-
Cisco MDS 9000 Family Fabric Manager Configuration Guide, Release 2.x
-
New and Changed Information
-
Index
-
Preface
- Part 1 - Fabric Manager Applications
- Part 2 - Cisco MDS SAN-OS Installation and Configuration Files
-
Part 3 - Switch Configuration
-
Cisco Fabric Services
-
VSAN Configuration
-
Dynamic VSAN Configuration
-
Zone Configuration
-
Inter-VSAN Routing Configuration
-
PortChannel Configuration
-
Interface Configuration
-
FCIP Configuration
-
Configuring the SAN Extension Tuner
-
iSCSI configuration
-
FICON Configuration
-
Configuring Intelligent Storage Services
-
Additional Configuration
-
- Part 4 - Security Configuration
- Part 5 - Network and Performance Monitoring
- Part 6 - Troubleshooting
-
GUI/CLI Usage Chart
-
Interface Nonoperational Reason Codes
-
Managing Cisco FabricWare
-
Table Of Contents
Fabric Manager Client Overview
Launching Fabric Manager Client
Setting Fabric Manager Preferences
Using Alias Names as Enclosures
Control of Administrator Access with Users and Roles
Fabric Manager Troubleshooting Tools
Fabric Manager Client
The Cisco Fabric Manager Client is a java based GUI application that provides easy access to the Fabric Manager applications from a remote workstation.
This chapter contains the following sections:
•
Fabric Manager Client Overview
•
Launching Fabric Manager Client
•
Setting Fabric Manager Preferences
•
Control of Administrator Access with Users and Roles
•
Fabric Manager Troubleshooting Tools
Fabric Manager Client Overview
The Cisco Fabric Manager is a Java and SNMP-based network fabric and device management tool with a GUI that displays real-time views of your network fabric, including Cisco MDS 9000 and third-party switches, hosts, and storage devices.
In addition to complete configuration and status monitoring capabilities for Cisco MDS 9000 switches, Fabric Manager client provides powerful Fibre Channel troubleshooting tools. These in-depth health and configuration analysis tools leverage unique MDS 9000 switch capabilities including Fibre Channel ping and traceroute.
Note
You must have the same release of Fabric Manager Client and Fabric Manager Server.
Fabric Manager Advanced Mode
Fabric Manager Release 2.1(1a) introduces Advanced Mode. Advanced Mode is enabled by default and provides the full suite of Fabric Manager features, including security, IVR, iSCSI, and FICON. Uncheck the Advanced check box in the upper right corner of Fabric Manager client to simplify the user interface. In this mode, you can access the basic MDS 9000 features like VSANs, zoning, and configuring interfaces.
Launching Fabric Manager Client
To launch Fabric Manager client, follow these steps:
Step 1
Double-click the Fabric Manager icon and follow the instructions described in "Launching the Management Software" section on page 1-10 to launch Fabric Manager Client from your desktop.
Step 2
To launch Fabric Manager Client from within a running instance of Fabric Manager, follow these steps:
a.
Choose Open Fabric from the Fabric Manager File menu.
b.
Click the Open Switch Fabric button from the Fabric Manager toolbar.
c.
Select the IP address of the fabric seed switch you want to access. If you do not see the fabric seed switch in the pop-up window, click the Options button to expand the pop-up window options.
d.
Click Open if the fabric you want to open has the same username and password as the fabric you already have open.
Fabric Manager displays the new fabric and adds a tab to the Fabric pane.
Step 3
Click each fabric's tab to view the fabric.
If the fabric you want to open has a different username and password, enter the username and password and click Open. You are prompted for whether or not you want the open fabric(s) to be monitored in the background. That fabric is then closed on the Fabric Manager client, and the new fabric is opened.
Note
Changes made using Fabric Manager are applied to the running configuration of the switches you are managing. If you have made changes to the configuration or performed an operation (such as activating zones), Fabric Manager prompts you to save your changes before you exit.
Using Fabric Manager Client
This section describes the Fabric Manager client interface, as shown in Figure 3-1.
Figure 3-1 Fabric Manager Main Window
Multiple Fabric Display
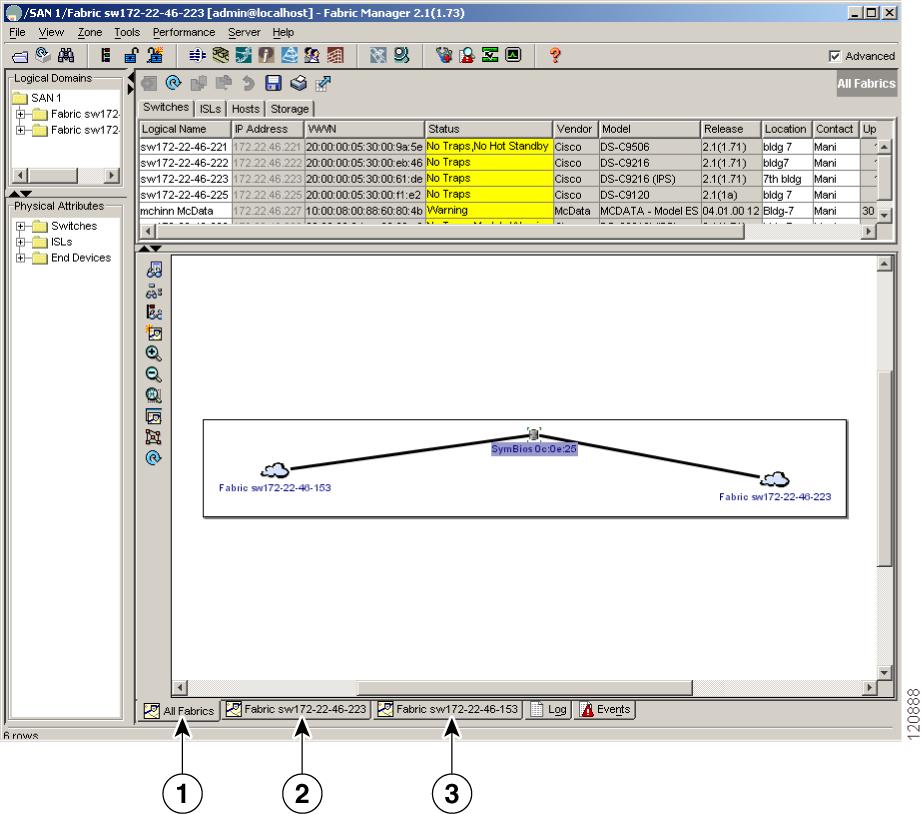
Fabric Manager can display multiple fabrics in the same pane (see Figure 3-2).
Figure 3-2 Fabric Manager's Multiple Fabric Display
Note
The same username and password must be used to log into multiple fabrics.
The information for both fabrics is displayed, with no need to select a seed switch. To see details of a fabric, select the tab for that fabric at the bottom of the Fabric pane, or double-click on the cloud icon for the fabric in the All Fabrics tab.
Contents Panes
The following sections describe the panes in the Fabric Manager view. You can resize each pane by dragging the boundaries between each region or by clicking the Minimize or Maximize controls.
Fabric Pane
The Fabric pane shows the graphical representation of your fabric. Table 3-1 explains the graphics you may see displayed, depending on which devices you have in your fabric.
If a switch or director is grayed out, Fabric Manager can no longer communicate with it.
There are multiple tabs on the bottom of the Fabric pane:
•
Fabric—When displaying multiple fabrics, each fabric has its own tab. You can switch between fabrics by clicking on their respective tabs.
•
Log—Displays messages that describe Fabric Manager operations, such as fabric discovery.
•
Events—Displays information about the SNMP traps received by the management station. This includes combination events as detected by discovery and important traps like license, SNMP, and FICON.
When viewing large fabrics in the Fabric pane, it is helpful to:
•
Turn off end device labels
•
Collapse loops
•
Collapse expanded multiple links (collapsed multiple links are shown as very thick single lines)
•
Dim or hide portions of your fabric by VSAN
Note
When a VSAN, zone, or zone member is selected in the VSAN tree, the map highlighting changes to identify the selected objects. To remove this highlighting, click the Clear Highlight button on the Fabric pane toolbar or choose Clear Highlight from the pop-up menu.
Saving the Map
You can save the map in the Fabric Pane as an image, or in Fabric Manager Release 2.1(2) or later, as an editable Visio diagram. You can save the map with or without labels on the links. The created Visio diagram is editable and saved in two layers:
•
Default layer that includes all switches and links in the fabric.
•
End devices layer that includes the end devices and can be turned off to remove end devices from the Visio diagram.
To save the map as a Visio diagram, select Files > Export > Visio and choose Map... or Map with link labels.... The saved Visio diagram retains the viewing options that you selected from the Fabric Pane. For example, if you collapse multiple links in the Map and export this as a Visio diagram, the Visio diagram shows those as one solid link.
The Show Tech Support option from the Tools menu also supports saving the map as a Visio diagram.
Purging Down Elements
The Fabric pane allows you to refresh the map at any time by clicking the refresh map icon. In Fabric Manager Release 2.1(2) or later, the refresh map icon redraws the map but does not purge down elements. To purge down elements you can:
•
Click Server > Purge. This purges all down elements in the fabric.
•
Right-click on the Fabric pane and select Purge Down Elements.
•
Right-click a down element and select Purge. This purges only this element from the fabric.
Note
If you select an element that is not down and purge it, that element will re-appear on the next fabric discovery cycle.
Main Menu
The menu bar at the top of the Fabric Manager main window provides options for managing and troubleshooting the current fabric and for controlling the display of information on the Fabric pane. The menu bar provides the following menus:
•
File—Opens a new fabric, rediscovers the current fabric, locates switches, sets preferences, prints the map, and clears (right-click on log) or exports the Fabric pane log.
•
View—Changes the appearance of the map (these options are duplicated on the Fabric pane toolbar).
•
Zone—Manages zones, zone sets, and inter-VSAN routing (IVR).
•
Tools—Verifies and troubleshoots connectivity and configuration, as described in the "Fabric Manager Troubleshooting Tools" section.
•
Performance—Runs and configures Performance Manager and Cisco Traffic Analyzer, and generate reports.
•
Server—Runs administrative tasks on clients and fabrics. Provides Fabric Manager Server management and a purge command. Lists switches being managed.
•
Help—Displays online help topics for specific dialog boxes in the Information pane.
Toolbar
The Fabric Manager main toolbar provides buttons for accessing the most commonly used menu bar options as shown inTable 3-2 .
Table 3-2 Fabric Manager Client Main Toolbar
Open switch fabric.
Rediscover current fabric.
Find in the map.
Create VSAN.
Launch DPVM wizard.
Edit full zone database.
Launch IVR zone wizard.
Launch PortChannel wizard.
Launch FCIP wizard.
Launch iSCSI wizard.
Launch QoS wizard.
Configure users and roles.
Launch IP-ACL wizard.
Launch License Install wizard.
Launch Software Install wizard.
Perform switch health analysis.
Perform fabric configuration analysis.
Perform end-to-end connectivity analysis.
Monitor ISL performance.
Show on-line help.
Information Pane
The Information pane displays tables of information associated with the option selected from the menu tree in the Logical Domains or Physical Attributes panes. The Information pane toolbar provides buttons for performing one or more of the operations shown in Table 3-3.
Table 3-3 Information Pane Toolbar
Apply Changes
Applies configuration changes.
Refresh Values
Refreshes table values.
Create Row
Opens the appropriate dialog box to create a new row in the table.
Delete Row
Deletes the currently hilighted rows from the table.
Copy/Ctrl+C
Copies data from one row to another.
Paste/Ctrl +V
Pastes the data from one row to another.
Undo Changes/Ctrl-Z
Undoes the most recent change.
Export
Exports and saves information to a file.
Print Table
Prints the contents of the Information pane.
Detach Table
Displays a non-editable copy of the table in the Information pane in its own window, which you can move around the screen.
Note
After making changes you must save the configuration or the changes will be lost when the device is restarted.
Note
The buttons that appear on the toolbar vary according to the option you select. They are activated or deactivated (dimmed) according to the field or other object that you select in the Information pane.
Logical Domains Pane
Use the Logical Domains pane to manage attributes for fabrics, VSANs, and zones.
To manage these things, right-click one of the folders in the tree and click a menu item from the pop-up menu. You see the appropriate configuration dialog box.
The default name for the fabric is the name, IP address, or WWN for the principal switch in VSAN 1. If VSAN 1 is segmented, the default name is chosen from a principal switch with the smallest WWN. In order, the fabric names you may see are:
•
Fabric <sysName>
•
Fabric <ipAddress>
•
Fabric <sWWN>
Physical Attributes Pane
Use the Physical Attributes pane to display a tree of the options available for managing the switches in the currently selected fabric, VSAN, or zone.
To select an option, click a folder to display the options available and then click the option. You see the table with information for the selected option in the Information pane. The Physical Attributes pane provides the following main folders:
•
Switches—Views and configures hardware, system, licensing, and configuration files.
•
Interfaces—Views and configures FC Physical, FC Logical, Ethernet, SVC, and PortChannel interfaces.
•
FC Services—Views and configures Fibre Channel network configurations.
•
IP—Views and configures IP storage and IP services.
•
Events—Views and configures events, alarms, thresholds, notifications, and informs.
•
Security—Views and configures MDS management and FC-SP security.
•
ISLs—Views and configures Inter-Switch Links.
•
End Devices—Views and configures end devices.
Status Bar
The status bar at the bottom of the Fabric Manager window shows the last entry displayed by the discovery process, and the possible error message on the right side. The status bar displays a message stating that something has changed in the fabric and a new discovery is needed. The status bar shows both short-term, transient messages (such as the number of rows displayed in the table), and long-term discovery issues.
Context Menus
When you right-click an icon in the Fabric pane, you see a pop-up menu with options that vary depending on the type of icon selected. The various options available for different objects include the following:
•
Open an instance of Device Manager for the selected switch.
•
Open a CLI session for the selected switch.
•
Copy the display name of the selected object.
•
Execute a ping or traceroute command for the device.
•
Show or hide end devices.
•
View attributes
•
Quiesce and disable members for PortChannels
•
Set the trunking mode for an ISL.
•
Create or add to a PortChannel for selected ISLs.
The Fabric pane has its own toolbar with options for saving, printing, and changing the appearance of the map. When you right-click on the map, a pop-up menu appears that provides options (duplicated on the toolbar) for changing the appearance of the map.
Note
You can launch web-based or non-web-based applications from the Fabric pane. To do this, you assign an IP address to the storage port or enclosure. Then right-click to bring up the pop-up menu, and select Device Manager.
Filtering
Fabric Manager has a built-in filtering mechanism that displays only the data you are interested in. To filter, first select the fabric, and VSAN from the Logical Domains pane. This narrows the scope of what is displayed in the Fabric pane. Any information that does not belong to the selected items is dimmed. Also, any information that does not belong to the selected items is not displayed in the tables in the Information pane. As shown in Figure 3-3, the filter you select is displayed at the top right of the Fabric Manager window.
To further narrow the scope, select attributes from the Physical Attributes pane. The Fabric Manager tables, display, and filter criteria change accordingly.
Figure 3-3 Fabric Manager's Filtering Mechanism
Detachable Tables
Fabric Manager Release 2.0(2b) introduced detachable tables in Fabric Manager. You can, for example, detach tables and move them to different areas on your desktop so you can compare similar tables from different VSANs. Or, you can keep informational tables open from one view while you examine a different area in Fabric Manager. To detach tables, click the Detach Table icon in the Information pane in Fabric Manager.
Setting Fabric Manager Preferences
To set your preferences for the behavior of the Fabric Manager, choose File > Preferences from the Fabric Manager menu bar. You see the Preferences dialog box with the following tabs for setting different components of the application:.
•
General
•
SNMP
•
Map
The default General preferences for Fabric Manager are:
•
Show Switch Name by—Displays the switches in the Fabric pane by IP address, DNS name, or logical name. The default setting for this value is Logical Name.
•
Show WorldWideName (WWN) Vendor—This displays the world wide name vendor name in any tables or listings displayed by Fabric Manager. If Prepend Name is checked, the name is displayed in front of the IP Address of the switch. If Replacing Vendor Bytes is checked, the name is displayed instead of the IP address. The default setting is enabled (checked) with the Prepend Name option.
•
Show End Device Using—Displays end devices in the Fabric pane using alias or pWWN alias. The default setting for this value is Alias.
•
Append Enclosures to End Device Names—The default setting for this value is OFF.
•
Show Shortened iSCSI Names—The default setting for this value is OFF.
•
Show Timestamps as Date/Time—Displays timestamps in the date/time format. If this preference is not checked, timestamps are displayed as elapsed time. The default setting is enabled (checked).
•
Telnet Path—The path for the telnet.exe file on your system. The default is telnet.exe, but you will need to browse for the correct location.
Note
If you browse for a path or enter a path and you have a space in the pathname (for example, c:\program files\telnet.exe), then the path will not work. To get the path to work, you must manually place quotes around it (for example, "c:\program files\telnet.exe").
•
Use Secure Shell instead of Telnet—Specifies whether to use SSH or Telnet when using the CLI to communicate with the switch. If enabled, you must specify the path to your SSH application. The default setting is disabled.
•
Confirm Deletion—Displays a confirmation pop-up when you delete part of your configuration using Fabric Manager. The default setting is enabled (checked).
•
Export Tables with Format—Specifies the type of file that is created when you export a table using Device Manager. The options are tab-delimited or XML. The default setting is Tab-Delimited.
The default SNMP preferences for Fabric Manager are:
•
Retry request 1 time(s) after 5 sec timeout—You can set the retry value to 0-5, and the timeout value to 3-30.
•
Trace SNMP packets in Log—The default setting for this value is OFF.
•
Enable Audible Alert when Event Received—The default setting for this value is OFF.
The default Map preferences for Fabric Manager are:
•
Display Unselected VSAN Members—Displays the unselected VSAN members in the Fabric pane. The default setting for this value is ON.
•
Display End Devices—Displays the fabric's end devices in the Fabric pane. The default setting for this value is ON.
•
Display End Device Labels—Displays the fabric's end device labels in the Fabric pane. The default setting for this value is ON.
•
Expand Loops—Displays the loops in the fabric as individual connections in the Fabric pane. The default setting for this value is OFF.
•
Expand Multiple Links—Displays multiple links in the Fabric pane as separate lines rather than as one thick line. The default setting for this value is ON.
•
Open New Device Manager Each Time—Opens a new instance of Device Manager each time you invoke it from a switch in your fabric. The default value is OFF, which means only one instance of Device Manager is open at a time.
•
Select Switch or Link from Table—Allows you to select a switch or link in the Fabric pane by clicking on the switch or link in a table in the information pane. The default setting for this value is disabled (unchecked), which means clicking on a switch or link in the table does not change the switch or link selection in the Fabric pane.
•
Layout New Devices Automatically—Automatically places new devices in the Fabric pane in an optimal configuration. The default setting for this value is OFF. In this mode, when you add a new device, you must manually reposition it if the initial position does not suit your needs.
•
Use Quick Layout when Switch has >=30 End Devices—The default setting for this value is 30. You can enter any number in this field. Enter 0 to disable Quick Layout.
•
Override Preferences for Non-default Layout—The default setting for this value is ON.
•
Automatically Save Layout—If this option is enabled, any changes in layout are automatically saved. The default setting for this value is ON.
•
Detach Overview Window—Allows you to more easily center the Fabric pane on the area of the fabric you want to see. (This is most useful for large fabrics that cannot be displayed entirely within the Fabric pane.) Bring up the overview window by clicking the Show/Hide Overview Window button. It overlays the fabric window and remains there until you click the Show/Hide Overview Window button again. If you enable this preference, you can detach the overview window and move it to one side while you access the Fabric pane. The default setting for this value is disabled (unchecked).
In Fabric Manager Release 2.1(2) or later, you can select the SNMP port that Fabric Manager client uses
Network Fabric Discovery
Cisco Fabric Manager collects information on the fabric topology through SNMP queries to the switches connected to Fabric Manager. The switch replies after having discovered all devices connected to the fabric by using the information coming from its FSPF technology database and the Name Server database, and collected using the Fabric Configuration Server's request/response mechanisms defined by the FC-GS-3/4 standard. When you start the Fabric Manager, you enter the IP address (or host name) of a "seed" switch for discovery.
After you start Fabric Manager and discovery completes, Fabric Manager presents you with a view of your network fabric, including all discovered switches, hosts, and storage devices.
Modifying Device Grouping
Because not all devices are capable of responding to FC-GS-3 requests, different ports of a single server or storage subsystem may be displayed as individual end devices on the Fabric Manager map. Fabric Manager Release 2.1(2a) auto-creates enclosures based on the OUI and vendor name for the devices.
Note
Two devices in isolated fabrics with the same alias name may cause Fabric Manager to link the two devices in the same enclosure and show the isolated fabrics as linked. Turn off auto-creation or manually modify the enclosure to create unique names in each fabric to show the fabrics as isolated in Fabric Manager.
To turn off auto-creation, edit the server.properties file to set fabric.autoAlias to false and then restart Fabric Manager Server.
To manually group end devices in a single enclosure to have them represented by a single icon on the map, follow these steps:
Step 1
Select Storage or Hosts from the Fabric Manager's Physical tree in the Navigation pane.
You see the end devices displayed in the Information pane.
Step 2
Click one of the devices or the Name field that you want to be in the enclosure.
Step 3
Enter a name to identify the new enclosure's icon on the Fabric Manager Fabric pane.
Step 4
Click once on the Name field for that device. To select more than one name, hold down the Shift key and click each of the other names.
Step 5
Press Ctrl-C to copy the selected name(s).
Step 6
Press Ctrl-V to paste the name into the Name field for that device.
Note
To remove devices from an enclosure, triple click on the name of the device and press Delete. To remove an enclosure, repeat this step for each device in the enclosure.
Using Alias Names as Enclosures
To create an enclosure that uses the alias name as the name of the enclosure, follow these steps:
Step 1
Select Hosts or Storage from the Physical Attributes pane. You see the list of devices in the Information pane.
Step 2
Select the NxPorts tab.
Step 3
Right-click the enclosure names that you want to convert to use alias names and select Alias > Enclosure.
Step 4
Click Apply Changes to save these changes or click Undo Changes to discard any unsaved changes.
Control of Administrator Access with Users and Roles
Cisco MDS 9000 Family switches support role-based management access whether using the CLI or the Cisco Fabric Manager. This lets you assign specific management privileges to particular roles and then assign one or more users to each role.
Cisco Fabric Manager uses SNMPv3 to establish role-based management access. After completing the setup routine, a single role, user name, and password are established. The role assigned to this user allows the highest level of privileges, which includes creating users and roles. Use the Cisco Fabric Manager to create roles and users, and to assign passwords as required for secure management access in your network.
Fabric Manager Wizards
Fabric Manager client provides a series of wizards to facilitate common configuration tasks. These wizards include:
•
VSAN—Creates VSANs on multiple switches in the fabric and sets VSAN attributes including interop mode, load balancing, and FICON.
•
Zone Edit Tool —Creates zone sets, zones, and aliases. Adds members to zones, and edits zone database.
•
IVR Zone—Creates IVR zone sets, zones, and aliases. Enables IVR NAT and auto-topology. Adds members to IVR zones, and edits IVR zone database.
•
PortChannel—Creates PortChannels from selected ISLs either manually or automatically. Sets PortChannel attributes like channel ID and trunking mode.
•
FCIP —Creates FCIP links between Gigabit Ethernet ports. Enables Fibre Channel Write Acceleration and IP compression
•
DPVM—Establishes dynamic port VSAN membership, enables auto learning, and activates the DPVM database.
•
iSCSI—Zones iSCSI initiators and adds VSAN to target allowed VSAN list.
•
QoS—Sets QoS attributes for zones in the selected VSAN.
•
IP ACL—Creates ordered IP access control lists and distributes to selected switches in the fabric.
•
License Install—Facilitates download and installation of licenses in selected switches in the fabric.
•
Software Install—Verifies image compatibility and installs software images on selected switches in the fabric.
Fabric Manager Troubleshooting Tools
Fabric Manager has several troubleshooting tools available from the toolbar or Tools menu. Procedures for using these tools are described in Chapter 35, "Troubleshooting Your Fabric." Here is a brief description of each tool.
•
Zone Merge Analysis—The zone merge analysis tool (available from the Zone menu) enables you to determine if zones will merge successfully when two Cisco MDS switches are interconnected. If the interconnected switch ports allow VSANs with identical names or contain zones with identical names, then Fabric Manager verifies that the zones contain identical members. The merge analysis tool can be run before attempting a merge or after fabrics are interconnected to determine zone merge failure causes.
•
End-to-End Connectivity—Fabric Manager's end-to-end connectivity analysis tool uses FC Ping to verify interconnections between Cisco MDS switches and end-device (HBAs and storage devices) in a particular VSAN. In addition to basic connectivity, Fabric Manager can optionally verify that:
–
Paths are redundant.
–
Zones contain at least two members.
End devices are connected to a manageable switch (have an currently active in-band or out-of-band management path.)
•
Switch Health Analysis—You can run an in-depth switch health analysis with Fabric Manager. It verifies the status of all critical Cisco MDS switches, modules, ports, and Fibre Channel services. Over 40 conditions are checked. This tool provides a very fast, simple, and thorough way to assess Cisco MDS switch health.
•
Fabric Configuration Analysis—Fabric Manager includes a fabric configuration analysis tool. It compares the configurations of all Cisco MDS switches in a fabric to a reference switch or a policy file. You can define what functions to check and what type of checks to perform. The analysis can look for mismatched values, and missing or extra values. If all configuration checking is performed for all functions, over 200 checks are performed for each Cisco MDS switch.
After the analysis is run, the results are displayed with details about the issues that were discovered. You can automatically resolve configuration differences by selecting them and clicking the Resolve button. Fabric Manager automatically changes the configuration to match the reference switch or policy file.

 Feedback
Feedback