Cisco Rugged Enterprise Networking Solution Overview
Available Languages
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
Securely extend the enterprise network to uncarpeted spaces
For any large organization, whether it’s a corporate headquarters, a hospital, a university campus, or a shopping complex, networking isn’t just about connecting devices inside buildings-it involves a much wider range of environments and needs. Enterprises are recognizing that outdoor and uncarpeted spaces are no longer just utilitarian, but rather valuable extensions of their campus, and are modernizing such networks to enhance security and safety, improve operational efficiency, and deliver new user experiences.
Traditionally, networks for these uncarpeted spaces were siloed, unmanaged, and composed of disparate vendor hardware. This lack of unified architecture creates deployment friction and results in significant challenges involving complexity, security, and long-term operating costs.

Enterprise networking needs stretch beyond traditional campus and branch to non-climate-controlled spaces
Cisco’s solution for rugged enterprise networking provides an infrastructure that is purpose-built to operate reliably and securely in uncarpeted and non-climate-controlled environments where standard enterprise equipment would fail. Its core function is to extend the enterprise network, with its management and security policies, beyond the campus to the outdoors and rugged spaces.
The Cisco® solution is an integrated architecture made of products from both its enterprise and ruggedized networking portfolios. This joint portfolio provides a unified, secure, and scalable architecture that allows organizations to extend the innovations in their enterprise network, such as centralized management and robust security, to uncarpeted areas.
Rugged enterprise networking use cases and business outcomes
In modern enterprises, network coverage is frequently needed outside of office walls where typical IT hardware and connectivity solutions are inadequate or impractical.
Such spaces include:
● Parking lots: Adding networking to parking lots and garages provides a wide range of benefits for both the organization and the people who use the space. For users it improves safety and enhances their experience. For the organization, it increases operational efficiency and unlocks new business opportunities. With a robust network in place, organizations can:
◦ Enhance user convenience by adding sensors to help people find available parking spaces quickly and to power displays for occupancy information.
◦ Provide enterprise Wi-Fi and extend the office environment’s convenience and connectivity beyond the building.
◦ Improve physical safety with high-resolution surveillance cameras, gate access control for entry and exit authorization, emergency call boxes, etc.
◦ Place secure point-of-sale terminals, which are often vulnerable due to their remote and exposed nature.
◦ Provide staff amenities such as charging stations for electric vehicles.
● Networking across the campus: A campus-wide network enables seamless connectivity and consistent security across the entire organization. A wireless network can provide communication between buildings and remote objects, especially in situations where it’s impractical, too costly, or physically impossible to lay fiber optic cable.
◦ Between buildings: Eliminate the high costs and logistical challenges of trenching, acquiring permits, and installing physical cables while maintaining high throughput for interbuilding communications.
◦ Outdoor work areas: Extend the corporate network to outdoor areas to give staff more places to work. Connecting previously disconnected spaces can help staff stay productive with reliable Wi-Fi and the ability to access information and applications without returning to a building.
◦ Safety and security: Enhance safety by deploying surveillance cameras to monitor activity and deter theft or vandalism, environmental sensors to monitor hazardous conditions like gas leaks or extreme temperatures, and other equipment along the campus perimeter and avoid laying physical fiber cables.
● Temporary ad hoc locations: Robust networking is required in a variety of temporary locations where a reliable and secure network must be quickly deployed and then dismantled. Examples include:
◦ Construction sites that need temporary networks to connect a wide range of devices including site offices, security cameras, material tracking systems, and sensors.
◦ Pop-up events such as temporary shops, sporting events, festivals, etc. that require secure networking for kiosks, ticketing, fan zones, security cameras, and vendor communications, among other needs.
● Building management: A rugged network is essential in building management systems for areas where standard IT equipment cannot withstand the environmental conditions. Examples include:
◦ Locations that are hot, dusty, and have high levels of vibrations such as utility and mechanical rooms housing HVAC systems, generators, elevators, and pumps.
◦ Safety equipment such as surveillance cameras for monitoring and badge readers for access control.
● Remote and mobile assets: A robust network connecting moveable objects ensures reliable, continuous communication and data exchange critical for operational efficiency and service delivery. Examples include:
◦ Mobile clinics: Reliable cellular connectivity enables real-time access to patient data, remote monitoring, and seamless communication between healthcare providers and administrative staff regardless of location.
◦ ATMs and kiosks: Robust connectivity ensures continuous, secure, and reliable communication with the corporate network, which is critical for transaction processing and real-time monitoring.
Extending the network to rugged spaces presents significant challenges related to the physical environment, management, and security, which standard enterprise networks don’t face.
● Physical resilience: Network equipment in uncarpeted and non-climate-controlled environments is exposed to unregulated temperatures, dust, moisture, etc., all of which can cause components to fail prematurely, leading to network outages.
The most fundamental requirement is to use equipment that is engineered to withstand outdoor non-climate-controlled conditions. This includes switches, routers, and wireless access points that are certified to operate in a wide range of temperatures, resist dust and moisture (high IP ratings), and tolerate shocks and vibrations.
● Security: Many such networks are also unmanaged and unsecured. Unmanaged networks pose significant security risks because they lack the built-in controls and visibility of managed networks and create a “shadow IT” problem in which devices operate outside the knowledge and control of the IT and security teams. Coupled with the fact that these devices connect back into the campus network, this blind spot leaves the door open for attackers to compromise the entire organization. In addition, because these devices are easily accessible, they are more vulnerable to tampering. For example, an attacker could plug a rogue device into a camera’s network port to gain access.
● Management and troubleshooting: Unmanaged networks are difficult to troubleshoot because they operate with fixed, default settings and lack the diagnostic tools, traffic visibility, and control features found in a managed network. For example, if a video feed from a surveillance camera is not coming through, you can’t see whether the problem is caused by a port experiencing errors, because of high traffic, or due to a failing device. Without logs or performance metrics, an outage becomes a guessing game. This makes it impossible to proactively address performance degradation before it becomes a major problem.
● Power usage and optimization: Rugged networks often extend into difficult-to-reach locations like outdoor facilities, or remote areas where power outlets are scarce. Power over Ethernet (PoE) eliminates the need to run separate power cables to each device, such as sensors, cameras, or wireless access points, providing the flexibility to place devices exactly where they are needed for optimal performance. However, without visibility into PoE usage and an effective way to optimize power allocation, imbalances can occur across switches, with some overloaded and others underutilized, and there is no assurance that the available power is sufficient for all powered devices. These situations can lead to power issues and device failures.
Cisco’s solution for rugged enterprise networking
Cisco’s approach to rugged enterprise networking is based on three pillars: a standardized portfolio across campus, branch, and uncarpeted areas, unified management across the domains, and integrated security across the whole organization.
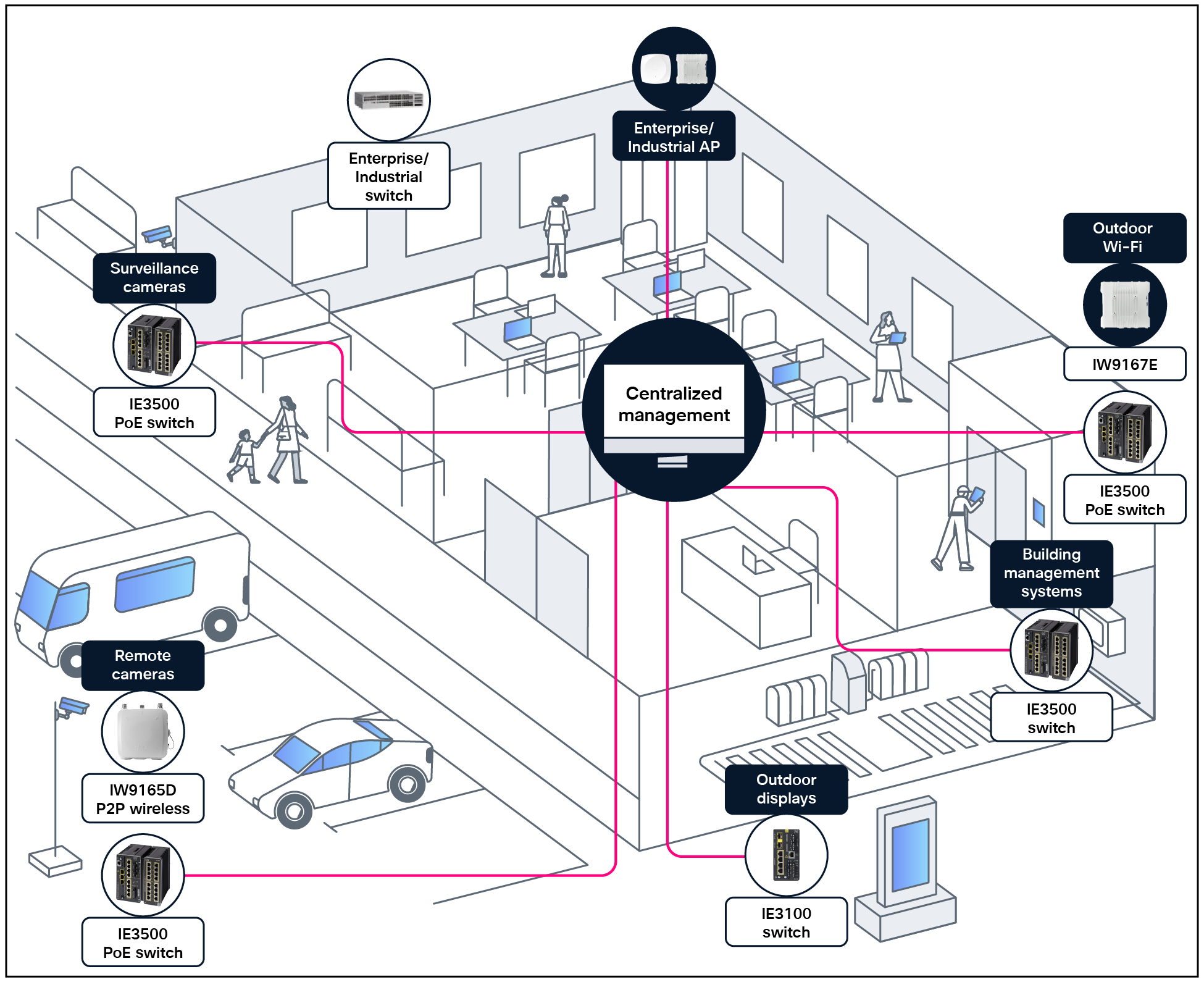
A centrally managed and secured campus and rugged network
The value proposition for Cisco’s rugged enterprise networking solution stems from its core strengths.
Uniform integrated infrastructure
Cisco’s enterprise and industrial network devices share a unified hardware and software architecture, built on the same core operating system, Cisco IOS® XE, providing a consistent interface and feature set. Instead of investing time and resources in learning new skills and separate tools, IT teams can leverage their expertise to manage this expansion of the enterprise network. Standardizing network devices across both enterprise and rugged environments eliminates the complexities and challenges that arise from managing two separate, dissimilar network infrastructures.
Rugged switches
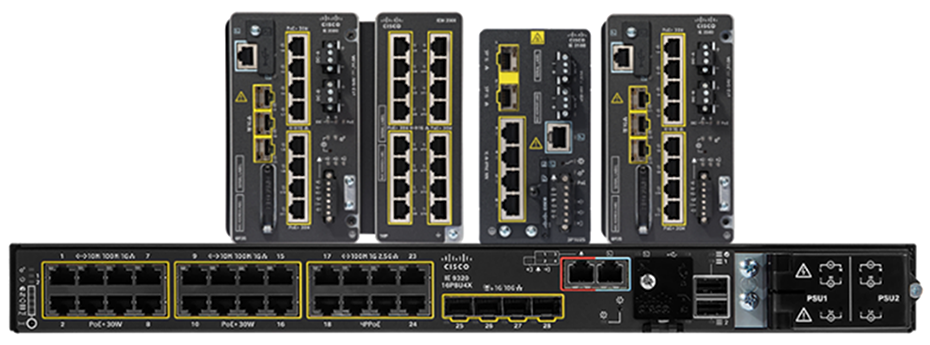
Cisco offers a comprehensive portfolio of purpose-built ruggedized switches that are resistant to an extended range of temperature, dust, moisture, and vibration. These switches run the same IOS XE operating system as Cisco’s enterprise switches, providing a unified, programmable, and secure interface that simplifies network management and operations.
Cisco switches come in a range of form factors, including the traditional 19-inch rack mount as well as compact DIN rail mounts suitable for installation in space-constrained outdoor cabinets.
Security features built into Cisco industrial switches, such as Cisco TrustSec® technology for zero-trust segmentation and Cisco Secure Equipment Access for zero-trust remote access to connected devices, integrate security into the network infrastructure, mitigating cybersecurity threats that can arise when expanding the enterprise network into rugged spaces.
Cisco industrial switches offer robust PoE capabilities tailored for harsh environments. They support various PoE standards, including PoE, PoE+, and PoE++/4PPoE, with power budgets up to 90W per port and 720W per switch, depending on the model.
They are ideal for connecting and powering devices such as surveillance cameras, Wi-Fi access points, sensors, digital displays, and more. They also offer advanced features that help minimize downtime and support reliable, continuous operation of devices.
Rugged wireless clients and access points
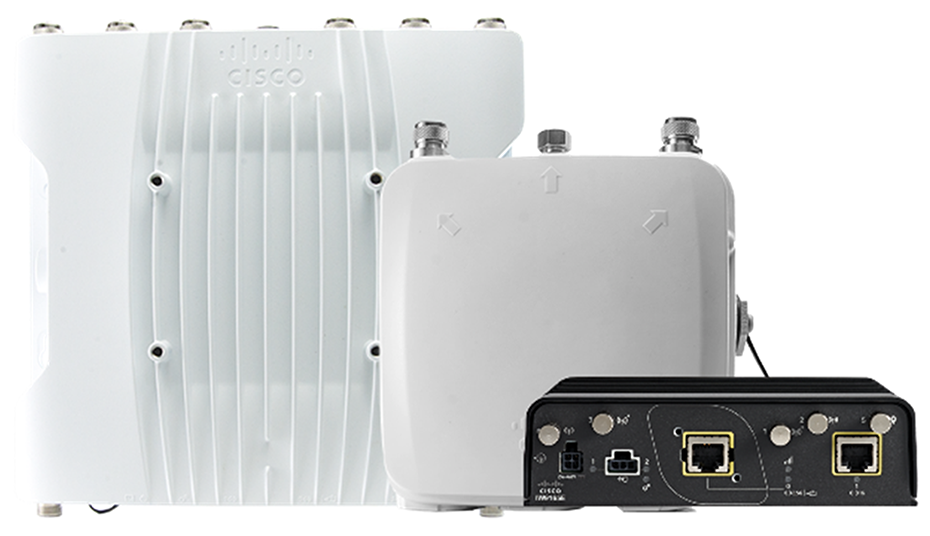

Cisco ruggedized wireless products provide a unified offering that combines Wi-Fi 6/6E and Cisco Ultra-Reliable Wireless Backhaul (URWB) technologies to support a broad range of applications and use cases. While Wi-Fi provides connectivity to laptops, phones, sensors, and other devices, URWB provides low-latency, highly reliable, long-range, and high-bandwidth connections and is an excellent alternative to wired connectivity for various locations around the campus. URWB is ideal for connecting remote surveillance cameras or far-flung buildings that would be cost-prohibitive to connect via fiber. URWB is also ideal for providing connectivity to temporary ad hoc sites or mobile assets on a campus, such as autonomous vehicles or private buses.
Rugged routers

Cisco’s ruggedized routers provide a highly flexible and secure connectivity solution. They are engineered to deliver reliable network access over a variety of mediums, including 5G cellular, Wi-Fi, and Gigabit Ethernet, helping ensure that field assets and remote locations remain connected regardless of the available infrastructure. For streamlined operations, these routers can be centrally managed through Cisco Catalyst Center or Cisco SD-WAN Manager, simplifying deployment and policy enforcement across a WAN. With built-in security features, including a Next-Generation Firewall (NGFW), they protect against cyberthreats. Their expandability via Pluggable Interface Modules (PIMs) allows for easy customization and futureproofing, enabling organizations to adapt to evolving connectivity needs without replacing the entire device. Cisco industrial routers are ideal for providing connectivity to temporary ad hoc sites or mobile assets on a campus.
Consistent security
Built-in security features in both Cisco industrial and enterprise networking equipment work together to create a uniform security fabric across the entire organization. The same security policies and measures can be applied and enforced consistently. This approach simplifies management and helps ensure that all parts of the business are protected with the same level of security, regardless of their physical location or function. It removes security silos, allowing security teams to have a single, holistic view of all activities, and enables better event correlation, threat detection, and response so there is no gap in defense.
As enterprises increasingly rely on universal zero-trust network access to address evolving security challenges, it is important for them to enforce consistent, identity-driven, least-privilege access policies across all users and devices, regardless of location—whether on-premises or remote. Zero-trust security principles help ensure that bad actors cannot connect to your network in case they gain physical access to the equipment. Securing every port of your field networking equipment is key.
Cisco Identity Services Engine (ISE) helps ensure that only the devices you specify are granted access. All other devices are denied access by default. ISE provides a comprehensive framework for identity and access management by enforcing strict access controls and continuous monitoring based on user identity, device health, and contextual data and embodying the zero-trust principle of “never trust, always verify.” Given the vulnerable nature of devices in uncarpeted areas, such a framework is essential to protect the enterprise.
Centralized management
A standardized network environment allows for a single, centralized management platform. Instead of using separate tools and processes for campus and rugged networks, administrators can use a unified system to manage the entire infrastructure. This simplifies tasks such as deployment and configurations so that devices can be brought online and provisioned faster and more consistently. Troubleshooting becomes easier and IT staff can more easily diagnose and resolve issues across the entire network. Network automation reduces the time spent on manual, error-prone, repetitive tasks like software image updates.
Cisco Catalyst Center
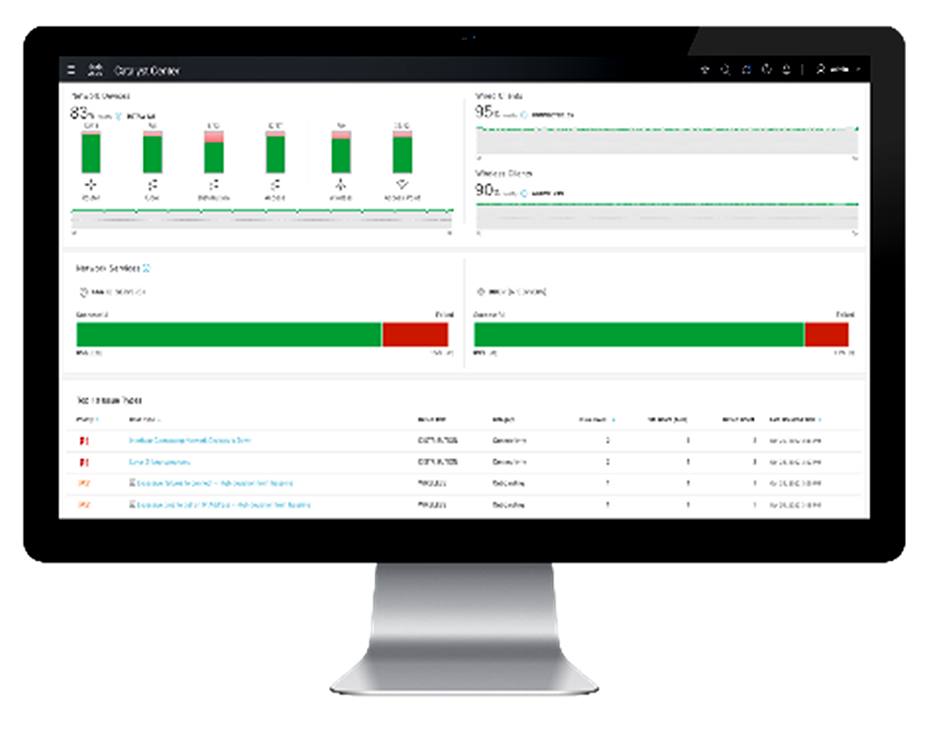
The Catalyst Center management platform provides a single, centralized console that simplifies and automates network operations across all networking environments. Using Catalyst Center, IT teams can see, monitor, and manage devices whether they are on the main corporate campus, at a remote branch office, or at an outdoor site. This eliminates the complexity of switching between different management systems for different network domains.
Catalyst Center automates the onboarding of network equipment, the initial provisioning, and software updates, and manages configurations over the entire network regardless of a device’s location. It also collects telemetry data to offer a complete real-time view of network health and performance. This visibility simplifies troubleshooting, allowing IT to quickly pinpoint and resolve issues.
The PoE Assurance dashboard in Catalyst Center helps network administrators efficiently monitor, troubleshoot, and optimize PoE usage, helping ensure that power is effectively managed and sustainability goals are supported. Using this dashboard, administrators can check operational states, get details on powered devices such as wattage being consumed, receive insights on switches supplying power to critical devices, display current power usage and budget to help plan appropriately, view PoE port availability, and get details on which wireless access points can be placed in low-power mode for savings.
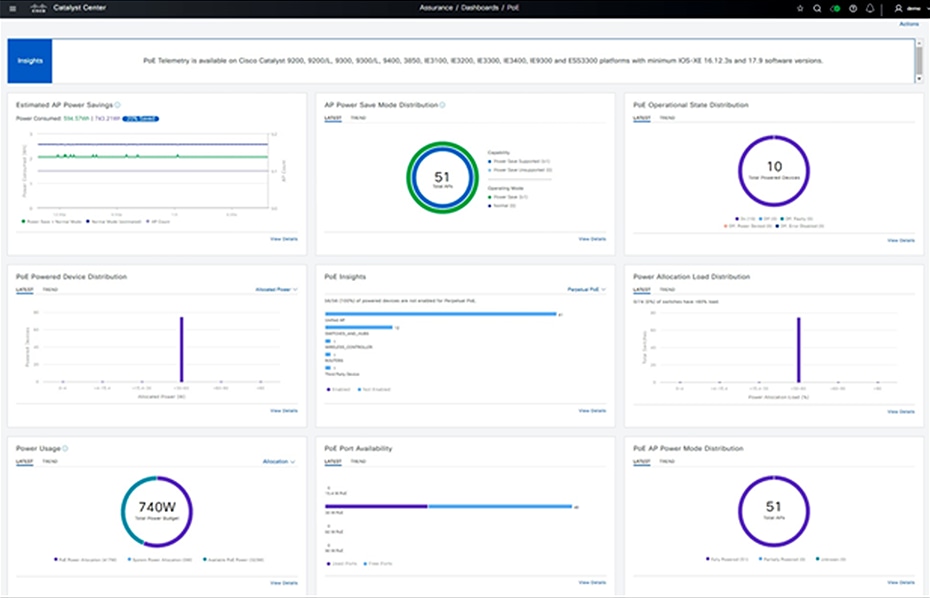
Plan and optimize energy usage via the Catalyst Center PoE Assurance dashboard
Meraki dashboard
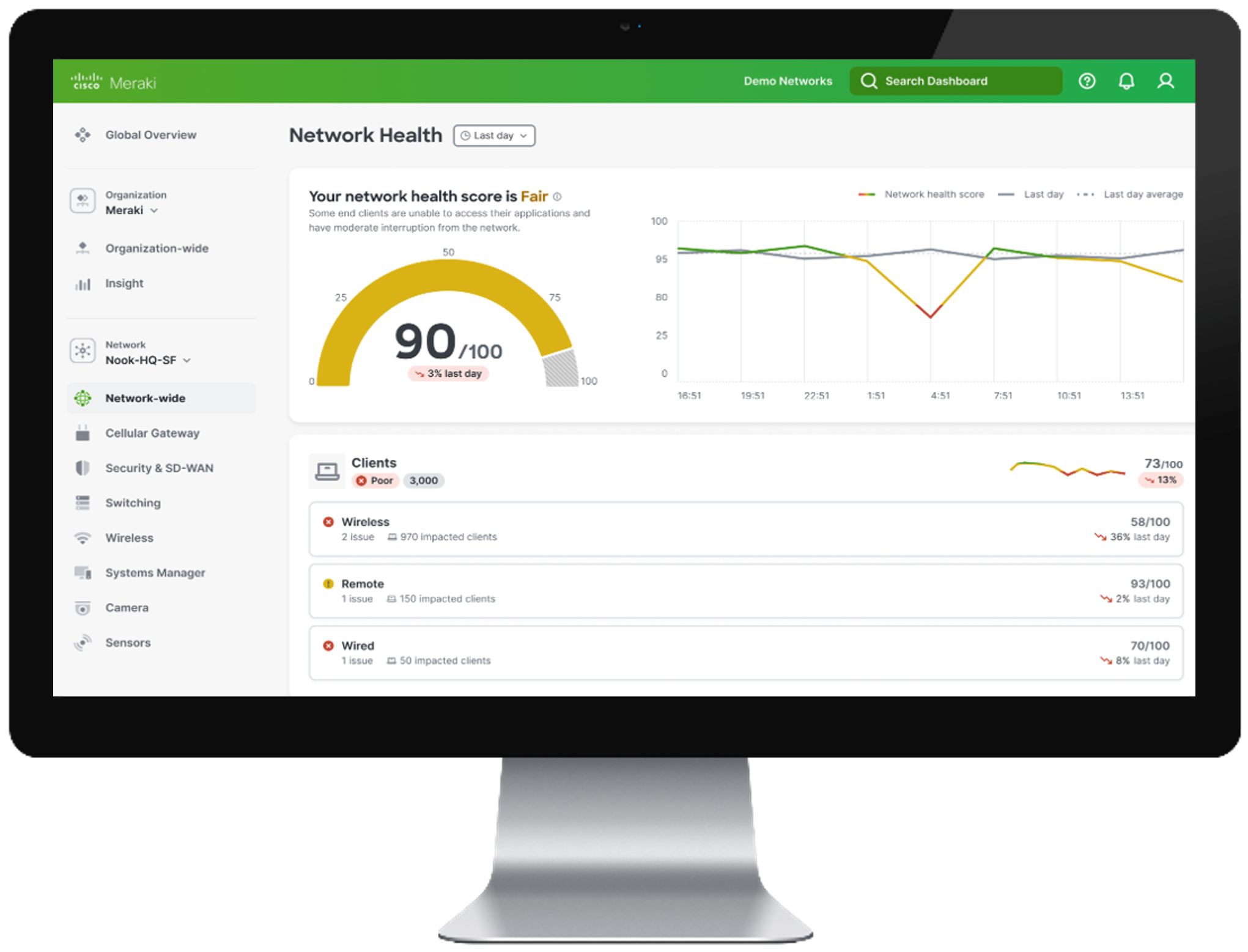
Meraki offers a cloud-managed dashboard that enables centralized management of networks of all sizes, from small sites to massive deployments with thousands of switches and access points. This allows seamless management of both campus and rugged enterprise environments from a single pane of glass. It enables zero-touch provisioning, real-time network analytics, and comprehensive visibility into network health and performance. It unifies management across Meraki and Catalyst devices, simplifying operations, enhancing network reliability, and enabling IT teams to proactively optimize performance and resolve issues efficiently from anywhere.
These benefits enable enterprises to extend their campus networks securely and efficiently into non-climate-controlled, uncarpeted spaces using Cisco ruggedized switches, while maintaining centralized control, visibility, and consistent policies across all environments.
Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN Manager
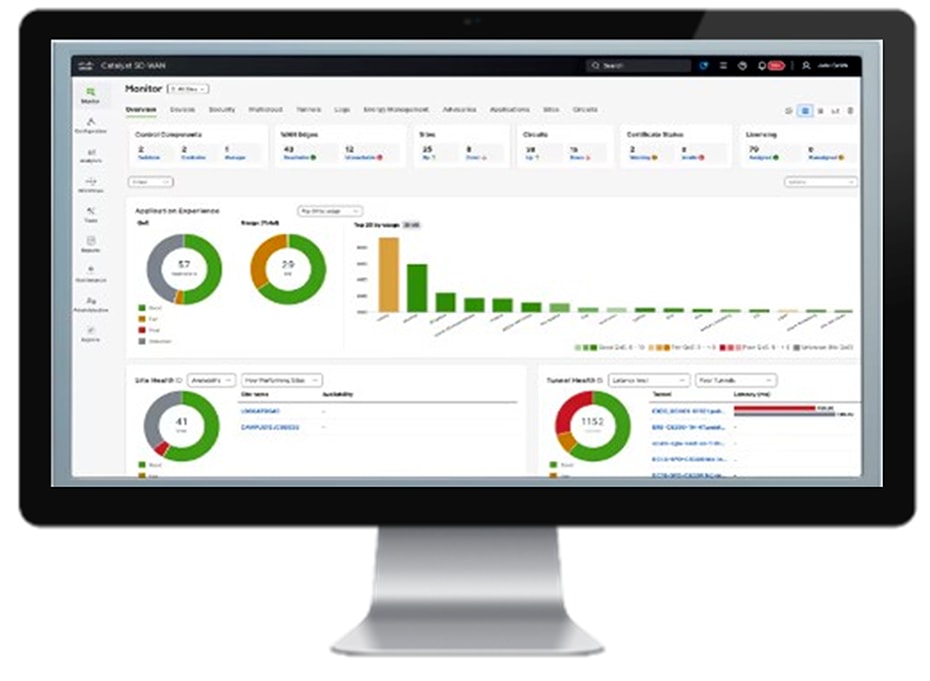
Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN Manager provides uniform management for both enterprise and ruggedized routers by enabling centralized, scalable, and secure control across diverse network environments. It supports ruggedized routers like the Cisco IR1101 and IR8100 series, which are designed for harsh environments, and integrates them into the broader SD-WAN fabric. This unified management approach allows IT teams to deploy, configure, monitor, and update both enterprise and ruggedized routers from a single pane of glass, simplifying operations and reducing complexity.
Cisco SD-Access is a networking solution that automates user and device policy across wired and wireless networks, ensuring secure segmentation and simplified network management. Cisco Catalyst Center serves as the centralized management platform for SD-Access, providing end-to-end visibility, automation, and assurance to efficiently deploy, monitor, and troubleshoot the network.
Cisco SD-WAN is a software-defined wide area networking solution that enables organizations to securely connect users, devices, and branch offices across multiple locations while optimizing application performance. Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN plays a key role in simplifying the management, monitoring, and automation of these networks.
Modern enterprises rely on SD-Access to simplify and secure their Local Area Networks (LAN) while leveraging SD-WAN to optimize and protect their Wide Area Network (WAN) connectivity across distributed locations.
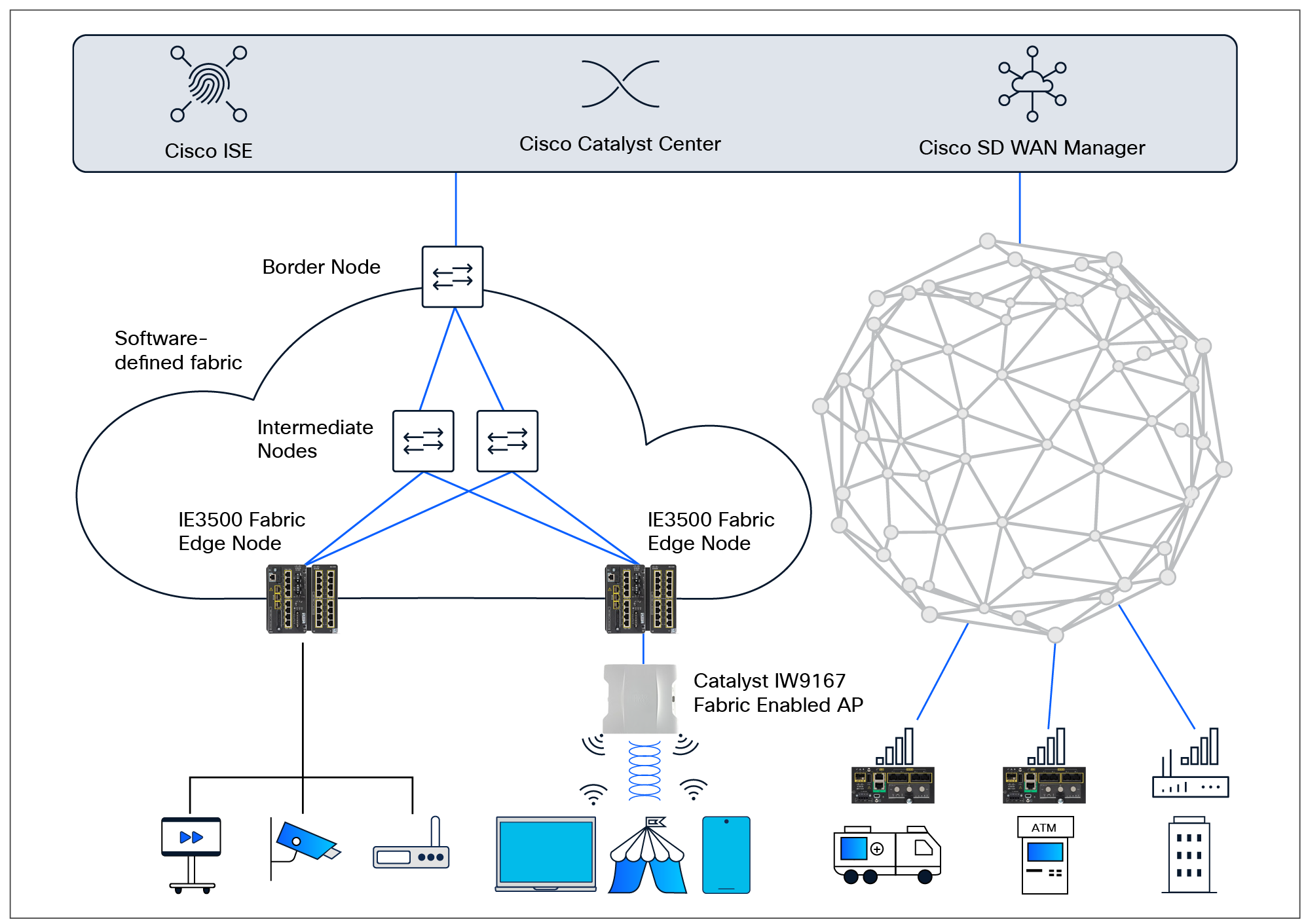
Seamlessly extend the campus fabric to rugged spaces
Both these architectures can easily be extended to rugged networking. Figure 4 shows how SD-Access and SD-WAN can extend to devices in outdoor and uncarpeted spaces for easier integration into the enterprise network.
Cisco delivers a consistent, secure, and high-performance network architecture that spans traditional campus and branch environments and extends seamlessly into uncarpeted spaces with purpose-built hardware and unified management and security frameworks.
Only Cisco’s networking portfolio has the breadth required to deliver high-performance networking both in offices and in outdoor and rugged environments. Only Cisco embeds security within its network equipment that acts as a sensor and enforcer for comprehensive network visibility and protection. Only Cisco provides a set of validated designs that serve as tested and proven blueprints for network architecture, simplifying and accelerating deployments while reducing risks.
Reliable, secure networking for an enterprise’s outdoor and uncarpeted areas is critical for modern operations, security, and efficiency. These areas are often exposed to environmental and physical stressors that standard networking equipment can’t handle. Cisco provides a complete portfolio of ruggedized networking equipment that can be managed by the same proven management systems used in the indoor spaces and secured by applications that IT teams have grown to know and trust. Cisco also publishes Cisco Validated Designs that are technical blueprints and end-to-end architectures, tested and proven in the field, that lead to faster deployment with less risk and increased predictability.
IT teams, it’s time to extend your expertise beyond the office and into uncarpeted spaces. By leveraging your existing skills and familiar tools, you can unify the entire organizational network. Instead of allowing facility managers or external contractors to deploy basic, unmanaged networking equipment – creating fragmented, unsecure silos – you can take charge. You can not only ensure consistent management and visibility but also close critical security gaps and protect your entire organization from breaches that can originate from these unmanaged silos.
To explore further, and for a free no-obligation one-on-one consultation with one of our experts, please contact us and we will reach out to you to schedule a session.