The AI Opportunity for Service Providers:
Unlocking New Revenue Streams, Powered by Cisco Innovations White Paper
Available Languages
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
AI is reshaping the global economy at unprecedented speed, redefining how organizations create value, how people work, and how entire industries operate. This AI revolution is transforming how and where organizations capture, process, and interact with data. At the same time, communications service providers (CSPs) are looking for ways to create new revenue streams by becoming an essential member of the fast-evolving AI ecosystem.
As the industry focus transitions from primarily capital-intensive large language model (LLM) buildouts to widespread enterprise adoption of AI, CSPs have an opportunity to become pivotal players in the AI economy. If LLMs are the brains of the AI-driven enterprise, agents and digital employees are the limbs that execute decisions. What ties them together is the central nervous system, which connects and activates them. It’s a role that CSPs are best qualified to play, one that represents a once-in-a-generation opportunity to create new business models and revenue streams by leveraging and building upon their wealth of existing assets, including infrastructure, geographic presence, domain expertise, partnerships, and longstanding relationships with enterprise customers across a wide range of industries.
The most obvious route to revenue is via services that leverage traditional provider capabilities to deliver, optimize, and assure their customers’ AI lifecycle and workflows through intelligent networking services. For CSPs ready to expand into new territory, AI also creates a plethora of additional high-value service opportunities that include AI workload hosting, managed edge offerings, compliance, monitoring and security services, and more. Challenged with the high cost and fast pace of innovation, the need to monetize existing investments, the complexity of legacy infrastructure, and constraining regulations, CSPs need to act quickly and partner wisely to catch the AI wave.
Cisco has a proven track record providing secure, scalable networking and infrastructure to the world’s largest service providers and enterprises for over a quarter of a century. Cisco has built a broad set of leading-edge platforms – spanning networking, compute, optics, security, and observability – which are helping providers simplify operations, monetize their networks, and capture emerging AI-driven markets.
“With the growing demand for AI infrastructure, telcos have an opportunity to serve as the backbone of the AI era.”1
McKinsey 2025
AI trends driving new CSP opportunities
As this technological and social revolution continues to unfold, several important trends are rapidly transforming the AI landscape and unlocking new sources of revenue for CSPs. These include the emergence of agentic AI, the rise of small language models (SLMs), a surge in real-time sensor data, and increasing demand for sovereign AI services.
Agentic AI - the emergence of digital employees
The rise of inference and agentic AI are shifting the focus from predominantly centralized mass-scale data centers to a model where data and infrastructure are highly distributed and interconnected. According to Menlo Ventures, 46% of AI processing by 2027 will be inferencing.2 With agentic AI, systems can perceive, reason, act, and learn autonomously to orchestrate complex workflows across different industries and applications. Gartner estimates that by 2028, at least 15% of day-to-day business decisions will be made autonomously through agentic AI machine workflows for rule-based tasks, up from 0% in 2024.3 The result is that a variety of distributed, non-human AI workers – including agents, robots, and even humanoids – will interact with humans, LLMs and inference systems continuously at machine speed and generate data flows that are much more dynamic and less predictable than those generated purely by humans.
46% of AI processing by 2027 will be inferencing.
Menlo Ventures 2024
It’s especially important to recognize the growing need for resiliency. As this “digital employee” era begins, a major challenge will be a growing hyper-dependence on the inference infrastructure. As agentic systems become more multi-faceted and business critical, the challenge – and necessity – of maintaining optimal reliability and security are immense. The integrity and performance of the “central nervous system” connecting AI agents to LLMs will be particularly important. When an agentic AI workflow is disrupted, the productivity of non-human agentic employees goes from 100% to 0% and related business processes and customer experiences are severely impacted.
To support these fundamental characteristics, CSPs have an opportunity to deliver AI-optimized services that ensure consistent low latency, security and hyper-resiliency across all the distributed elements of the agentic workflow. In addition, the ubiquitous reach of CSPs positions them to provide enterprises with crucial end-to-end performance monitoring, predictive analysis, and security of these complex workflows – from the cloud to the edge.
Another emerging trend in AI involves the rise of small language models (SLMs), which are rapidly gaining traction across different industries. Unlike LLMs, which require enormous compute power, SLMs can be built and employed more efficiently and have a much smaller footprint. They are particularly valuable for AI use cases that require instantaneous decision-making and where responses must be delivered in milliseconds.
According to STL partners, the shift to a hybrid architecture that balances centralized and edge compute, creates a potential opportunity for CSPs to offer hosting and deployment of distributed compute infrastructure for SLM inference at sites with existing edge presence or network aggregation points.4 The benefits of this approach include improving operational efficiencies and reliability, minimizing latency, meeting regulatory or data sovereignty requirements, and overcoming the power and space constraints of centralized data centers.
Real-time sensor data is surging
The surge of real-time sensor data used to enhance context, responsiveness, and automation of AI systems, is another major development driving opportunities for CSPs in the last mile. IoT Analytics projects an astonishing 39 billion connected IoT devices by 2030.5 This isn’t just about more devices; it’s also about the explosion of data being generated and processed directly at the edge, right where the action happens. According to Mobile Experts, new AI-assistants will drive an increase in uplink traffic that is unprecedented, exceeding the capacity of current 5G networks as soon as 2028.6
Examples of this include Industry 4.0 and digital industrialization, with AI-enabled IoT and robotics driving new data and connectivity models. This phenomenon extends to diverse industries and use cases, such as patient health-monitoring devices, environmental data streams, and temperature, security, and other data from consumer IoT sensors. According to STL Research, AI will have a noticeable impact on access network traffic, driven by growth in AI-generated video traffic, upstream sensor traffic and the introduction of new enterprise use cases.7 This multi-modal data needs to be shared with distributed agents and LLMs to support learning, inference and process automation.
The importance of this data to enterprises represents another business opportunity for CSPs to create and monetize new services that support new levels of reach, security, scalability, and latency control.
Sovereign AI services are in demand
In many parts of the world, most notably Europe and parts of Asia, concerns about digital sovereignty for AI have risen to the top of the agenda. As demand rises for localized AI, and governments tighten regulations to ensure private data stays within national boundaries or complies with cross-border data transfer regulations, data sovereignty is receiving significant attention. Policy requirements and customer priorities require trust in digital systems with clear and demonstrable control over access to systems and data. This is especially true for industries that are considered “critical infrastructure” – the banks, healthcare providers, public services, and energy networks. For these organizations, the systems must keep running, no matter what. These factors are driving investments in AI infrastructure that can meet stringent security, compliance, performance, and operational requirements.
AI will have a noticeable impact on access network traffic driven by growth in AI-generated video traffic, upstream sensor traffic and the introduction of new enterprise use cases.
STL Partners 2025
The AI ecosystem: infrastructure trends and challenges
These trends, along with other advancements in AI, are proving to be major drivers for AI infrastructure buildouts within massive, centralized AI data centers, smaller regional data centers, and edge environments, as well as for the secure interconnectivity required between these environments. Across the various participants of the ecosystem (Figure 1), AI infrastructure investments continue to grow rapidly, with global capital investment in data center IT equipment forecast to reach as much as $4.7 trillion in aggregate between 2025 and 2030.8 These forecasts include servers, accelerators like GPUs, networking, optics, and storage.
CSPs can play an important part in this exponential market opportunity by developing valuable services to meet the needs of enterprises and the other members of the AI ecosystem. Increasingly, service providers and colocation providers are joining forces with hyperscalers, neoclouds, and sovereign cloud providers to deliver service offerings that meet evolving customer needs.
Established hyperscaler cloud providers like AWS, Google Cloud, Meta, and Azure, as well as newer neocloud providers are making significant investments in AI data centers and AI clusters to address the exploding LLM training demands of AI model builders and the fast-growing inferencing demands of enterprises. By the early 2030s, it’s expected that nearly 11,000 data centres will be in operation by these AI Cloud and colocation providers worldwide to meet this demand.9 In many cases these data centers are being built in remote locations where cheaper land and more sustainable power are available in abundance. Beyond the vast infrastructure demands of their centralized data centers, these organizations need to interconnect extended AI clusters and distributed, often remotely located, AI cloud data centers.
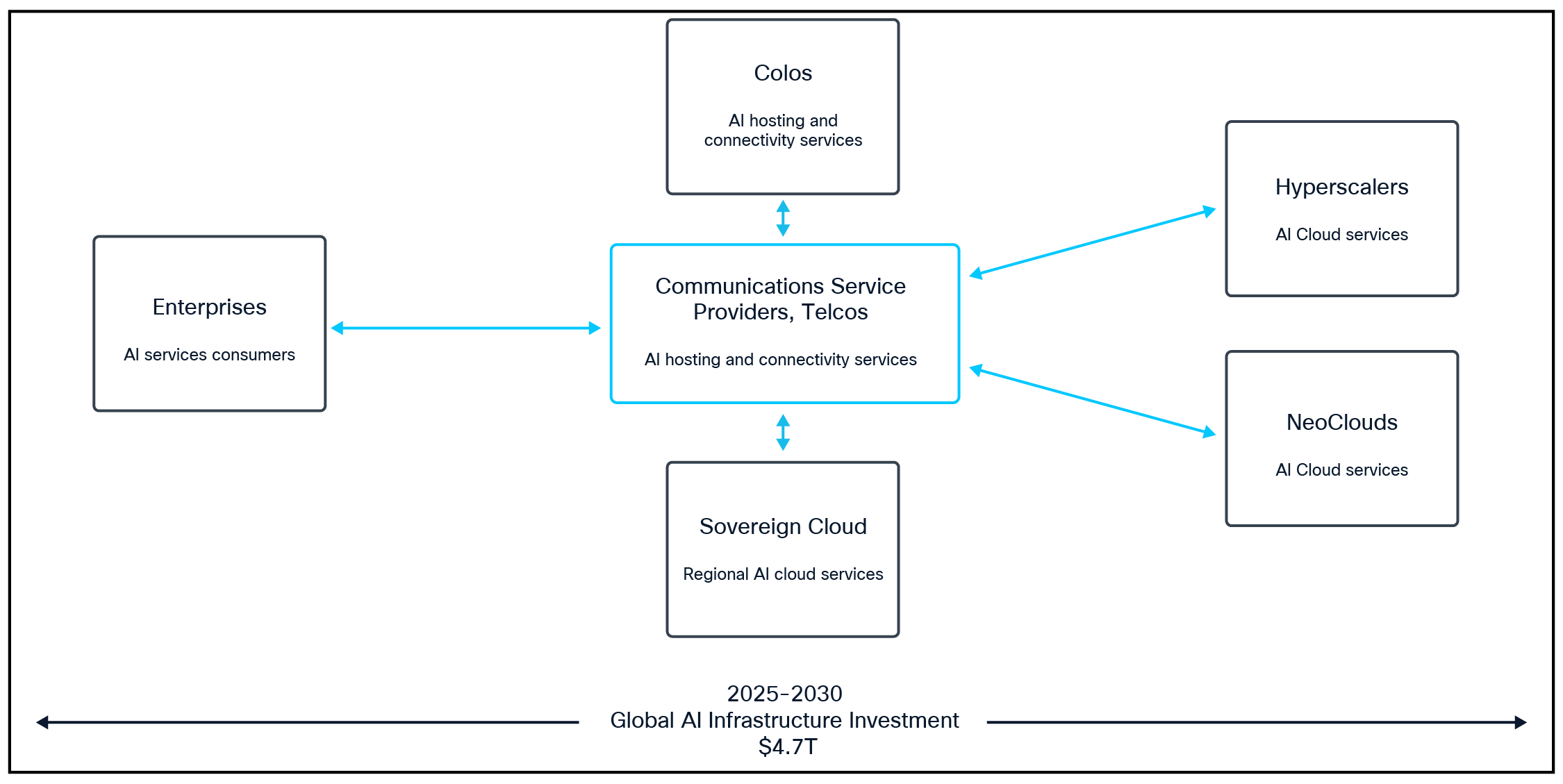
Service Providers: The backbone of the AI ecosystem value chain
Data sovereignty requirements are likewise creating a new segment of local sovereign cloud providers that deliver the highest levels of security and privacy to address specific industry or governmental regulatory and compliance needs. Consumers of these AI cloud services need secure connectivity to access them, often in a hybrid model that combines the organization’s own AI data center and edge infrastructure. This creates an opportunity for CSPs to partner with AI cloud providers to deliver services that provide reliable, efficient, and secure connectivity between their dispersed data centers and to their enterprise customers.
As they ramp up efforts to operationalize AI, including agentic AI, enterprise organizations in every sector also face a complex array of technology challenges. The Cisco Readiness Index 2025 highlights a tension between the 83% of companies that plan to deploy agentic AI and mounting pressures on enterprises that struggle to scale for the complexity that agents introduce.10 Highly distributed AI workflows have very strict performance, latency, security, and privacy requirements, as well as bursty bandwidth demands. Above all, enterprises will need reliability in their AI workflows because in the event of a workflow interruption, the AI-driven processes and digital employees will come to a complete standstill. As a result, organizations need to think carefully where, how, and with whom they want to host and interconnect language models, inference, agents, and sensors.
The industry is still learning the full implications of distributed AI workflows on compute and network infrastructure. However, a consensus is forming that existing data center and network architectures lack the necessary capacity, performance, resilience, and flexibility to support them. According to a recent survey of enterprise organizations, security, privacy, and regulatory compliance are fundamental pain points that represent significant barriers to AI deployments.11 Simultaneously, organizations face a global shortage of AI talent that they need to bridge to deliver on accelerated timelines, uphold quality standards, and remain competitive.
It is critical for CSPs to build the expertise required to understand the fundamental and industry-specific AI infrastructure and governance challenges that their enterprise customers are facing. With this knowledge, they will be well positioned to offer the full range of differentiated services that will help enterprises overcome these challenges.
CSP monetization opportunities and challenges
CSPs can secure their place in the AI value chain by delivering critical AI infrastructure and services that enable enterprises to unlock the full potential of AI and also help AI cloud providers scale to deliver AI services.
Five key avenues to monetization are emerging for CSPs:
1. AI connectivity services;
2. AI data center infrastructure services;
3. Sovereign AI services;
4. Edge AI services; and
5. Security and observability managed services.
Five Key AI Monetization Opportunities for CSPs
CSPs can create the central nervous system for the AI economy by building on their existing core networking competencies and assets to offer AI connectivity services to their customers. There are two main areas related to AI connectivity services.
The first involves providing intelligent AI-optimized connectivity services that can handle unpredictable, chatty, and latency-sensitive AI traffic between millions of proliferating endpoints and agents and multiple inference and LLM instances. As large numbers of AI data centers are increasingly located in less-populated areas with cheaper land and more sustainable energy requirements, there is a growing need for extensive data backhauling, which significantly increases WAN traffic. Cisco is currently observing monthly AI WAN traffic growth of 40%, along with 60% year-over-year AI transaction growth, with AI agents multiplying the numbers of LLM requests per query by 8 to 10 times.12
In anticipation, CSPs can build on existing services to offer AI-optimized IP services that provide connectivity across a mix of cloud data center LLMs, on-premises inference and edge nodes. These services would interconnect SLMs running at the edge to process user prompts in real time; larger models running in the core data center or in the public cloud to provide deeper reasoning; and multiple AI agents that communicate to execute complex tasks autonomously. Multi-agent AI workflows are typically very dynamic and unpredictable, requiring a network that is extraordinarily agile and can sense, predict, and automate changes that support the seamless transport of data. The network must also have the intelligence to deliver differentiated service levels, sovereign paths, and resilience.
By adopting AI-enabled automation and assurance, CSPs can maintain service levels, reliability, and efficiency at scale, in the context of changing traffic flows, making AIOps a critical capability for managing connectivity across cloud, AI data centers, and edge deployments.
Looking forward, CSPs can enhance AI workflows by offering a programmable routing service that automatically directs AI queries and responses between the nearest or most capable model endpoint based on latency, workload, and context. They will also be able to optimize managed services by applying agentic AI models to drastically improve operational efficiencies for their enterprise customers, accelerating dynamic provisioning, reducing costs, and overcoming resource constraints. These and other innovative network services offer new revenue opportunities, while enabling enterprises to benefit from superior performance, flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and security.
The second area involves providing connectivity between AI cloud and/or enterprise AI data centers, a service often called Data Center Interconnect (DCI). Service providers that have traditionally supported wholesale bandwidth and fiber connectivity services are now also addressing the increasing need for connectivity between data center sites – for customers that include hyperscalers, neoclouds and even enterprises. This data-center-to-data-center traffic can be orders of magnitude greater than user-to-datacenter traffic, a trend that is driving the adoption of 400 Gbps coherent pluggable optical modules and fastemerging 800G coherent modules.
A notable emerging DCI use case involves connecting data center AI cluster back-ends with what is termed “scale-across” connectivity. The remarkable growth in scaling of AI training GPU clusters, reaching hundreds of thousands of power-hungry GPUs, has made data center power consumption the primary limiting factor. To mitigate rising power constraints, large AI clusters are being distributed across data centers in two or more locations. To address this requirement service providers can offer advanced interconnect services that leverage innovative deep buffer routing, robust security, and optical technologies.13
According to McKinsey, demand for AI data center capacity will account for 70% of total data center demand by 2030 and is the main driver of a growing facilities deficit.14 At the same time, inference and agentic applications are driving the need for more decentralized AI compute deployments.
Many CSPs own under-utilized data center facilities or central office space with large-scale network hubs, metro connectivity and dark fiber. A growing number are beginning to generate new revenue from these facilities by offering colocation and transport services to enterprises that need to host and connect their own AI workloads. Simultaneously, AI cloud providers are increasingly partnering with CSPs to accelerate access to regional data center facilities and infrastructure, rather than building their own, a process that can take several years to complete. Partnering with hyperscalers or neocloud providers that can bring their AI expertise and AI stack to a CSP hosting facility is becoming increasingly common.
CSPs can also use their facilities to build and also manage dedicated AI infrastructure that encompasses a full compute, storage, and networking stack for hosting small language models and inference applications to generate new revenue streams.
Some may decide to go one step further and build and operate an AI-accelerated compute service like GPU as a Service (GPUaaS) that they can rent on demand to enterprises, start-ups, researchers, and others on a pay-per-use basis. These CSPs will need to deploy state-of-the-art data center facilities and infrastructure and adopt a cloud operating model.
Providing AI infrastructure services is not without its challenges. Many CSP data centers were not built to meet the stringent requirements of large-scale AI clusters, which demand dense power, advanced cooling, and high-bandwidth interconnects. Without upgrades to these facilities, any services offered will be constrained within the current power and cooling envelope. In addition, choosing to deliver AI cloud services comes with considerable investment and uncertainty around return on investment (ROI), and operational and integration complexity.
Demand for AI data center capacity will account for 70% of total data center demand by 2030 and is the main driver of a growing facilities deficit.
McKinsey
In the AI era, digital sovereignty – the ability to have control over your own digital destiny, including the data, hardware, and software that organizations and nations rely on – is critical. Sovereign AI is a comprehensive framework for maintaining complete autonomy and control across the entire AI lifecycle – from raw data acquisition through model training, deployment, inference, and ongoing governance using trusted infrastructure and owned, curated datasets. Data classification is the foundation for selecting the right cloud strategy. By categorizing data from regular to highly confidential, it can be mapped to the appropriate cloud solution – whether public cloud, hybrid cloud, or fully air-gapped environments. This ensures jurisdictional control, encryption, and compliance while maintaining flexibility in managing intellectual property, customer and constituent privacy, and sensitive national security data.
These requirements are prompting sovereign cloud providers, and more recently CSPs, to invest in local sovereign AI offerings by building new regional data centers or upgrading existing ones. CSPs looking to offer these services need to deploy the cloud architecture that meets customers’ compliance needs while balancing factors such as cost, scalability and availability with control, trust, and security.
CSPs can leverage their existing regional and national data center facilities to build and manage secure AI infrastructure services that meet privacy and regulatory needs. With their established distributed infrastructure, they can bring sovereign capabilities closer to the data source, enabling new use cases that hyperscalers, neocloud, and other sovereign cloud providers struggle to serve directly. By combining edge computing and sovereign cloud, they can enable local data processing and retention for AI, IoT, and analytics workloads. Alternatively, some CSPs are partnering with hyperscalers, neocloud, and sovereign cloud providers to host their sovereign cloud stacks in the CSPs’ regional data center facilities.
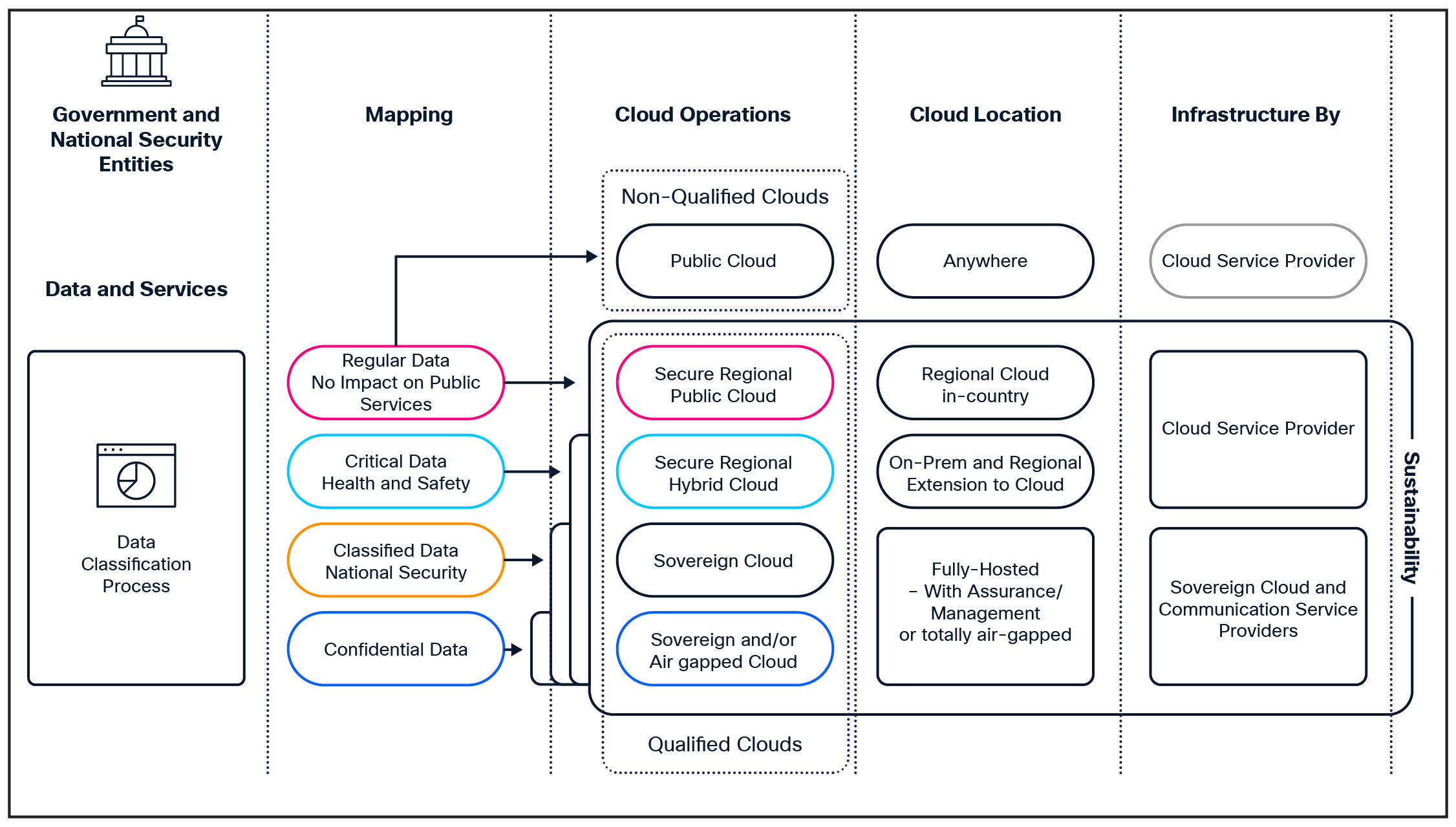
Data classifications and cloud mapping
CSPs are also uniquely positioned to ensure that any data traversing the network outside the data center is routed intelligently and exclusively across compliant network routes and nodes that are deemed to be trusted. For example, a policy can be applied to certain traffic flows to ensure they only traverse router nodes that are assured to be trustworthy. Policy can be set to apply MACsec encryption or quantum-safe cryptography to certain traffic. When combining their own or partner sovereign cloud services with sovereign data in transit, CSPs can assure end-to-end compliance for their customers.
By offering sovereign cloud services, CSPs can enable their customers to use their most sensitive data to develop, train, and run their own AI models in a location they prefer, under their full control, without the risk of exposing that data to third-parties.
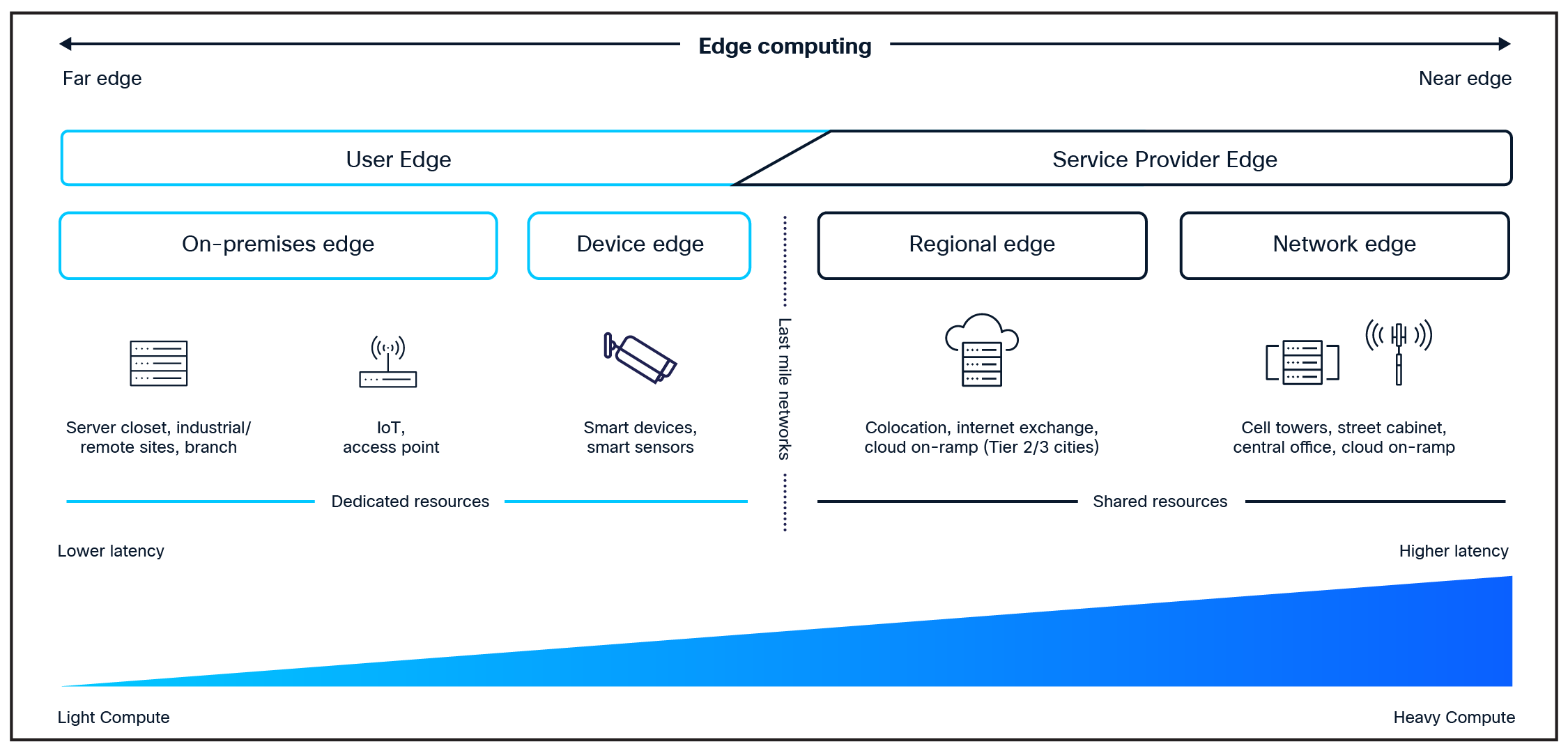
There is a significant ongoing shift in data processing, moving from centralized data centers towards the on-premises edge. IDC projects that global spending on edge computing will reach $261 billion by 2025, driven by the need to process and analyze data locally.15
A good example of the growing importance of the edge is Meta’s own hybrid approach, which is designed to deliver a responsive user experience by combining the localized, low-latency benefits of distributed edge points of presence with the computational power of centralized AI data centers.16 By deploying a distributed global point of presence network and edge computing closer to the end customer, Meta ensures low latency and high performance for user requests and services like video streaming, augmented reality, and AI inference.
In the specific case of edge AI, the increasing demand for real-time data processing, reliability and security is driving a crucial need for more localized processing and networking capabilities. Underscoring the growing importance of edge computing to meet the demands of artificial intelligence, the global edge AI market size is calculated at $25.65 billion in 2025 and is anticipated to reach around $143.06 billion by 2034.17
This growth trajectory presents an emerging monetization opportunity for CSPs as enterprises require their AI inference workloads closer to data sources. However, deploying AI infrastructure at the edge introduces operational complexity, making it challenging for enterprises to securely connect and manage distributed compute environments, especially where local technical expertise and resources like power and cooling are limited. In addition, the rapid evolution of AI models requires continuous lifecycle management, monitoring, and security enforcement, which can strain existing operational capabilities.
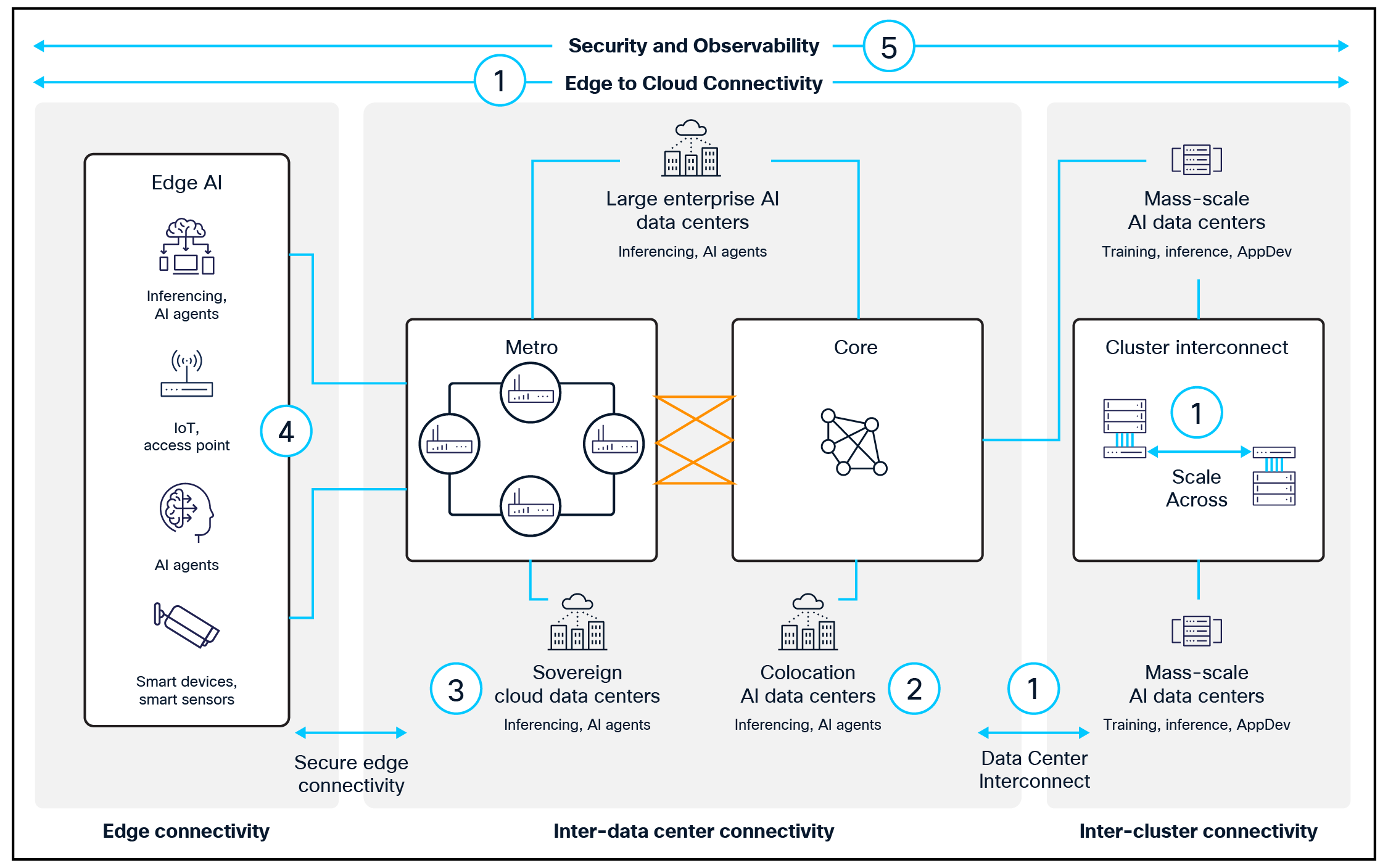
By leveraging their existing infrastructure – such as regional points of presence and the next generation of AI-native wireless networks – CSPs can offer their enterprise customers low-latency, high-bandwidth, and secure AI processing along with connectivity capabilities that centralized cloud architectures alone cannot provide. The service provider edge, which refers to the distributed compute and network infrastructure operated by CSPs near end users – typically at cell sites, regional central offices, metro data centers, and colocation facilities – offers multiple benefits. It can host and manage applications, network functions, and services closer to remote branches and users to reduce latency, improve performance, and enable new edge-native use cases for enterprises and consumers (Figure 4).
The proximity offered by these deployments enables real-time inferencing and supports applications that depend on rapid responsiveness, such as those in healthcare, manufacturing, transportation, and smart cities. By meeting the needs of these and other industry verticals, CSPs can evolve beyond their traditional role as connectivity providers to become managed service providers that deliver tailored AI services, including inferencing at the edge, small language model (SLM) deployments, and infrastructure as a service.
The service provider edge provides a valuable resource for delivering edge AI services
As organizations continue to deploy ever more sophisticated, disaggregated agentic AI solutions, there will be an acute need for comprehensive security and insights into the performance of all elements of these business-critical systems.
Organizations repeatedly identify security as their top roadblock when rolling out their AI projects. Security teams are challenged with finding ways to securely adopt AI throughout their enterprises, while threat actors are using AI to increase the frequency and reduce the cost of launching sophisticated cyberattacks. As AI extends beyond centralized cloud data centers to on-premises and edge environments, this task becomes daunting.
Service providers have a unique opportunity to secure AI workflows end to end at all layers of the infrastructure – beginning with the infrastructure devices themselves, through the networks and data in transit, all the way to the AI models, agents and applications. This can provide a robust foundation for revenue-generating security services in the area that enterprise customers have most concerns.
At the same time, there is an often-over-looked opportunity for service providers to better use the billions of data points that they are collecting daily from their networks, customers, and connected devices. Properly applied, this data can be used as the basis for optimizing internal operations as well as for high-value services that can be offered to enterprises. For example, enterprises will be increasingly challenged with monitoring the health of progressively more complex and distributed AI systems that have the potential to experience deteriorating performance anywhere along the business-critical workflow.
With their reach and expertise in securing and operating highly distributed environments, CSPs are well positioned to deliver security and observability managed services.
How Cisco can help - Cisco AI infrastructure for service providers
With the help of the Cisco AI infrastructure portfolio (Figure 5), CSPs can confidently develop services that capitalize on each of these opportunities. It offers an unparalleled choice of technologies, platforms, and solutions to empower providers to support the diverse business and technical priorities of enterprise customers across all industries. Cisco is helping leading CSPs worldwide accelerate their AI infrastructure deployments from the edge to the cloud. In Saudi Arabia, Jain is partnering with Cisco to bring GPU-as-a-Service to enterprises, delivering scalable AI compute on demand. Lumen leverages Cisco solutions for high-performance data center interconnect, ensuring AI clusters and workloads can be seamlessly connected across sites. Telenor is building its AI Factory with high performance compute and renewable energy to provide sovereign AI services in the Nordic region. Meanwhile, Cisco is partnering with Arelion to optimize AI traffic delivery, improving performance, reliability, and operational efficiency. These partnerships showcase Cisco’s leadership in helping service providers modernize networks, data centers, and customer offerings for the AI era.
With the Cisco Agile Services Networking architecture, CSPs can deliver flexible and efficient cloud-to-edge WAN connectivity. Meanwhile, Cisco coherent optics, optical systems, and new “scale across” systems are optimized for data center interconnect and AI inter-cluster connectivity. Cisco’s robust set of AI data center full-stack solutions and technologies comprising compute, networking, and storage allow CSPs to deliver AI infrastructure and sovereign cloud services to organizations of all sizes. Cisco SD-WAN, Unified Edge, and 5G mobility offerings allow CSPs to deliver differentiated edge AI services across a range of use cases. Cisco security and observability for AI solutions deliver industry-leading solutions that help enterprises protect and optimize their AI workflows and data within and beyond the data center.
The Cisco Silicon One architecture provides the underlying network innovation engine by delivering an extensive range of capacity, scale, and interface options to meet the full spectrum of use cases from cloud to access.
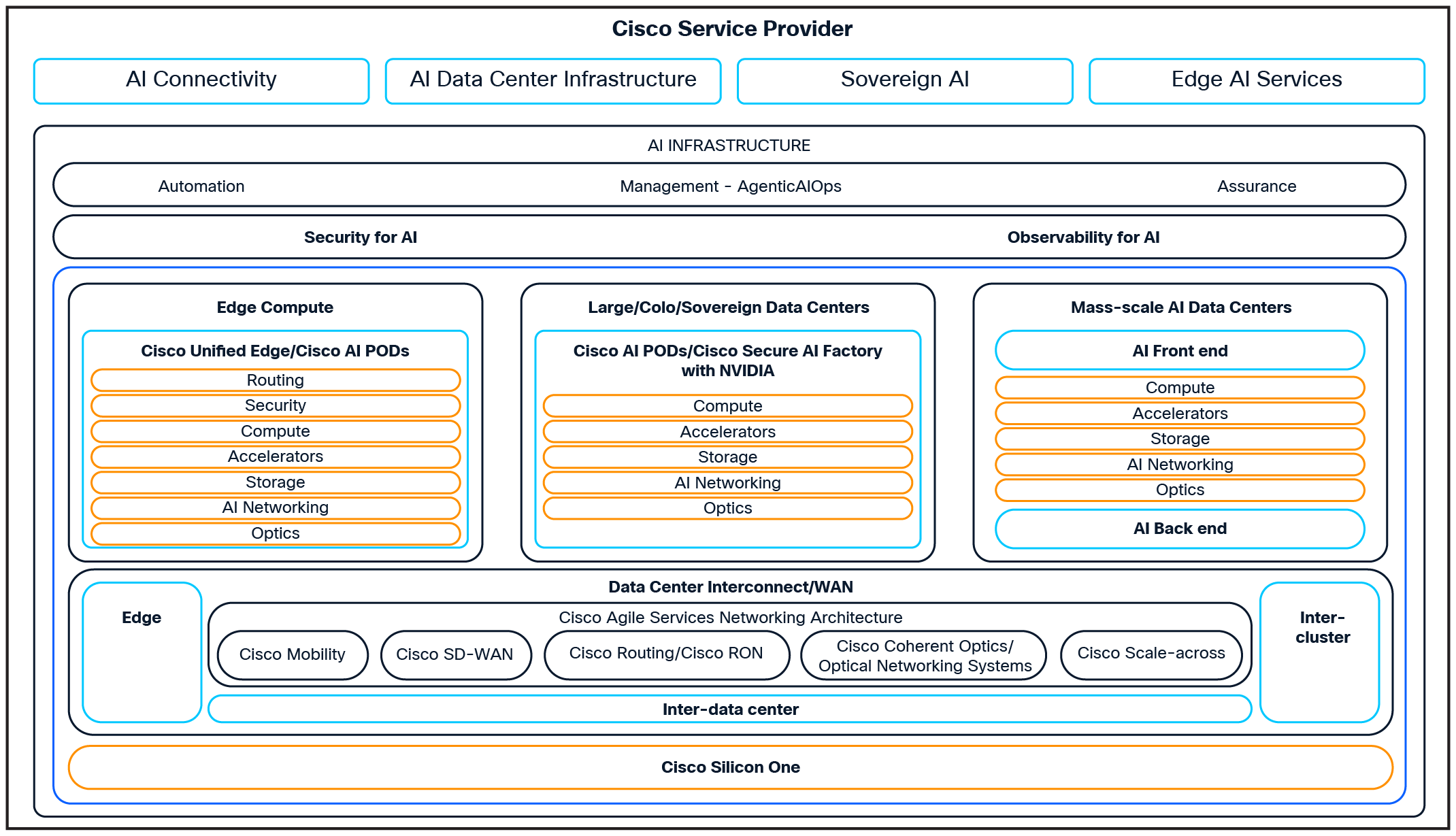
Cisco AI infrastructure portfolio: supporting provider growth opportunities
Cisco Solutions for AI connectivity services
Cisco Agile Services Networking is an architecture for AI connectivity that enables service providers to monetize the delivery of assured services and networking, including providing connectivity for the complete agentic AI workflow, data center interconnect, and “scale-across” connectivity between AI clusters.
With Cisco Agile Services Networking (Figure 6), CSPs can:
● Monetize services deployed closer to end-user demand from a network architecture optimized for intelligent service delivery;
● Remove complexity with simplified networks that converge network layers and services;
● Assure experiences with resilient networks and services enabled by AI-powered automation, observability, and security.
Cisco Agile Services Networking provides a robust and flexible architecture for delivering services over IP from the cloud to the edge. It delivers:
Traffic differentiation, resiliency and agility with flexible any-to-any connectivity and segment routing programmability: Cisco Agile Services Networking enables precise traffic differentiation, ensuring that critical applications receive the required bandwidth and performance. The solution’s built-in resiliency and support for network slicing allow service providers to create dedicated, isolated network segments tailored to different customer or application needs. Flexible any to-any connectivity combined with segment routing programmability empowers dynamic and efficient routing, adapting quickly to changing network demands.
Security and sovereignty of data in-transit, together with quantum-safe MacSec: Cisco’s architecture provides robust protection for data in transit, maintaining confidentiality and integrity across the network. Support for quantum-safe MacSec further ensures that encryption methods remain resilient against emerging threats, including those posed by quantum computing advancements. This approach enables compliance with regional data sovereignty requirements and control over where their data moves.
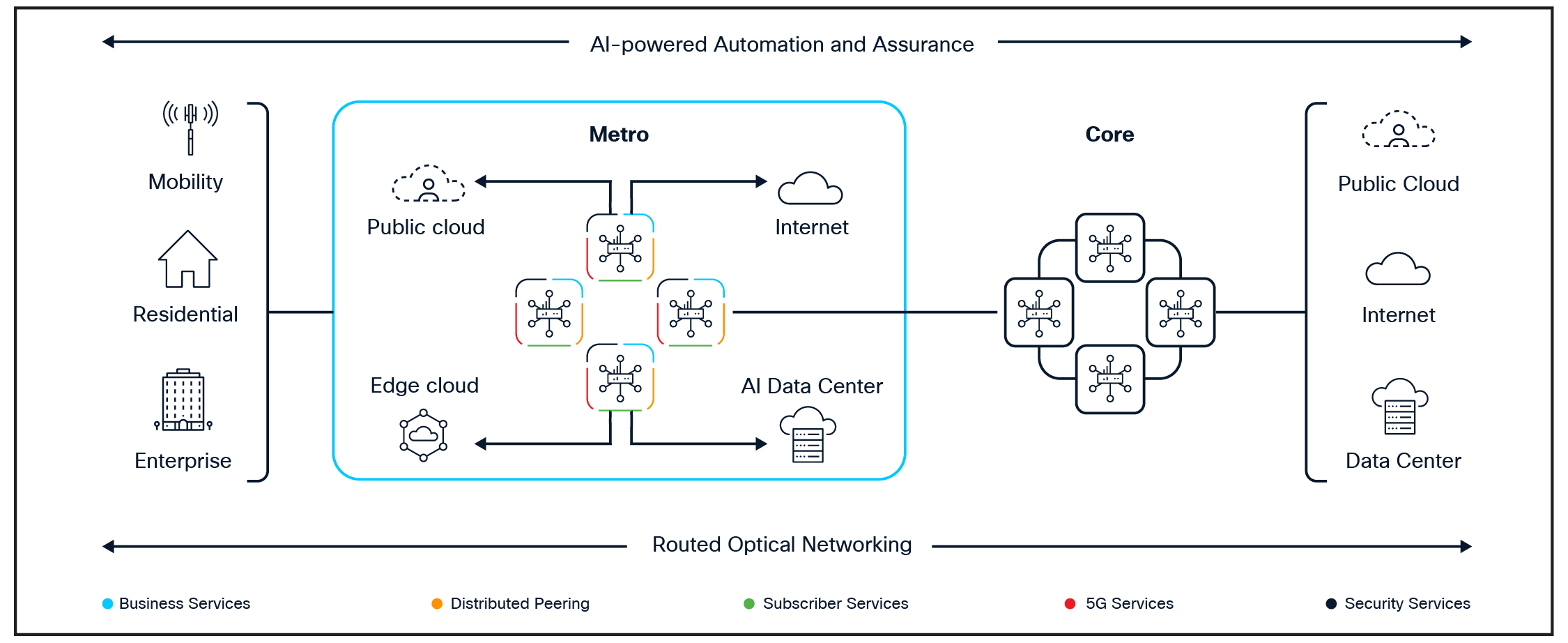
Cisco Agile Services Network Architecture
Sustainability and space optimization with Routed Optical Networking: Routed Optical Networking integrates high-capacity optical transport with IP routing, reducing the need for multiple network layers and simplifying infrastructure. This streamlined approach not only optimizes physical space in data centers and network nodes, but also lowers energy consumption, supporting broader sustainability goals. CSPs benefit from reduced operational costs while contributing to greener, more efficient networks.
Visibility and automated health with advanced telemetry, service health and network health: Advanced telemetry capabilities provide real-time, granular visibility into network and service performance, enabling proactive management and troubleshooting. Automated monitoring of both service health and overall network health helps identify and address issues before they impact customers. This results in improved reliability, faster resolution times, and an enhanced end-user experience.
The growing need for data center interconnects (DCIs) for dispersed AI data centers is ramping up demand for high-speed optical networking. In response, a significant portion of CSPs (58%) plan to deploy of 800G coherent pluggable optics between 2026 and 2028, according to Heavy Reading.18 Cisco Coherent Pluggable Optics, Cisco Routed Optical Networking and Cisco Optical Networking Systems provide the reliable, power-efficient, high-bandwidth solutions CSPs can rely on for connecting two or more AI data centers. Cisco coherent optical modules are enabling the industry’s most complete coverage of DCI applications from shorter reach campus and metro applications to long-haul and even subsea.
For large-scale GPU training that extends AI clusters between data centers, Cisco offers a new and innovative “scale-across” approach. The impact of even minor data disruptions over a large training run can potentially lead the model to converge to a suboptimal or completely erroneous state, rendering long, costly training efforts useless. An analysis from Meta found that a single slow GPU link or failed network connection can reduce cluster performance by up to 40%, leaving expensive GPUs idle and investments stranded.20 With Cisco 8223 Silicon One-based deep buffer routers, which include integrated security and advanced optics, CSPs can confidently extend customers’ large AI training and inference clusters across campus and metro data center locations.
The unpredictable nature of AI makes unprecedented demands in network flexibility, requiring advanced AI-driven network automation. Cisco CrossWorks Network Automation is a comprehensive software platform that helps CSPs simplify and modernize their operations through automation. It enables them to plan, implement, and deploy services faster than ever before, reduce costs, make smarter business decisions, and improve efficiency. Likewise, Cisco Provider Connectivity Assurance is an AIOps platform that delivers comprehensive, real-time visibility and control over network and application performance. As networks evolve in the AI era, Provider Connectivity Assurance delivers end-to-end, service-centric monitoring, enabling CSP IT and network operations teams to proactively detect, diagnose, and resolve issues before they impact business outcomes.
Looking to the future, the Cisco Crosswork Multi-Agentic AI framework powers the growing Cisco portfolio of intelligent features and capabilities. This framework creates a flexible environment where AI agents can be built, deployed, and linked together to address complex problems, dynamic infrastructure requirements and key customer use cases.
As hyperscalers and service providers build out to support AI, Cisco coherent optical modules are already being deployed in these DCI builds, and customers are projecting increasing bandwidth requirements to support these architectures.19
Bill Gartner, Cisco
Cisco Solutions for AI data center infrastructure services
Cisco AI data center infrastructure solutions empower CSPs to host, deploy, secure, and manage full-stack solutions to provide infrastructure services, such as dedicated AI infrastructure services and even GPUaaS to their customers. Cisco helps providers operate reliably, securely, and at peak performance by enabling the integration of Cisco’s purpose-built AI security and observability suites at every layer. Cisco AI data center solutions enable CSPs to maximize GPU scale, performance, and efficiency and minimize job completion times, building on the industry’s highest-performing, non-blocking Ethernet network infrastructure.
For providers that want to follow specific guidelines from NVIDIA, Cisco’s silicon, switches, and full-stack solutions support NVIDIA enterprise and cloud partner reference architectures and designs. Cisco Secure AI Factory with NVIDIA (Figure 7) is a secure, high-performance AI infrastructure that integrates security, observability, networking, compute, optics, AI software, and storage into a scalable full-stack system. Featuring built-in security at every layer, superior networking, and seamless integration with the NVIDIA AI Enterprise software platform, it is purpose-built to streamline the development, deployment, and protection of AI workloads.
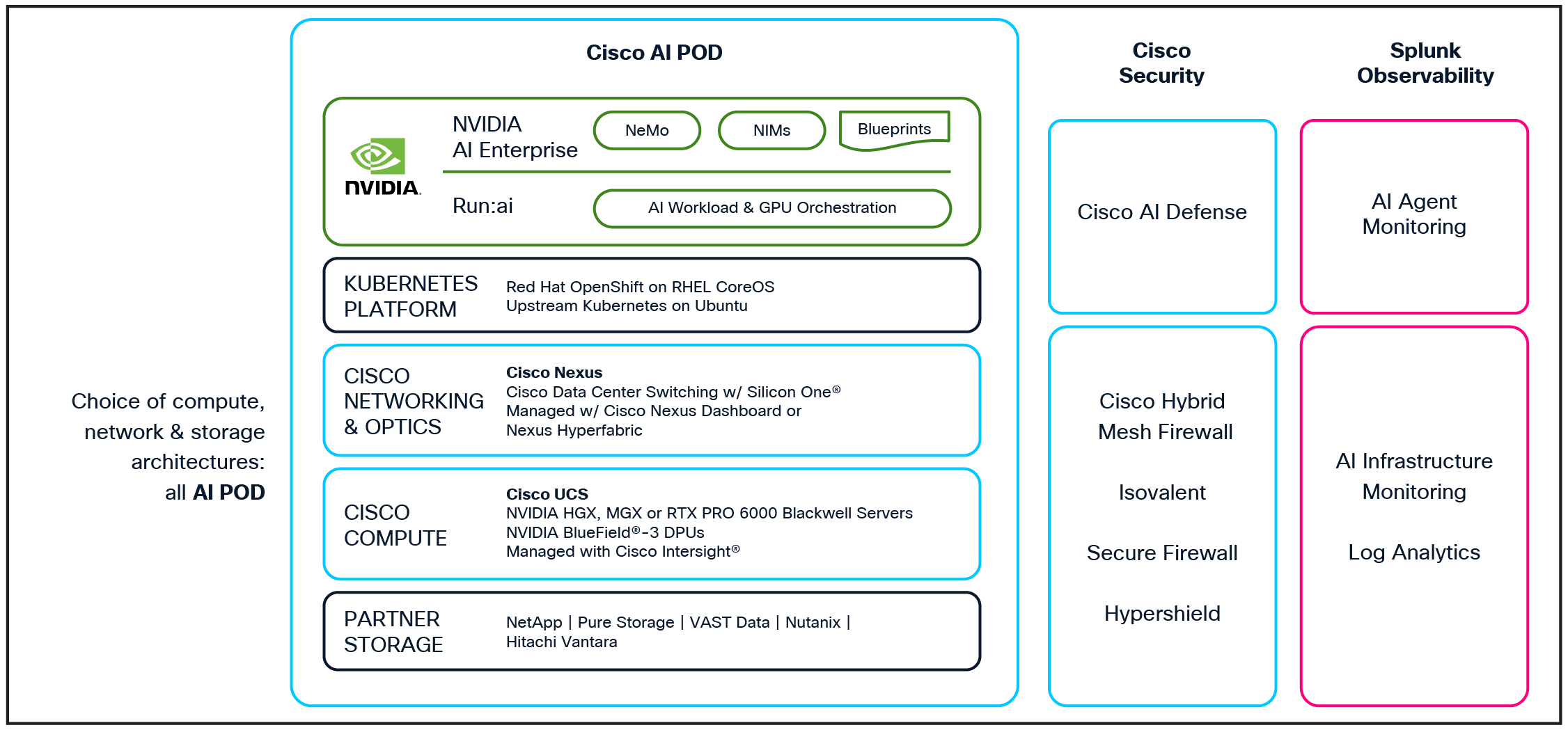
Cisco Secure AI Factory with NVIDIA
The Cisco Secure AI Factory with NVIDIA offers unparalleled deployment flexibility through pre-validated, modular stacks delivered via a modular Cisco AI POD approach or integrated turnkey stacks delivered by Cisco Nexus Hyperfabric AI. Cisco AI-PODs provide modular, secure, and pre-validated full-stack building blocks designed for simplicity, flexibility, and rapid deployment. They integrate Cisco compute (UCS servers), high-performance Cisco Nexus networking, leading GPU/AI platforms, and a choice of partner storage systems into a unified, configurable system. This modular design enables providers to start small and expand incrementally with scalable units, ensuring predictable performance and effortless expansion for diverse AI applications. Providers can operationalize GPUaaS using Cisco AI-POD system offerings by exposing the infrastructure through self-service, multitenant consumption models offered by Cisco partners like Rafay.
As an integral part of these full-stack solutions, Cisco AI Networking spans the entire AI networking infrastructure continuum from silicon to software. Built on Cisco Silicon One programmable ASICs, the Cisco Nexus 9300 series and Cisco 8100 series switches are engineered to meet the demands of mass-scale AI workloads. Support for high-density 400G and 800G fabrics and a massive 512 radix makes them ideal for scalable, next-generation leaf-and-spine network designs. These switches use advanced load balancing, innovative congestion management, and flow control algorithms to help improve job completion times (JCTs). They also provide the low latency and telemetry required to meet the design and operational requirements of AI fabrics.
Cisco has also partnered with NVIDIA to deliver the new Cisco Nexus 9100 switch with NVIDIA Spectrum-X switch silicon, which offers high-performance switching for AI-scale deployments. This Cisco platform is the only third-party switching platform to achieve NVIDIA Cloud Partner (NCP) Reference Architecture compliance.
Cisco Solutions for Sovereign AI services
Cisco has built a Sovereign Cloud Operating Framework to meet diverse sovereignty needs. This framework allows for secure and compliant cloud operations tailored to specific regulatory requirements. It ensures policy-driven governance and centralized management, fostering greater control and operational efficiency. This framework supports multiple sovereign cloud models – including air-gapped, hybrid cloud, and multicloud – allowing organizations to map data classification levels from regular to highly confidential (Figure 8) to appropriate cloud environments. It ensures jurisdictional control, encryption, compliance, and flexibility in managing intellectual property, privacy, and sensitive national security data.
Security is embedded at every layer of Cisco’s sovereign AI cloud solutions. The framework (Figure 9) incorporates zero trust principles, encryption, access control, confidential computing, and privacy-enhancing technologies to protect AI workloads. The solutions integrate security, networking, compute, optics, AI software, and storage into a scalable full-stack system with built-in security. This ensures that AI model training, deployment, and inference occur within a secure and compliant environment.
Cisco Secure AI Factory with NVIDIA is a cornerstone of sovereign AI cloud infrastructure. It enables CSPs to build and manage sovereign AI infrastructure services that meet stringent privacy, regulatory, and performance requirements.
Cisco’s zero trust approach extends to data in transit with quantum-safe MACsec encryption along with intelligent routing policies that enforce data sovereignty by ensuring traffic only traverses trusted, compliant network nodes.
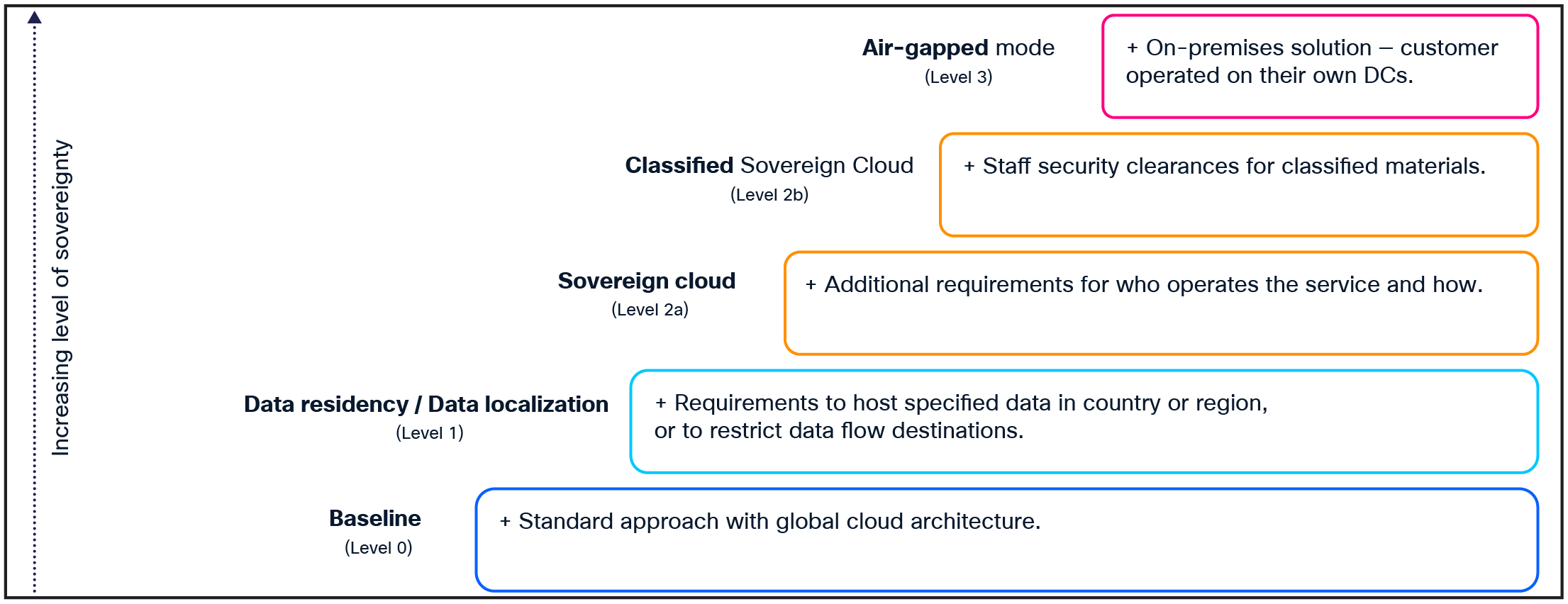
Data sovereignty spectrum – Sovereign AI Cloud
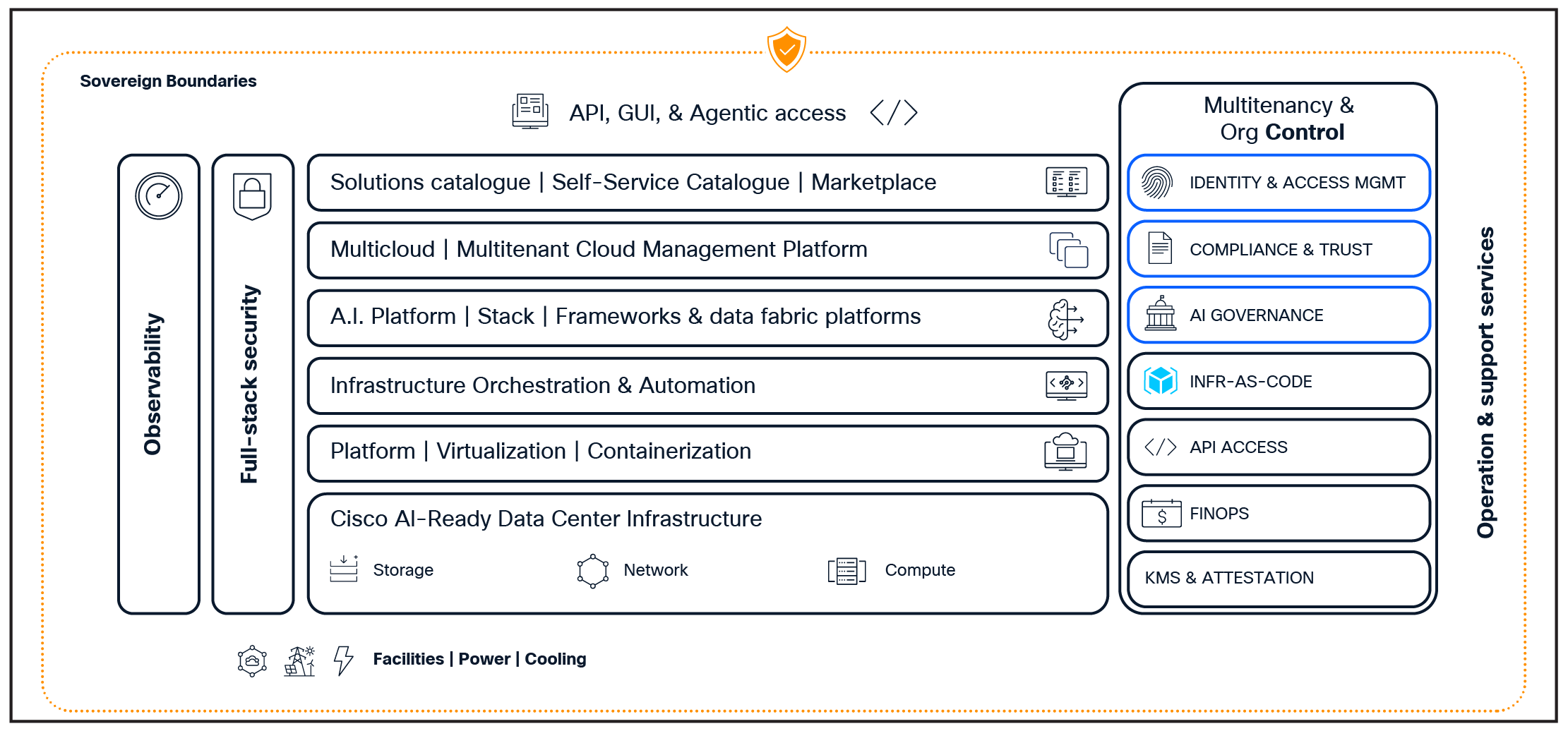
Cisco Sovereign AI Cloud Functional Reference Architecture
To secure data in transit, Cisco Agile Services Networking delivers intelligent, segment routing programmability and flexible any-to-any connectivity. This architecture supports traffic differentiation, network slicing for isolated segments, and quantum-safe MACsec encryption, enabling compliance with regional data sovereignty mandates.
Cisco’s Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) framework complements sovereign cloud services by providing unified, end-to-end security and policy enforcement across the cloud-to-edge continuum. It delivers advanced zero trust network access (ZTNA), secure private access, and cloud-delivered firewall capabilities, ensuring protection of sensitive AI data and compliance with data sovereignty requirements.
Together, these technologies enable CSPs to offer sovereign AI cloud services that empower enterprise customers to develop, train, and run AI models within their preferred jurisdictions under full control, without exposing sensitive data to third parties. CSPs can leverage their regional data centers and distributed infrastructure to bring sovereign capabilities closer to data sources, combining edge computing and sovereign cloud to support AI, IoT, and analytics workloads securely and efficiently.
This comprehensive sovereign AI cloud solution positions CSPs as trusted partners in the AI ecosystem, delivering secure, compliant, high-performance AI infrastructure and connectivity that meet the evolving demands of enterprises and governments worldwide.
Cisco continues to work with customers on implementing AI infrastructure for sovereign cloud initiatives. In 2025, Cisco partnered with the AI company Humain to build foundational sovereign AI infrastructure for the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. This initiative includes sovereign cloud data centers featuring Cisco Silicon One-based fabrics optimized for nonblocking AI workloads, ensuring high performance and scalability for AI applications under full local control.
Cisco Solutions for Edge AI services
CSPs are uniquely positioned to capitalize on the growing demand for edge computing. Specifically, providers can deliver edge AI services effectively by leveraging any combination of Cisco AI PODs, Cisco Unified Edge, Cisco Agile Services Networking, Cisco AI-native wireless networks, and SD-WAN managed services, to create a comprehensive, scalable, and secure edge AI infrastructure.
Cisco AI PODs provide pre-validated, modular full-stack AI infrastructure that allows CSPs to accelerate AI adoption at the edge, while meeting the demands of distributed AI applications with low-latency and high bandwidth.
Providers can also offer enterprise edge AI infrastructure managed services with the new Cisco Unified Edge – an integrated, AI-ready compute system designed specifically for the edge that includes built-in support for storage, networking, security and analytics. Zero-touch deployment and centralized cloud management make it well suited for offering managed services to customers with large numbers of branch sites.
Cisco Agile Services Networking also plays a critical role in providing intelligent connectivity for Edge AI services to ensure resilient, low-latency, and secure transport of AI traffic from edge locations to data centers and cloud environments, addressing the unique traffic patterns and performance requirements of AI workloads.
To complement the physical infrastructure and intelligent networking, CSPs can offer Cisco SD-WAN managed services to provide flexible overlay connectivity that securely and efficiently connects distributed Edge AI workloads to cloud resources. SD-WAN optimizes network resource utilization by intelligently routing traffic based on application needs and network conditions, ensuring consistent performance for AI inferencing workflows. In particular, by integrating SD-WAN overlay network application classification with transport network traffic engineering, CSPs can enforce policy to deliver better levels of service assurance for AI flows from edge to cloud.
The integration of SD-WAN into Cisco’s secure access service edge (SASE) framework provides end-to-end security and policy enforcement across the cloud-to-edge continuum, protecting sensitive AI data and maintaining compliance with data sovereignty requirements.
Agentic and physical AI often rely on the connectivity of a large number of intelligent end-devices – such as robots, industrial equipment, vehicles, sensors and cameras. These agents learn, reason, and act, requiring real-time data and decision-making. To achieve this ubiquitous, always-on connectivity at scale, Cisco is pioneering AI native wireless networks by infusing AI into the fabric of mobile networks. This gives mobile networks the ability to sense, learn and act in real time, empowering service providers to deliver high-value services that enable agentic and physical AI deployments.
Cisco’s wireless for AI architecture transforms the network into a distributed AI engine that can dynamically allocate compute, storage, network and wireless spectrum to sustain inference traffic. Cisco’s distributed User Plane Function (dUPF), integrated with the NVIDIA accelerated computing platform, brings mobile data processing to the network edge, enabling ultra-low latency, security, and resilient performance so AI agents can sense, decide, and act in real-time. By using this architecture, providers can deliver services that keep traffic local, optimize bandwidth, safeguard sensitive data, and deliver trusted outcomes over mission-critical 5G Advanced and 6G mobile infrastructure.
These technologies provide CSPs with a choice of options to deliver differentiated, programmable Edge AI services that meet enterprise demands for responsiveness, security, and scalability. This positions CSPs as key enablers in the AI ecosystem, accelerating the adoption of Edge AI and unlocking new revenue streams.
Cisco Solutions for Security and observability managed services for AI
Cisco equips CSPs to deliver a powerful suite of security and observability managed services designed to help organizations better protect data and eliminate blind spots across and between their AI stack – from application to infrastructure to network.
Cisco Security Cloud Control is a unified, AI-powered management platform that provides centralized oversight and multi-organization management through a single pane of glass for navigating across managed entities, subscriptions, and access controls. It empowers service providers to offer managed security services to enterprises, reducing administrative overhead and streamlining customer onboarding and permission structures. It provides centralized management for Cisco’s Hybrid Mesh Firewall, a distributed security solution optimized to block advanced threats and protect against vulnerabilities, including those in AI models. It also enables zero-trust segmentation across data centers, clouds, and edge sites and uses network and workload identities to create micro-perimeters, applying segmentation and AI-driven threat protection at the app edge and within workloads. This hyper-distributed security enables organizations to define policy centrally and enforce it everywhere. Policy can be centrally managed across Cisco firewalls, Cisco Smart Switches, Cisco Hypershield, Cisco Isovalent, workload agents leveraging eBPF, and even third-party firewalls.
With Splunk and AppDynamics, Cisco provides Observability for AI for unparalleled visibility into every layer of the environment, including GPU infrastructure, GenAI, LLM outputs, and AI applications. It allows organizations to monitor performance and directly link technical insights to business outcomes and scale AI across hybrid, on-prem, and cloud environments. Likewise, Cisco ThousandEyes provides visibility into cloud and internet connectivity, helping providers better anticipate problems, accelerate response, and deliver always-on digital experiences. With Cisco Provider Connectivity Assurance (PCA), CSPs can deliver the most comprehensive visibility for end-to-end network performance by continuously measuring latency, jitter, throughput, and packet loss metrics and benchmarking performance for large language models, inference, training, and agent traffic. PCA flags anomalies early before AI processing is disrupted.
With Splunk IT Service Intelligence organizations can correlate and analyze all the data to attain AI-driven incident prediction, detection, and resolution all from one place.
Providers will need to prioritize the services that make the most business sense based on their current assets, skill sets, market conditions, and business strategy. For most providers, the starting point needs to be ensuring the network provides the foundational platform with the capacity, operational efficiency, agility, and security required to deliver the end-to-end service levels and experiences required in the AI era. Once that foundation is in place, providers will have more freedom to embrace other opportunities. Figure 10 shows an example of a possible roadmap of a CSP that has chosen to expand from the core network infrastructure to optimized AI connectivity services, data center services, sovereign cloud, and edge services.
While having a holistic AI blueprint plan is important, providers should not wait to take advantage of near-term opportunities, since the market is changing quickly and real experience will be a critical factor in developing new revenue streams.
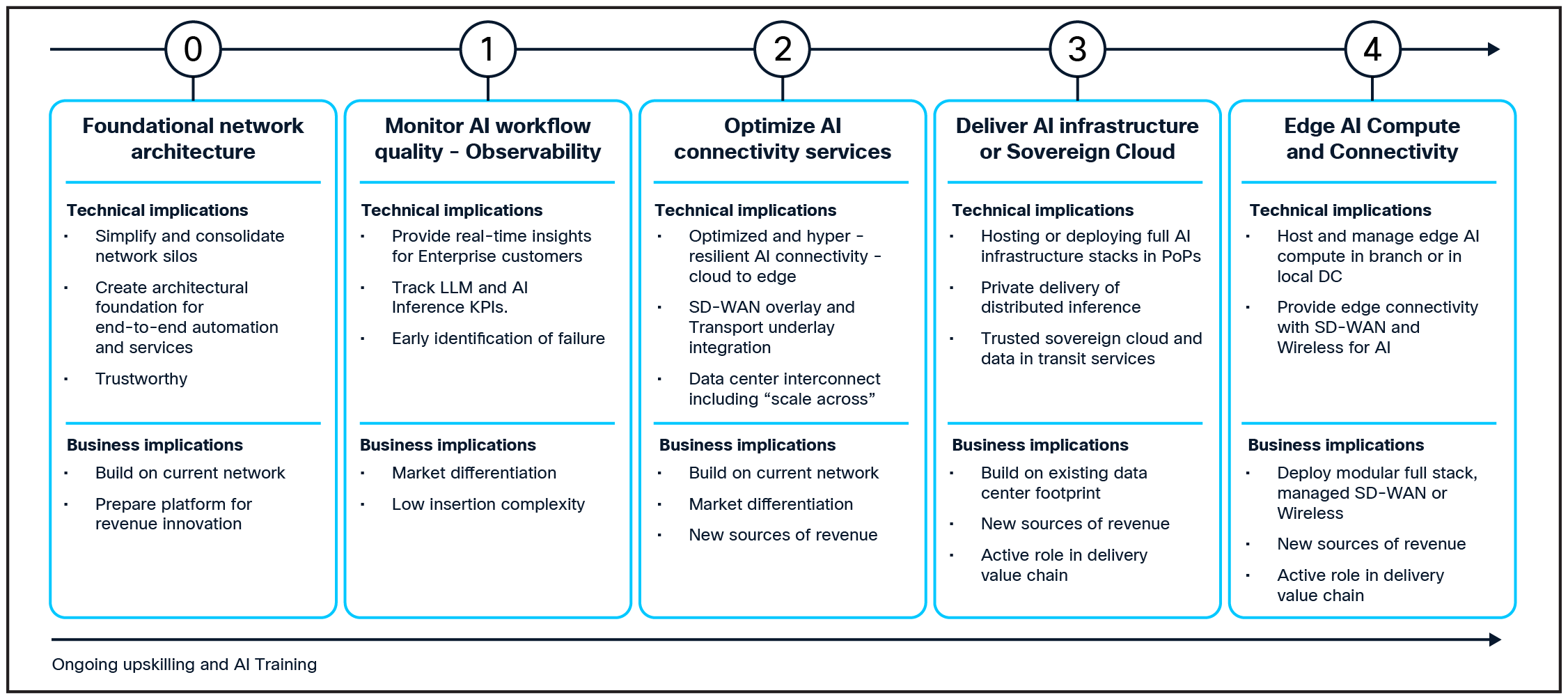
Example of “CSP Services for AI” Roadmap
As AI continues to dramatically reshape the technology landscape, communications service providers (CSPs) stand at a crossroads. The convergence of a multitude of factors – such as the rise of agentic AI, changing traffic patterns, near universal AI adoption among enterprises, and the tightening of data sovereignty regulations – presents an unprecedented opportunity for CSPs to transform their infrastructure into a foundation for innovation and revenue growth. Cisco’s proven track record in secure, scalable networking and infrastructure – trusted by the world’s largest service providers and enterprises for over 25 years – provides the ideal platforms for providers seeking to simplify operations, monetize their networks, and capture emerging AI-driven markets.
By partnering with Cisco, CSPs can build the critical infrastructure necessary for the AI era, and develop the agility and AI expertise required to lead in this transformation. Cisco’s comprehensive AI infrastructure portfolio, which spans Cisco-built silicon, networking, compute, optics, routing, security, and observability, empowers providers to deliver differentiated, high-value services. These services include AI connectivity, data center infrastructure, edge AI, and sovereign cloud. With Cisco’s global enterprise reach and deep ecosystem of technology partners, providers gain maximum flexibility and choice to design services that meet the performance, reliability, and trust requirements of modern AI workloads.
As AI systems increasingly depend on autonomous agents for business-critical operations, the importance of resilient, secure, and high-performance infrastructure can’t be overstated. A momentary disruption can bring AI-driven productivity to a standstill – making visibility, reliability, and security essential differentiators. Service providers, working alongside Cisco, are uniquely positioned to deliver end-to-end AI observability and security services – from the cloud to the edge and everywhere in between.
AI offers an extraordinary opportunity for service providers to play a central and transformative role. In collaboration with Cisco, providers have the key to unlocking new revenue streams by turning networks into platforms for innovation, growth, and lasting value in the AI economy.
Explore how the Cisco AI infrastructure portfolio can help your organization grow your revenue here.
1AI infrastructure: A new growth avenue for telco operators, McKinsey, February 2025.
22024: State of GenAI in the Enterprise, Menlo Ventures, November 2024.
3Intelligent Agents in AI Really Can Work Alone. Here’s How., Gartner, October 2024.
4.How can telcos become more relevant enablers of AI?, STL Partners, June 2025.
5Connected IoT device market, IoT Analytics, October 2025.
6AI will spike Uplink Traffic, Mobile Experts, September 2024.
7How can telcos become more relevant enablers of AI?, STL Partners, June 2025.
8The cost of compute: A $7 trillion race to scale data centers, McKinsey, April 2025.
9AI Infrastructure: A new growth opportunity for telco operators, McKinsey, February 2025.
10Cisco AI Readiness Index 2025, Cisco, October 2025.
11Enterprise AI: What are the best opportunities for telcos? STL Partners September 2025.
12Openrouter.ai/rankings and Cisco Provider Connectivity Assurance metrics, 2025.
13The New Benchmark for Distributed AI Networking, Cisco blog, October 2025.
14AI Infrastructure: A new growth opportunity for telco operators, McKinsey & Company, February 2025.
15Worldwide Edge Spending Guide, IDC, March 2025.
16Meta’s Hyperscale Infrastructure: Overview and Insights, Communications of the ACM, February 2025.
17Edge AI Market Size, Share and Trends 2025 to 2034, Precedence Research, November 2025.
18IP over DWDM Reality Check: 2025 Heavy Reading Survey Results, Heavy Reading, August 2025.
19Transforming Infrastructure for the AI Era, Bill Gartner, Cisco Blog, Sept 2025.
20Special Requirements for Optics in AI Clusters – Meta, Lightcounting, August 2024.