-
Cisco MDS 9000 Family Fabric Manager Configuration Guide, Release 2.x
-
New and Changed Information
-
Index
-
Preface
- Part 1 - Fabric Manager Applications
- Part 2 - Cisco MDS SAN-OS Installation and Configuration Files
-
Part 3 - Switch Configuration
-
Cisco Fabric Services
-
VSAN Configuration
-
Dynamic VSAN Configuration
-
Zone Configuration
-
Inter-VSAN Routing Configuration
-
PortChannel Configuration
-
Interface Configuration
-
FCIP Configuration
-
Configuring the SAN Extension Tuner
-
iSCSI configuration
-
FICON Configuration
-
Configuring Intelligent Storage Services
-
Additional Configuration
-
- Part 4 - Security Configuration
- Part 5 - Network and Performance Monitoring
- Part 6 - Troubleshooting
-
GUI/CLI Usage Chart
-
Interface Nonoperational Reason Codes
-
Managing Cisco FabricWare
-
Table Of Contents
Using Cisco Traffic Analyzer with Performance Manager
Understanding Cisco Traffic Analyzer
Using Cisco Traffic Analyzer with Fabric Manager Web Services
Installing and Launching Cisco Traffic Analyzer
Configuring Cisco Traffic Analyzer
Discovering Cisco Traffic Analyzer from Fabric Manager Web Services
Accessing Cisco Traffic Analyzer from Fabric Manager Web Services
Configuring Cisco Traffic Analyzer for Fabric Manager Releases Prior to 2.1(2)
Cisco Traffic Analyzer
Cisco Traffic Analyzer is a version of network top (ntop) software that is modified to support Fibre Channel and SCSI.
This chapter contains the following sections:
•
Using Cisco Traffic Analyzer with Performance Manager
•
Using Cisco Traffic Analyzer with Fabric Manager Web Services
•
Configuring Cisco Traffic Analyzer for Fabric Manager Releases Prior to 2.1(2)
Using Cisco Traffic Analyzer with Performance Manager
Performance Manager works in conjunction with Cisco Traffic Analyzer to monitor and manage the traffic on your fabric. Using Cisco Traffic Analyzer with Performance Manager requires the following components:
•
A configured Fibre Channel Switched Port Analyzer (SPAN) destination (SD) port to forward Fibre Channel traffic.
•
A Port Analyzer Adapter 2 (PAA-2) to convert the Fibre Channel traffic to Ethernet traffic.
•
Cisco Traffic Analyzer software to analyze the traffic from the PAA-2.
Figure 8-1 shows how Performance Manager works with Cisco Traffic Analyzer to monitor traffic on your fabric.
Figure 8-1 Overview of Performance Manager Working with Cisco Traffic Analyzer
Understanding SPAN
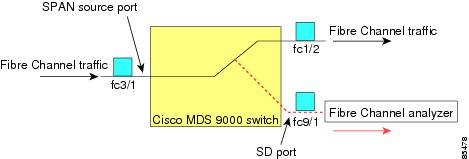
The SPAN feature is specific to switches in the Cisco MDS 9000 Family. It monitors network traffic though a Fibre Channel interface. Traffic through any Fibre Channel interface can be replicated to a special port called the SPAN destination port (SD port). Any Fibre Channel port in a switch can be configured as an SD port. Once an interface is in SD port mode, it cannot be used for normal data traffic. You can attach a Fibre Channel analyzer to the SD port to monitor SPAN traffic (see the "Configuring World Wide Names" section on page 24-3).
SD ports do not receive frames, they merely transmit a copy of the SPAN source traffic. The SPAN feature is nonintrusive and does not affect switching of network traffic for any SPAN source ports (see Figure 8-2).
Figure 8-2 SPAN Transmission
For information on configuring SPAN, refer to the Cisco MDS 9000 Family Configuration Guide.
Understanding the PAA-2
The PAA-2 enables effective, low-cost analysis of Fibre Channel traffic. The device is a standalone Fibre Channel-to-Ethernet adapter, designed primarily to analyze SPAN traffic from a Fibre Channel port on a Cisco MDS 9000 Family switch. The main function of the Port Analyzer Adapter 2 is to encapsulate Fibre Channel frames into Ethernet frames. This allows low-cost analysis of Fibre Channel traffic while leveraging the existing Ethernet infrastructure.
The PAA-2 allows you to examine Fibre Channel frames of various sizes. Fibre Channel frames from Layers 2, 3, and 4 may be examined without network disruption.
Understanding Cisco Traffic Analyzer
Performance Manager collects Fibre Channel level performance statistics using SNMP to access counters on Cisco MDS 9000 Family switches. To view detailed SCSI I/O statistics, you need to look at the data on an SD port with the help of Cisco Traffic Analyzer, which uses the Cisco Port Analyzer Adapter 2 (PAA-2).
Cisco Traffic Analyzer provides real-time analysis of SPAN traffic or analysis of captured traffic through a Web browser user interface. Traffic encapsulated by one or more Port Analyzer Adapter 2 products can be analyzed concurrently with a single workstation running Cisco Traffic Analyzer, which is based on ntop, a public domain software enhanced by Cisco for Fibre Channel traffic analysis.
Round-trip response times, SCSI I/Os per second, SCSI read or traffic throughput and frame counts, SCSI session status, and management task information are monitored. Additional statistics are also available on Fibre Channel frame sizes and network management protocols.
For seamless performance analysis and troubleshooting, Cisco Traffic Analyzer can be launched in-context from Fabric Manager. Port World Wide Name (pWWN), Fibre Channel ID (FC ID), FC alias, and VSAN names are passed to Cisco Traffic Analyzer.
Cisco Traffic Analyzer must be downloaded and installed separately from the following website:
http://www.cisco.com/public/sw-center/sw-stornet.shtml.
Cisco Traffic Analyzer software is available under the Port Analyzer Adapter link. See the "Installing and Launching Cisco Traffic Analyzer" section.
CautionCisco Traffic Analyzer for Fibre Channel throughput values are not accurate when used with the original Cisco Port Analyzer Adapter (PAA) if data truncation is enabled. PAA Version 2 (product ID DS-PAA_2) is required to achieve accurate results with truncation, because it adds a count that enables Cisco Traffic Analyzer to determine how many data bytes were actually transferred.
Note
Refer to the Cisco MDS 9000 Family Configuration Guide for information on configuring the settings for your span destination port. It is important that the data you collect through this port matches the data collected by Performance Manager through the mgmt0 port. If the data does not match, you cannot view Cisco Traffic Analyzer information through a Traffic Analyzer link on the detail page of a Performance Manager report.
Using Cisco Traffic Analyzer with Fabric Manager Web Services
You can run Cisco Traffic Analyzer from within Fabric Manager Web Services in Fabric Manager Release 2.1(2) or later.
Note
Running Traffic Analyzer changed with Fabric Manager Release 2.1(2). You can still run Cisco Traffic Analyzer from within Fabric Manager Web Services. However, with Fabric Manager Release 2.1(2) or later, you can no longer access Traffic Analyzer from the Fabric Manager Client. For more information on releases prior to Fabric Manager Release 2.1(2), see "Configuring Cisco Traffic Analyzer for Fabric Manager Releases Prior to 2.1(2)" section
To use Cisco Traffic Analyzer from Fabric Manager Web Services, follow these steps:
Step 1
Install and launch Cisco Traffic Analyzer. See the "Installing and Launching Cisco Traffic Analyzer" section.
Step 2
Configure Cisco Traffic Analyzer to use PAA-2. See the "Configuring Cisco Traffic Analyzer" section.
Step 3
Discover instances of Cisco Traffic Analyzer from Fabric Manager Web Services. See the "Discovering Cisco Traffic Analyzer from Fabric Manager Web Services" section.
Step 4
Access Cisco Traffic Analyzer from Fabric Manager Web Services. "Accessing Cisco Traffic Analyzer from Fabric Manager Web Services" section.
Installing and Launching Cisco Traffic Analyzer
You must launch Cisco Traffic Analyzer before you can discover and access it from Fabric Manager Web Services. At a minimum , you need to provide the directory where Cisco Traffic Analyzer stores its database, including the RRD files that it creates for trending.
Note
Do not use the /tmp directory for storing the Cisco Traffic Analyzer database on UNIX or Linux workstations. Many distributions of Linux periodically clean up the /tmp directory, thereby affecting Cisco Traffic Analyzer. Instead you can use the /var/ntop directory.
Verify that you have sufficient space in the partition where the Cisco Traffic Analyzer database is stored.
To install and launch Cisco Traffic Analyzer on a UNIX workstation, follow these steps:
Step 1
Open a browser and go to the following website to access the web page where Cisco Traffic Analyzer is available:
http://cisco.com/cgi-bin/tablebuild.pl/mds-fm.Step 2
Download fc-ntop.tar.gz and install it using the instructions at the following website:
http://www.ntop.org.Step 3
Launch ntop using the following UNIX command:
ntop -P database_directoryWhere database_directory is the directory where you want Cisco Traffic Analyzer to save its database files (for example, /var/ntop).
Note
If another application uses port 3000, you can change the port that Cisco Traffic Analyzer uses by entering the following in Step 3:
ntop.exe /c -P tmp -w port_number where port_number is equal to the port that you want Cisco Traffic Analyzer to use. Set the port number to 3001 if you want to use SSL. Fabric Manager Web Services can only detect Cisco Traffic Analyzer if you use port 3000 (the default port).Step 4
Verify that the Fibre Channel port on the PAA-2 is connected to the SD port on the switch (Figure 8-1).
Step 5
Verify that the Ethernet port on the PAA-2 is connected to the workstation running Cisco Traffic Analyzer.
Step 6
Click Interfaces > SPAN... in Device Manager to configure SPAN on the required switch ports.
Step 7
Click Interfaces > SPAN... in Device Manager to verify that the Fibre Channel port connected to the PAA-2 is configured as an SD port. The port mode of the destination interface must be SD.
Step 8
Click the Sessions tab in Device Manager to verify the correct destination and source of traffic (ingress).
CautionCisco Traffic Analyzer must not be used with the PAA-2 in Management mode (MNM). Refer to the Cisco MDS 9000 Family Port Analyzer Adapter 2 Installation and Configuration Note.
Under Windows, you can use the \tmp directory provided with the distribution to store the Cisco Traffic Analyzer database.
To install and launch Cisco Traffic Analyzer on a Windows workstation, follow these steps:
Step 1
Open a browser and go to the following website to access the web page where Cisco Traffic Analyzer is available:
http://cisco.com/cgi-bin/tablebuild.pl/mds-fm.Step 2
Download ntop-win32.zip and save it on your workstation.
Step 3
Unzip the downloaded file.
Note
You need the WinPcap version 3.1 or later library file to use Cisco Traffic Analyzer on a Microsoft Windows system. You can download this file from the Cisco CD that shipped with your product, or from the following website:
http://winpcap.polito.it/.Step 4
Open a command prompt and change directories to your ntop installation directory.
Step 5
Enter ntop.exe /c -P database_directory or install ntop as a service on Windows by following these steps:
a.
Enter ntop /i to install ntop as a service.
b.
Choose Start > Programs > Administrative Tools > Services to access the Windows Services Panel.
c.
Right-click ntop and choose properties. You see the Properties dialog box.
d.
Set the Start Parameters to -P database_ directory, where database directory is the directory where you want Cisco Traffic Analyzer to store its database (for example, D:\ntop\tmp.
Note
If launching Cisco Traffic Analyzer as a Windows service, you must specify the complete path for the database directory using the -P option.
Note
If another application uses port 3000, you can change the port that Cisco Traffic Analyzer uses by entering the following in Step 5:
ntop.exe /c -P tmp -w port_number, where port_number is equal to the port that you want Cisco Traffic Analyzer to use. Set the port number to 3001 if you want to use SSL. Fabric Manager Web Services can only detect Cisco Traffic Analyzer if you use port 3000 (the default port).e.
Click Start to start ntop on that interface.
Note
Subsequent restarts of the ntop service do not require setting the -i option. unless you are changing the interface that connects to the PAA-2.
Step 6
Optionally, choose Admin > Startup Preferences > Capture to set the interface that Cisco Traffic Analyzer uses after Cisco Traffic Analyzer opens.
Step 7
Select the interfaces that are receiving PAA-2 traffic that Cisco Traffic Analyzer will capture packets on.
Step 8
Verify that the Fibre Channel port on the PAA-2 is connected to the SD port on the switch (Figure 8-1).
Step 9
Verify that the Ethernet port on the PAA-2 is connected to the workstation running Cisco Traffic Analyzer.
Step 10
Click Interfaces > SPAN... in Device Manager to configure SPAN on the required switch ports.
Step 11
Click the Sources tab in Device Manager to verify that the Fibre Channel port connected to the PAA-2 is configured as an SD port. The port mode of the destination interface must be SD.
Step 12
Click the Sessions tab in Device Manager to verify the correct destination and source of traffic (ingress).
Tip
To modify the script that launches ntop (ntop.sh or ntop.bat), follow the instructions provided within the script file. Create a backup of the original script before modifying the file.
—Linux platforms use the shell script path. The ntop output is sent to the syslog file (/var/log/messages by default).
—Windows platforms use the batch file. The ntop output is sent to a file located in the same directory as the one from which ntop is launched.You can remove Cisco Traffic Analyzer as a service by entering the following command at the Windows command prompt:
ntop.exe /rConfiguring Cisco Traffic Analyzer
At a minimum, you must configure Cisco Traffic Analyzer to recognize the IP address and switch port of the switch that Cisco Traffic Analyzer connects to through the PAA-2.
To initially configure Cisco Traffic Analyzer, follow these steps:
Step 1
Choose Admin > Configure > Startup Preferences > Capture from the Cisco Traffic Analyzer menu.
Step 2
Set the IP address and switch port for the switch that Cisco Traffic Analyzer connects to through the PAA-2.
Note
You must repeat this for all interfaces that are receiving PAA-2 traffic.
Step 3
Save the new configuration.
Step 4
Choose Admin > Shutdown, and then relaunch Cisco Traffic Analyzer. Cisco Traffic Analyzer uses the new configuration.
Discovering Cisco Traffic Analyzer from Fabric Manager Web Services
Fabric Manager Release 2.1(2) or later supports discovering instances of Cisco Traffic Analyzer and SPAN ports configured within your fabric.
Fabric Manager Web Services supports the following Traffic Analyzer integration features:
•
SCSI I/O Traffic Analyzer pages can be viewed within the Web client .
•
Traffic Analyzer can reside on a different server than Performance Manager.
•
Performance Manager integrates with multiple servers running Traffic Analyzer.
•
Instances of Traffic Analyzer servers can be discovered by Fabric Manager Server.
•
Web client report lists SPAN destination ports and associations with Traffic Analyzers.
To discover instances of Traffic Analyzer running in your fabric from Fabric Manager Web Services, follow these steps:
Step 1
Choose Performance > Traffic Analyzer. You see a summary table of all SPAN destination ports and configured Traffic Analyzers in your fabric.
Step 2
Navigate to the fabric where you want to rediscover instances of Traffic Analyzer from the navigation bar.
Step 3
Set Search on Subnet to the subnet that you want to rediscover.
Step 4
Click Rediscover to find instances of Traffic Analyzer within the selected fabric or VSAN and subnet.
Note
Fabric Manager Web Services can only detect instances of Traffic Analyzer that use port 3000.
Accessing Cisco Traffic Analyzer from Fabric Manager Web Services
To access an instance of Cisco Traffic Analyzer running in your fabric from Fabric Manager Web Services, follow these steps
Step 1
Choose Performance > Traffic Analyzer. You see a summary table of all SPAN destination ports and configured Traffic Analyzers in your fabric. The source column shows the ports that are monitored by the SPAN destination port.
Step 2
Click a Traffic Analyzer to launch that Traffic Analyzer within Fabric Manager Web Services.
If you did not configure the switch and switch port information in Cisco Traffic Analyzer, you can still discover it, but Fabric Manager Web Services cannot associate that instance of Cisco Traffic Analyzer with any fabric. Cisco Traffic Analyzer also cannot inherit the device alias information from Fabric Manager Web Services.
Fabric Manager Web Services updates Cisco Traffic Analyzer with the latest device alias information every five minutes.
Configuring Cisco Traffic Analyzer for Fabric Manager Releases Prior to 2.1(2)
To configure Performance Manager to work with Cisco Traffic Analyzer for Fabric Manager releases prior to Release 2.1(2), follow these steps:
Step 1
Get the following three pieces of information:
•
The IP address of the management workstation on which you are running Performance Manager and Cisco Traffic Analyzer.
•
The path to the directory where Cisco Traffic Analyzer is installed.
•
The port that is used by Cisco Traffic Analyzer (the default is 3000).
Step 2
Start Cisco Traffic Analyzer.
a.
Choose Performance > Traffic Analyzer > Open.
b.
Enter the URL for Cisco Traffic Analyzer, in the format
http://ip_address:port_numberwhere ip_address is the address of the management workstation on which you have installed the Cisco Traffic Analyzer, and :port_number is the port that is used by Cisco Traffic Analyzer (the default is :3000).
c.
Click OK.
d.
Choose Performance > Traffic Analyzer > Start.
e.
Enter the location of Cisco Traffic Analyzer, in the format
D:<directory\ntop.batwhere D: is the drive letter for the disk drive where Cisco Traffic Analyzer is installed, and
directory is the directory containing the ntop.bat file.
f.
Click OK.
Step 3
Create the flows you want Performance Manager to monitor, using the Flow Configuration Wizard.
Step 4
Define the data collection you want Performance Manager to gather, using the Performance Manager Configuration Wizard.
a.
Choose the VSAN you want to collect information for or choose All VSANs.
b.
Check the types of items you want to collect information for (hosts, ISLs, storage devices, and flows).
c.
Enter the URL for Cisco Traffic Analyzer in the format
http://<ip address>/<directory>where:
<ip address> is the address of the management workstation on which you have installed Cisco Traffic Analyzer, and <directory> is the path to the directory where Cisco Traffic Analyzer is installed.
d.
Click Next.
e.
Review the end devices and links that you selected to make sure this is the data you want to collect.
f.
Click Finish to begin collecting data.
Note
Data is not collected for JBOD or for virtual ports. If you change the data collection configuration parameters during a data collection, you must stop and restart the collection process for your changes to take effect.
Step 5
Click Cisco Traffic Analyzer at the top of the Host or Storage detail pages to view Cisco Traffic Analyzer information, or choose Performance > Traffic Analyzer > Open. Cisco Traffic Analyzer will not open unless ntop has been started already.
Note
For information on capturing a SPAN session and starting a Cisco Traffic Analyzer session to view it, refer to the Cisco MDS 9000 Family Port Analyzer Adapter 2 Installation and Configuration Note.
Note
For information on viewing and interpreting your Performance Manager data, see the "Historical Performance Monitoring" section on page 33-2.
For information on viewing and interpreting your Cisco Traffic Analyzer data, refer to the Cisco MDS 9000 Family Port Analyzer Adapter 2 Installation and Configuration Note.For performance drill-down, Fabric Manager Server can launch Cisco Traffic Analyzer in-context from the Performance Manager graphs. The aliases associated with hosts, storage devices, and VSANs are passed to Cisco Traffic Analyzer to provide consistent, easy identification.

 Feedback
Feedback