authentication Serial Number slide-in pane, enter the device authentication serial number. It can contain up to 255 characters. |
|
Step 7 |
(Optional) From the Attribute List Name drop-down list, choose an attribute list. To create an attribute list, see Create an attribute list for a Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller. |
|
Step 8 |
Click Review and Provision. |
|
Step 9 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
|
Step 10 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to create a device authentication MAC address for a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Security and click AAA. |
|
Step 4 |
Hover your cursor over AAA Advanced and choose MAC Addresses. |
|
Step 5 |
Click Add. |
|
Step 6 |
In the MAC Address field of the Create Device Authentication MAC Address slide-in pane, enter the device authentication MAC address. It can contain up to 64 characters. |
|
Step 7 |
(Optional) From the Attribute List Name drop-down list, choose an attribute list. To create an attribute list, see Create an attribute list for a Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller. |
|
Step 8 |
(Optional) In the Description field, enter a description. |
|
Step 9 |
(Optional) From the WLAN Profile Name drop-down list, choose a WLAN profile. To create a WLAN profile, see Create a WLAN profile for a Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller. |
|
Step 10 |
Click Review and Provision. |
|
Step 11 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
|
Step 12 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to create an AAA policy profile for a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Security and click AAA Policy. |
|
Step 4 |
Click Add. |
|
Step 5 |
In the Policy Name field of the Create AAA Policy Profile slide-in pane, enter a name for the AAA policy. |
|
Step 6 |
From the NAS ID option drop-down lists, choose the required RADIUS NAS ID options. |
|
Step 7 |
Click Review and Provision. |
|
Step 8 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
|
Step 9 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to create an IPv4 ACL for a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||||||||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||||||||
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Security and click ACL. |
||||||||
|
Step 4 |
Hover your cursor over IPv4/IPv6, under IPv4, choose Standard. |
||||||||
|
Step 5 |
Click Add. |
||||||||
|
Step 6 |
In the ACL Name field of the Create IPv4 Standard ACL slide-in pane, enter a name for the IPv4 ACL. |
||||||||
|
Step 7 |
(Optional) Under Rules, configure the required rules.
|
||||||||
|
Step 8 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||||||||
|
Step 9 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||||
|
Step 10 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to create an IPv4 role-based ACL for a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||||||||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||||||||
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Security and click ACL. |
||||||||
|
Step 4 |
Hover your cursor over IPv4/IPv6, under IPv4, choose Role-based. |
||||||||
|
Step 5 |
Click Add. |
||||||||
|
Step 6 |
In the ACL Name field of the Create IPv4 Role-based ACL slide-in pane, enter a name for the IPv4 ACL. |
||||||||
|
Step 7 |
(Optional) Under Rules, configure the required rules.
|
||||||||
|
Step 8 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||||||||
|
Step 9 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||||
|
Step 10 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to create an IPv4 extended ACL for a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||||||||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||||||||
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Security and click ACL. |
||||||||
|
Step 4 |
Hover your cursor over IPv4/IPv6, under IPv4, choose Extended. |
||||||||
|
Step 5 |
Click Add. |
||||||||
|
Step 6 |
In the ACL Name field of the Create IPv4 Extended ACL slide-in pane, enter a name for the IPv4 extended ACL. |
||||||||
|
Step 7 |
(Optional) Under Rules, configure the required rules.
|
||||||||
|
Step 8 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||||||||
|
Step 9 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||||
|
Step 10 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to create an IPv6 ACL for a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||||||||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||||||||
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Security and click ACL. |
||||||||
|
Step 4 |
Hover your cursor over IPv4/IPv6, under IPv6, choose IPv6. |
||||||||
|
Step 5 |
Click Add. |
||||||||
|
Step 6 |
In the ACL Name field of the Create IPv6 ACL slide-in pane, enter a name for the IPv6 ACL. |
||||||||
|
Step 7 |
(Optional) Under Rules, configure the required rules.
|
||||||||
|
Step 8 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||||||||
|
Step 9 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||||
|
Step 10 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to create an IPv6 role-based ACL for a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||||||||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||||||||
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Security and click ACL. |
||||||||
|
Step 4 |
Hover your cursor over IPv4/IPv6, under IPv6, choose Role-based. |
||||||||
|
Step 5 |
Click Add. |
||||||||
|
Step 6 |
In the ACL Name field of the Create IPv6 Role-based ACL slide-in pane, enter a name for the IPv6 ACL. |
||||||||
|
Step 7 |
(Optional) Under Rules, configure the required rules.
|
||||||||
|
Step 8 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||||||||
|
Step 9 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||||
|
Step 10 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to create a MAC-based ACL for a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||||||||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||||||||
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Security and click ACL. |
||||||||
|
Step 4 |
Click the MAC-Based tab. |
||||||||
|
Step 5 |
Click Add. |
||||||||
|
Step 6 |
In the ACL Name field of the Create MAC-Based ACL slide-in pane, enter a name for the MAC-based ACL. |
||||||||
|
Step 7 |
(Optional) Under Rules, configure the required rules.
|
||||||||
|
Step 8 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||||||||
|
Step 9 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||||
|
Step 10 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to create a local EAP profile for a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||||||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||||||
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Security and click EAP. |
||||||
|
Step 4 |
In the Local EAP Profiles tab, click Add. |
||||||
|
Step 5 |
In the Local EAP Profile Name field of the Create Local EAP Profiles slide-in pane, enter a name for the local EAP profile. |
||||||
|
Step 6 |
(Optional) Check the required check boxes to allow the corresponding EAP methods. |
||||||
|
Step 7 |
(Optional) Based on the EAP method that you chose, complete these configurations.
|
||||||
|
Step 8 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||||||
|
Step 9 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||
|
Step 10 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to create an EAP-FAST profile for a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Security and click EAP. |
|
Step 4 |
Click the EAP-FAST Profiles tab. |
|
Step 5 |
Click Add. |
|
Step 6 |
In the Create EAP-FAST Profiles slide-in pane, enter data in these fields.
|
|
Step 7 |
Click Review and Provision. |
|
Step 8 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
|
Step 9 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to configure the advanced EAP profile for a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Security and click EAP. |
|
Step 4 |
Click the Advanced tab. |
|
Step 5 |
Enter data in these fields.
|
|
Step 6 |
(Optional) Check the EAP Max-Login Ignore Identity Response check box to limit the number of clients that can be connected to the device with the same username. |
|
Step 7 |
Enter data in these fields.
|
|
Step 8 |
Click Review and Provision. |
|
Step 9 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
|
Step 10 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to create a basic URL filter for a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||||||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||||||
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Security and click URL Filters. |
||||||
|
Step 4 |
In the Basic tab, click Add. |
||||||
|
Step 5 |
In the Url List Name field of the Create Basic URL Filter slide-in pane, enter a name for the URL filter. |
||||||
|
Step 6 |
From the Filter Type drop-down list, choose the authentication that is used for the URL filter. If you chose POST-AUTH, enter data in these fields.
|
||||||
|
Step 7 |
From the Action drop-down list, choose an action to indicate if the URLs in the URL filter are allowed or blocked. |
||||||
|
Step 8 |
(Optional) Under URLs, configure URL domain names for the URL filter.
|
||||||
|
Step 9 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||||||
|
Step 10 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||
|
Step 11 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Enhanced URL filters are the Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) ACLs that are applied to the wireless network.
Use this procedure to create an enhanced URL filter for a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||||||||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||||||||
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Security and click URL Filters. |
||||||||
|
Step 4 |
Click the Enhanced tab. |
||||||||
|
Step 5 |
Click Add. |
||||||||
|
Step 6 |
In the Url List Name field of the Create Enhanced URL Filter slide-in pane, enter a name for the enhanced URL filter. |
||||||||
|
Step 7 |
(Optional) Under Rules, configure rules for the URL filter.
|
||||||||
|
Step 8 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||||||||
|
Step 9 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||||
|
Step 10 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to create a guest user for a wireless controller and provision.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||||
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Security and click Guest User. |
||||
|
Step 4 |
Click Add. |
||||
|
Step 5 |
In the Create Guest User slide-in pane, under General, complete these configurations.
|
||||
|
Step 6 |
Under Lifetime, enter data in these fields.
|
||||
|
Step 7 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||||
|
Step 8 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||
|
Step 9 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to configure the web authentication parameters for a wireless controller and provision.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Security and click Web Auth. |
|
Step 4 |
In the Global tab, complete these configurations. |
|
Step 5 |
Click Review and Provision. |
|
Step 6 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
|
Step 7 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to create a web authentication profile for a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Security and click Web Auth. |
|
Step 4 |
Click the Web Auth Profiles tab. |
|
Step 5 |
Click Add. |
|
Step 6 |
In the General tab of the Create Web Auth slide-in pane, complete these configurations.
|
|
Step 7 |
Click Review and Provision. |
|
Step 8 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
|
Step 9 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to configure SGT Exchange Protocol (SXP) for Cisco TrustSec (CTS) for a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Security and click Trustsec. |
|
Step 4 |
(Optional) In the SXP tab, complete these configurations. |
|
Step 5 |
Click Review and Provision. |
|
Step 6 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
|
Step 7 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
If you enable the support for CTS SXP, in the Peer Connections table, you can optionally add, edit, or delete the peer connections.
To add a peer connection, click Add and complete these configurations.
Use this procedure to create a CTS SXP AP profile for a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||||||||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||||||||
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Security and click Trustsec. |
||||||||
|
Step 4 |
Click the AP tab. |
||||||||
|
Step 5 |
Click Add. |
||||||||
|
Step 6 |
In the Profile Name field of the Create SXP AP Profiles slide-in pane, enter a name for the profile. |
||||||||
|
Step 7 |
(Optional) Click the Status toggle button to enable the CTS SXP configuration. |
||||||||
|
Step 8 |
Enter data in these fields.
|
||||||||
|
Step 9 |
(Optional) Under CTS SXP Profile Connections, configure CTS SXP profile connections.
|
||||||||
|
Step 10 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||||||||
|
Step 11 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||||
|
Step 12 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to create a service template for a local policy for a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Security and click Local Policy. |
|
Step 4 |
In the Service Template tab, click Add. |
|
Step 5 |
Enter data in these fields of the Create Service Template slide-in pane.
|
|
Step 6 |
(Optional) From these drop-down lists, choose the required options.
|
|
Step 7 |
Click Review and Provision. |
|
Step 8 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
|
Step 9 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to create a policy map and map it to a service template for a local policy for a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||||||||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||||||||
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Security and click Local Policy. |
||||||||
|
Step 4 |
Click the Policy Map tab. |
||||||||
|
Step 5 |
Click Add. |
||||||||
|
Step 6 |
In the Policy Map Name field of the Create Policy Map slide-in pane, enter a name for the policy map. |
||||||||
|
Step 7 |
(Optional) Under Match Criteria List, configure the required match criteria list.
|
||||||||
|
Step 8 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||||||||
|
Step 9 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||||
|
Step 10 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to configure rogue policies to detect rogue APs for a wireless controller and provision them.
The default AP profile and these global rogue parameters are automatically configured for the high, low, or critical rogue detection security levels and you can't edit them:
Adhoc Rogue AP,
Auto Containment Level,
Detect and Report Adhoc Networks,
Expiration timeout for Rogue APs (seconds),
Valid client on Rogue AP,
Validate Rogue Clients Against AAA,
Validate Rogue APs Against AAA,
Rogue AP Expiration Timeout (sec),
Rogue Auto Contain Ad Hoc,
Rogue Init Timer (sec),
Rogue Polling Interval (sec), and
Using our SSID
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Security and click Wireless Protection Policies. |
|
Step 4 |
In the Rogue Policies tab, from the Rogue Detection Security Level drop-down list, choose a security level. |
|
Step 5 |
If you chose the Custom security level, complete these configurations. |
|
Step 6 |
In the Rogue Detection Client Number Threshold field, enter the threshold for rogue client per rogue AP SNMP trap. The valid range is from 0 to 256. The default value is 56. |
|
Step 7 |
Use the Syslog Notification check box to enable or disable the rogue event notifications through syslog. |
|
Step 8 |
In the AP Authentication Alarm Threshold field, enter the threshold for AP authentication alarm. The valid range is from 1 to 255. The default value is 22. |
|
Step 9 |
Click Review and Provision. |
|
Step 10 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
|
Step 11 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to create a rogue AP rule for a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||||||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||||||
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Security and click Wireless Protection Policies. |
||||||
|
Step 4 |
Click the Rogue AP Rules tab. |
||||||
|
Step 5 |
Click Add. |
||||||
|
Step 6 |
In the Rule Name field of the Create Rogue AP Rules slide-in pane, enter a name for the rogue AP rule. |
||||||
|
Step 7 |
In the Priority field, enter a number to indicate the priority of the rogue AP rule. A lower number indicates a higher priority. |
||||||
|
Step 8 |
From the Type drop-down list, choose a classification type. |
||||||
|
Step 9 |
Based on the classification type, complete these configurations.
|
||||||
|
Step 10 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||||||
|
Step 11 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||
|
Step 12 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to configure client exclusion policies for a wireless controller and provision.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Security and click Wireless Protection Policies. |
|
Step 4 |
Click the Client Exclusion Policies tab. |
|
Step 5 |
(Optional) Check the required check boxes to exclude clients for the corresponding events.
|
|
Step 6 |
Click Review and Provision. |
|
Step 7 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
|
Step 8 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
This section provides information about the per-device global radio configurations for a Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller.
Cisco CleanAir technology uses silicon-level intelligence to create a spectrum-aware, self-healing, and self-optimizing wireless network that mitigates the impact of wireless interference.
Use this procedure to configure the CleanAir parameters for a wireless controller and provision.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Global Radio Configurations and click CleanAir. |
||||||||||
|
Step 4 |
In the 6 GHz tab, complete these configurations. |
||||||||||
|
Step 5 |
In the 5 GHz tab, complete these configurations. |
||||||||||
|
Step 6 |
In the 2.4 GHz tab, complete these configurations. |
||||||||||
|
Step 7 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||||||||||
|
Step 8 |
If the wireless controller manages APs that don't meet the license requirements, Catalyst Center displays a dialog box with the details. In the dialog box, choose the required option.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 9 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||||||
|
Step 10 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to configure the high throughput parameters for a wireless controller and provision the configuration.
 Important |
Configuring high throughput on operational bands results in loss of client connectivity. |
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Global Radio Configurations and click High Throughput. |
||||||||||
|
Step 4 |
In the 6 GHz tab, configure the high throughput parameters for the 6-GHz band. |
||||||||||
|
Step 5 |
In the 5 GHz tab, configure the high throughput parameters for the 5-GHz band. |
||||||||||
|
Step 6 |
In the 2.4 GHz tab, configure the high throughput parameters for the 2.4-GHz band. |
||||||||||
|
Step 7 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||||||||||
|
Step 8 |
If the wireless controller manages APs that don't meet the license requirements, Catalyst Center displays a dialog box with the details. In the dialog box, choose the required option.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 9 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||||||
|
Step 10 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to configure the video and voice media parameters for a wireless controller and provision the configuration.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Global Radio Configurations and click Media Parameters. |
||||||||||
|
Step 4 |
Hover your cursor over 6 GHz, 5 GHz, or 2.4 GHz, click Media, and configure the required parameters. |
||||||||||
|
Step 5 |
Hover your cursor over 6 GHz, 5 GHz, or 2.4 GHz, click Voice, and configure the required voice parameters. |
||||||||||
|
Step 6 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||||||||||
|
Step 7 |
If the wireless controller manages APs that don't meet the license requirements, Catalyst Center displays a dialog box with the details. In the dialog box, choose the required option.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 8 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||||||
|
Step 9 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to configure the network parameters for a wireless controller and provision the configuration.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Global Radio Configurations and click Network Parameters. |
||||||||||
|
Step 4 |
In the 6 GHz tab, configure the required parameters for the 6-GHz band. |
||||||||||
|
Step 5 |
In the 5 GHz tab, configure the required parameters for the 5-GHz band. |
||||||||||
|
Step 6 |
In the 2.4 GHz tab, configure the required parameters for the 2.4-GHz band. |
||||||||||
|
Step 7 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||||||||||
|
Step 8 |
If the wireless controller manages APs that don't meet the license requirements, Catalyst Center displays a dialog box with the details. In the dialog box, choose the required option.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 9 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||||||
|
Step 10 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to configure the global radio parameters for a wireless controller and provision the configuration.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Global Radio Configurations and click Global Parameters. |
||||||||||
|
Step 4 |
In the 6 GHz tab, configure the required parameters for the 6-GHz band. |
||||||||||
|
Step 5 |
In the 5 GHz tab, configure the required parameters for the 5-GHz band. |
||||||||||
|
Step 6 |
In the 2.4 GHz tab, configure the required parameters for the 2.4-GHz band. |
||||||||||
|
Step 7 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||||||||||
|
Step 8 |
If the wireless controller manages APs that don't meet the license requirements, Catalyst Center displays a dialog box with the details. In the dialog box, choose the required option.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 9 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||||||
|
Step 10 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to configure the Radio Resource Management (RRM) parameters on the 6-GHz band for a wireless controller and provision the configuration.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Global Radio Configurations and click RRM. |
||||||||||
|
Step 4 |
Hover your cursor over 6 GHz, choose General, and complete these configurations. |
||||||||||
|
Step 5 |
Hover your cursor over 6 GHz, choose Coverage, and complete these configurations. |
||||||||||
|
Step 6 |
Hover your cursor over 6 GHz, choose DCA, and complete these configurations. |
||||||||||
|
Step 7 |
Hover your cursor over 6 GHz, choose TPC, and complete these configurations. |
||||||||||
|
Step 8 |
Hover your cursor over 6 GHz, choose RF Grouping, and complete these configurations. |
||||||||||
|
Step 9 |
Hover your cursor over 6 GHz, choose Spatial Reuse, and complete these configurations. |
||||||||||
|
Step 10 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||||||||||
|
Step 11 |
If the wireless controller manages APs that don't meet the license requirements, Catalyst Center displays a dialog box with the details. In the dialog box, choose the required option.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 12 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||||||
|
Step 13 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to configure the RRM parameters on the 5-GHz band for a wireless controller and provision the configuration.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Global Radio Configurations and click RRM. |
||||||||||
|
Step 4 |
Hover your cursor over 5 GHz, choose General, and complete these configurations. |
||||||||||
|
Step 5 |
Hover your cursor over 5 GHz, choose Coverage, and complete these configurations. |
||||||||||
|
Step 6 |
Hover your cursor over 5 GHz, choose DCA, and complete these configurations. |
||||||||||
|
Step 7 |
Hover your cursor over 5 GHz, choose TPC, and complete these configurations. |
||||||||||
|
Step 8 |
Hover your cursor over 5 GHz, choose RF Grouping, and complete these configurations. |
||||||||||
|
Step 9 |
Hover your cursor over 5 GHz, choose Spatial Reuse, and complete these configurations. |
||||||||||
|
Step 10 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||||||||||
|
Step 11 |
If the wireless controller manages APs that don't meet the license requirements, Catalyst Center displays a dialog box with the details. In the dialog box, choose the required option.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 12 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||||||
|
Step 13 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to configure the RRM parameters on the 2.4-GHz band for a wireless controller and provision the configuration.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Global Radio Configurations and click RRM. |
||||||||||
|
Step 4 |
Hover your cursor over 2.4 GHz, choose General, and complete these configurations. |
||||||||||
|
Step 5 |
Hover your cursor over 2.4 GHz, choose Coverage and complete these configurations. |
||||||||||
|
Step 6 |
Hover your cursor over 2.4 GHz, choose DCA, and complete these configurations. |
||||||||||
|
Step 7 |
Hover your cursor over 2.4 GHz, choose TPC, and complete these configurations. |
||||||||||
|
Step 8 |
Hover your cursor over 2.4 GHz, choose RF Grouping, and complete these configurations. |
||||||||||
|
Step 9 |
Hover your cursor over 2.4 GHz, choose Spatial Reuse and complete these configurations. |
||||||||||
|
Step 10 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||||||||||
|
Step 11 |
If the wireless controller manages APs that don't meet the license requirements, Catalyst Center displays a dialog box with the details. In the dialog box, choose the required option.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 12 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||||||
|
Step 13 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to configure the RRM FRA parameters for a wireless controller and provision the configuration.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Global Radio Configurations and click RRM. |
||||||||||
|
Step 4 |
Click the FRA tab. |
||||||||||
|
Step 5 |
Under 5/6 GHz Flexible Radio Assignment, complete these configurations.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 6 |
Under 2.4/5 GHz Flexible Radio Assignment, complete these configurations. |
||||||||||
|
Step 7 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||||||||||
|
Step 8 |
If the wireless controller manages APs that don't meet the license requirements, Catalyst Center displays a dialog box with the details. In the dialog box, choose the required option.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 9 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||||||
|
Step 10 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
This section provides information about the per-device global wireless configurations for a Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller.
Use this procedure to configure the Air Time Fairness (ATF) parameters for a wireless controller.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Global Wireless Configurations and click Airtime Fairness. |
||||||||||
|
Step 4 |
Click either the 5 GHz or 2.4 GHz tab and complete these configurations. |
||||||||||
|
Step 5 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||||||||||
|
Step 6 |
If the wireless controller manages APs that don't meet the license requirements, Catalyst Center displays a dialog box with the details. In the dialog box, choose the required option.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 7 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||||||
|
Step 8 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to create an Air Time Fairness (ATF) policy for a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Global Wireless Configurations and click Airtime Fairness. |
||||||||||
|
Step 4 |
Click the Policy tab. |
||||||||||
|
Step 5 |
Click Add. |
||||||||||
|
Step 6 |
In the ATF Policy Name field of the Create ATF Policy slide-in pane, enter a unique name for the ATF policy. |
||||||||||
|
Step 7 |
In the ID field, enter a unique ID for the ATF policy. The valid range is from 0 to 511. |
||||||||||
|
Step 8 |
In the Weight field, enter a policy weight for the ATF policy. The valid range is from 5 to 100. The default value is 10. |
||||||||||
|
Step 9 |
(Optional) Check the Client Sharing check box to enable fair client sharing for an ATF policy. |
||||||||||
|
Step 10 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||||||||||
|
Step 11 |
If the wireless controller manages APs that don't meet the license requirements, Catalyst Center displays a dialog box with the details. In the dialog box, choose the required option.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 12 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||||||
|
Step 13 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to create a guest LAN profile for a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Global Wireless Configurations and click Guest LAN. |
||||||||||
|
Step 4 |
In the Guest LAN Profiles tab, click Add. |
||||||||||
|
Step 5 |
In the General tab of the Create Guest LAN Profile slide-in pane, complete these configurations. |
||||||||||
|
Step 6 |
(Optional) Click the Security tab and complete these configurations. |
||||||||||
|
Step 7 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||||||||||
|
Step 8 |
If the wireless controller manages APs that don't meet the license requirements, Catalyst Center displays a dialog box with the details. In the dialog box, choose the required option.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 9 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||||||
|
Step 10 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to create a guest LAN map for a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Global Wireless Configurations and click Guest LAN. |
||||||||||
|
Step 4 |
Click the Guest LAN Map tab. |
||||||||||
|
Step 5 |
Click Add. |
||||||||||
|
Step 6 |
In the Map Name field of the Create Guest LAN Map slide-in pane, enter a unique name for the guest LAN map. |
||||||||||
|
Step 7 |
(Optional) Under Guest LAN - Policy Map, configure guest LAN and policy map profile.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 8 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||||||||||
|
Step 9 |
If the wireless controller manages APs that don't meet the license requirements, Catalyst Center displays a dialog box with the details. In the dialog box, choose the required option.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 10 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||||||
|
Step 11 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to configure the media stream parameters for a wireless controller and provision the configuration.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Global Wireless Configurations and click Media Stream. |
||||||||||
|
Step 4 |
In the General tab, use the Enable Multicast Direct toggle button to enable or disable the multicast-direct configuration. |
||||||||||
|
Step 5 |
(Optional) Under Session Message Configuration, complete these configurations. |
||||||||||
|
Step 6 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||||||||||
|
Step 7 |
If the wireless controller manages APs that don't meet the license requirements, Catalyst Center displays a dialog box with the details. In the dialog box, choose the required option.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 8 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||||||
|
Step 9 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to create a media stream profile for a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Global Wireless Configurations and click Media Stream. |
||||||||||
|
Step 4 |
Click the Streams tab. |
||||||||||
|
Step 5 |
Click Add. |
||||||||||
|
Step 6 |
In the Media Stream Name field of the Create Media Stream Profile slide-in pane, enter a name for the media stream group. |
||||||||||
|
Step 7 |
In the Maximum Expected Bandwidth (Kbps), enter the expected bandwidth for the media stream. The valid range is from 1 to 35000. The default value is 1000. |
||||||||||
|
Step 8 |
Under Multicast Destination, enter data in these fields.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 9 |
Under Resource Reservation Control (RRC) Parameters, from the drop-down lists, complete these configurations. |
||||||||||
|
Step 10 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||||||||||
|
Step 11 |
If the wireless controller manages APs that don't meet the license requirements, Catalyst Center displays a dialog box with the details. In the dialog box, choose the required option.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 12 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||||||
|
Step 13 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to configure the global wireless parameters for a wireless controller and provision the configuration.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Global Wireless Configurations and click Advanced. |
||||||||||
|
Step 4 |
In the Global tab, enter data in these fields.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 5 |
Check the required check boxes to enable the corresponding configurations.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 6 |
Under Assisted Roaming, enter data in these fields.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 7 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||||||||||
|
Step 8 |
If the wireless controller manages APs that don't meet the license requirements, Catalyst Center displays a dialog box with the details. In the dialog box, choose the required option.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 9 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||||||
|
Step 10 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to configure the load-balancing parameters on the 5-GHz and 2.4-GHz bands for a wireless controller and provision the configuration.
For the 6-GHz band, global parameters like Aggressive Load Balancing Window and Aggressive Load Balancing Denial Count are configured in the RF profile.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Global Wireless Configurations and click Advanced. |
||||||||||
|
Step 4 |
Click the Load Balancing tab. |
||||||||||
|
Step 5 |
Under 5 GHz and 2.4 GHz, enter data in these fields.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 6 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||||||||||
|
Step 7 |
If the wireless controller manages APs that don't meet the license requirements, Catalyst Center displays a dialog box with the details. In the dialog box, choose the required option.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 8 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||||||
|
Step 9 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to configure the band selection parameters per WLAN for a wireless controller and provision the configuration.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Global Wireless Configurations and click Advanced. |
||||||||||
|
Step 4 |
Click the Band Select tab. |
||||||||||
|
Step 5 |
(Optional) Enter data in these fields.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 6 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||||||||||
|
Step 7 |
If the wireless controller manages APs that don't meet the license requirements, Catalyst Center displays a dialog box with the details. In the dialog box, choose the required option.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 8 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||||||
|
Step 9 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to configure the optimized roaming parameters for a wireless controller and provision the configuration.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Global Wireless Configurations and click Advanced. |
||||||||||
|
Step 4 |
Click the Optimized Roaming tab. |
||||||||||
|
Step 5 |
Under 6 Ghz, 5 Ghz, and 2.4 Ghz, complete these configurations. |
||||||||||
|
Step 6 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||||||||||
|
Step 7 |
If the wireless controller manages APs that don't meet the license requirements, Catalyst Center displays a dialog box with the details. In the dialog box, choose the required option.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 8 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||||||
|
Step 9 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to configure the high-density parameters on the 5-GHz and 2.4-GHz bands for a wireless controller and provision the configuration.
For the 6-GHz band, the global high-density parameters like Rx SOP Threshold and Multicast Data Rate are configured in the RF profile.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Global Wireless Configurations and click Advanced. |
||||||||||
|
Step 4 |
Click the High Density tab. |
||||||||||
|
Step 5 |
Under Rx SOP Threshold, from these drop-down lists, choose the required options.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 6 |
Under Multicast Data Rate, from these drop-down lists, choose the required options.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 7 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||||||||||
|
Step 8 |
If the wireless controller manages APs that don't meet the license requirements, Catalyst Center displays a dialog box with the details. In the dialog box, choose the required option.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 9 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||||||
|
Step 10 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to add a preferred call for a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Global Wireless Configurations and click Advanced. |
||||||||||
|
Step 4 |
Click the Preferred Calls tab. |
||||||||||
|
Step 5 |
Click Add. |
||||||||||
|
Step 6 |
In the Call Index field of the Create Preferred Calls slide-in pane, enter the SIP index for the call. The valid range is from 1 to 6. |
||||||||||
|
Step 7 |
In the Call Number field, enter the SIP preferred call number. |
||||||||||
|
Step 8 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||||||||||
|
Step 9 |
If the wireless controller manages APs that don't meet the license requirements, Catalyst Center displays a dialog box with the details. In the dialog box, choose the required option.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 10 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||||||
|
Step 11 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to configure the radio frequency identification (RFID) parameters for a wireless controller and provision the configuration.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Global Wireless Configurations and click Advanced. |
||||||||||
|
Step 4 |
Click the RFID tab. |
||||||||||
|
Step 5 |
Use the RFID State toggle button to enable or disable the RFID tag tracking. |
||||||||||
|
Step 6 |
In the RFID Timeout (sec) field, enter the timeout value in seconds to clean up the stale RFID entries. The valid range is from 60 to 7200. |
||||||||||
|
Step 7 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||||||||||
|
Step 8 |
If the wireless controller manages APs that don't meet the license requirements, Catalyst Center displays a dialog box with the details. In the dialog box, choose the required option.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 9 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||||||
|
Step 10 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to configure the cellular steering parameters for a wireless controller and provision the configuration.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Global Wireless Configurations and click Advanced. |
||||||||||
|
Step 4 |
Click the Cellular Steering tab. |
||||||||||
|
Step 5 |
Enter the RSSI threshold value in dBm to trigger the Wi-Fi to cellular steering for the
|
||||||||||
|
Step 6 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||||||||||
|
Step 7 |
If the wireless controller manages APs that don't meet the license requirements, Catalyst Center displays a dialog box with the details. In the dialog box, choose the required option.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 8 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||||||
|
Step 9 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to configure the 6-GHz client steering parameters per WLAN for a wireless controller and provision the configuration.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Global Wireless Configurations and click Advanced. |
||||||||||
|
Step 4 |
Click the 6 GHz Client Steering tab. |
||||||||||
|
Step 5 |
(Optional) Enter data in these fields.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 6 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||||||||||
|
Step 7 |
If the wireless controller manages APs that don't meet the license requirements, Catalyst Center displays a dialog box with the details. In the dialog box, choose the required option.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 8 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||||||
|
Step 9 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to configure the global wireless multicast parameters for a wireless controller and provision the configuration.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Global Wireless Configurations and click Multicast. |
|
Step 4 |
In the General tab, use the Global Wireless Multicast toggle button to enable or disable global wireless multicast. If you enable global wireless multicast, you can optionally check the Wireless mDNS Bridging check box to enable mDNS bridging. |
|
Step 5 |
From the AP CAPWAP Multicast drop-down, choose a delivery mechanism for the multicast. If you chose the Multicast option, you can optionally enter data in these fields.
|
|
Step 6 |
Click Review and Provision. |
|
Step 7 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
|
Step 8 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to configure Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) snooping for a wireless controller and provision the configuration.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Global Wireless Configurations and click Multicast. |
|
Step 4 |
Click the IGMP Snooping tab. |
|
Step 5 |
(Optional) Check the IGMP Snooping check box to enable the IGMP snooping for VLANs. If you enable IGMP snooping, in the Last Member Query Interval (msec) field, enter the last member query interval in milliseconds. The valid range is from 100 to 32767. |
|
Step 6 |
Click Review and Provision. |
|
Step 7 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
|
Step 8 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to configure global Multicast Listener Discovery (MLD) snooping for a wireless controller and provision the configuration.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Global Wireless Configurations and click Multicast. |
|
Step 4 |
Click the MLD Snooping tab. |
|
Step 5 |
(Optional) Check the Snooping check box to enable global MLD snooping for VLANs. If you enable MLD snooping, in the MLD Query Interval (msec) field, enter the last listener query interval in milliseconds. The valid range is from 100 to 32768. |
|
Step 6 |
Click Review and Provision. |
|
Step 7 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
|
Step 8 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to configure the location parameters for a wireless controller and provision the configuration.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Global Wireless Configurations and click Location. |
|
Step 4 |
From the Algorithm drop-down list, choose an algorithm used for averaging the RSSI and SNR values.
|
|
Step 5 |
Enter data in these fields.
|
|
Step 6 |
From these drop-down lists, choose the required options.
|
|
Step 7 |
Click Review and Provision. |
|
Step 8 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
|
Step 9 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Excluded clients can be used for troubleshooting or security purposes. By excluding the required clients, you can ensure that certain devices aren’t able to access the network.
Use this procedure to add an excluded client for a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Global Wireless Configurations and click Excluded Clients. |
|
Step 4 |
Click Add. |
|
Step 5 |
In the Create Client Exclusion slide-in pane, enter data in these fields.
|
|
Step 6 |
Click Review and Provision. |
|
Step 7 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
|
Step 8 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to create a QoS policy for a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Global Wireless Configurations and click QoS. |
||||||||||
|
Step 4 |
Click Add. |
||||||||||
|
Step 5 |
In the Policy Name field of the Create QoS Policy slide-in pane, enter a name for the QoS policy. |
||||||||||
|
Step 6 |
(Optional) In the Description field, enter a description. |
||||||||||
|
Step 7 |
Under Class Default, complete these configurations. |
||||||||||
|
Step 8 |
(Optional) Under Class Maps, configure class maps. |
||||||||||
|
Step 9 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||||||||||
|
Step 10 |
If the wireless controller manages APs that don't meet the license requirements, Catalyst Center displays a dialog box with the details. In the dialog box, choose the required option.
|
||||||||||
|
Step 11 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||||||
|
Step 12 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to configure country codes for a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||||||||||||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||||||||||||
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Global Wireless Configurations and click Country. |
||||||||||||
|
Step 4 |
Configure the country codes. Use these options to manage country codes:
|
||||||||||||
|
Step 5 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||||||||||||
|
Step 6 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||||||||
|
Step 7 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
This section provides information about the per-device mDNS configurations for a Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller.
Use this procedure to configure a multicast Domain Name System (mDNS) gateway for a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, click MDNS. |
|
Step 4 |
In the Global tab, use the mDNS Gateway toggle button to enable or disable the mDNS gateway. |
|
Step 5 |
If you enable the mDNS gateway, complete these configurations.
|
|
Step 6 |
Click Review and Provision. |
|
Step 7 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
|
Step 8 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to create an mDNS service definition for a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||||||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||||||
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, click MDNS. |
||||||
|
Step 4 |
Hover your cursor over Service Policy and choose Service Definition. |
||||||
|
Step 5 |
Click Add. |
||||||
|
Step 6 |
In the Service Definition Name field of the Create Service Definition slide-in pane, enter a name for the service definition. |
||||||
|
Step 7 |
(Optional) In the Description field, enter a description. |
||||||
|
Step 8 |
Under Service Types, configure service types.
|
||||||
|
Step 9 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||||||
|
Step 10 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||
|
Step 11 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
You can create mDNS service lists for the ingress and egress directions. Use this procedure to create an mDNS service list for a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||||||||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||||||||
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, click MDNS. |
||||||||
|
Step 4 |
Hover your cursor over Service Policy and choose Service List. |
||||||||
|
Step 5 |
Hover your cursor over Add and choose one of the directions.
|
||||||||
|
Step 6 |
In the Service List Name field of the Create Service List slide-in pane, enter a name for the service list. |
||||||||
|
Step 7 |
(Optional) Click the Assign All Services toggle button to assign all services to the service list.
|
||||||||
|
Step 8 |
(Optional) If the Assign All Services toggle button isn’t enabled, under Assigned Services, configure the services.
|
||||||||
|
Step 9 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||||||||
|
Step 10 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||||
|
Step 11 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to create an mDNS service policy for a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, click MDNS. |
|
Step 4 |
Hover your cursor over Service Policy and choose Service Policy. |
|
Step 5 |
Click Add. |
|
Step 6 |
In the Service Policy Name field of the Create Service Policy slide-in pane, enter a name for the service policy. |
|
Step 7 |
(Optional) From these drop-down lists, choose the required options.
|
|
Step 8 |
If you chose the regex option for location-based filtering using a regular-expression string, complete these configurations.
|
|
Step 9 |
Click Review and Provision. |
|
Step 10 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
|
Step 11 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to create an mDNS wired filter for a wireless controller and provision.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||||||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||||||
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, click MDNS. |
||||||
|
Step 4 |
Hover your cursor over Service Policy and choose Wired Filter. |
||||||
|
Step 5 |
Click Add. |
||||||
|
Step 6 |
In the Wired Filter Name field of the Create Wired Filter slide-in pane, enter a name for the wired filter. |
||||||
|
Step 7 |
In the VLAN List field, enter the list of VLAN IDs. The valid range for VLAN IDs is from 1 to 4094. You can enter
|
||||||
|
Step 8 |
Under MAC Address, configure the MAC addresses.
|
||||||
|
Step 9 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||||||
|
Step 10 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||
|
Step 11 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to create an mDNS flex profile for a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, click MDNS. |
|
Step 4 |
Click the mDNS Flex Profile tab. |
|
Step 5 |
Click Add. |
|
Step 6 |
In the mDNS Flex Profile Name field of the Create mDNS Flex Profile slide-in pane, enter a name for the mDNS flex profile. |
|
Step 7 |
(Optional) Enter data in these fields.
|
|
Step 8 |
From the Wired Service Policy drop-down list, choose a service policy. To create a service policy, see Create an mDNS service policy for a Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller. |
|
Step 9 |
Click Review and Provision. |
|
Step 10 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
|
Step 11 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
This section provides information about the per-device Ethernet over GRE (EoGRE) configurations for a Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller.
Use this procedure to configure the EoGRE global parameters for a wireless controller and provision the configuration.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, click EoGRE. |
|
Step 4 |
In the Global tab, enter data in these fields.
|
|
Step 5 |
From the Interface Name drop-down list, choose an interface. To manage physical interfaces, Configure an Ethernet port for a Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller To create an SVI profile, see Create an SVI profile for a Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller. |
|
Step 6 |
Click Review and Provision. |
|
Step 7 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
|
Step 8 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to create an EoGRE tunnel gateway for a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||||||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||||||
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, click EoGRE. |
||||||
|
Step 4 |
Click the Gateways tab. |
||||||
|
Step 5 |
Click Add. |
||||||
|
Step 6 |
In the Tunnel ID field of the Create Gateway slide-in pane, enter the tunnel ID. |
||||||
|
Step 7 |
Under Destination IP Address, choose an IP address option. |
||||||
|
Step 8 |
(Optional) From the Source Interface drop-down list, choose an interface. To manage physical interfaces, see Configure an Ethernet port for a Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller. To create an SVI profile, see Create an SVI profile for a Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller. |
||||||
|
Step 9 |
(Optional) Based on the destination IP address option that you chose, complete these configurations.
|
||||||
|
Step 10 |
(Optional) Click the AAA Proxy toggle button to enable AAA proxy and complete these configurations.
|
||||||
|
Step 11 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||||||
|
Step 12 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||
|
Step 13 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to create an EoGRE tunnel domain for a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, click EoGRE. |
|
Step 4 |
Click the Domains tab. |
|
Step 5 |
Click Add. |
|
Step 6 |
In the Domain Name field of the Create Domain slide-in pane, enter a name for the tunnel domain. |
|
Step 7 |
(Optional) Click the Status toggle button to enable the tunnel domain. |
|
Step 8 |
Choose a primary and secondary tunnel gateway from the corresponding drop-down lists. |
|
Step 9 |
(Optional) Check the Revertive Redundancy check box to enable the revertive redundancy model. |
|
Step 10 |
Click Review and Provision. |
|
Step 11 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
|
Step 12 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to create an EoGRE wireless tunnel profile for a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||||||||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||||||||
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, click EoGRE. |
||||||||
|
Step 4 |
Click the Tunnel Profiles tab. |
||||||||
|
Step 5 |
Click Add. |
||||||||
|
Step 6 |
In the General tab of the Create Tunnel Profile slide-in pane, complete these configurations. |
||||||||
|
Step 7 |
(Optional) Click the Rules tab and configure the required rules.
|
||||||||
|
Step 8 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||||||||
|
Step 9 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||||
|
Step 10 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
This section provides information about the per-device Layer 2 configurations for a Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller.
Use this procedure to create a Switched VLAN Interface (SVI) profile for a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Layer 2 and click VLAN. |
|
Step 4 |
In the SVI tab, click Add. |
|
Step 5 |
In the General tab of the Create SVI slide-in pane, complete these configurations. |
|
Step 6 |
(Optional) Click the Advanced tab and complete these configurations. |
|
Step 7 |
Click Review and Provision. |
|
Step 8 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
|
Step 9 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to create a VLAN profile for a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Layer 2 and click VLAN. |
|
Step 4 |
Click the VLAN tab. |
|
Step 5 |
Click Add. |
|
Step 6 |
In the VLAN ID field of the Create VLAN slide-in pane, enter a VLAN ID. The valid range is from 1 to 4094. |
|
Step 7 |
In the Vlan Name field, enter a VLAN name. |
|
Step 8 |
From the State drop-down list, choose an operational state for the VLAN. |
|
Step 9 |
Click Review and Provision. |
|
Step 10 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
|
Step 11 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to create a VLAN group profile for a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Layer 2 and click VLAN. |
|
Step 4 |
Click the VLAN Group tab. |
|
Step 5 |
Click Add. |
|
Step 6 |
In the VLAN Group Name field of the Create VLAN Group slide-in pane, enter a VLAN group name. |
|
Step 7 |
In the VLAN List field, enter a value for the VLAN list. You can enter either
|
|
Step 8 |
Click Review and Provision. |
|
Step 9 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
|
Step 10 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to configure an Ethernet port for a wireless controller and provision the configuration.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Layer 2 and click Interfaces. |
|
Step 4 |
In the Ethernet tab, click the radio button next to the Ethernet port that you want to configure. |
|
Step 5 |
Hover your cursor over Actions and choose Edit. |
|
Step 6 |
(Optional) In the General tab of the Edit Ethernet Ports slide-in pane, in the Description field, enter a description for the port. |
|
Step 7 |
(Optional) In the Advanced tab, choose the inbound and outbound IPv4 and IPv6 ACLs from the corresponding drop-down lists. To create an IPv4 ACL, see Create an IPv4 ACL for a Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller. To create an IPv6 ACL, see Create an IPv6 ACL for a Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller. |
|
Step 8 |
Click Review and Provision. |
|
Step 9 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
|
Step 10 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
The wireless management interface is used for all communications between the wireless controller and APs. A wireless controller has a single wireless management interface.
Use this procedure to create the wireless management interface for a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Layer 2 and click Interfaces. |
|
Step 4 |
Click the Wireless tab. |
|
Step 5 |
Click Add. |
|
Step 6 |
In the Create Wireless Management Interface slide-in pane, under General, complete these configurations.
|
|
Step 7 |
Click Review and Provision. |
|
Step 8 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
|
Step 9 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to configure discovery protocols for a wireless controller and provision the configuration.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Layer 2 and click Discovery Protocols. |
|
Step 4 |
Under CDP, complete these configurations. |
|
Step 5 |
Under LLDP, complete these configurations. |
|
Step 6 |
Click Review and Provision. |
|
Step 7 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
|
Step 8 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
This section provides information about the per-device network settings configurations for a Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller.
Use this procedure to create an IPv4 DHCP pool for a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Network Settings and click DHCP Pools. |
|
Step 4 |
Hover your cursor over DHCP Pools and choose IPv4. |
|
Step 5 |
Click Add. |
|
Step 6 |
In the General tab of the Create DHCP Pools slide-in pane, complete these configurations. |
|
Step 7 |
(Optional) In the Advanced tab, complete these configurations. |
|
Step 8 |
Click Review and Provision. |
|
Step 9 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
|
Step 10 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to create an IPv6 DHCP pool for a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||||||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||||||
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Network Settings and click DHCP Pools. |
||||||
|
Step 4 |
Hover your cursor over DHCP Pools and choose IPv6. |
||||||
|
Step 5 |
Click Add. |
||||||
|
Step 6 |
In the DHCP Pool Name field of the Create DHCP Pools slide-in pane, enter a name for the DHCP pool. |
||||||
|
Step 7 |
(Optional) Under Domain Names, configure domain names.
|
||||||
|
Step 8 |
Under DNS Server, configure DNS servers.
|
||||||
|
Step 9 |
Under IPV6 Address Allocation, configure IPv6 address allocation.
|
||||||
|
Step 10 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||||||
|
Step 11 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||
|
Step 12 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to configure HTTP and HTTPS for a wireless controller and provision the configuration.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Network Settings and click HTTP/HTTPS. |
||
|
Step 4 |
Check the required check boxes to enable the corresponding configurations.
|
||
|
Step 5 |
From the Authentication drop-down list, choose an authentication method. If you chose aaa, from these drop-down lists, you can optionally choose the required options.
|
||
|
Step 6 |
Under HTTP Trustpoint, use the Enable TrustPoint toggle button to enable or disable the HTTP trustpoint. If you enable HTTP trustpoint, from the Secure Trustpoint drop-down list, choose a secure server certificate trustpoint.
|
||
|
Step 7 |
Under Timeout Policy, in the Session Idle Timeout(secs) field, enter the HTTP server session idle timeout in seconds. The valid range is from 180 to 1200. |
||
|
Step 8 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||
|
Step 9 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||
|
Step 10 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to configure the general SNMP parameters for a wireless controller and provision the configuration.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Network Settings and click SNMP. |
|
Step 4 |
In the General tab, enter data in these fields.
|
|
Step 5 |
Click Review and Provision. |
|
Step 6 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
|
Step 7 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to configure SNMP wireless traps for a wireless controller and provision the configuration.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Network Settings and click SNMP. |
|
Step 4 |
Click the Wireless Traps tab. |
|
Step 5 |
Use the Enable toggle button under each area to enable or disable the corresponding traps. |
|
Step 6 |
Click Review and Provision. |
|
Step 7 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
|
Step 8 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
An SNMP community string is a password that is used to authenticate access to the managed devices. It can also be used for device discovery.
 Note |
If an SNMP community string used for device discovery is deleted, the device enters into an Unmanaged state on Catalyst Center. |
Use this procedure to add an SNMP community string for a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Network Settings and click SNMP. |
|
Step 4 |
Click the Community Strings tab. |
|
Step 5 |
Click Add. |
|
Step 6 |
In the Community Name field of the Add Community String slide-in pane, enter the SNMP community string. |
|
Step 7 |
From the Access Mode drop-down list, choose a mode in which the SNMP management station can retrieve information from the device. |
|
Step 8 |
Click Review and Provision. |
|
Step 9 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
|
Step 10 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to create an SNMP host for a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Network Settings and click SNMP. |
|
Step 4 |
Click the Hosts tab. |
|
Step 5 |
Click Add. |
|
Step 6 |
In the IP Address field of the Create SNMP Host slide-in pane, enter the IP address of the host. |
|
Step 7 |
From the Version drop-down list, choose an SNMP version to send the trap. |
|
Step 8 |
From the Community String drop-down list, choose an SNMP community string. To add a community string, see Add an SNMP community string for a Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller. |
|
Step 9 |
(Optional) In the UDP Port field, enter the number for the SNMP destination port. The valid range is from 0 to 65535. The default value is 162. |
|
Step 10 |
From the Type drop-down list, choose the type of SNMP notifications.
|
|
Step 11 |
Click Review and Provision. |
|
Step 12 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
|
Step 13 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to create a Network Time Protocol (NTP) server profile for a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
||||||
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
||||||
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Network Settings and click NTP. |
||||||
|
Step 4 |
In the NTP tab, click Add. |
||||||
|
Step 5 |
In the Host Name field of the Create NTP Serve Profile slide-in pane, enter the host name. You can enter an IPv4 address, IPv6 address, or a Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN). |
||||||
|
Step 6 |
(Optional) Check the Prefer check box to use this NTP server profile by default. |
||||||
|
Step 7 |
From the Source Address drop-down list, choose an interface that is used to communicate with the NTP server.
|
||||||
|
Step 8 |
(Optional) Check the Enable Authentication check box to enable authentication against the NTP server. If you check this check box, from the Key drop-down list, choose a key index that is used for authentication. To create an authentication key profile, see Create an authentication key profile for a Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller. |
||||||
|
Step 9 |
Click Review and Provision. |
||||||
|
Step 10 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
||||||
|
Step 11 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Use this procedure to create an authentication key profile to authenticate against an NTP server for a wireless controller and provision it.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Network Settings and click NTP. |
|
Step 4 |
Click the Authentication Keys tab. |
|
Step 5 |
Click Add. |
|
Step 6 |
In the Authentication Key Number field of the Create Authentication Key Profile slide-in pane, enter an authentication key number. The valid range is from 1 to 4294967295. |
|
Step 7 |
In the Authentication Key field, enter an authentication key for MD5 authentication. |
|
Step 8 |
Click Review and Provision. |
|
Step 9 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
|
Step 10 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
This section provides information about the per-device Layer 3 configurations for a Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller.
Use this procedure to create a static route for a wireless controller and provision it.
 Note |
Catalyst Center doesn't support Virtual Routing and Forwarding (VRF) for static routes. |
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Layer 3 and click Routing. |
|
Step 4 |
In the Static tab, hover your cursor over Add and choose the required static route option. |
|
Step 5 |
If you chose IPv4, in the Create Static Route slide-in pane, complete these configurations. |
|
Step 6 |
If you chose IPv6, in the Create Static Route slide-in pane, complete these configurations. |
|
Step 7 |
Click Review and Provision. |
|
Step 8 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
|
Step 9 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
This section provides information about the per-device administrative configurations for a Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller.
Use this procedure to configure the device administration settings for a wireless controller and provision the configuration.
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to the required wireless controller in the inventory.
|
|
Step 2 |
Open the device details window for the required wireless controller.
|
|
Step 3 |
In the left pane of the device details window, under CONFIGURATION, expand Administration and click Device. |
|
Step 4 |
In the Host Name field of the General tab, enter the host name. The host name can contain uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, hyphens (-), underscores (_), and periods (.). The host name must not contain only numbers. |
|
Step 5 |
Click Review and Provision. |
|
Step 6 |
Schedule the task for deployment. Depending on Visibility and Control of Configurations settings, you can either:
|
|
Step 7 |
On the Tasks window, monitor the task deployment. |
Inter-Release Controller Mobility (IRCM) supports seamless mobility and wireless services across different Cisco Wireless Controllers with different software versions.
Catalyst Center supports the guest anchor feature for device combinations, including:
Configuration of a Cisco AireOS controller as a foreign controller with a Cisco AireOS controller as an anchor controller.
Configuration of a Cisco AireOS controller as a guest anchor controller with a Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller as a foreign controller.
Configuration of a Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller as a foreign controller with a Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller as an anchor controller.
Configuring IRCM on controller devices has limitations, including:
Configuration of a Cisco AireOS controller as a foreign controller and Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller as an anchor controller is not supported.
Configuration of a fabric guest anchor is not supported.
Only guest SSID is supported.
Broadcast of a nonguest anchor SSID in guest anchor mode is not supported.
Use this procedure to configure a guest anchor Cisco Wireless Controller.
|
Step 1 |
Design a network hierarchy, with sites, buildings, floors, and so on. For more information, see Create, edit, and delete a site and Add, edit, and delete a building. |
||
|
Step 2 |
Configure network servers, such as AAA, DHCP, and DNS servers. For more information, see Configure global network servers and Add Cisco ISE or other AAA servers. |
||
|
Step 3 |
Create SSIDs for a guest wireless network with external web authentication and central web authentication along with configuring Cisco Identity Services Engine. For more information, see Create SSIDs for a guest wireless network. |
||
|
Step 4 |
Discover the wireless controller using the Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) or an IP address range, and make sure that the devices are in the window and in the Managed state. For more information, see Discovery overview. |
||
|
Step 5 |
Provision a foreign wireless controller as the active main wireless controller. See Provision a Cisco AireOS Controller.
|
||
|
Step 6 |
Choose the role for the wireless controller as guest anchor and provision the guest anchor controllers. For more information, see Provision a Cisco AireOS Controller.
|
||
|
Step 7 |
Configure device credentials, such as CLI, SNMP, HTTP, and HTTPS. For more information, see Add global CLI credentials, Add global SNMPv2c credentials, Add global SNMPv3 credentials, and Add global HTTPS credentials. |
Discover the Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller and Cisco AireOS Controllers.
You must enable NETCONF and set the port to 830 to discover the Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller. NETCONF provides a mechanism to install, manipulate, and delete the configurations of network devices.
For more information, see Discover your network using CDP or Discover your network using an IP address range or CIDR.
Design your network hierarchy by adding sites, buildings, and floors so that later you can easily identify where to apply design settings or configurations.
To create a new network hierarchy, see Create, edit, and delete a site and Add, edit, and delete a building.
Add the location information of APs, and position them on the floor map to visualize the heatmap coverage.
For more information, see Work with APs on a floor map.
Define network settings, such as AAA (Cisco ISE is configured for Network and Client Endpoint), NetFlow Collector, NTP, DHCP, DNS, syslog, and SNMP traps. These network servers become the default for your entire network. You can add a TACACS server while adding a AAA server.
For more information, see Network settings overview, Configure global network servers, and Add AAA server.
Create SSIDs for a guest wireless network.
For more information, see Create SSIDs for a guest wireless network.
The WLAN profile name of the foreign controller and anchor controller should be the same for mobility.
|
Step 1 |
From the main menu, choose . The window display with the discovered devices listed. |
||
|
Step 2 |
Check the check box next to the Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller that you want to provision as a foreign controller. |
||
|
Step 3 |
From the Actions drop-down list, choose . |
||
|
Step 4 |
In the Assign Site window, click Choose a Site to assign a site for the Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller device. |
||
|
Step 5 |
In the Add Sites window, check the check box next to the site name to associate a Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller. |
||
|
Step 6 |
Click Save. |
||
|
Step 7 |
Click Apply. |
||
|
Step 8 |
Click Next. |
||
|
Step 9 |
Select a role for the Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller as Active Main WLC. |
||
|
Step 10 |
For an active main wireless controller, you need to configure interface and VLAN details. |
||
|
Step 11 |
Under the Assign Interface area, do these steps:
|
||
|
Step 12 |
Click Next. |
||
|
Step 13 |
In the Summary window, review the configuration settings. |
||
|
Step 14 |
Click Deploy to provision the Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller as a foreign controller. |
||
|
Step 15 |
On the window, check the check box next to the Cisco AireOS Controller that you want to provision as a guest anchor controller. |
||
|
Step 16 |
Repeat Step 3 through Step 8. |
||
|
Step 17 |
Select a role for the Cisco AireOS Controller as Guest Anchor. |
||
|
Step 18 |
For a guest anchor wireless controller, you need to configure the interface and VLAN details. |
||
|
Step 19 |
Repeat Step 11 through Step 14. |
Integrate the Meraki dashboard with Catalyst Center. See Integrate the Meraki dashboard.
Create the SSID. See Create SSIDs for an enterprise wireless network.
 Note |
The Meraki dashboard supports these types of SSIDs:
For every SSID, you can choose an interface name. If you choose the Management interface in Catalyst Center and the VLAN ID is 0, the configuration is not supported in the Meraki dashboard and VLAN tagging is disabled in the Meraki dashboard. If you create a custom interface for the SSID in Catalyst Center, an AP tag is created with the custom interface name and VLAN ID in the Meraki dashboard. |
Create the network profile and assign it to the sites for which the SSID is provisioned.
 Note |
The Network Hierarchy in Catalyst Center corresponds to in the Meraki dashboard. We recommend that you choose Buildings in the Add Sites to Profile window in the workflow. |
 Note |
Catalyst Center creates the Meraki network and provisions the SSIDs to the network. The Meraki dashboard provisions the Meraki network configuration to the Meraki devices. |
This procedure explains how to provision SSIDs for Cisco Meraki devices managed by a Meraki dashboard.
|
Step 1 |
From the main menu, choose . The window displays with the discovered devices listed. |
||
|
Step 2 |
To view the Meraki dashboard, expand the Global site in the left pane, and choose a building. All Meraki dashboards available in the chosen building display. |
||
|
Step 3 |
Check the check box next to the Meraki dashboard name that you want to provision. |
||
|
Step 4 |
From the Actions drop-down list, choose . The Assign Site window displays, which is where you can view the Meraki dashboard and the associated building. |
||
|
Step 5 |
To change the associated building, click Choose a site. |
||
|
Step 6 |
In the Choose a site window, select a building and click Save. |
||
|
Step 7 |
Click Next. The Configuration window displays. You can view the managed building in the primary location. |
||
|
Step 8 |
Click Select Secondary Managed AP Locations to choose the secondary managed location for the Meraki dashboard. |
||
|
Step 9 |
In the Managed AP Location window, check the check box next to the building name. |
||
|
Step 10 |
Click Save. |
||
|
Step 11 |
Click Next.
|
||
|
Step 12 |
Click Deploy. |
||
|
Step 13 |
In the Provision Devices window, do these steps to preview the CLI configuration:
|
These topics explain the components of remote teleworker sites and the procedure for provisioning remote teleworker devices.
The Cisco remote teleworker deployment is built around three main components: Cisco wireless controllers, Cisco OfficeExtend access points (APs) and a Corporate firewall. These models are supported in this deployment:
Wireless Controllers: Cisco 5520 Wireless Controller, Cisco 8540 Wireless Controller, Cisco 3504 Wireless Controller2, Cisco Catalyst 9800-40 Wireless Controller, Cisco Catalyst 9800-80 Wireless Controller, Cisco Catalyst 9800-CL Wireless Controller, and Cisco Catalyst 9800-L Wireless Controller.
Access Points: Cisco Aironet 1815T (Teleworker) Access Point, Cisco Aironet 1815I Access Point, Cisco Aironet 1815W Access Point, Cisco Aironet 1840I Access Point, Cisco Aironet 2800 Series Access Points, Cisco Aironet 3800 Series Access Points, Cisco Aironet 4800 Series Access Points, Cisco Catalyst 9115 Access Point, Cisco Catalyst 9120 Access Point, and Cisco Catalyst 9130 Access Point.
Cisco controllers are responsible for system-wide WLAN functions, such as security policies, intrusion prevention, RF management, quality of service (QoS), and mobility. They work in conjunction with Cisco APs to support business-critical wireless applications for teleworkers. Controllers provide the control, scalability, security, and reliability that network managers need to build a secure, scalable teleworker environment.
To allow users to connect their corporate devices to the organization's on-site wireless network, the remote teleworking solution offers the same wireless Secure Set Identifiers (SSIDs) at a teleworker's home as those that support data and voice inside the organization.
APs cannot act independently of controllers. As an AP communicates with the controller resources, it downloads its configuration and synchronizes its software or firmware image, if required. The AP establishes a secure Datagram Transport Layer Security (DTLS) connection to the controller, which offers remote WLAN connectivity using the same profile as at the corporate office. Secure tunneling allows all traffic to be validated against centralized security policies and minimizes the management overhead associated with home-based firewalls.
The controller should be placed in a demilitarized zone (DMZ) and the corporate firewall must allow CAPWAP control and data traffic through the firewall to the controller. The general configuration on the firewall is to allow CAPWAP control and CAPWAP management port numbers through the firewall. The UDP 5246 and 5247 ports need to be opened on the firewall for communication between the controller and the AP.
For the most flexible and secure remote teleworker configuration, deploy a dedicated controller pair in a dedicated to the Internet edge DMZ. Traffic from the Internet terminates in the DMZ versus in the internal network, while the remote AP is still directly connected to the internal network.
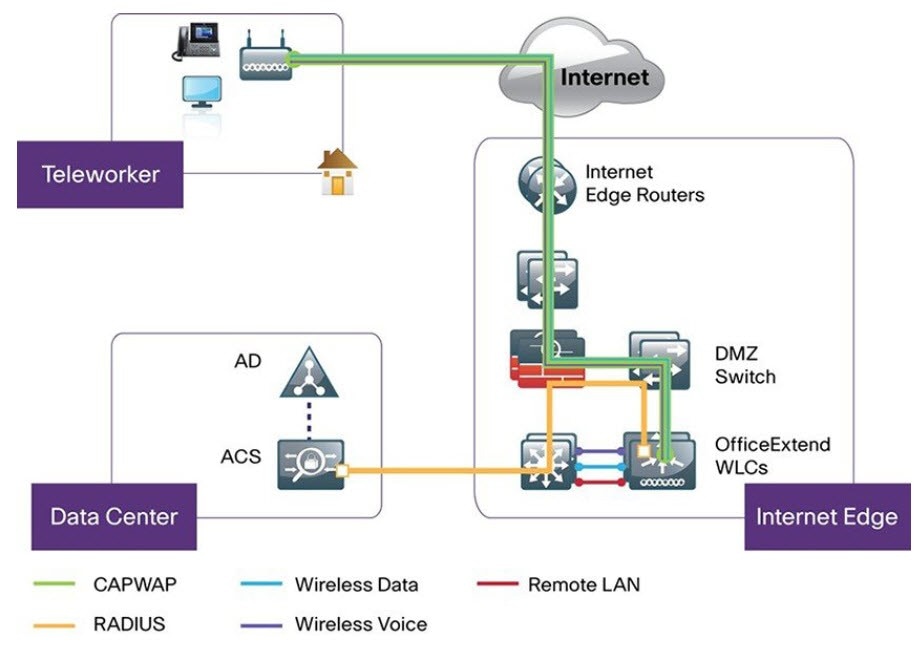
A remote teleworker site is a dedicated site that is used only to manage wireless controllers and remote teleworker access points (APs). To create a remote teleworker site, you need to enable the remote teleworker function on the site. When enabled, the remote teleworker function can’t be independently disabled for a site, building, or floor within the site's hierarchy. The site can only manage remote teleworker functions.
In a teleworker site, switching is performed centrally from the controller. You can’t configure the network profile for FlexConnect with local switching.
Understand the supported devices that are used in a teleworker deployment.
Make sure that you have a Cisco Wireless Controller and Cisco APs in your inventory. If not, discover the devices or add them manually. For more information, see Discover Your Network or Add a network device.
Configure global wireless network settings appropriate for your network. For more information, see Configure global wireless settings.
For remote teleworker APs, we recommend that you create an AP profile with remote teleworker enabled and configure custom site tags. For more information, see Configure additional settings for an AP profile for Cisco IOS XE devices and Add AP groups, flex groups, site tags, and policy tags to a network profile.
For Cisco AireOS devices, you must map the AP profile to the custom AP group of the site that will be used for the remote teleworker AP. For more information, see Create network profiles for wireless and Add AP groups, flex groups, site tags, and policy tags to a network profile.
|
Step 1 |
Create a site to manage remote teleworker APs. See Create, edit, and delete a site. |
||
|
Step 2 |
Add buildings and floors. See Add, edit, and delete a building. |
||
|
Step 3 |
Configure the wireless network settings for the remote teleworker site.
|
||
|
Step 4 |
Assign the controller to the site. See Assign an unprovisioned device to a site. |
||
|
Step 5 |
Assign the APs to the site. See Assign an unprovisioned device to a site. You can use serial numbers or MAC addresses but not a mixture of both, or you can upload a CSV file. |
||
|
Step 6 |
In the wireless network settings, add the APs to the authorized APs list. |
||
|
Step 7 |
Provision the controller.
|
||
|
Step 8 |
After the Cisco Wireless Controller is provisioned, you can provision the APs. |