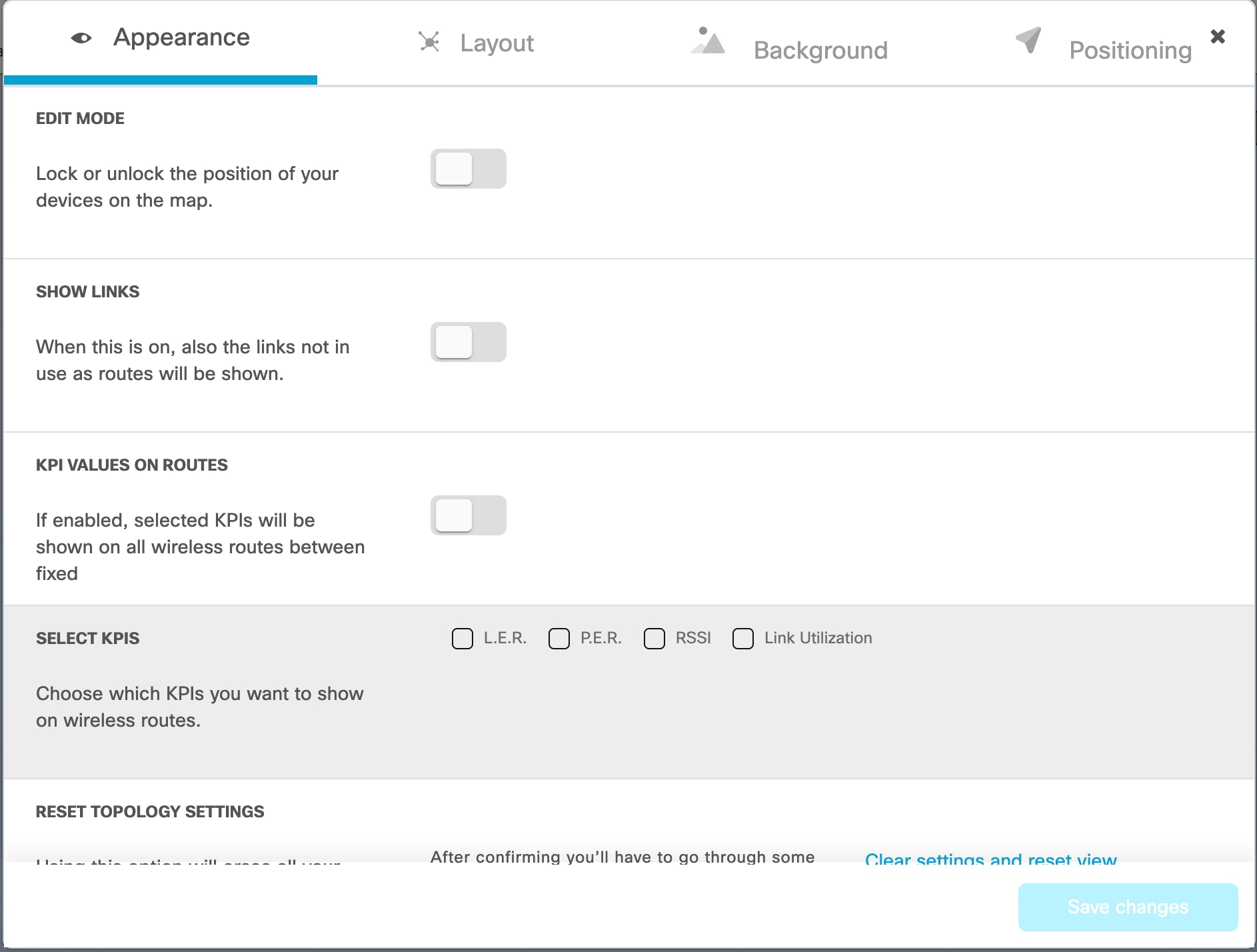
Viewing the Network Statistics
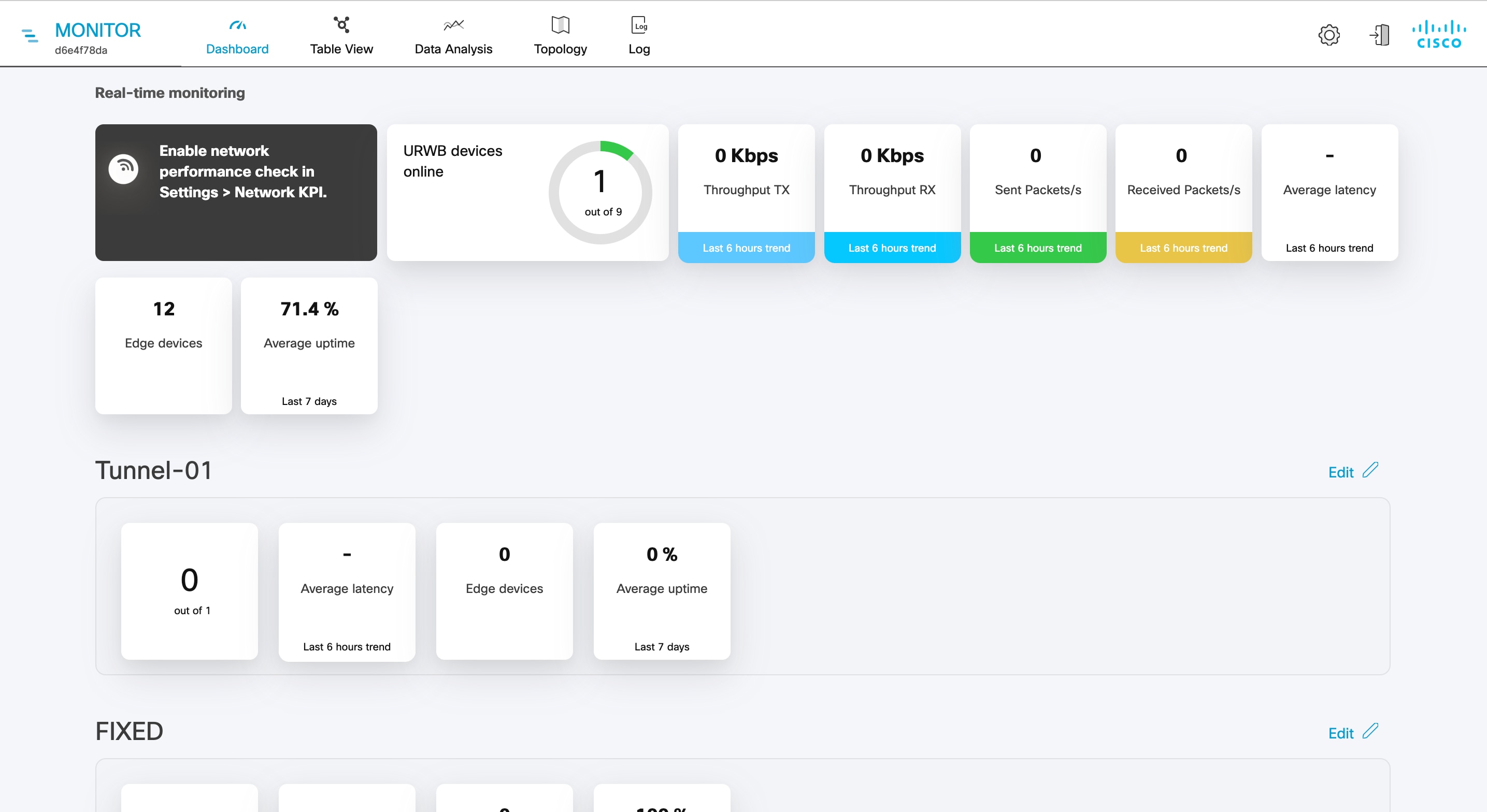
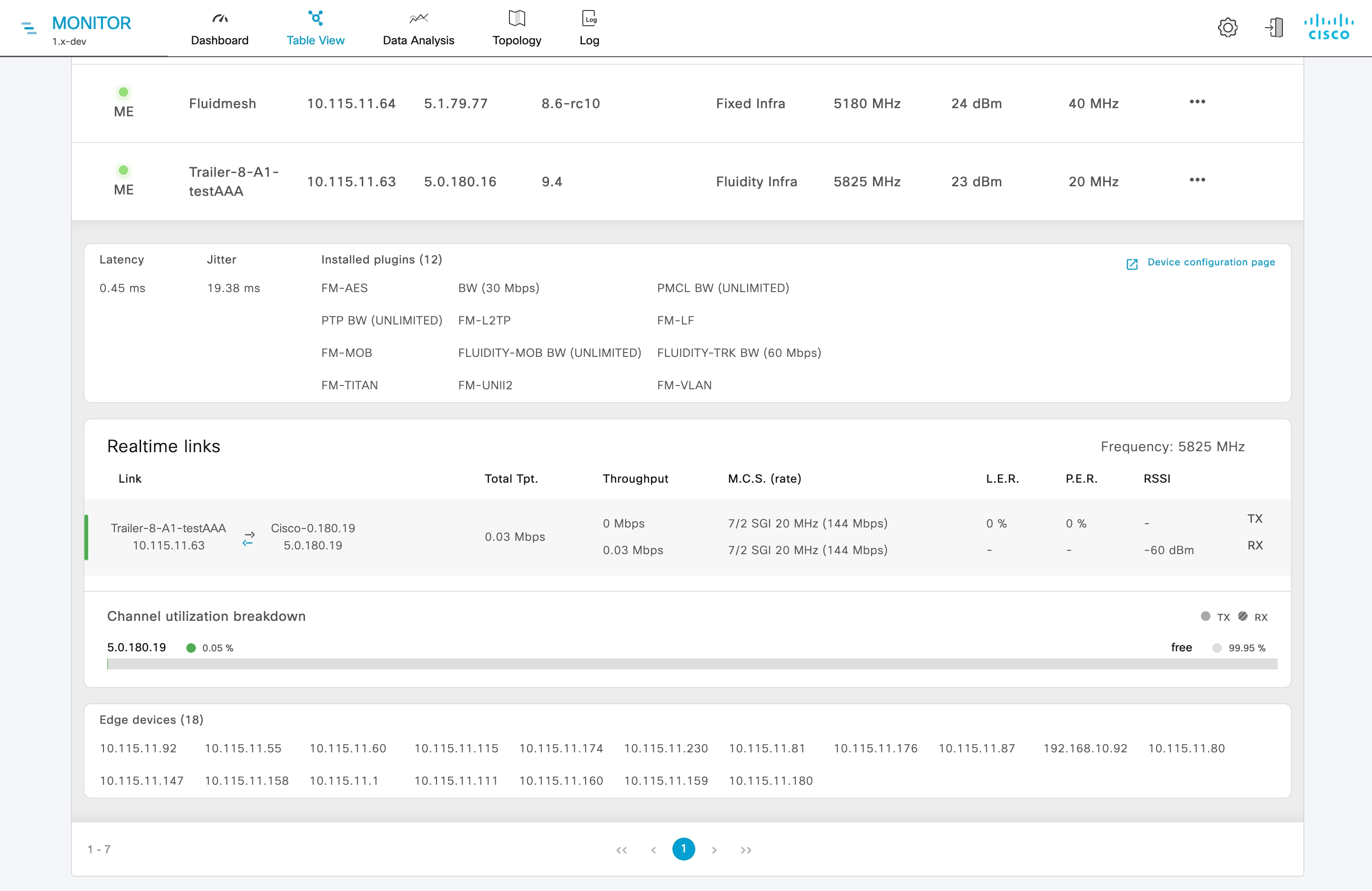
The real-time monitoring shows the performance of the combined network. Each box shows information about performance of a specified network section. In each network section, the blocks show operating parameters of the devices in the network such as:
-
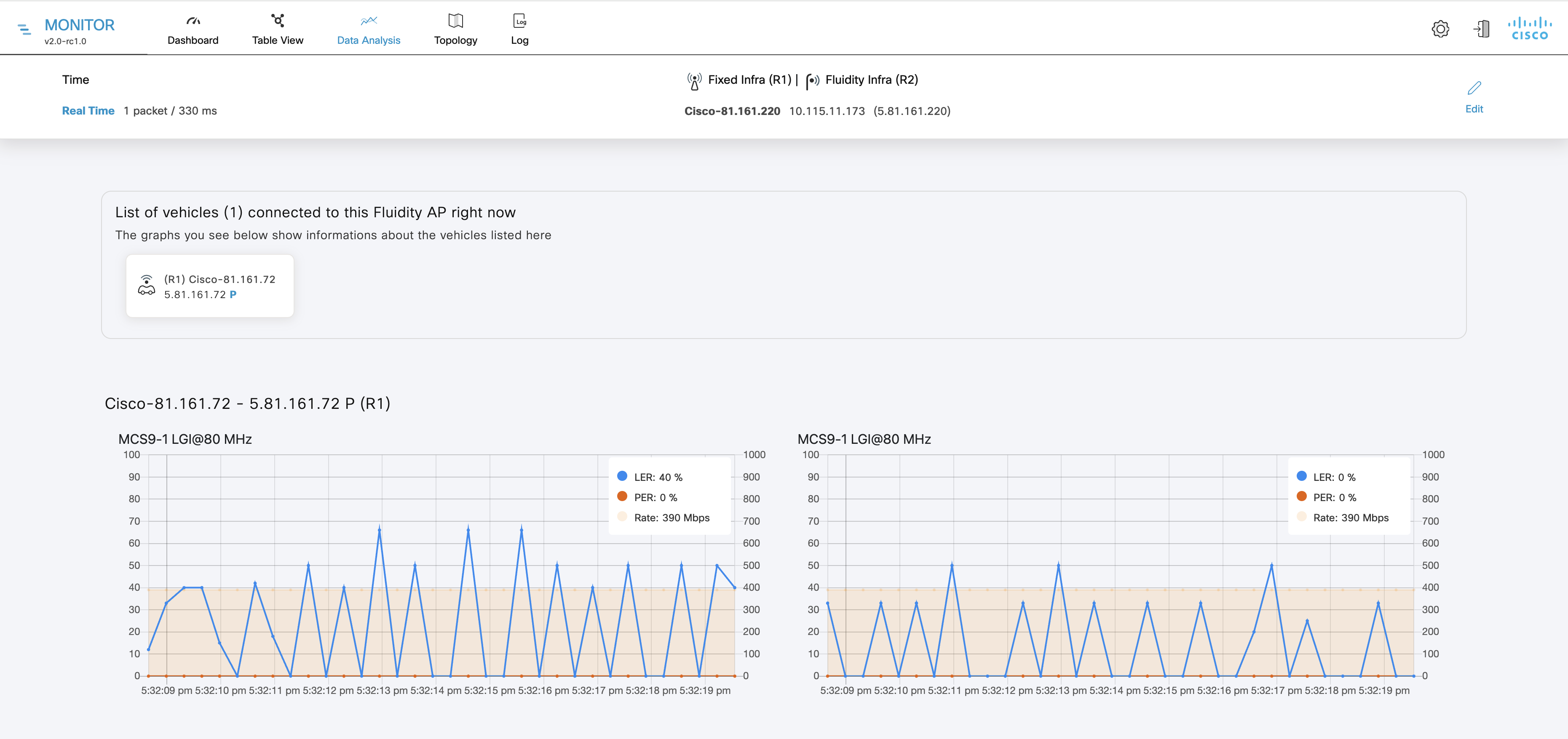
Number of devices currently connected to IW Monitor, in relation to the total number of devices associated to IW Monitor.
-
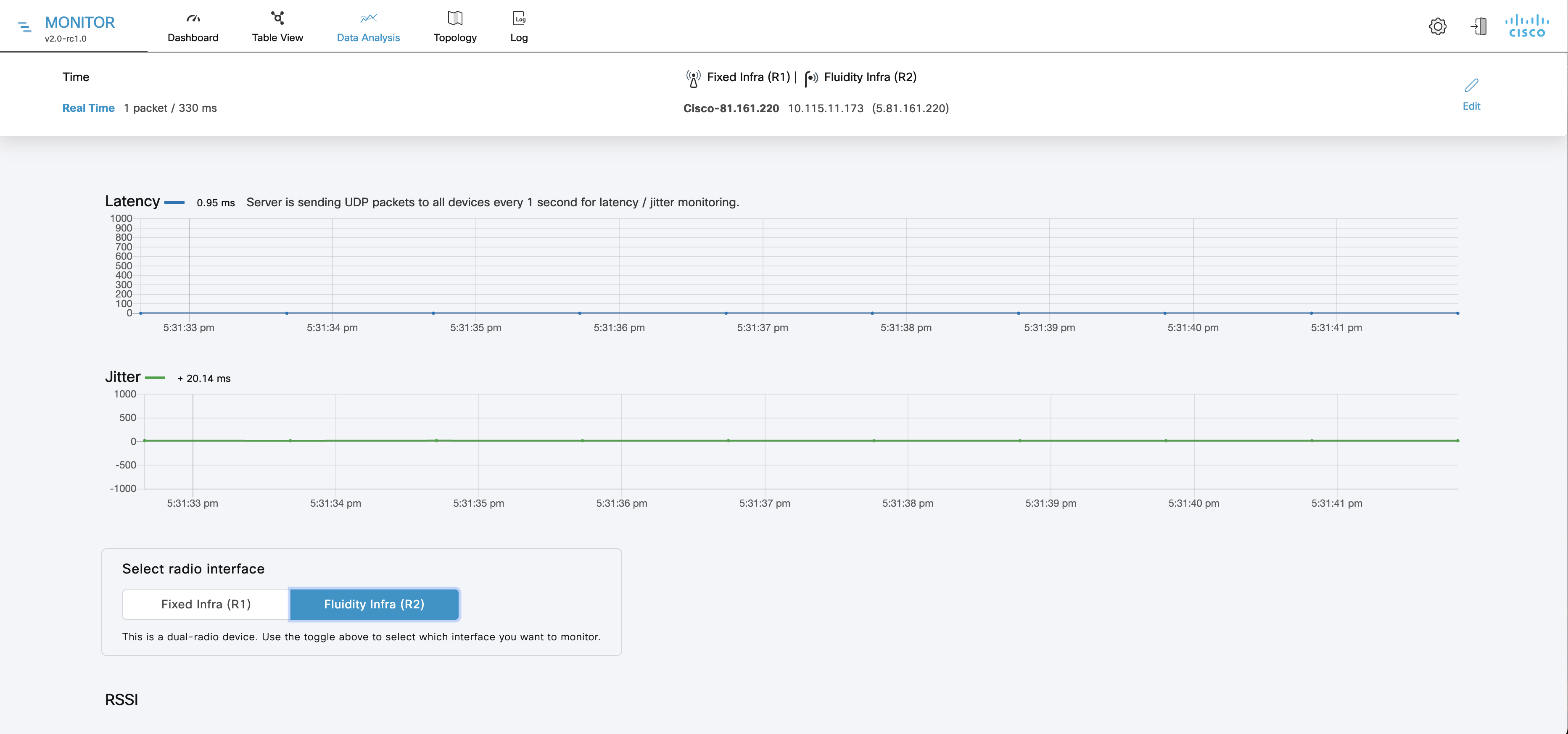
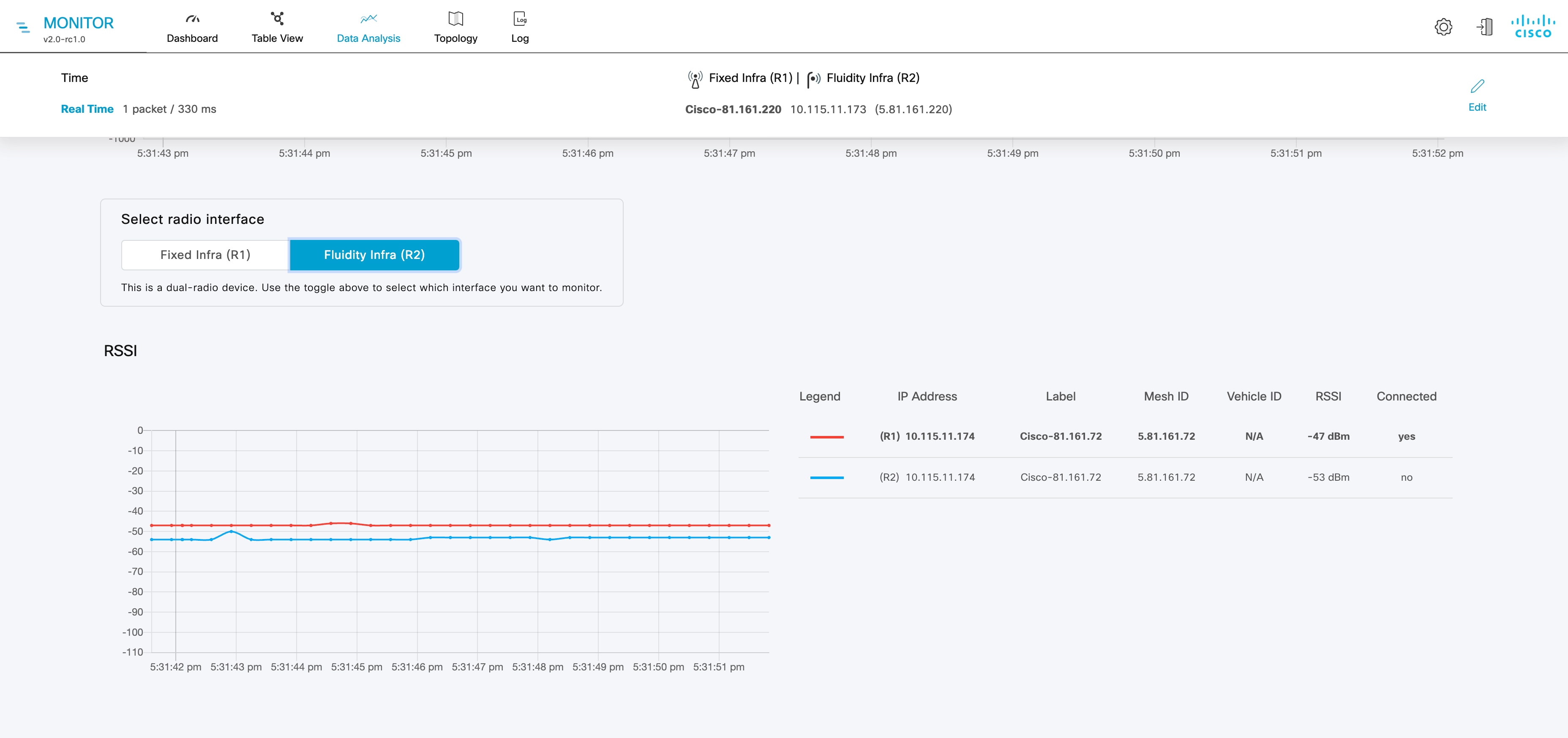
Device latency (Average latency) values across the network or section during the last six hours.
-
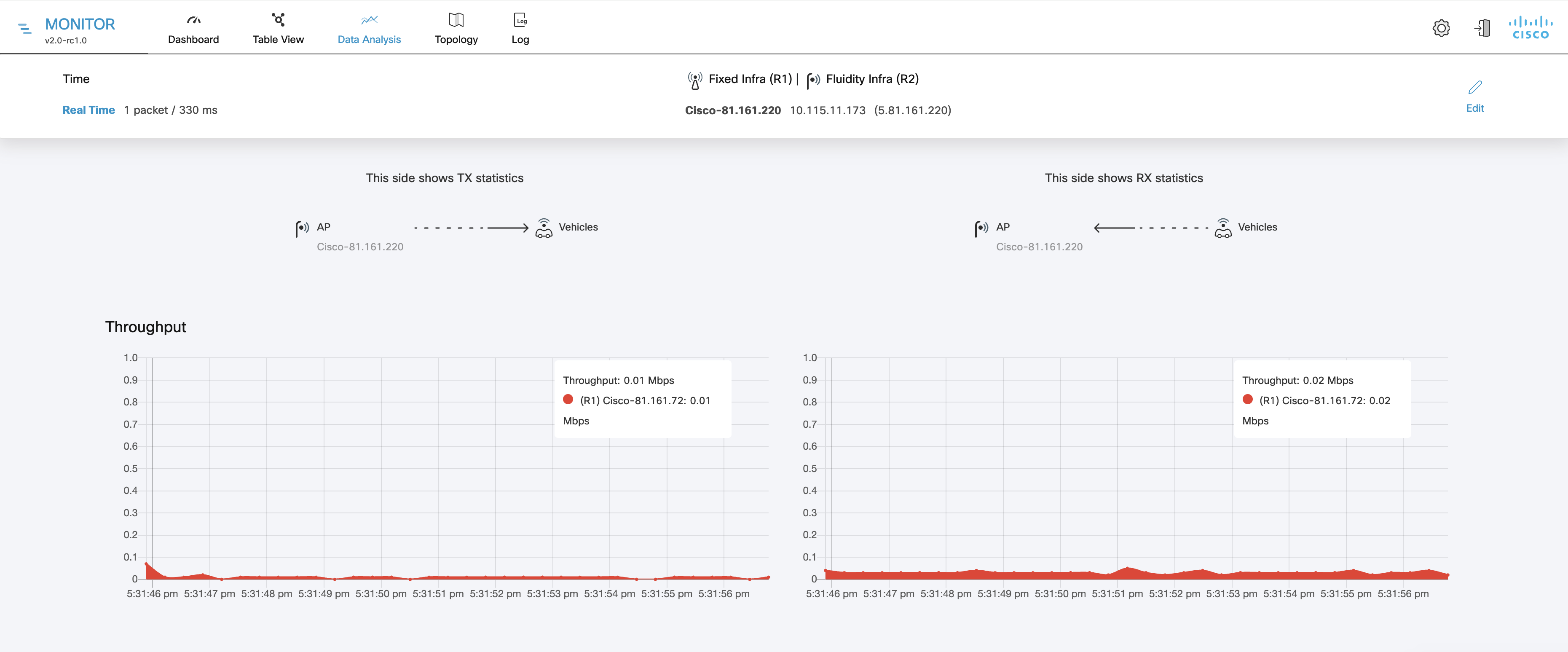
Aggregate network throughput transmitted (Throughput TX) by all devices in the network during the last six hours.
-
Aggregate network throughput received (Throughput RX) by all devices in the network during the last six hours.
-
Aggregate number of data packets sent (Sent Packets/s) by all devices in the network during the last six hours.
-
Aggregate number of data packets received (Received Packets/s) by all devices in the network during the last six hours.
-
Current number of edge devices (Edge devices).
-
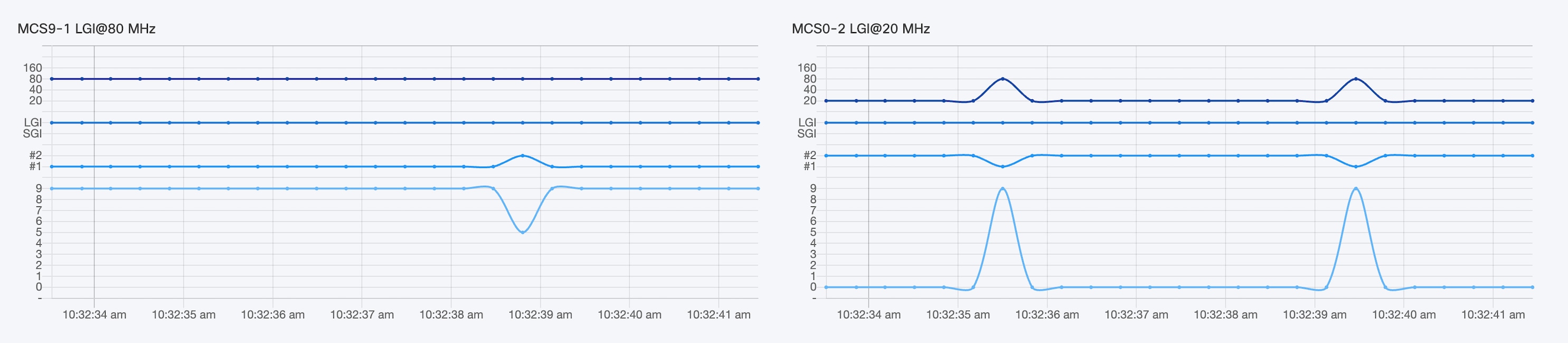
Average network or section uptime value (Average uptime). The average uptime value is the combined percentage of time for each network device or section connected to the IW Monitor in the last seven days.
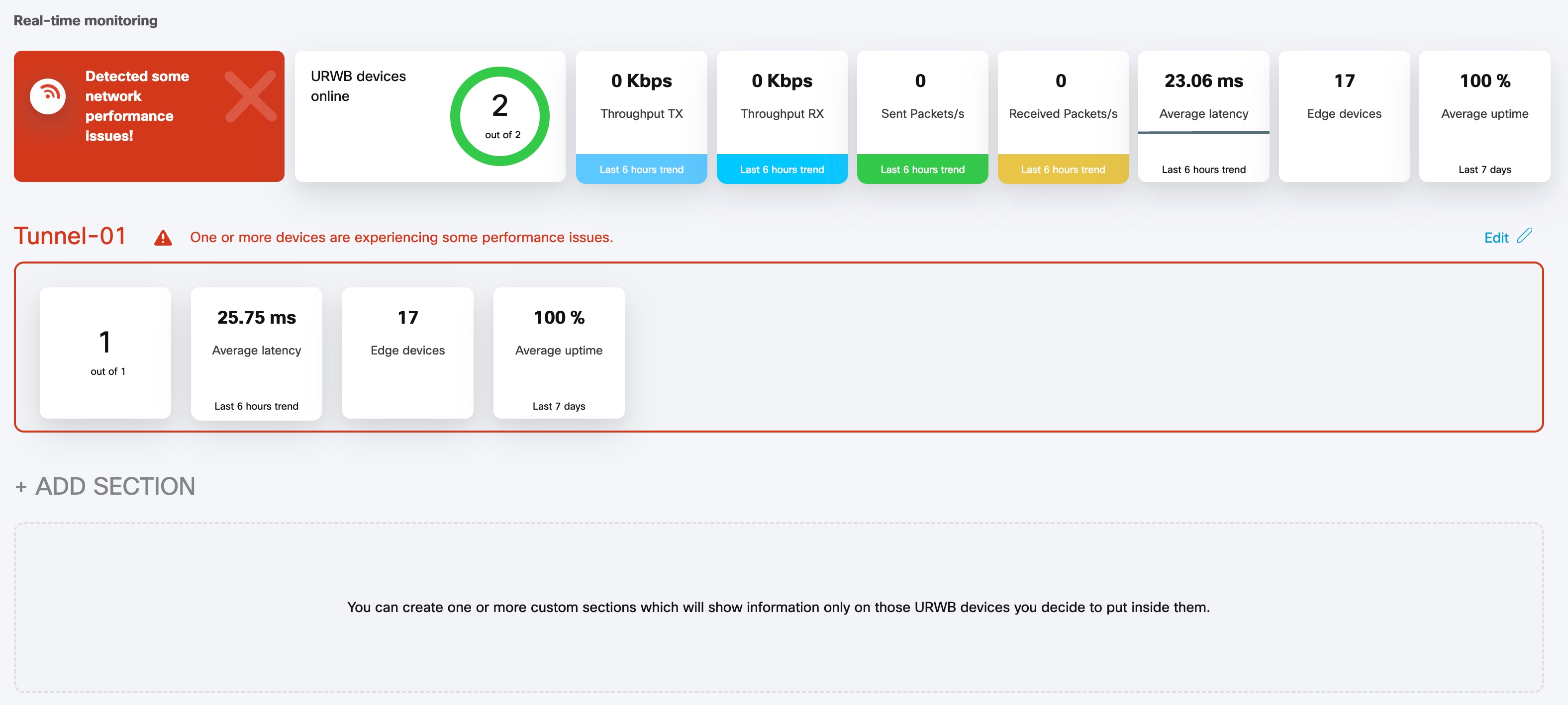
A thin red box appears around the section if any performance-related faults arise and need immediate investigation. The + ADD SECTION at the bottom allows you to customize the section with the device information you want to monitor. To add a new section to an existing network, see Create a new Section.
 Feedback
Feedback