-
Cisco MDS 9000 Family Fabric Manager Configuration Guide, Release 2.x
-
New and Changed Information
-
Index
-
Preface
- Part 1 - Fabric Manager Applications
- Part 2 - Cisco MDS SAN-OS Installation and Configuration Files
-
Part 3 - Switch Configuration
-
Cisco Fabric Services
-
VSAN Configuration
-
Dynamic VSAN Configuration
-
Zone Configuration
-
Inter-VSAN Routing Configuration
-
PortChannel Configuration
-
Interface Configuration
-
FCIP Configuration
-
Configuring the SAN Extension Tuner
-
iSCSI configuration
-
FICON Configuration
-
Configuring Intelligent Storage Services
-
Additional Configuration
-
- Part 4 - Security Configuration
- Part 5 - Network and Performance Monitoring
- Part 6 - Troubleshooting
-
GUI/CLI Usage Chart
-
Interface Nonoperational Reason Codes
-
Managing Cisco FabricWare
-
Table Of Contents
PortChannel Configuration
PortChannels refer to the aggregation of multiple physical interfaces into one logical interface to provide higher aggregated bandwidth, load balancing, and link redundancy. PortChannels can connect to interfaces across switching modules, so a failure of a switching module cannot bring down the PortChannel link.
This chapter describes how to use the PortChannel wizard to configure PortChannels. This chapter contains the following sections:
PortChannel Functionality
A PortChannel has the following functionality:
•
Provides a point-to-point connection over ISL (E ports) or EISL (TE ports). Multiple links can be combined into a PortChannel.
•
Increases the aggregate bandwidth on an ISL by distributing traffic among all functional links in the channel.
•
Load balances across multiple links and maintains optimum bandwidth utilization. Load balancing is based on the source ID, destination ID, and exchange ID (OX ID).
•
Provides high availability on an ISL. If one link fails, traffic previously carried on this link is switched to the remaining links. If a link goes down in a PortChannel, the upper protocol is not aware of it. To the upper protocol, the link is still there, although the bandwidth is diminished. The routing tables are not affected by link failure. PortChannels may contain up to 16 physical links and may span multiple modules for added high availability.
PortChanneling and trunking are used separately across an ISL:
•
PortChanneling, which enables several links to be combined into one aggregated link, can be done between E ports and TE ports.
•
Trunking, which permits carrying traffic on multiple VSANs between switches, can be done only between TE ports.
The Cisco MDS 9000 Family of switches supports 128 PortChannels with 16 interfaces per PortChannel. A PortChannel number refers to the unique (to each switch) identifier associated with each channel group. This number ranges from 1 to 128.
Using the PortChannel Wizard
To create a PortChannel with the PortChannel Wizard in Fabric Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the PortChannel Wizard icon in the toolbar (see Figure 17-1).
You see the first PortChannel Wizard screen.
Figure 17-1 PortChannel Wizard Icon
Step 2
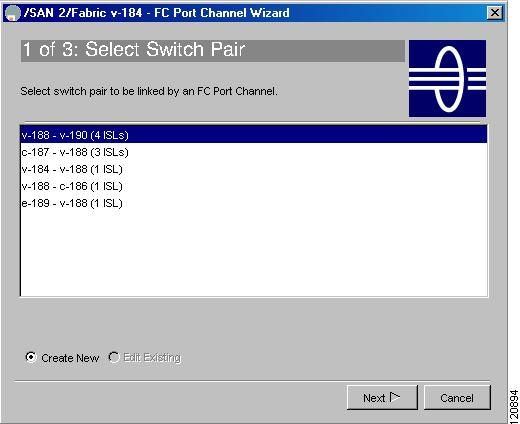
Select a switch pair. Figure 17-2 shows a list of the switch pairs.
Figure 17-2 Select Switch Pairs
Step 3
Click Next.
Step 4
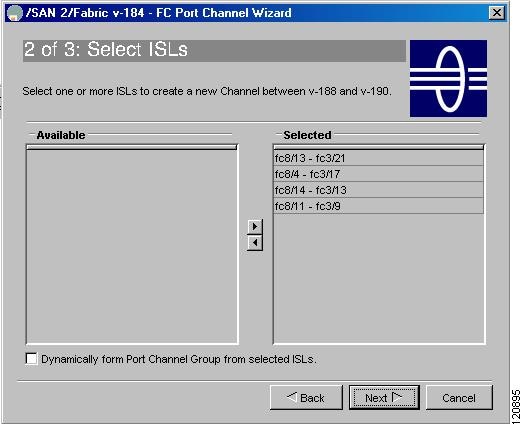
Select the ISLs.
Figure 17-3 shows a list of the ISLs.
Figure 17-3 Select ISLs
Step 5
Optionally, check the Dynamically form Port Channel Group from selected ISLs check box if you want to dynamically create the PortChannel and make the ISL properties identical for Admin, Trunk, Speed, and VSAN attributes.
Step 6
Click Next.
Step 7
If you chose to dynamically form a portChannel from selected ISLs, you see the the final PortChannel Wizard screen as shown in Figure 17-4. Set the VSAN List and TrunkMode and proceed to Step 11.
Figure 17-4 Dynamically Form a PortChannel
Step 8
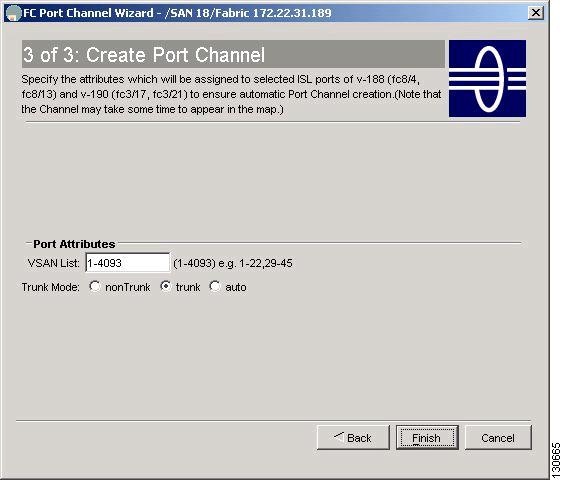
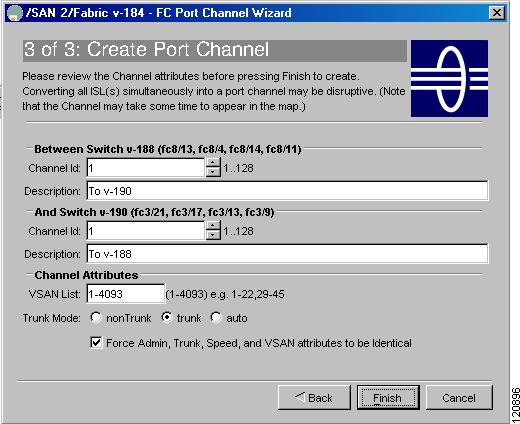
If you did not choose to dynamically form a PortChannel, you see the third PortChannel Wizard screen as shown in Figure 17-5.
Figure 17-5 Create a PortChannel
Step 9
Change the channel ID or description for each switch, if necessary.
Step 10
Review the attributes at the bottom of the screen, and set them if applicable.
The following attributes are shown in Figure 17-5:
•
VSAN List—The list of VSANs to which the ISLs belong.
•
Trunk Mode—You can enable trunking on the links in the PortChannel. Select trunking if your link is between TE ports. Select nontrunking if your link is between E ports (for example, if your link is between an MDS switch and another vendor's switch). Select auto if you are not sure.
•
Force Admin, Trunk, Speed, and VSAN attributes to be identical—This ensures that the same parameter settings are used in all physical ports in the channel. If these settings are not identical, the ports cannot become part of the PortChannel.
Step 11
Click OK.
The PortChannel is created. Note that it may take a few minutes before the new PortChannel is visible in the Fabric pane.
Modifying PortChannels
To modify an existing PortChannel configuration using Fabric Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1
Choose ISLs > Port Channels from the Physical Attributes Pane. You see the PortChannels configured in the Information pane.
Step 2
Choose the Channels to modify an existing PortChannel.
Step 3
Choose the Protocols tab to change the mode for an existing PortChannel.
Step 4
Click the Apply Changes icon to save any modifications or click Undo Changes to discard any changes.

 Feedback
Feedback