4900-4990 MHz frequency support for US and Canada with license enforcement
From UIW Release 17.16.1, the Cisco Catalyst IW9167E, IW9165D, and IW9165E APs introduces additional support 4.9 GHz frequency band in URWB mode for Canada (-A) and -B (United States) domains.
When operating in the 4.9 GHz frequency bands for -A and -B domains, devices use 10 MHz and 20 MHz channel bandwidths with 5 MHz channel spacing.
The 4.9 GHz frequency bands are available on both the radio slot 1 and slot 2 and is disabled by default.
 Note |
The -A and -B domains do not support IEEE 802.11ax rates when operating in 4.9 GHz. |
|
Channel |
Channel bandwidth (10 MHz) |
Channel bandwidth (20 MHz) |
|---|---|---|
|
11 |
4945 |
NA |
|
19 |
4985 |
NA |
|
20 |
4950 |
4950 |
|
21 |
4955 |
4955 |
|
22 |
4960 |
4960 |
|
23 |
4965 |
4965 |
|
24 |
4970 |
4970 |
|
25 |
4975 |
4975 |
|
26 |
4980 |
4980 |
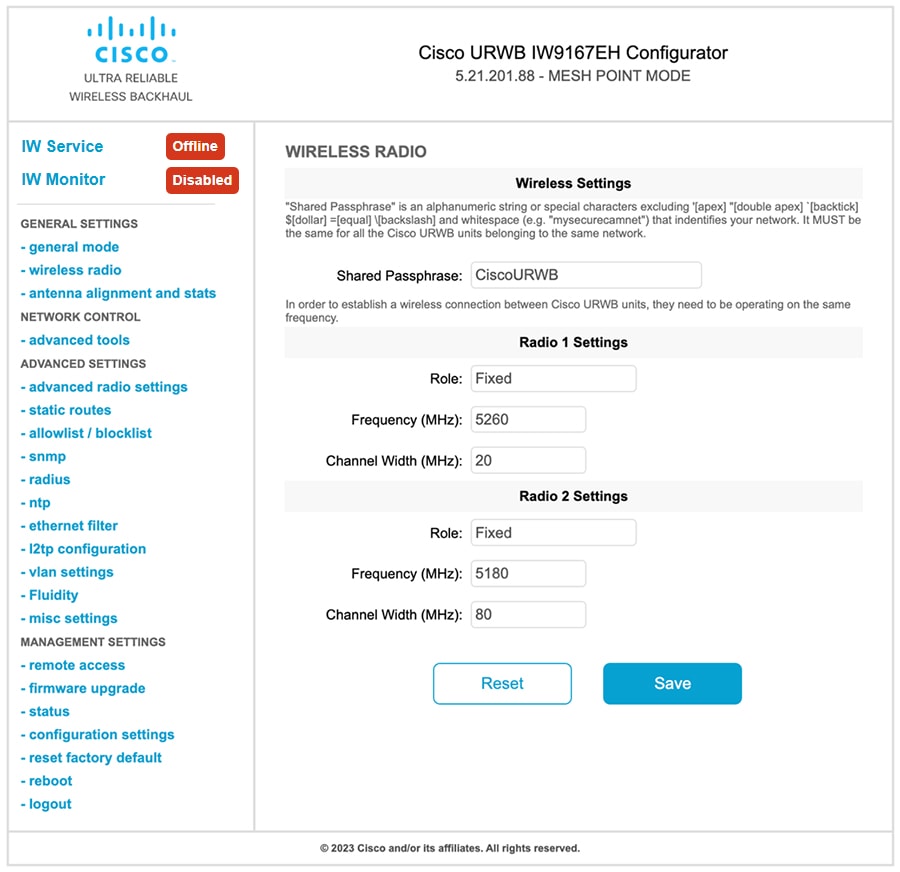
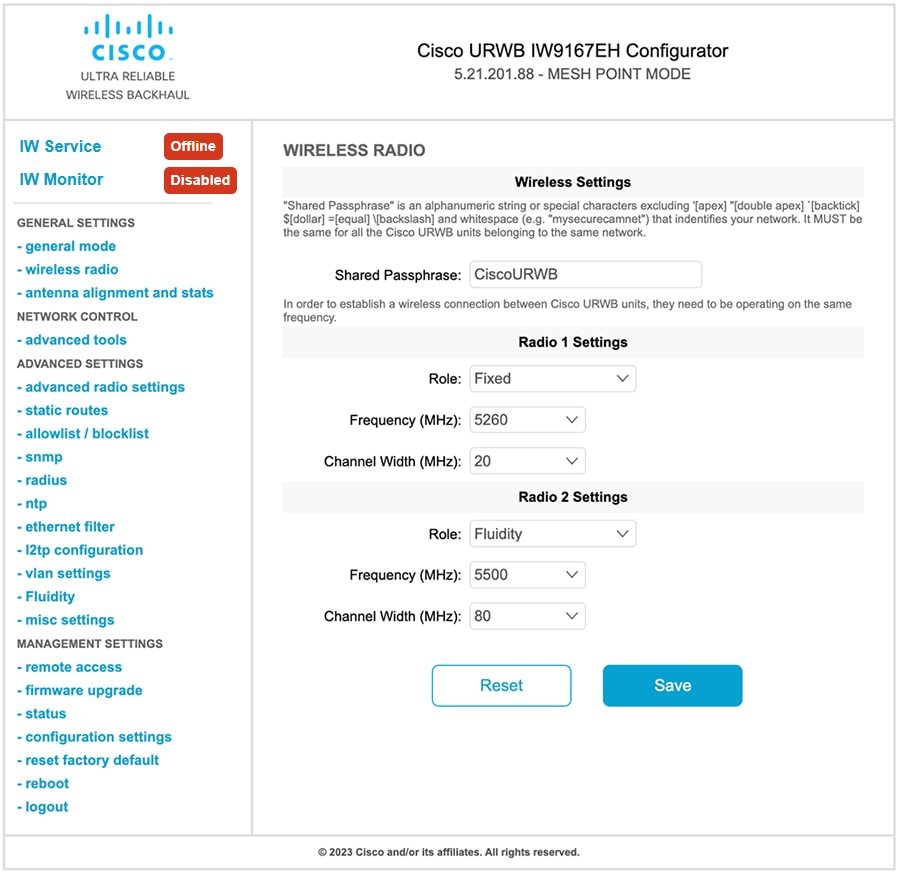
Enable 4900-4990 MHz frequency bands
The IW Service sends the 4.9 GHz frequency band enablement configuration to the AP.
Use this task to enable the 4.9 GHz frequency bands on the AP.
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Configure the 4.9 GHz frequency band enablement using IW Service Cloud-Managed or offline deployment mode. For more information on how to configure the 4.9 GHz band enablement from IW Service, see the Introduction to Industrial Wireless. |
||
|
Step 2 |
Use the configure dot11Radio interface 4.9G high-throughput enable command to enable 802.11an/ac rates. When enabled, the radios are allowed to operate at higher rates, limiting the power profile.
|
 Feedback
Feedback