-
Cisco MDS 9000 Family Fabric Manager Configuration Guide, Release 2.x
-
New and Changed Information
-
Index
-
Preface
- Part 1 - Fabric Manager Applications
- Part 2 - Cisco MDS SAN-OS Installation and Configuration Files
-
Part 3 - Switch Configuration
-
Cisco Fabric Services
-
VSAN Configuration
-
Dynamic VSAN Configuration
-
Zone Configuration
-
Inter-VSAN Routing Configuration
-
PortChannel Configuration
-
Interface Configuration
-
FCIP Configuration
-
Configuring the SAN Extension Tuner
-
iSCSI configuration
-
FICON Configuration
-
Configuring Intelligent Storage Services
-
Additional Configuration
-
- Part 4 - Security Configuration
- Part 5 - Network and Performance Monitoring
- Part 6 - Troubleshooting
-
GUI/CLI Usage Chart
-
Interface Nonoperational Reason Codes
-
Managing Cisco FabricWare
-
Table Of Contents
Troubleshooting Tools and Techniques
Analyzing Switch Device Health
Online System Health Management
Loopback Test Configuration Frequency
Analyzing Switch Fabric Configuration
Analyzing End-to-End Connectivity
About the Cisco Fabric Analyzer
Configuring the Cisco Fabric Analyzer
Sending Captures to Remote IP Addresses
Using Traceroute and Other Troubleshooting Tools
Analyzing the Results of Merging Zones
Issuing the Show Tech Support Command
Getting Oversubscription Information in Device Manager
Troubleshooting Your Fabric
There are several things you can do to use Fabric Manager to troubleshoot your fabric.
This chapter contains the following topics:
•
Troubleshooting Tools and Techniques
•
Analyzing Switch Device Health
•
Analyzing Switch Fabric Configuration
•
Analyzing End-to-End Connectivity
•
Configuring a Fabric Analyzer
•
Using Traceroute and Other Troubleshooting Tools
•
Analyzing the Results of Merging Zones
•
Issuing the Show Tech Support Command
•
Getting Oversubscription Information in Device Manager
Troubleshooting Tools and Techniques
Multiple techniques and tools are available to monitor and trouble shoot the Cisco MDS 9000 Family of switches. These tools provide a complete, integrated, multi-level analysis solution.
Fabric Manager Server—The Cisco Fabric Manager Server provides a long-term, high level view of storage network performance. Fabric wide performance trends can be analyzed using Performance Manager. It provides the starting point for deeper analysis to resolve network hot-spots.
Device Manager—If a performance problem is detected with the Fabric Manager Server, the Cisco Device Manager can be used to view port level statistics in real-time. Details on protocols, errors, discards, byte and frame counts are available. Samples can be taken as frequently as every 2 seconds, and values can be viewed in text form or graphically as pie, bar, area and line changes.
Traffic Analyzer—Another option is to launch the Cisco Traffic Analyze for Fibre Channel from the Fabric Manager Server to analyze the traffic in greater depth. The Cisco Traffic Analyzer allows you to breakdown traffic by VSANs and protocols and to examine SCSI traffic at a logical unit number (LUN) level.
Protocol Analyzer—If even deeper investigation is needed, the Cisco Protocol Analyzer for Fibre Channel can be launched in-context from the Cisco Traffic Analyzer. The Cisco Protocol Analyzer enables you to examine actual sequences of Fibre Channel frames easily using the Fibre Channel and SCSI decoders Cisco developed for Ethereal.
Port Analyzer Adapter—Fabric Manager Server and Device Manager use SNMP to gather statistics. They fully utilize the built in MDS statistics counters. Even so, there are limits to what the counters can collect.
Integration with the Cisco Traffic Analyzer and Cisco Protocol Analyzer extend the MDS analysis capabilities by analyzing the Fibre Channel traffic itself. The Cisco MDS 9000 Family Switched Port Analyzer (SPAN) enables these solutions via a flexible, non-intrusive technique to mirror traffic selectively from one or more ports to another MDS port within a fabric.
The Cisco Port Analyzer Adapter (PAA) encapsulates SPAN traffic in an Ethernet header for transport to a PC or workstation for analysis. Both Fibre Channel control and data plane traffic are available using SPAN. The PAA broadcasts the Ethernet packets, so they cannot be routed across IP networks. Hubs and switches can be used, provided they are in the same Ethernet subnet. Direct connections between a PAA and the PC are also supported. The PAA can reduce Ethernet traffic by truncating Fibre Channel data.
Both the Cisco Traffic Analyzer and Cisco Protocol Analyzer required the PAA to transport MDS SPAN traffic to a PC or workstation.
Note
The Cisco Traffic Analyzer works best with the Cisco Port Analyzer Adapter 2, because it provides a length value for truncated data, enabling accurate byte count reporting.
Cisco Traffic Analyzer
The Cisco Traffic Analyzer for Fibre Channel provides real-time analysis of SPAN traffic or traffic captured previously using the Cisco Protocol Analyzer. The Fibre Channel traffic from multiple Cisco Port Analyzer Adapters (PAA) can be aggregated and analyzed by the Cisco Traffic Analyzer.
There are limits to how may SPAN sources can be sent to a single SPAN destination port on an MDS. Aggregation extends the amount of information that can be analyzed in a unified set of reports by the Cisco Traffic Analyzer.
Note
The aggregation capabilities are restricted to the information collect by Ethernet connections to a single PC. Aggregation across multiple PCs is NOT available.
The Cisco Traffic Analyzer presents it reports through a Web server, so you can view them locally or remotely. The traffic analysis functions are provided by `ntop' open-source software, which was enhanced by Cisco to add Fibre Channel and SCSI analysis and MDS enhanced inter-switch link (ISL) header support for SPAN. ntop is available on the Cisco.com software download center, under the Cisco Port Analyzer Adapter. ntop is also available on the Internet at http://www.ntop.org/ntop.html. The Cisco enhanced ntop runs under Microsoft Windows and Linux operating systems.
The Cisco Traffic Analyzer for Fibre Channel presents reports with network wide statistics. The Summary Traffic report shows what percentage of traffic was within different ranges of frames sizes. A breakdown of the percentage of traffic for each protocol like SCSI, ELS, etc. is provided. The average and peak throughput for the SPAN traffic being analyzed are also provided.
Fibre Channel traffic can be analyzed on a per VSAN basis with the Cisco Traffic Analyzer. The Domain Traffic Distribution graphs indicate how much traffic (bytes) were transmitted or received by a switch for a particular VSAN. FC Traffic Matrix graphs show how much traffic is transmitted and received between Fibre Channel sources and destinations. The total byte and frame counts for each VSAN are also provided.
Statistics can be analyzed for individual host and storage ports. You can see the percentage of SCSI read vs. write traffic, SCSI vs. other traffic, and percentage of transmitted vs. received bytes and frames. The peak and average throughput values are available for data transmitted and received by each port.
Cisco Protocol Analyzer
The Cisco Protocol Analyzer for Fibre Channel enables you to view Fibre Channel traffic frames in real-time or from a capture file. Fibre Channel and SCSI decoders enable you to view and analyze traffic at the frame level. It matches response with request for complete decoding, which greatly simplifies navigation. Response time between response and status are presented.
The Cisco Protocol Analyzer is VSAN aware, so VSANs can be used as criteria for capture and display filters, and to colorize the display. VSAN #s can also be displayed in a column. Summary statistics are available for protocol distribution percentages and total bytes/frames transferred between specific Fibre Channel source/destination pairs. File capture and filtering controls are available. Captured files can be analyzed by either the Cisco Protocol Analyzer or the Cisco Traffic Analyzer.
Numerous features have been included for ease-of-use. You can find frames that meet particular criteria and mark them. Entries in the frame (packet) list can be colorized to highlight items of interest, and columns can be added/removed as desired.
The protocol analysis functions are provided by `Ethereal' open-source software, which was enhanced by Cisco to decode Fibre Channel and SCSI protocols and support MDS enhanced inter-switch link (ISL) headers for SPAN. Ethereal is available on the Cisco.com software download center, under the Cisco Port Analyzer Adapter. Ethereal is also available on the Internet at http://www.ethereal.com. Ethereal runs under Microsoft Windows, Solaris, and Linux operating systems.
Analyzing Switch Device Health
The Switch Health option lets you determine the status of the components of a specific switch.
To use the Switch Health option, follow these steps:
Step 1
Select Switch Health from the Fabric Manager Tools menu.
You see the Switch Health Analysis window.
Step 2
Click Start to identify any problems that may currently be affecting the selected switch.
You see any problems affecting the selected switches.
Step 3
Click Clear to remove the contents of the Switch Health Analysis window.
Step 4
Click Close to close the window.
Online System Health Management
The Online Health Management System (system health) is a hardware fault detection and recovery feature. It ensures the general health of switching, services, and supervisor modules in any switch in the Cisco MDS 9000 Family as of Cisco MDS SAN-OS Release 1.3(4) and later.
The system health application runs on all Cisco MDS modules and runs multiple tests on each module to test individual module components and system hardware. The tests run at preconfigured intervals, cover all major fault points, and isolate any failing component in the MDS switch. The system health running on the active supervisor maintains control over all other system health components running on all other modules in the switch. The system health application running in the standby supervisor module only monitors the standby supervisor module—if that module is available in the HA standby mode.
On detecting a fault, the system health application attempts the following recovery actions:
•
Sends Call Home and system messages and exception logs as soon as it detects a failure.
•
Shuts down the failing module or component (such as an interface).
•
Isolates failed ports from further testing.
•
Reports the failure to the appropriate software component.
•
Switches to the standby supervisor module if an error is detected on the active supervisor module, and a standby supervisor module exists in the Cisco MDS switch. After the switchover, the new active supervisor module restarts the active supervisor tests.
•
Reloads the switch if a standby supervisor module does not exist in the switch.
•
Provides CLI support to view, test, and obtain test run statistics or change the system health test configuration on the switch.
•
Performs tests to focus on the problem area.
•
Retrieves its configuration information from persistent storage.
Each module is configured to run the test relevant to that module. You can change the default parameters of the test in each module as required.
By default, the system health feature is enabled in each switch in the Cisco MDS 9000 Family.
Loopback Test Configuration Frequency
Loopback tests are designed to identify hardware errors in the data path in the module(s) and the control path in the supervisors. One loopback frame is sent to each module at a preconfigured frequency-it passes through each configured interface and returns to the supervisor module.
The loopback tests can be run at frequencies ranging from 5 seconds (default) to 255 seconds. The configured value is used for all modules. To configure the frequency of loopback tests, refer to the Cisco MDS 9000 Family Configuration Guide.
Performing Internal Loopbacks
Internal loopback tests send and receive FC2 frames to and from the same ports and provides the round trip time taken in microseconds. These tests are available for both Fibre Channel and iSCSI interfaces.
Choose Interface > Diagnostics > Internal to perform an internal loopback test from Device Manager.
Performing External Loopbacks
External loopback tests send and receive FC2 frames to and from the same port. You need to connect a cable (or a plug) to loop the Rx port to the Tx port before running the test. This test is only available for Fibre Channel interfaces.
Choose Interface > Diagnostics > External to perform an external loopback test from Device Manager.
Hardware Failure Action
By default, no action is taken if a failure is determined and the failed component is isolated from further testing. Failure action is controlled at individual test levels (per module), at the module level (for all tests), or for the entire switch. To configure a failure action for the switch, refer to the Cisco MDS 9000 Family Configuration Guide.
Analyzing Switch Fabric Configuration
The Fabric Configuration option lets you analyze the configuration of a switch by comparing the current configuration to a specific switch or to a policy file. You can save a switch configuration to a file and then compare all switches against the configuration in the file.
To use the Fabric Configuration option to analyze the configuration of a switch, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click Fabric Configuration from the Fabric Manager Tools menu.
You see the Fabric Configuration Analysis dialog box.
Step 2
Decide whether you want to compare the selected switch to another switch, or to a Policy File.
•
If you are making a switch comparison, select Policy Switch and then click the drop-down arrow to see a list of switches.
•
If you are making a policy comparison, select Policy File. Then click the button to the right of this option to browse your file system and select a policy file (*.XML).
Step 3
Click Rules... to set the rules to apply when running the Fabric Configuration Analysis tool.
You see the Rules window.
Step 4
Change the default rules as required and click OK.
Step 5
Click Compare.
The system analyzes the configuration and displays issues that arise as a result of the comparison.
Step 6
Click to place a checkmark in the Resolve column for the issues you want to resolve.
Step 7
Resolve them by clicking Resolve Issues.
Step 8
Click Clear to remove the contents of the window.
Step 9
Click Close to close the window.
Analyzing End-to-End Connectivity
You can use the End to End Connectivity option to determine connectivity and routes among devices with the switch fabric. The connectivity tool checks to see that every pair of end devices can talk to each other, using a Ping test and by determining if they are in the same VSAN or in the same active zone. This option uses versions of the ping and traceroute commands modified for Fibre Channel networks.
- End to End Connectivity
The ping and redundancy tests are now mutually exclusive, you cannot run both at the same time.
To use this option, follow these steps:
Step 1
Choose End to End Connectivity from the Fabric Manager Tools menu.
You see the End to End Connectivity Analysis dialog box.
Step 2
Select the VSAN in which you want to verify connectivity from the VSAN dropdown list.
Step 3
Select whether you want to perform the analysis for all active zones or for the default zone.
Step 4
Click Ensure that members can communicate to perform a Fibre Channel ping between the selected end points.
Step 5
Identify the number of packets, the size of each packet, and the timeout in milliseconds.
Step 6
Analyze the redundant paths between endpoints by checking the Ensure that redundant paths exist between members checkbox.
Step 7
Check the Report errors for checkbox to see a report of zone and device errors.
Step 8
Click Analyze.
The End to End Connectivity Analysis window displays the selected end points with the switch to which each is attached, and the source and target ports used to connect it.
The output shows all the requests which have failed. The possible descriptions are:
•
Ignoring empty zone—No requests are issued for this zone.
•
Ignoring zone with single member—No requests are issued for this zone.
•
Source/Target are unknown—No nameserver entries exist for the ports or we have not discovered the port during discovery.
•
Both devices are on the same switch.
•
No paths exist between the two devices.
•
VSAN does not have an active zone set and the default zone is denied.
•
Average time ... micro secs—The latency value was more than the threshold supplied.
Step 9
Click Clear to remove the contents of the window.
Step 10
Click Close to close the window.
Configuring a Fabric Analyzer
Fibre Channel protocol analyzers capture, decode, and analyze frames and ordered sets on a link. Existing Fibre Channel analyzers can capture traffic at wire rate speed. They are expensive and support limited frame decoding. Also, to snoop traffic, the existing analyzers disrupt the traffic on the link while the analyzer is inserted into the link.
Cisco has brought protocol analysis within a storage network to a new level with the Cisco Fabric Analyzer. You can capture Fibre Channel control traffic from a switch and decode it without having to disrupt any connectivity, and without having to be local to the point of analysis.
The Cisco Fibre Channel protocol analyzer is based on two popular public-domain software applications:
•
libpcap—See http://www.tcpdump.org.
•
Ethereal—See http://www.ethereal.com.
Note
The Cisco Fabric Analyzer is useful in capturing and decoding control traffic, not data traffic. It is suitable for control path captures, and is not intended for high-speed data path captures.
This section explains the following topics:
•
About the Cisco Fabric Analyzer
•
Configuring the Cisco Fabric Analyzer
About the Cisco Fabric Analyzer
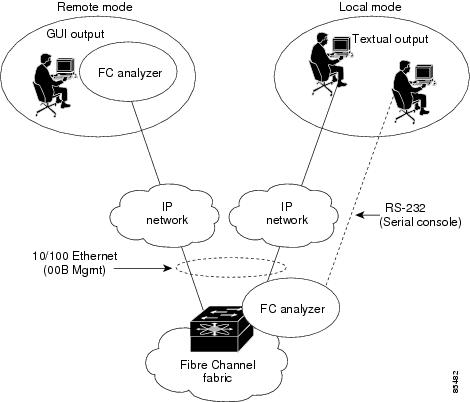
The Cisco Fabric Analyzer comprises of two separate components (see Figure 35-1):
•
Software that runs on the Cisco MDS 9000 Family switch and supports two modes of capture:
–
A text-based analyzer that supports local capture and decodes captured frames
–
A daemon that supports remote capture
•
GUI-based client that runs on a host that supports libpcap such as Windows or Linux and communicates with the remote capture daemon in a Cisco MDS 9000 Family switch.
Figure 35-1 Cisco Fabric Analyzer Usage
Local Text-Based Capture
This component is a command-line driven text-based interface that captures traffic to and from the supervisor module in a Cisco MDS 9000 Family switch. It is a fully functional decoder that is useful for quick debug purposes or for use when the remote capture daemon is not enabled. Additionally, because this tool is accessed from within the Cisco MDS 9000 Family switch, it is protected by the roles-based policy that limits access in each switch.
Remote Capture Daemon
This daemon is the server end of the remote capture component. The Ethereal analyzer running on a host is the client end. They communicate with each other using the Remote Capture Protocol (RPCAP). RPCAP uses two endpoints, a TCP-based control connection and a TCP or UDP-based data connection based on TCP (default) or UDP. The control connection is used to remotely control the captures (start or stop the capture, or specify capture filters). Remote capture can only be performed to explicitly configured hosts. This technique prevents an unauthorized machine in the network from snooping on the control traffic in the network.
RPCAP supports two setup connection modes based on firewall restrictions.
•
Passive mode (default)—The configured host initiates connection to the switch. Multiple hosts can be configured to be in passive mode and multiple hosts can be connected and receive remote captures at the same time.
•
Active mode—The switch initiates the connection to a configured host—one host at a time.
Using capture filters, you can limit the amount of traffic that is actually sent to the client. Capture filters are specified at the client end—on Ethereal, not on the switch.
GUI-Based Client
The Ethereal software runs on a host, such as a PC or workstation, and communicates with the remote capture daemon. This software is available in the public domain from http://www.ethereal.com. The Ethereal GUI front-end supports a rich interface such as a colorized display, graphical assists in defining filters, and specific frame searches. These features are documented on Ethereal's website.
While remote capture through Ethereal supports capturing and decoding Fibre Channel frames from a Cisco MDS 9000 Family switch, the host running Ethereal does not require a Fibre Channel connection to the switch. The remote capture daemon running on the switch sends the captured frames over the out-of-band Ethernet management port. This capability allows you to capture and decode Fibre Channel frames from your desktop or laptop.
Configuring the Cisco Fabric Analyzer
You can configure the Cisco Fabric Analyzer to perform one of two captures.
•
Local capture—The command setting to enable a local capture cannot be saved to persistent storage or synchronized to standby. Launches the textual version on the fabric analyzer directly on the console screen. The capture can also be saved on the local file system.
•
Remote capture—The command setting to enable a remote capture can be saved to persistent storage. It can be synchronized to the standby supervisor module and a stateless restart can be issued, if required.
To use the Cisco Fabric Analyzer feature, traffic should be flowing to or from the supervisor module.
Sending Captures to Remote IP Addresses
CautionYou must use the eth2 interface to capture control traffic on a supervisor module.
To capture remote traffic, use one of the following options:
•
The capture interface can be specified in Ethereal as the remote device:
rpcap://<ipaddress or switch hostname>/eth2For example:
rpcap://cp-16/eth2rpcap://17.2.1.1/eth2•
The capture interface can be specified either in the capture dialog box or by using the -i option at the command line when invoking Ethereal.
ethereal -i rpcap://<ipaddress|hostname>[:<port>]/<interface>For example:
ethereal -i rpcap://172.22.1.1/eth2or
ethereal -i rpcap://customer-switch.customer.com/eth2
Note
For example, in a Windows 2000 setup, click Start on your desktop and select Run. In the resulting Run window, type the required command line option in the Open field.
Displaying Captured Frames
You can selectively view captured frames by using the display filters feature. For example, instead of viewing all the frames from a capture, you may only want to view ELP request frames. This feature only limits the captured view—it does not affect the captured or the saved frames. Procedures to specify, use, and save display filters are already documented in the Ethereal website (http://www.ethereal.com). Some examples of how you can use this feature are as follows:
•
To view all packets in a specified VSAN, use this expression:
mdshdr.vsan == 2•
To view all SW_ILS frames, use this expression:
fcswils•
To view class F frames, use this expression:
mdshdr.sof == SOFf•
To view all FSPF frames, use this expression:
swils.opcode == HLO || swils.opcode == LSU || swils.opcode == LSA•
To view all FLOGI frames, use this expression:
fcels.opcode == FLOGI•
To view all FLOGI frames in VSAN 1, use this expression:
fcels.opcode == FLOGI && mdshdr.vsan == 2•
To view all name server frames, use this expression:
dNSDefining Display Filters
Display filters limit the frames that can be displayed, but not what is captured (similar to any view command). The filters to be displayed can be defined in multiple ways in the GUI application:
•
Auto-definition
•
Manual definition
•
Assisted manual definition
•
Only manual definition in local capture
•
No assists
Regardless of the definition, each filter must be saved and identified with a name.
Note
This GUI-assisted feature is part of Ethereal and you can obtain more information from http://www.ethereal.com.
Capture Filters
You can limit what frames are captured by using the capture filters feature in a remote capture. This feature limits the frames that are captured and sent from the remote switch to the host. For example, you can capture only class F frames. Capture filters are useful in restricting the amount of bandwidth consumed by the remote capture.
Unlike display filters, capture filters restrict a capture to the specified frames. No other frames are visible until you specify a completely new capture.
The syntax for capture filter is different from the syntax for display filters. Capture filters use the Berkeley Packet Filter (BPF) library that is used in conjunction with the libpcap freeware. The list of all valid Fibre Channel capture filter fields are provided later in this section.
Procedures to configure capture filters are already documented in the Ethereal website (http://www.ethereal.com). Some examples of how you can use this feature as follows:
•
To capture frames only on a specified VSAN, use this expression:
vsan = 1•
To capture only class F frames, use this expression:
class_f•
To capture only class Fibre Channel ELS frames, use this expression:
els•
To capture only name server frames, use this expression:
dns•
To capture only SCSI command frames, use this expression:
fcp_cmd
Note
This feature is part of libpcap and you can obtain more information from http://www.tcpdump.org.
Permitted Capture Filters
This section lists the permitted capture filters.
o vsan o src_port_idx o dst_port_idx o sof o r_ctl o d_id o s_id o type o seq_id o seq_cnt o ox_id o rx_id o els o swils o fcp_cmd (FCP Command frames only) o fcp_data (FCP data frames only) o fcp_rsp (FCP response frames only) o class_f o bad_fc o els_cmd o swils_cmd o fcp_lun o fcp_task_mgmt o fcp_scsi_cmd o fcp_status o gs_type (Generic Services type) o gs_subtype (Generic Services subtype) o gs_cmd o gs_reason o gs_reason_expl o dns (name server) o udns (unzoned name server) o fcs (fabric configuration server) o zs (zone server) o fc (use as fc[x:y] where x is offset and y is length to compare) o els (use as els[x:y] similar to fc) o swils (use as swils[x:y] similar to fc) o fcp (use as fcp[x:y] similar to fc) o fcct (use as fcct[x:y] similar to fc)Using the Ping Tool
You can use the Ping tool to determine connectivity from another switch to a port on your switch.
To use the Ping tool, follow these steps:
Step 1
Select Ping from the Fabric Manager Tools menu. You can also select it from the right-click context menus for hosts and storage devices in the Fabric pane.
You see the Ping dialog box.
Step 2
Select the source switch from the Source Switch drop-down list.
Step 3
Select the VSAN in which you want to verify connectivity from the VSAN drop-down list.
Step 4
Select the target end port for which you want to verify connectivity from the Target Endport drop-down list.
Step 5
Click Start to perform the ping between your switch and the selected port.
Step 6
In a few seconds, you see the results in the Results area of the dialog box.
Step 7
Click Clear to clear the contents of the window and perform another ping, or click Close to close the window.
Using Traceroute and Other Troubleshooting Tools
You can use the following options on the Tools menu to verify connectivity to a selected object or to open other management tools:
•
Traceroute—Verify connectivity between two end devices that are currently selected on the Fabric pane.
•
Device Manager— Launch the Device Manager for the switch selected on the Fabric pane.
•
Command Line Interface—Open a Telnet or SSH session for the switch selected on the Fabric pane.
To use the Traceroute option to verify connectivity, follow these steps:
Step 1
Select Traceroute from the Fabric Manager Tools menu.
You see the Traceroute dialog box.
Step 2
Select the source switch from the Source Switch drop-down list.
Step 3
Select the VSAN in which you want to verify connectivity from the VSAN drop-down list.
Step 4
Select the target end port for which you want to verify connectivity from the Target Endport drop-down list.
Step 5
Click Start to perform the traceroute between your switch and the selected port.
Step 6
In a few seconds, you see the results in the Results area of the dialog box.
Step 7
Click Clear to clear the contents of the window and perform another traceroute, or click Close to close the window.
Analyzing the Results of Merging Zones
You can use the Zone Merge option on the Fabric Manager Zone menu to determine if two connected switches have compatible zone configurations.
To use the Zone Merge option, follow these steps:
Step 1
Choose Merge Analysis from the Fabric Manager Zone menu.
The Zone Merge Analysis dialog is displayed.
Step 2
Select a switch from each drop-down list.
Step 3
Select the VSAN for which you want to perform the zone merge analysis.
Step 4
Click Analyze.
The Zone Merge Analysis window displays any inconsistencies between the zone configuration of the two selected switches.
Step 5
Click Clear to remove the contents of the window.
Step 6
Click Close to close the window.
Issuing the Show Tech Support Command
The show tech support command is useful when collecting a large amount of information about your switch for troubleshooting purposes. The output can be provided to technical support representatives when reporting a problem.
You can issue a show tech support command from Fabric Manager for one or more switches in a fabric. The results of each command are written to a text file, one file per switch, in a directory you specify. You can then view these files using Fabric Manager.
You can also save the Fabric Manager map as a JPG file. The file is saved with the name of the seed switch (for example, 172.22.94.250.jpg).
You can zip up all the files (the show tech support output and the map file image) and send the resulting zipped file to technical support.
To issue the show tech support command in Fabric Manager , follow these steps.
Step 1
Select Show Tech Support from the Tools menu.
You see the Show Tech Support dialog box.
Step 2
Select the switches for which you want to view Show Tech Support information by checking the check boxes next to their IP addresses.
Step 3
Set the timeout value.
The default is 30 seconds.
Step 4
Select the folder where you want the text files (containing the Show Tech Support information) to be written.
Step 5
Check the Save Map check box if you want to save a screenshot of your map as a JPG file.
Step 6
Check the Compress all files as check box to compress the files into a zip file.
Step 7
Click the OK button to start issuing the show tech support command to the switches you specified, or click the Close button to close the Show Tech Support dialog box without issuing the show tech support command.
In the Status column next to each switch, a highlighted status is displayed. A yellow highlight indicates that the Show Tech Support command is currently running on that switch. A red highlight indicates an error. A green highlight indicates that the Show Tech Support command has completed successfully. On successful completion, a button becomes available in the View column for each switch.
Step 8
If prompted, enter your username and password in the appropriate fields for the switch in question.
Note that in order for Fabric Manager to successfully issue the show tech support command on a switch, that switch must have this username and password. Fabric Manager is unable to log into a switch that does not have this username and password, and an error is returned for that switch.
Note
If you would like to view the Show Tech Support files without using Fabric Manager, you can open them with any text editor. Each file is named with the switch's IP address and has a .TXT extension (for example, 111.22.33.444.txt).
Locating Other Switches
The Locate Switches option uses SNMPv2 and discovers devices responding to SNMP requests with the read-only community string public. You can use this feature if:
•
You have third-party switches that do not implement the FC-GS3 FCS standard that provides management IP addresses.
•
You want to locate other Cisco MDS 9000 switches in the subnet but are not physically connected to the fabric (and therefore cannot be found via neighbors).
To locate switches that are not included in the currently discovered fabric, follow these steps:
Step 1
Select Locate Switches and Devices from the Fabric Manager File menu.
You see the Locate Switches dialog box.
Step 2
In the Comma Separated Subnets field, enter a range of specific addresses belonging to a specific subnet which limit the research for the switches. To look for a Cisco MDS 9000 switch belonging to subnet 192.168.199.0, use the following string:
192.168.100.[1-254]
Multiple ranges can be specified, separated by commas. For example, to look for all the devices in the two subnets 192.168.199.0 and 192.169.100.0, use the following string:
192.168.100.[1-254], 192.169.100.[1-254]
Step 3
Enter the appropriate read community string in the Read Community field.
The default value for this string is "public."
Step 4
Click Display Cisco MDS 9000 Only to display only the Cisco MDS 9000 Family switches in your network fabric.
Step 5
Click Search to discover switches and devices in your network fabric. You see the results of the discovery in the Locate Switches window.
Note
The number in the lower left corner of the screen increments as the device locator attempts to discover the devices in your network fabric. When the discovery process is complete, the number indicates the number of rows displayed.
Getting Oversubscription Information in Device Manager
To determine the oversubscription for a module using Device Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1
Right-click the module you want to check oversubscription on and select Check Oversubscription from the pop-up menu.You see the oversubscription dialog box.
Step 2
Click Close to close this dialog box.

 Feedback
Feedback