Power Supply Specifications
- 3000 W AC-Input Power Supply Specifications
- 3000 W Power Supply AC Power Cords
- Chassis and Module Power and Heat Values
3000 W AC-Input Power Supply Specifications
| Specification | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
|
AC-input type |
|
||
|
AC-input voltage |
Low-line (120 VAC nominal)—90 VAC (min) to 132 VAC (max) High-line (230 VAC nominal)—170 VAC (min) to 264 VAC (max) |
||
|
AC-input current |
16 A @ 240 VAC (3000 W output) 16 A @ 120 VAC (1300 W output) |
||
|
AC-input frequency |
50/60 Hz (nominal) (±3% for full range) |
||
|
Branch circuit requirement |
|
||
|
Power supply output capacity |
1400 W maximum (100 to 120 VAC) 3000 W maximum (200 to 240 VAC) |
||
|
Power supply output |
|||
|
Output holdup time |
20 ms minimum. |
||
|
kVA rating1 |
3520 W (total input power) or 3.6 kVA (high-line operation). |
||
|
Heat dissipation |
12,046 BTU /hour (approx.) |
||
|
Weight |
6 lb (2.72 kg) |
3000 W Power Supply AC Power Cords
The following table lists the specifications for the AC power cords that are available for the 3000 W AC-input power supply. The table also includes references to power cord illustrations.
 Note |
|
Locale |
AC Source Plug Type |
Cordset Rating |
Power Cord Part Number and Reference Illustration |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Argentina |
IRAM 2073 |
16 A, 250 VAC |
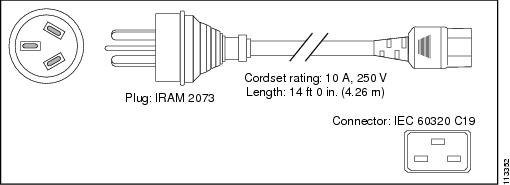 |
||
|
Australia, New Zealand |
AU20S3 |
16 A, 250 VAC |
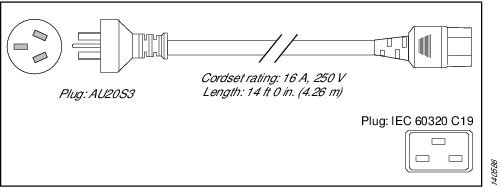 |
||
|
Brazil |
EN60320 / C19 |
16 A, 250 VAC |
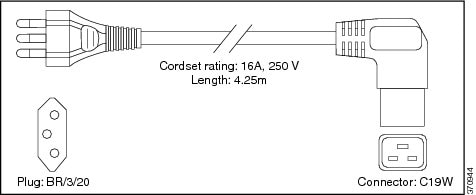 |
||
|
People's Republic of China |
GB16C |
16 A, 250 VAC |
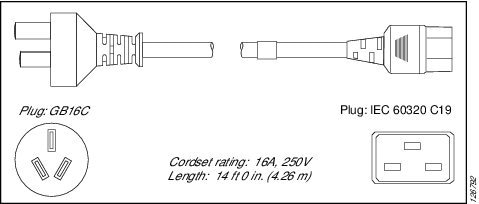 |
||
|
Continental Europe |
CEE 7/7 |
16 A, 250 VAC |
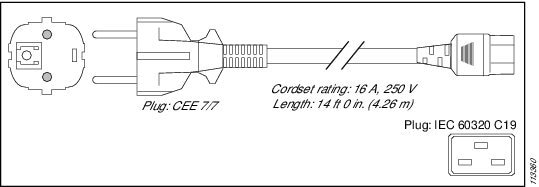 |
||
|
India |
EN60320/C19 |
16 A, 250 VAC |
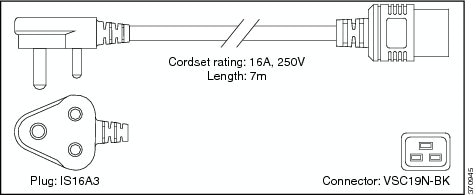 |
||
|
International |
IEC 309 |
16 A, 250 VAC |
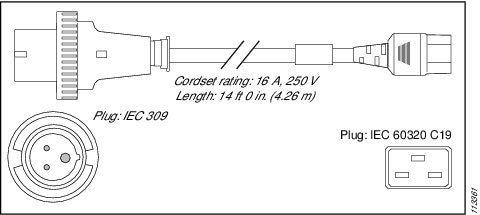 |
||
|
Israel |
SI16S3 |
16 A, 250 VAC |
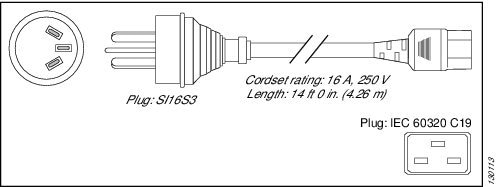 |
||
|
Italy |
CEI 23-16/7 |
16 A, 250 VAC |
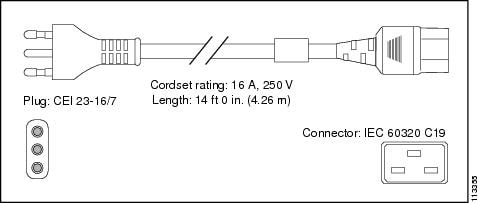
|
||
|
Japan, North America (Nonlocking Plug) 200 to 240 VAC Operation |
NEMA 6-20 |
16 A, 250 VAC |
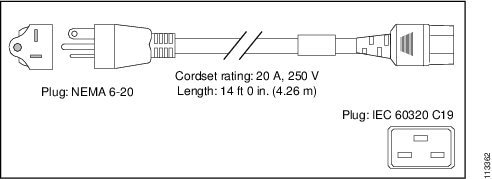 |
||
|
Japan, North America (Locking Plug)200 to 240 VAC Operation |
NEMA L6-20 |
16 A, 250 VAC |
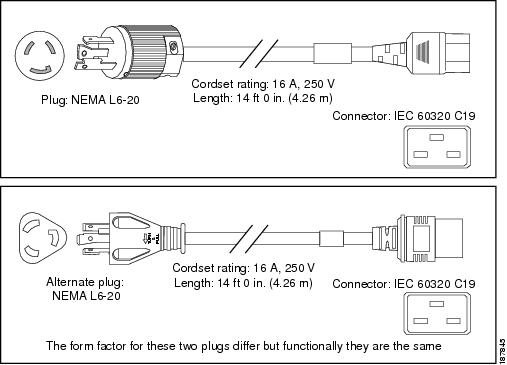
|
||
|
Japan, North America 100 to 120 VAC operation 2 |
NEMA 5-20 |
20 A, 125 VAC |
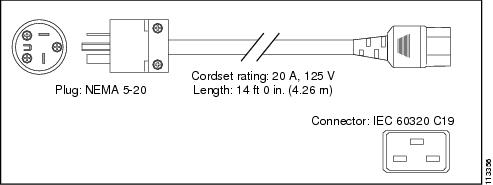 |
||
|
North America |
NEMA L5 -20 |
20 A, 125 VAC |
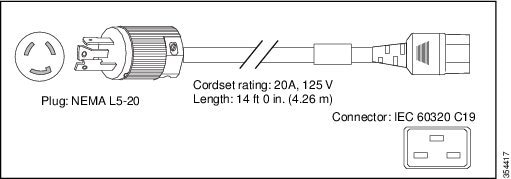 |
||
|
Power Distribution Unit (PDU) 3 |
IEC 60320 C19 IEC 60320 C20 |
16 A, 250 VAC |
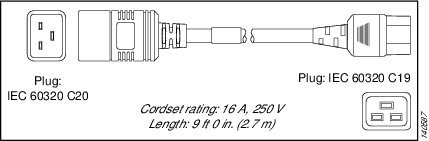 |
||
|
South Africa |
IEC 884-1 |
16 A, 250 VAC |
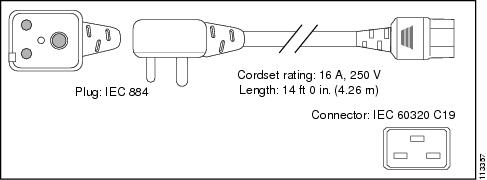 |
||
|
Switzerland |
SEV 5934-2 Type 23 |
16 A, 250 VAC |
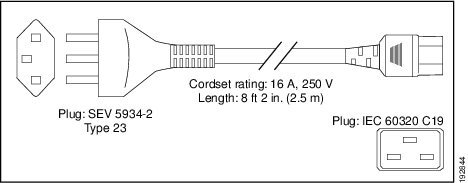 |
Chassis and Module Power and Heat Values
 Note | Module power is the output from the power supply (internal to the system). The AC-input power is the input from the outlet to the power supply. The percentage difference between the two values is the efficiency of the power supply. |
|
Model Number/ Module Type |
Module Current (A) @ 52V |
Module Power (Watts) (Power-Requested) |
AC-Input Power (Watts) (Power-Allocated) |
Heat Diss. (BTU/HR) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
C6807-XL-FAN |
5 |
260 |
260 |
887.15 |
|
Model Number/ Module Type |
Module Current (A) @ 52V |
Module Power (Watts) (Power-Requested) |
AC-Input Power (Watts) (Power-Allocated) |
Heat Diss. (BTU/HR) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
VS-S2T-10G |
6.80 |
353.60 |
353.60 |
1206.53 |
|
VS-S2T-10G-XL |
10.73 |
557.96 |
557.96 |
1903.83 |
|
C6800-SUP6T |
8.12 |
341 |
341 |
1370.18 |
|
C6800-SUP6T-XL |
8.43 |
354 |
354 |
1422.49 |
|
Model Number/ Module Type |
Module Current (A) @ 52V |
Module Power (Watts) (Power-Requested) |
AC-Input Power (Watts) (Power-Allocated) |
Heat Diss. (BTU/HR) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
VS-F6K-PFC4 |
2.5 |
130 |
130 |
507.45 |
|
VS-F6K-PFC4XL |
2.86 |
148.72 |
148.72 |
507.45 |
|
Model Number/ Module Type |
Module Current (A) @ 52V |
Module Power (Watts) (Power-Requested) |
AC-Input Power (Watts) (Power-Allocated) |
Heat Diss. (BTU/HR) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
WS-F6K-DFC4-E Distributed Forwarding Card E |
2.38 |
123.76 |
123.76 |
422.28 |
|
WS-F6K-DFC4-EXL Distributed Forwarding Card EXL |
2.74 |
142.48 |
142.48 |
486.16 |
|
WS-F6K-DFC4-A Distributed Forwarding Card A |
2.64 |
137.28 |
137.28 |
468.41 |
|
WS-F6K-DFC4-AXL Distributed Forwarding Card AXL |
2.76 |
143.52 |
143.52 |
489.71 |
|
Model Number/ Module Type |
Module Current (A) @ 52V |
Module Power (Watts) (Power-Requested) |
AC-Input Power (Watts) (Power-Allocated) |
Heat Diss. (BTU/HR) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
WS-X6724-SFP |
2.98 |
154.96 |
154.96 |
528.74 |
|
WS-X6748-SFP |
6.07 |
315.64 |
315.64 |
1077.00 |
|
WS-X6848-SFP |
8.08 |
420.16 |
420.16 |
1433.64 |
|
Model Number/ Module Type |
Module Current (A) @ 52V |
Module Power (Watts) (Power-Requested) |
AC-Input Power (Watts) (Power-Allocated) |
Heat Diss. (BTU /HR) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
WS-X6816-10G (WS-X6816-10G = WS-X6716-10GE + DFC4E) |
11.99 |
623.48 |
623.48 |
2127.40 |
|
WS-X6816-10G XL |
12.26 |
637.52 |
637.52 |
2175.30 |
|
WS-X6908-10G |
10.29 |
535.08 |
535.08 |
1828.22 |
|
WS-X6908-10 XL |
10.65 |
553.8 |
553.8 |
1889.64 |
|
WS-X6816-10T |
10.61 |
551.72 |
551.72 |
1882.54 |
|
WS-X6816-10TXL |
10.97 |
570.44 |
570.44 |
1946.42 |
|
Model Number/ Module Type |
Module Current (A) @ 52V |
Module Power (Watts) (Power-Requested) |
AC-Input Power (Watts) (Power-Allocated) |
Heat Diss. (BTU/HR) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
WS-X6748-GE-TX |
7.75 |
403.00 |
403.00 |
1375.09 |
|
WS-X6848-GE-TX |
9.76 |
507.52 |
507.52 |
1731.72 |
|
Model Number/ Module Type |
Module Current (A) @ 52V |
Module Power (Watts) (Power-Requested) |
AC-Input Power (Watts) (Power-Allocated) |
Heat Diss. (BTU/HR) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
WS-X6904-40G-2T |
11.15 |
579.8 |
598.52 |
1978.36 |
|
WS-X6904-40G-2TXL |
11.51 |
598.52 |
598.52 |
2042.23 |
|
Model Number/ Module Type |
Module Current (A) @ 52V |
Module Power (Watts) (Power-Requested) |
AC-Input Power (Watts) (Power-Allocated) |
Heat Diss. (BTU/HR) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
NAM3 |
8.83 |
370.86 |
370.86 |
1265.42 |
|
ASA-SM |
8.83 |
370.86 |
370.86 |
1265.42 |
|
WiSM2 |
5.35 |
224.70 |
224.70 |
766.70 |
|
ACE-30 |
7.98 |
335.16 |
335.16 |
1143.61 |
 Feedback
Feedback