- Preface
- Using the Command-Line Interface
-
- Configuring Spanning Tree Protocol
- Configuring Multiple Spanning-Tree Protocol
- Configuring Optional Spanning-Tree Features
- Configuring EtherChannels
- Configuring Link-State Tracking
- Configuring Flex Links and the MAC Address-Table Move Update Feature
- Configuring UniDirectional Link Detection
- Configuring Resilient Ethernet Protocol
-
- Security Features Overview
- Preventing Unauthorized Access
- Controlling Switch Access with Passwords and Privilege Levels
- Configuring TACACS+
- Configuring RADIUS
- Configuring Kerberos
- Configuring Local Authentication and Authorization
- Configuring Secure Shell (SSH)
- Configuring Secure Socket Layer HTTP
- Configuring IPv4 ACLs
- Configuring IPv6 ACLs
- Configuring DHCP
- Configuring IP Source Guard
- Configuring Dynamic ARP Inspection
- Configuring IEEE 802.1x Port-Based Authentication
- Configuring Web-Based Authentication
- Configuring Port-Based Traffic Control
- Configuring IPv6 First Hop Security
- Configuring Cisco TrustSec
- Configuring FIPS
- Index
Consolidated Platform Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE 15.2(2)E (Catalyst 2960-XR Switch)
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
- Updated:
- July 23, 2014
Chapter: Implementing IPv6 Multicast
- Finding Feature Information
- Information About Implementing IPv6 Multicast Routing
- Implementing IPv6 Multicast
Implementing IPv6 Multicast
- Finding Feature Information
- Information About Implementing IPv6 Multicast Routing
- Implementing IPv6 Multicast
Finding Feature Information
Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest caveats and feature information, see Bug Search Tool and the release notes for your platform and software release. To find information about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each feature is supported, see the feature information table at the end of this module.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to http://www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Information About Implementing IPv6 Multicast Routing
This chapter describes how to implement IPv6 multicast routing on the switch.
Traditional IP communication allows a host to send packets to a single host (unicast transmission) or to all hosts (broadcast transmission). IPv6 multicast provides a third scheme, allowing a host to send a single data stream to a subset of all hosts (group transmission) simultaneously.
- IPv6 Multicast Overview
- IPv6 Multicast Routing Implementation
- Protocol Independent Multicast
- Static Mroutes
- MRIB
- MFIB
- IPv6 Multicast Process Switching and Fast Switching
IPv6 Multicast Overview
An IPv6 multicast group is an arbitrary group of receivers that want to receive a particular data stream. This group has no physical or geographical boundaries--receivers can be located anywhere on the Internet or in any private network. Receivers that are interested in receiving data flowing to a particular group must join the group by signaling their local switch. This signaling is achieved with the MLD protocol.
Switches use the MLD protocol to learn whether members of a group are present on their directly attached subnets. Hosts join multicast groups by sending MLD report messages. The network then delivers data to a potentially unlimited number of receivers, using only one copy of the multicast data on each subnet. IPv6 hosts that wish to receive the traffic are known as group members.
Packets delivered to group members are identified by a single multicast group address. Multicast packets are delivered to a group using best-effort reliability, just like IPv6 unicast packets.
The multicast environment consists of senders and receivers. Any host, regardless of whether it is a member of a group, can send to a group. However, only members of a group can listen to and receive the message.
A multicast address is chosen for the receivers in a multicast group. Senders use that address as the destination address of a datagram to reach all members of the group.
Membership in a multicast group is dynamic; hosts can join and leave at any time. There is no restriction on the location or number of members in a multicast group. A host can be a member of more than one multicast group at a time.
How active a multicast group is, its duration, and its membership can vary from group to group and from time to time. A group that has members may have no activity.
IPv6 Multicast Routing Implementation
The Cisco IOS software supports the following protocols to implement IPv6 multicast routing:
MLD is used by IPv6 switches to discover multicast listeners (nodes that want to receive multicast packets destined for specific multicast addresses) on directly attached links. There are two versions of MLD: MLD version 1 is based on version 2 of the Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) for IPv4, and MLD version 2 is based on version 3 of the IGMP for IPv4. IPv6 multicast for Cisco IOS software uses both MLD version 2 and MLD version 1. MLD version 2 is fully backward-compatible with MLD version 1 (described in RFC 2710). Hosts that support only MLD version 1 will interoperate with a switch running MLD version 2. Mixed LANs with both MLD version 1 and MLD version 2 hosts are likewise supported.
PIM-SM is used between switches so that they can track which multicast packets to forward to each other and to their directly connected LANs.
PIM in Source Specific Multicast (PIM-SSM) is similar to PIM-SM with the additional ability to report interest in receiving packets from specific source addresses (or from all but the specific source addresses) to an IP multicast address.
MLD Access Group
The MLD access group provides receiver access control in Cisco IOS IPv6 multicast switches. This feature limits the list of groups a receiver can join, and it allows or denies sources used to join SSM channels.
Explicit Tracking of Receivers
The explicit tracking feature allows a switch to track the behavior of the hosts within its IPv6 network. This feature also enables the fast leave mechanism to be used with MLD version 2 host reports.
Protocol Independent Multicast
Protocol Independent Multicast (PIM) is used between switches so that they can track which multicast packets to forward to each other and to their directly connected LANs. PIM works independently of the unicast routing protocol to perform send or receive multicast route updates like other protocols. Regardless of which unicast routing protocols are being used in the LAN to populate the unicast routing table, Cisco IOS PIM uses the existing unicast table content to perform the Reverse Path Forwarding (RPF) check instead of building and maintaining its own separate routing table.
You can configure IPv6 multicast to use either PIM-SM or PIM-SSM operation, or you can use both PIM-SM and PIM-SSM together in your network.
- PIM-Sparse Mode
- IPv6 BSR: Configure RP Mapping
- PIM-Source Specific Multicast
- Routable Address Hello Option
- PIM IPv6 Stub Routing
PIM-Sparse Mode
IPv6 multicast provides support for intradomain multicast routing using PIM-SM. PIM-SM uses unicast routing to provide reverse-path information for multicast tree building, but it is not dependent on any particular unicast routing protocol.
PIM-SM is used in a multicast network when relatively few switches are involved in each multicast and these switches do not forward multicast packets for a group, unless there is an explicit request for the traffic. PIM-SM distributes information about active sources by forwarding data packets on the shared tree. PIM-SM initially uses shared trees, which requires the use of an RP.
Requests are accomplished via PIM joins, which are sent hop by hop toward the root node of the tree. The root node of a tree in PIM-SM is the RP in the case of a shared tree or the first-hop switch that is directly connected to the multicast source in the case of a shortest path tree (SPT). The RP keeps track of multicast groups and the hosts that send multicast packets are registered with the RP by that host's first-hop switch.
As a PIM join travels up the tree, switches along the path set up multicast forwarding state so that the requested multicast traffic will be forwarded back down the tree. When multicast traffic is no longer needed, a switch sends a PIM prune up the tree toward the root node to prune (or remove) the unnecessary traffic. As this PIM prune travels hop by hop up the tree, each switch updates its forwarding state appropriately. Ultimately, the forwarding state associated with a multicast group or source is removed.
A multicast data sender sends data destined for a multicast group. The designated switch (DR) of the sender takes those data packets, unicast-encapsulates them, and sends them directly to the RP. The RP receives these encapsulated data packets, de-encapsulates them, and forwards them onto the shared tree. The packets then follow the (*, G) multicast tree state in the switches on the RP tree, being replicated wherever the RP tree branches, and eventually reaching all the receivers for that multicast group. The process of encapsulating data packets to the RP is called registering, and the encapsulation packets are called PIM register packets.
IPv6 BSR: Configure RP Mapping
PIM switches in a domain must be able to map each multicast group to the correct RP address. The BSR protocol for PIM-SM provides a dynamic, adaptive mechanism to distribute group-to-RP mapping information rapidly throughout a domain. With the IPv6 BSR feature, if an RP becomes unreachable, it will be detected and the mapping tables will be modified so that the unreachable RP is no longer used, and the new tables will be rapidly distributed throughout the domain.
Every PIM-SM multicast group needs to be associated with the IP or IPv6 address of an RP. When a new multicast sender starts sending, its local DR will encapsulate these data packets in a PIM register message and send them to the RP for that multicast group. When a new multicast receiver joins, its local DR will send a PIM join message to the RP for that multicast group. When any PIM switch sends a (*, G) join message, the PIM switch needs to know which is the next switch toward the RP so that G (Group) can send a message to that switch. Also, when a PIM switch is forwarding data packets using (*, G) state, the PIM switch needs to know which is the correct incoming interface for packets destined for G, because it needs to reject any packets that arrive on other interfaces.
A small set of switches from a domain are configured as candidate bootstrap switches (C-BSRs) and a single BSR is selected for that domain. A set of switches within a domain are also configured as candidate RPs (C-RPs); typically, these switches are the same switches that are configured as C-BSRs. Candidate RPs periodically unicast candidate-RP-advertisement (C-RP-Adv) messages to the BSR of that domain, advertising their willingness to be an RP. A C-RP-Adv message includes the address of the advertising C-RP, and an optional list of group addresses and mask length fields, indicating the group prefixes for which the candidacy is advertised. The BSR then includes a set of these C-RPs, along with their corresponding group prefixes, in bootstrap messages (BSMs) it periodically originates. BSMs are distributed hop-by-hop throughout the domain.
Bidirectional BSR support allows bidirectional RPs to be advertised in C-RP messages and bidirectional ranges in the BSM. All switches in a system must be able to use the bidirectional range in the BSM; otherwise, the bidirectional RP feature will not function.
PIM-Source Specific Multicast
PIM-SSM is the routing protocol that supports the implementation of SSM and is derived from PIM-SM. However, unlike PIM-SM where data from all multicast sources are sent when there is a PIM join, the SSM feature forwards datagram traffic to receivers from only those multicast sources that the receivers have explicitly joined, thus optimizing bandwidth utilization and denying unwanted Internet broadcast traffic. Further, instead of the use of RP and shared trees, SSM uses information found on source addresses for a multicast group. This information is provided by receivers through the source addresses relayed to the last-hop switches by MLD membership reports, resulting in shortest-path trees directly to the sources.
In SSM, delivery of datagrams is based on (S, G) channels. Traffic for one (S, G) channel consists of datagrams with an IPv6 unicast source address S and the multicast group address G as the IPv6 destination address. Systems will receive this traffic by becoming members of the (S, G) channel. Signaling is not required, but receivers must subscribe or unsubscribe to (S, G) channels to receive or not receive traffic from specific sources.
MLD version 2 is required for SSM to operate. MLD allows the host to provide source information. Before SSM can run with MLD, SSM must be supported in the Cisco IOS IPv6 switch, the host where the application is running, and the application itself.
Routable Address Hello Option
When an IPv6 interior gateway protocol is used to build the unicast routing table, the procedure to detect the upstream switch address assumes the address of a PIM neighbor is always same as the address of the next-hop switch, as long as they refer to the same switch. However, it may not be the case when a switch has multiple addresses on a link.
Two typical situations can lead to this situation for IPv6. The first situation can occur when the unicast routing table is not built by an IPv6 interior gateway protocol such as multicast BGP. The second situation occurs when the address of an RP shares a subnet prefix with downstream switches (note that the RP switch address has to be domain-wide and therefore cannot be a link-local address).
The routable address hello option allows the PIM protocol to avoid such situations by adding a PIM hello message option that includes all the addresses on the interface on which the PIM hello message is advertised. When a PIM switch finds an upstream switch for some address, the result of RPF calculation is compared with the addresses in this option, in addition to the PIM neighbor's address itself. Because this option includes all the possible addresses of a PIM switch on that link, it always includes the RPF calculation result if it refers to the PIM switch supporting this option.
Because of size restrictions on PIM messages and the requirement that a routable address hello option fits within a single PIM hello message, a limit of 16 addresses can be configured on the interface.
PIM IPv6 Stub Routing
The PIM stub routing feature reduces resource usage by moving routed traffic closer to the end user.
In a network using PIM stub routing, the only allowable route for IPv6 traffic to the user is through a switch that is configured with PIM stub routing. PIM passive interfaces are connected to Layer 2 access domains, such as VLANs, or to interfaces that are connected to other Layer 2 devices. Only directly connected multicast receivers and sources are allowed in the Layer 2 access domains. The PIM passive interfaces do not send or process any received PIM control packets.
When using PIM stub routing, you should configure the distribution and remote routers to use IPv6 multicast routing and configure only the switch as a PIM stub router. The switch does not route transit traffic between distribution routers. You also need to configure a routed uplink port on the switch. The switch uplink port cannot be used with SVIs.
You must also configure EIGRP stub routing when configuring PIM stub routing on the switch. For more information, see the EIGRPv6 Stub Routing section.
The redundant PIM stub router topology is not supported. The redundant topology exists when there is more than one PIM router forwarding multicast traffic to a single access domain. PIM messages are blocked, and the PIM assert and designated router election mechanisms are not supported on the PIM passive interfaces. Only the non-redundant access router topology is supported by the PIM stub feature. By using a non-redundant topology, the PIM passive interface assumes that it is the only interface and designated router on that access domain.
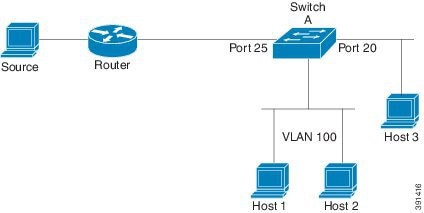
In the figure shown below, Switch A routed uplink port 25 is connected to the router and PIM stub routing is enabled on the VLAN 100 interfaces and on Host 3. This configuration allows the directly connected hosts to receive traffic from multicast source. See the Configuring PIM IPv6 Stub Routing section for more information.
Static Mroutes
IPv6 static mroutes behave much in the same way as IPv4 static mroutes used to influence the RPF check. IPv6 static mroutes share the same database as IPv6 static routes and are implemented by extending static route support for RPF checks. Static mroutes support equal-cost multipath mroutes, and they also support unicast-only static routes.
MRIB
The Multicast Routing Information Base (MRIB) is a protocol-independent repository of multicast routing entries instantiated by multicast routing protocols (routing clients). Its main function is to provide independence between routing protocols and the Multicast Forwarding Information Base (MFIB). It also acts as a coordination and communication point among its clients.
Routing clients use the services provided by the MRIB to instantiate routing entries and retrieve changes made to routing entries by other clients. Besides routing clients, MRIB also has forwarding clients (MFIB instances) and special clients such as MLD. MFIB retrieves its forwarding entries from MRIB and notifies the MRIB of any events related to packet reception. These notifications can either be explicitly requested by routing clients or spontaneously generated by the MFIB.
Another important function of the MRIB is to allow for the coordination of multiple routing clients in establishing multicast connectivity within the same multicast session. MRIB also allows for the coordination between MLD and routing protocols.
MFIB
The MFIB is a platform-independent and routing-protocol-independent library for IPv6 software. Its main purpose is to provide a Cisco IOS platform with an interface with which to read the IPv6 multicast forwarding table and notifications when the forwarding table changes. The information provided by the MFIB has clearly defined forwarding semantics and is designed to make it easy for the platform to translate to its specific hardware or software forwarding mechanisms.
When routing or topology changes occur in the network, the IPv6 routing table is updated, and those changes are reflected in the MFIB. The MFIB maintains next-hop address information based on the information in the IPv6 routing table. Because there is a one-to-one correlation between MFIB entries and routing table entries, the MFIB contains all known routes and eliminates the need for route cache maintenance that is associated with switching paths such as fast switching and optimum switching.
Distributed MFIB
 Note | Distributed MFIB has its significance only in a stacked environment where the Master distributes the MFIB information to the other stack members. In the following section the line cards are nothing but the member switches in the stack. |
Distributed MFIB (dMFIB) is used to switch multicast IPv6 packets on distributed platforms. dMFIB may also contain platform-specific information on replication across line cards. The basic MFIB routines that implement the core of the forwarding logic are common to all forwarding environments.
dMFIB implements the following functions:
-
Distributes a copy of the MFIB to the line cards.
-
Relays data-driven protocol events generated in the line cards to PIM.
-
Provides an MFIB platform application program interface (API) to propagate MFIB changes to platform-specific code responsible for programming the hardware acceleration engine. This API also includes entry points to switch a packet in software (necessary if the packet is triggering a data-driven event) and to upload traffic statistics to the software.
-
Provides hooks to allow clients residing on the RP to read traffic statistics on demand. (dMFIB does not periodically upload these statistics to the RP.)
The combination of dMFIB and MRIB subsystems also allows the switch to have a "customized" copy of the MFIB database in each line card and to transport MFIB-related platform-specific information from the RP to the line cards.
IPv6 Multicast Process Switching and Fast Switching
A unified MFIB is used to provide both fast switching and process switching support for PIM-SM and PIM-SSM in IPv6 multicast. In process switching, the Route Processor must examine, rewrite, and forward each packet. The packet is first received and copied into the system memory. The switch then looks up the Layer 3 network address in the routing table. The Layer 2 frame is then rewritten with the next-hop destination address and sent to the outgoing interface. The RP also computes the cyclic redundancy check (CRC). This switching method is the least scalable method for switching IPv6 packets.
IPv6 multicast fast switching allows switches to provide better packet forwarding performance than process switching. Information conventionally stored in a route cache is stored in several data structures for IPv6 multicast switching. The data structures provide optimized lookup for efficient packet forwarding.
In IPv6 multicast forwarding, the first packet is fast-switched if the PIM protocol logic allows it. In IPv6 multicast fast switching, the MAC encapsulation header is precomputed. IPv6 multicast fast switching uses the MFIB to make IPv6 destination prefix-based switching decisions. In addition to the MFIB, IPv6 multicast fast switching uses adjacency tables to prepend Layer 2 addressing information. The adjacency table maintains Layer 2 next-hop addresses for all MFIB entries.
The adjacency table is populated as adjacencies are discovered. Each time an adjacency entry is created (such as through ARP), a link-layer header for that adjacent node is precomputed and stored in the adjacency table. Once a route is determined, it points to a next hop and corresponding adjacency entry. It is subsequently used for encapsulation during switching of packets.
A route might have several paths to a destination prefix, such as when a switch is configured for simultaneous load balancing and redundancy. For each resolved path, a pointer is added for the adjacency corresponding to the next-hop interface for that path. This mechanism is used for load balancing across several paths.
Implementing IPv6 Multicast
Enabling IPv6 Multicast Routing
Beginning in privileged EXEC mode, follow these steps:
Customizing and Verifying the MLD Protocol
Customizing and Verifying MLD on an Interface
Beginning in privileged EXEC mode, follow these steps:
Implementing MLD Group Limits
Per-interface and global MLD limits operate independently of each other. Both per-interface and global MLD limits can be configured on the same switch. The number of MLD limits, globally or per interface, is not configured by default; the limits must be configured by the user. A membership report that exceeds either the per-interface or the global state limit is ignored.
Configuring Explicit Tracking of Receivers to Track Host Behavior
The explicit tracking feature allows a switch to track the behavior of the hosts within its IPv6 network and enables the fast leave mechanism to be used with MLD version 2 host reports.
Beginning in privileged EXEC mode, follow these steps:
Resetting the MLD Traffic Counters
Beginning in privileged EXEC mode, follow these steps.
Clearing the MLD Interface Counters
Beginning in privileged EXEC mode, follow these steps.
| Command or Action | Purpose |
|---|
Configuring PIM
This section explains how to configure PIM.
- Configuring PIM-SM and Displaying PIM-SM Information for a Group Range
- Configuring PIM Options
- Resetting the PIM Traffic Counters
- Clearing the PIM Topology Table to Reset the MRIB Connection
Configuring PIM-SM and Displaying PIM-SM Information for a Group Range
Beginning in privileged EXEC mode, follow these steps:
Configuring PIM Options
Beginning in privileged EXEC mode, follow these steps:
Resetting the PIM Traffic Counters
If PIM malfunctions or in order to verify that the expected number of PIM packets are received and sent, the user can clear PIM traffic counters. Once the traffic counters are cleared, the user can enter the show ipv6 pim traffic command to verify that PIM is functioning correctly and that PIM packets are being received and sent correctly.
Beginning in privileged EXEC mode, follow these steps:
Clearing the PIM Topology Table to Reset the MRIB Connection
No configuration is necessary to use the MRIB. However, users may in certain situations want to clear the PIM topology table in order to reset the MRIB connection and verify MRIB information.
Beginning in privileged EXEC mode, follow these steps:
Configuring PIM IPv6 Stub Routing
The PIM Stub routing feature supports multicast routing between the distribution layer and the access layer. It supports two types of PIM interfaces, uplink PIM interfaces, and PIM passive interfaces. A routed interface configured with the PIM passive mode does not pass or forward PIM control traffic, it only passes and forwards MLD traffic.
- PIM IPv6 Stub Routing Configuration Guidelines
- Default IPv6 PIM Routing Configuration
- Enabling IPV6 PIM Stub Routing
- Monitoring IPv6 PIM Stub Routing
PIM IPv6 Stub Routing Configuration Guidelines
- Before configuring PIM stub routing, you must have IPv6 multicast routing configured on both the stub router and the central router. You must also have PIM mode (sparse-mode) configured on the uplink interface of the stub router.
- The PIM stub router does not route the transit traffic between the distribution routers. Unicast (EIGRP) stub routing enforces this behavior. You must configure unicast stub routing to assist the PIM stub router behavior. For more information, see the EIGRPv6 Stub Routing section.
- Only directly connected multicast (MLD) receivers and sources are allowed in the Layer 2 access domains. The PIM protocol is not supported in access domains.
- The redundant PIM stub router topology is not supported.
Default IPv6 PIM Routing Configuration
Enabling IPV6 PIM Stub Routing
PIM stub routing is disabled in IPv6 by default. Beginning in privileged EXEC mode, follow these steps to enable PIM stub routing on an interface.
1.
enable
3.
ipv6 multicast pim-passive-enable
5.
ipv6 pim
6.
ipv6 pim
{bsr} | {dr-priority |
value} | {hello-interval |
seconds} | {join-prune-interval |
seconds} | {passive}
DETAILED STEPS
Monitoring IPv6 PIM Stub Routing
|
Command |
Purpose |
|---|---|
|
show ipv6 pim interface
Switch# show ipv6 pim interface
|
Displays the PIM stub that is enabled on each interface. |
|
show ipv6 mld groups
Switch# show ipv6 mld groups
|
Displays the interested clients that have joined the specific multicast source group. |
|
show ipv6 mroute
Switch# show ipv6 mroute
|
Verifies that the multicast stream forwards from the source to the interested clients. |
Configuring a BSR
The tasks included here are described below.
- Configuring a BSR and Verifying BSR Information
- Sending PIM RP Advertisements to the BSR
- Configuring BSR for Use Within Scoped Zones
- Configuring BSR Switches to Announce Scope-to-RP Mappings
Configuring a BSR and Verifying BSR Information
Beginning in privileged EXEC mode, follow these steps:
Sending PIM RP Advertisements to the BSR
Beginning in privileged EXEC mode, follow these steps:
Configuring BSR for Use Within Scoped Zones
Beginning in privileged EXEC mode, follow these steps:
Configuring BSR Switches to Announce Scope-to-RP Mappings
IPv6 BSR switches can be statically configured to announce scope-to-RP mappings directly instead of learning them from candidate-RP messages. A user might want to configure a BSR switch to announce scope-to-RP mappings so that an RP that does not support BSR is imported into the BSR. Enabling this feature also allows an RP positioned outside the enterprise's BSR domain to be learned by the known remote RP on the local candidate BSR switch.
Beginning in privileged EXEC mode, follow these steps:
Configuring SSM Mapping
When the SSM mapping feature is enabled, DNS-based SSM mapping is automatically enabled, which means that the switch will look up the source of a multicast MLD version 1 report from a DNS server.
You can use either DNS-based or static SSM mapping, depending on your switch configuration. If you choose to use static SSM mapping, you can configure multiple static SSM mappings. If multiple static SSM mappings are configured, the source addresses of all matching access lists will be used.
 Note | To use DNS-based SSM mapping, the switch needs to find at least one correctly configured DNS server, to which the switch may be directly attached. |
Beginning in privileged EXEC mode, follow these steps:
Configuring Static Mroutes
Static multicast routes (mroutes) in IPv6 can be implemented as an extension of IPv6 static routes. You can configure your switch to use a static route for unicast routing only, to use a static multicast route for multicast RPF selection only, or to use a static route for both unicast routing and multicast RPF selection.
Beginning in privileged EXEC mode, follow these steps:
Using MFIB in IPv6 Multicast
Multicast forwarding is automatically enabled when IPv6 multicast routing is enabled.
Verifying MFIB Operation in IPv6 Multicast
Beginning in privileged EXEC mode, follow these steps:
Resetting MFIB Traffic Counters
Beginning in privileged EXEC mode, follow these steps:
| Command or Action | Purpose |
|---|
 Feedback
Feedback