- Release 15.5SY Supervisor Engine 6T Software Configuration Guide
- Preface
- Product Overview
- Command-Line Interfaces
- Smart Port Macros
- Virtual Switching Systems (VSS)
- Enhanced Fast Software Upgrade (eFSU)
- Fast Software Upgrades
- Stateful Switchover (SSO)
- Non-Stop Forwarding (NSF)
- RPR Supervisor Engine Redundancy
- Interface Configuration
- UniDirectional Link Detection (UDLD)
- Instant Access
- EnergyWise
- Power Management
- Environmental Monitoring
- Online Diagnostics
- Onboard Failure Logging (OBFL)
- Switch Fabric Functionality
- Cisco IP Phone Support
- Power over Ethernet
- Layer 2 LAN Port Configuration
- Flex Links
- EtherChannels
- IEEE 802.1ak MVRP and MRP
- VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP)
- VLANs
- Private VLANs (PVLANs)
- Private Hosts
- IEEE 802.1Q Tunneling
- Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling
- Spanning Tree Protocols (STP, MST)
- Optional STP Features
- IP Unicast Layer 3 Switching
- Policy Based Routing (PBR)
- Layer 3 Interface Configuration
- Unidirectional Ethernet (UDE) and unidirectional link routing (UDLR)
- Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS)
- MPLS VPN Support
- Ethernet over MPLS (EoMPLS)
- Virtual Private LAN Services (VPLS)
- L2VPN Advanced VPLS (A-VPLS)
- Ethernet Virtual Connections (EVC)
- Layer 2 over Multipoint GRE (L2omGRE)
- Campus Fabric
- IPv4 Multicast Layer 3 Features
- IPv4 Multicast IGMP Snooping
- IPv4 PIM Snooping
- IPv4 Multicast VLAN Registration (MVR)
- IPv4 IGMP Filtering
- IPv4 Router Guard
- IPv4 Multicast VPN Support
- IPv6 Multicast Layer 3 Features
- IPv6 MLD Snooping
- NetFlow Hardware Support
- System Event Archive (SEA)
- Backplane Platform Monitoring
- Local SPAN, RSPAN, and ERSPAN
- SNMP IfIndex Persistence
- Top-N Reports
- Layer 2 Traceroute Utility
- Mini Protocol Analyzer
- PFC QoS Guidelines and Restrictions
- PFC QoS Overview
- PFC QoS Classification, Marking, and Policing
- PFC QoS Policy Based Queueing
- PFC QoS Global and Interface Options
- AutoQoS
- MPLS QoS
- PFC QoS Statistics Data Export
- Cisco IOS ACL Support
- Cisco TrustSec (CTS)
- AutoSecure
- MAC Address-Based Traffic Blocking
- Port ACLs (PACLs)
- VLAN ACLs (VACLs)
- Policy-Based Forwarding (PBF)
- Denial of Service (DoS) Protection
- Control Plane Policing (CoPP)
- Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Snooping
- Configuring IGMP Proxy
- IP Source Guard
- Dynamic ARP Inspection (DAI)
- Traffic Storm Control
- Unknown Unicast and Multicast Flood Control
- IEEE 802.1X Port-Based Authentication
- Configuring Web-Based Authentication
- Port Security
- Lawful Intercept
- Online Diagnostic Tests
Port ACLs (PACLs)
- Prerequisites for PACls
- Restrictions for PACLs
- Information About PACLs
- Interface Template ACLs
- Interface Template ACLs
- How to Configure Interface Template ACLs

Note ●![]() For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, see these publications:
For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, see these publications:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps11846/prod_command_reference_list.html
- Cisco IOS Release 15.4SY supports only Ethernet interfaces. Cisco IOS Release 15.4SY does not support any WAN features or commands.
- Port ACLs do not support the access-list keywords log or reflexive. These keywords in the access list are ignored. OAL does not support PACLs.
- PACLs are not supported on private VLANs.
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/hw/switches/ps708/tsd_products_support_series_home.html
Participate in the Technical Documentation Ideas forum
Prerequisites for PACls
Restrictions for PACLs
- There can be at most one IP access list and one MAC access list applied to the same Layer 2 interface per direction.
- PACLs are not applied to MPLS or ARP messages.
- An IP access list filters only IPv4 and IPv6 packets. For IP access lists, you can define a standard, extended, or named access-list.
- A MAC access list filters ingress packets that are of an unsupported type (not IP, ARP, or MPLS packets) based on the fields of the Ethernet datagram. A MAC access list is not applied to IP, MPLS, or ARP messages. You can define only named MAC access lists.
- The number of ACLs and ACEs that can be configured as part of a PACL are bounded by the hardware resources on the switch. Those hardware resources are shared by various ACL features (such as VACLs) that are configured on the system. If there are insufficient hardware resources to program a PACL in hardware, the PACL is not applied.
- PACL does not support the access-list log and reflect/evaluate keywords. These keywords are ignored if you add them to the access list for a PACL.
- OAL does not support PACLs.
- The access group mode can change the way PACLs interact with other ACLs. To maintain consistent behavior across Cisco platforms, use the default access group mode (merge mode).
- PACLs cannot filter Physical Link Protocols and Logical Link Protocols, such as CDP, VTP, DTP, PAgP, UDLD, and STP, because the protocols are redirected to the RP before the ACL takes effect. You can apply CoPP or QoS to Physical Link Protocol and Logical Link Protocol traffic.
- Layer 2 ports do not support Layer 3 ACLs.
- An Interface Template ACL can be applied on an interface only when there is no other ACL directly configured on the same interface. An ACL that is configured directly on an interface takes priority over an Interface Template ACL that is applied on the same interface. The Interface Template takes effect once the ACL directly applied on the interface has been removed.
Information About PACLs
- PACL Overview
- EtherChannel and PACL Interactions
- Dynamic ACLs (Applies to Merge Mode Only)
- Trunk Ports
- Layer 2 to Layer 3 Port Conversion
- Port-VLAN Association Changes
PACL Overview
PACLs filter incoming traffic on Layer 2 interfaces, using Layer 3 information, Layer 4 header information, or non-IP Layer 2 information.
The PACL feature uses standard or extended IP ACLs or named MAC-extended ACLs that you want to apply to the port.
Port ACLs perform access control on all traffic entering the specified Layer 2 port.
PACLs and VACLs can provide access control based on the Layer 3 addresses (for IP protocols) or Layer 2 MAC addresses (for non-IP protocols).
The port ACL (PACL) feature provides the ability to perform access control on specific Layer 2 ports. A Layer 2 port is a physical LAN or trunk port that belongs to a VLAN. Port ACLs are applied only on the ingress traffic. The port ACL feature is supported only in hardware (port ACLs are not applied to any packets routed in software).
When you create a port ACL, an entry is created in the ACL TCAM. You can use the show tcam counts command to see how much TCAM space is available.
The PACL feature does not affect Layer 2 control packets received on the port.
You can use the access-group mode command to change the way that PACLs interact with other ACLs.
PACLs use the following modes:
- Prefer port mode—If a PACL is configured on a Layer 2 interface, the PACL takes effect and overwrites the effect of other ACLs (Cisco IOS ACL and VACL). If no PACL feature is configured on the Layer 2 interface, other features applicable to the interface are merged and are applied on the interface.
- Merge mode—In this mode, the PACL, VACL, and Cisco IOS ACLs are merged in the ingress direction following the logical serial model shown in Figure 35-2. This is the default access group mode.
You configure the access-group mode command on each interface. The default is merge mode.

Note![]() A PACL can be configured on a trunk port only after prefer port mode has been selected. Trunk ports do not support merge mode.
A PACL can be configured on a trunk port only after prefer port mode has been selected. Trunk ports do not support merge mode.
To illustrate access group mode, assume a physical port belongs to VLAN100, and the following ACLs are configured:
- Cisco IOS ACL R1 is applied on routed interface VLAN100.
- VACL (VLAN filter) V1 is applied on VLAN100.
- PACL P1 is applied on the physical port.
In this situation, the following ACL interactions occur:
- In prefer port mode, Cisco IOS ACL R1 and VACL V1 are ignored.
- In merge mode, Cisco IOS ACL R1, VACL V1 and PACL P1 are merged and applied on the port.

Note![]() The CLI syntax for creating a PACL is identical to the syntax for creating a Cisco IOS ACL. An instance of an ACL that is mapped to a Layer 2 port is called a PACL. An instance of an ACL that is mapped to a Layer 3 interface is called a Cisco IOS ACL. The same ACL can be mapped to both a Layer 2 port and a Layer 3 interface.
The CLI syntax for creating a PACL is identical to the syntax for creating a Cisco IOS ACL. An instance of an ACL that is mapped to a Layer 2 port is called a PACL. An instance of an ACL that is mapped to a Layer 3 interface is called a Cisco IOS ACL. The same ACL can be mapped to both a Layer 2 port and a Layer 3 interface.
The PACL feature supports MAC ACLs, IPv4, and IPv6 ACLs. The PACL feature does not support ACLs for ARP or Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) traffic.
EtherChannel and PACL Interactions
This section describes the guidelines for the EtherChannel and PACL interactions:
- PACLs are supported on the main Layer 2 channel interface but not on the port members. A port that has a PACL configured on it may not be configured as an EtherChannel member port. The EtherChannel configuration commands are unavailable on ports that are configured with a PACL.
- Changing the configuration on the logical port affects all the ports in the channel. When an ACL is mapped to the logical port belonging to a channel, it is mapped to all ports in the channel.
Dynamic ACLs (Applies to Merge Mode Only)
Dynamic ACLs are VLAN-based and are used by two features: CBAC and GWIP. The merge mode does not support the merging of the dynamic ACLs with the PACLs. In merge mode, the following configurations are not allowed:
Trunk Ports
To configure a PACL on a trunk port, you must first configure port prefer mode. The configuration commands to apply a PACL on a trunk or dynamic port will not be available until you configure the port in port prefer mode by entering the access-group mode prefer port interface command. Trunk ports do not support merge mode.
Layer 2 to Layer 3 Port Conversion
If you reconfigure a port from Layer 2 to Layer 3, any PACL configured on the port becomes inactive but remains in the configuration. If you subsequently configure the port as Layer 2, any PACL configured on the port becomes active again.
Port-VLAN Association Changes
You can enter port configuration commands that alter the port-VLAN association, which triggers an ACL remerge.
Unmapping and then mapping a PACL, VACL, or Cisco IOS ACL automatically triggers a remerge.
In merge mode, online insertion or removal of a switching module also triggers a remerge, if ports on the module have PACLs configured.
PACL and VACL Interactions
PACL Interaction with VACLs and Cisco IOS ACLs
This section describes the guidelines for the PACL interaction with the VACLs and Cisco IOS ACLs.
For an incoming packet on a physical port, the PACL is applied first. If the packet is permitted by the PACL, the VACL on the ingress VLAN is applied next. If the packet is Layer 3 forwarded and is permitted by the VACL, it is filtered by the Cisco IOS ACL on the same VLAN. The same process happens in reverse in the egress direction. However, there is currently no hardware support for output PACLs.
The PACLs override both the VACLs and Cisco IOS ACLs when the port is configured in prefer port mode. The one exception to this rule is when the packets are forwarded in the software by the route processor (RP). The RP applies the ingress Cisco IOS ACL regardless of the PACL mode. Two examples where the packets are forwarded in the software are as follows:
Bridged Packets
Figure 35-1 shows a PACL and a VACL applied to bridged packets. In merge mode, the ACLs are applied in the following order:
Figure 35-1 Applying ACLs on Bridged Packets
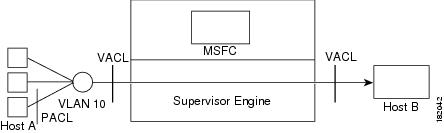
In prefer port mode, only the PACL is applied to the ingress packets (the input VACL is not applied).
Routed Packets
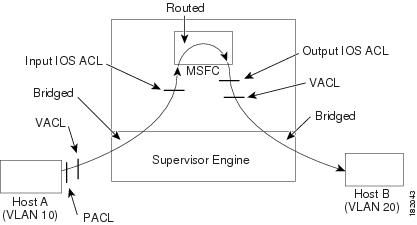
Figure 35-2 shows how ACLs are applied on routed and Layer 3-switched packets. In merge mode, the ACLs are applied in the following order:
In prefer port mode, only the PACL is applied to the ingress packets (the input VACL and Cisco IOS ACL are not applied).
Figure 35-2 Applying ACLs on Routed Packets
Multicast Packets
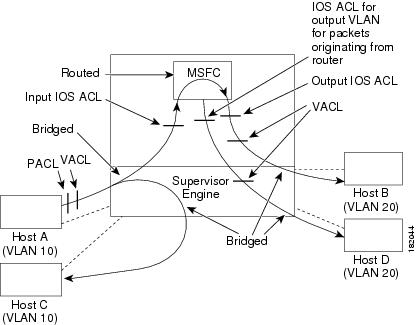
Figure 35-3 shows how ACLs are applied on packets that need multicast expansion. For packets that need multicast expansion, the ACLs are applied in the following order:
1.![]() Packets that need multicast expansion:
Packets that need multicast expansion:
2.![]() Packets after multicast expansion:
Packets after multicast expansion:
3.![]() Packets originating from router:
Packets originating from router:
In prefer port mode, only the PACL is applied to the ingress packets (the input VACL and Cisco IOS ACL are not applied).
Figure 35-3 Applying ACLs on Multicast Packets
Interface Template ACLs
This section describes the Interface Template ACL feature on Catalyst 6500 series Switches. An interface template provides a mechanism to configure multiple commands at the same time and associate it with a target such as an interface. An interface template is a container of configurations or policies that can be applied to specific ports.
Interface Templates provide an efficient way to apply ACLs along with other commands on interfaces. Template ACLs can be applied on an interface by first configuring an ACL inside an interface template, and then applying the template to any number of desired interfaces. A single template having an ACL can be applied to any number of physical or virtual interfaces either statically or dynamically.
The support for configuring Interface Template ACLs was introduced on Catalyst 6500 series Switches starting with the 15.5(1)SY2 release.
How to Configure PACLs
- Configuring IP and MAC ACLs on a Layer 2 Interface
- Configuring Access-group Mode on Layer 2 Interface
- Applying ACLs to a Layer 2 Interface
- Applying ACLs to a Port Channel
- Displaying an ACL Configuration on a Layer 2 Interface
Configuring IP and MAC ACLs on a Layer 2 Interface
IP and MAC ACLs can be applied to Layer 2 physical interfaces. Standard (numbered, named) and Extended (numbered, named) IP ACLs, and Extended Named MAC ACLs are supported.
To apply IP or MAC ACLs on a Layer 2 interface, perform this task:
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
This example shows how to configure the Extended Named IP ACL simple-ip-acl to permit all TCP traffic and implicitly deny all other IP traffic:
This example shows how to configure the Extended Named MAC ACL simple-mac-acl to permit source host 000.000.011 to any destination host:
Configuring Access-group Mode on Layer 2 Interface
To configure the access mode on a Layer 2 interface, perform this task:
This example shows how to configure an interface to use prefer port mode:
This example shows how to configure an interface to use merge mode:
Applying ACLs to a Layer 2 Interface
To apply IP and MAC ACLs to a Layer 2 interface, perform one of these tasks:
|
|
|
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
This example applies the extended named IP ACL simple-ip-acl to interface GigabitEthernet 6/1 ingress traffic:
This example applies the extended named MAC ACL simple-mac-acl to interface GigabitEthernet 6/1 ingress traffic:
Applying ACLs to a Port Channel
To apply IP and MAC ACLs to a port channel logical interface, perform this task:
|
|
|
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
This example applies the extended named IP ACL simple-ip-acl to port channel 3 ingress traffic:
Displaying an ACL Configuration on a Layer 2 Interface
To display information about an ACL configuration on Layer 2 interfaces, perform one of these tasks:
|
|
|
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
This example shows that the IP access group simple-ip-acl is configured on the inbound direction of interface fa6/1:
This example shows that MAC access group simple-mac-acl is configured on the inbound direction of interface Gigabit Ethernet 6/1:
This example shows that access group merge is configured on interface Gigabit Ethernet 6/1:
How to Configure Interface Template ACLs
- Configuring an IPv4 ACL by Statically Applying an Interface Template
- Configuring an IPv6 ACL by Statically Applying an Interface Template
- Configuration Examples for Template ACL Configuration
Configuring an IPv4 ACL by Statically Applying an Interface Template
To configure an IPv4 ACL on an interface by statically applying a template, perform this task:
Configuring an IPv6 ACL by Statically Applying an Interface Template
Configuration Examples for Template ACL Configuration
Configuration of IPv4 and IPv6 ACLs by Statically Applying an Interface Template
The following example shows the configuration of IPv4 and IPv6 ACLs on an interface using an interface template:
Verifying Template Details
The following example shows the sample output for show template binding target interface-name command for a statically applied Interface Template:
Viewing Access List details
The following examples shows the access list details for a given ACL:
The following examples show the access list details configured inside a given Template:
Verifying ACL Configuration on an Interface with a Statically Applied Template
The following example shows the sample output for show running-config interface interface-name command:
Verifying ACL Configuration on an Interface with a Dynamically Applied Template
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/hw/switches/ps708/tsd_products_support_series_home.html
Participate in the Technical Documentation Ideas forum
 Feedback
Feedback