Introduction
This document describes how to configure mutual redistribution between EIGRP and BGP.
Prerequisites
Requirements
Cisco recommends that you have knowledge of these topics:
Components Used
The information in this document is based on the Cisco 7200 Series Router with Cisco IOS®Software Release 15.0(1).
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, ensure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Configure
In this example, routers R1 and R2 communicate with each other using EIGRP. Routers R2 and R3 use eBGP. In order to mutually redistribute the eBGP routes in to EIGRP, use the redistribute bgp command with EIGRP metrics. Similarly, in order to redistribute EIGRP routes in to BGP, use the redistribute eigrp AS number command.
Network Diagram
This document uses this network setup:
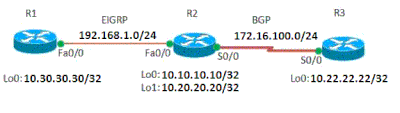 Network Diagram
Network Diagram
Configurations
This document uses these configurations:
| Router R1 |
!
hostname R1
!
ip cef
!
!
interface Loopback0
ip address 10.30.30.30 255.255.255.255
!
interface FastEthernet0/0
ip address 192.168.1.101 255.255.255.0
duplex auto
speed auto
!
router eigrp 100
network 10.30.0.0
network 192.168.1.0
no auto-summary
!
end
|
| Router R2 |
!
hostname R2
!
ip cef
!
!
interface Loopback0
ip address 10.10.10.10 255.255.255.255
!
interface Loopback1
ip address 10.20.20.20 255.255.255.255
!
interface FastEthernet0/0
ip address 192.168.1.100 255.255.255.0
duplex auto
speed auto
!
interface Serial0/0
ip address 172.16.100.50 255.255.255.0
serial restart-delay 0
clock rate 2000000
!
router eigrp 100
redistribute static
redistribute bgp 1000 metric 100 1 255 1 1500
network 10.0.0.0
network 192.168.1.0
no auto-summary
!
router bgp 1000
no synchronization
bgp log-neighbor-changes
network 10.20.20.20 mask 255.255.255.255
redistribute connected
redistribute static
redistribute eigrp 100
neighbor 172.16.100.51 remote-as 2000
neighbor 172.16.100.51 next-hop-self
no auto-summary
!
end
|
| Router R3 |
!
hostname R3
!
ip cef
!
interface Loopback0
ip address 10.22.22.22 255.255.255.255
!
interface Serial0/0
ip address 172.16.100.51 255.255.255.0
serial restart-delay 0
clock rate 2000000
!
router bgp 2000
no synchronization
bgp log-neighbor-changes
network 10.22.22.22 mask 255.255.255.255
network 172.16.100.0 mask 255.255.255.0
neighbor 172.16.100.50 remote-as 1000
neighbor 172.16.100.50 default-originate
default-information originate
!--- Default route is configured!
no auto-summary
!
end
|
Verify
Use this section in order to confirm that your configuration works properly.
TheCLI Analyzer is used in order to view an analysis of show command output.

Note: Only registered Cisco users can access internal Cisco tools and information.
Show Commands
In order to verify that EIGRP is receiving the redistributed routes, use the show ip route eigrp command.
| show ip route eigrp |
|
In router R1
R1#show ip route eigrp
10.20.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
D EX 10.20.20.20
[170/25625856] via 192.168.1.100, 01:00:33, FastEthernet0/0
10.22.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
D EX 10.22.22.22
[170/25625856] via 192.168.1.100, 00:59:49, FastEthernet0/0
10.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
D 10.10.10.10 [90/409600] via 192.168.1.100, 00:55:17, FastEthernet0/0
D*EX 0.0.0.0/0 [170/25625856] via 192.168.1.100, 00:46:24, FastEthernet0/0
!--- Shows the default route from router R3.
!--- EX indicates that the routes are EIGRP external routes.
|
In order to verify that EIGRP routes are redistributed in BGP properly, use the show ip route bgpcommand in router R3.
| show ip route bgp |
|
In router R3
R3#show ip route bgp
show ip route bgp
10.20.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
B 10.20.20.20 [20/0] via 172.16.100.50, 01:03:02
10.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
B 10.10.10.10 [20/0] via 172.16.100.50, 01:03:02
B 192.168.1.0/24 [20/0] via 172.16.100.50, 01:03:02
10.30.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
B 10.30.30.30 [20/409600] via 172.16.100.50, 00:59:06
!--- The output indicates that the EIGRP routes are
!--- redistributed in BGP.
|
Related Information


 Feedback
Feedback