Frequently Asked Questions
Log Files:
Log files get stored inside the <install-location>/logs or <install-location>/log folder. The log files get monitored and rotated through the Secure Workload services.
Agent Deployment
Linux
rpm -Uvh tet-sensor-1.101.2-1.el6-dev.x86_64.rpm
error: cannot create transaction lock on /var/lib/rpm/.rpm.lock (Permission denied).
A: If you do not have the right privileges to install the agents, either switch to root or use sudo to install the agents.
Q: What happens when you run “sudo rpm -Uvh tet-sensor-1.0.0-121.1b1bb546.el6-dev.x86_64.rpm” and encounter the following error:
Preparing... ########################################### [100%]
which: no lsb_release in (/sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/usr/X11R6/bin)
error: %pre(tet-sensor-site-1.0.0-121.1b1bb546.x86_64) scriptlet failed, exit status 1
error: install: %pre scriptlet failed (2), skipping tet-sensor-site-1.0.0-121.1b1bb546
A: The system does not satisfy the requirements to install the agents. In this particular case, lsb_release tool is not installed.
For more information, see the Software Agents Deployment Label section and install the required dependencies.
Q: What happens whn you run “sudo rpm -Uvh tet-sensor-1.0.0-121.1b1bb546.el6-dev.x86_64.rpm” and encounter the following error:
Unsupported OS openSUSE project
error: %pre(tet-sensor-1.101.1-1.x86_64) scriptlet failed, exit status 1
error: tet-sensor-1.101.1-1.x86_64: install failed
warning: %post(tet-sensor-site-1.101.1-1.x86_64) scriptlet failed, exit status 1A: Your OS is not supported to run software agents (in this particular case, “openSUSE project” is a non- supported platform).
For more information, see the Software Agents Deployment Label section.
Q: After I have installed all the dependencies and run installation with proper privileges with no errors. How do I know the agents installation was successful?
A: After you have installed the agents, to verify if the installation, run the following command:
$ ps -ef | grep -e csw-agent -e tet-
root 14158 1 0 Apr03 ? 00:00:00 csw-agent
root 14160 14158 0 Apr03 ? 00:00:00 csw-agent watch_files
root 14161 14158 0 Apr03 ? 00:00:03 csw-agent check_conf
root 14162 14158 0 Apr03 ? 00:01:03 tet-sensor -f conf/.sensor_config
root 14163 14158 0 Apr03 ? 00:02:38 tet-main --sensoridfile=./sensor_id
root 14164 14158 0 Apr03 ? 00:00:22 tet-enforcer --logtostderr
tet-sen+ 14173 14164 0 Apr03 ? 00:00:21 tet-enforcer --logtostderr
tet-sen+ 14192 14162 0 Apr03 ? 00:07:23 tet-sensor -f conf/.sensor_configYou must see three entries of csw-agent and at least two entries of tet-sensor. If the services are not running, ensure that the following directories are available, else the installation has failed.
-
/usr/local/tet for most Linux distributions
-
/opt/cisco/tetration for AIX, Ubuntu
-
/opt/cisco/secure-workload for Solaris, Debian
Windows
Q: When I run the PowerShell agent installer script, I get one of the following errors:
-
The underlying connection was closed: An unexpected error occurred on a receive.
-
The client and server cannot communicate, because they do not possess a common algorithm
[Net.ServicePointManager]::SecurityProtocol
[Net.ServicePointManager]::SecurityProtocol = [System.Net.SecurityProtocolType]’Ssl3,Tls,Tls11,Tls12’
This installation package could not be opened. Verify that the package exists and that you can access it, or contact the application vendor to verify that this is a valid Windows Installer package.
msiexec /i “TetrationAgentInstaller.msi” /l*v “msi_install.log” /norestartQ: I have observed that Windows Sensor software fails to upgrade if underlying NIC is Nutanix VirtIO Network Driver.
A: There is an incompatibility issue between Npcap 0.9990 and Nutanix VirtIO Network Driver version earlier than 1.1.3 and Receive Segment Coalescing is enabled.
The resolution for this is to upgrade Nutanix VirtIO Network Driver to version 1.1.3 or later.
Q: I have installed windows sensor. The sensor doesnt seem to register and the sensor_id file contains the following: uuid-invalid-platform
set PATH=%PATH%;C:\Windows\System32\Q: I am not receiving the network flows from Kubernetes Pods on Windows Nodes.
A: To verify if the required sessions are running to capture the flows from Kubernetes pods on Windows nodes, perform the following:
-
Run cmd.exe with administrative privileges.
-
Run the following command:
logman query -etsEnsure that the following sessions are running:
-
CSW_MonNet: Captures network flows
-
CSW_MonHCS: Monitors creation of pods
-
CSW_MonNat: Monitors NATed flows
-
Kubernetes
If the installer script fails during Kubernetes Daemonset Installation, there are a large number of possible reasons.
Q: Is the Docker Registry serving images reachable from nodes ?
A: Debug Direct or HTTPS Proxy issues with the cluster pulling images from Cisco Secure Workload cluster
Q: Is the container runtime complaining about SSL/TLS insecure errors ?
A: Verify that the Secure Workload HTTPS CA certificates are installed on all Kubernetes nodes in the appropriate location for the container runtime.
Q: Docker Registry authentication and authorization of image downloads failures ?
A: From each node, attempt to manually docker pull the images from the registry urls in the Daemonset spec using the Docker pull secrets from the secret created by the Helm Chart. If the manually image pull also fails, need to pull logs from the Secure Workload Cluster registryauth service to debug the issue further.
Q: Is the Kubernetes cluster hosted inside the Secure Workload appliance heathy ?
A: Check the service status page for the cluster to ensure all related services are healthy. Run the dstool snapshot from the explore page and retrieve the logs generated.
Q: Are the Docker Image Builder daemons running ?
A: Verify from the dstool logs that the build daemons are running.
Q: Are the jobs that build Docker images failing ?
A: Verify from the dstool logs that the images have not been built. Docker build pod logs can be used to debug errors during the buildkit builds. Enforcement Coordinator logs can also be used to debug the build failures further.
Q: Are the jobs creating Helm Charts failing ?
A: Verify from the dstool logs that the Helm Charts have not been built. Enforcement Coordinator logs will contain the output of the helm build jobs and can be used to debug the exact reason for the Helm Chart build job failures.
Q: Installation bash script was corrupt ?
A: Attempt to download the installation bash script again. The bash script contains binary data appended to it. If the bash script is edited in any way with a text editor or saved as a text file, special characters in the binary data may be mangled/modified by the text editor.
Q: Kubernetes cluster configuration – too many variants and flavors, we support classic K8s.
A: If the customer is running a variant of Kubernetes, there can be many failure modes at different stages of the deployment. Classify the failure stage - kubectl command run failure, helm command run failures, pod image download failures, pod privileged mode options rejected, pod image trust content signature failures, pod image security scan failures, pod binaries fail to run (architecture mismatch), pods run but the Secure Workload services fail to start, Secure Workload services start but have runtime errors due to unusual operating environment.
Q: Are the Kubernetes RBAC credentials failing ?
A: In order to run privileged daemonsets, we need admin privileges to the K8s cluster. Verify the the kubectl config file has its default context pointing towards the target cluster and admin-equivalent user for that cluster.
Q: Busybox image available or downloadable from all cluster nodes ?
A: Fix the connectivity issues and manually test that the busybox image can be downloaded. The exact version of busybox that is used in the pod spec must be available (pre-seeded) or downloadable on all cluster nodes.
Q: API Server and etcd errors or a general timeout during the install ?
A: Due to the instantiation of daemonset pods on all nodes in the Kubernetes cluster, the CPU/Disk/Network load on the cluster can spike suddenly. This is highly dependent on the customer specific installation details. Due to the overload, the installation process (images pulled on all nodes and written to disks) might take too long or overload the Kubernetes API server or the Secure Workload Docker Registry endpoint or, if configured, the proxy server temporarily. After a brief wait for image pulls on all nodes to complete and a reduction in CPU/Disk/Network load on the Kubernetes cluster nodes, retry the installation script again. API Server and etcd errors from the Kubernetes control plane indicate that the Kubernetes control plane nodes may be underprovisioned or affected by the sudden spike in activity.
Q: Secure Workload Agent experiencing runtime issues with its operations ?
A: Refer to the Linux Agent troubleshooting section if the pods are correctly deployed and the agent has started running but is experiencing runtime issues. The troubleshooting steps are the same once the Kubernetes deployment has successfully installed and started the pods.
Anamoly Types
These are the most common issues encountered on the workflow when using and managing Secure Workload Agents.
Agent Inactivity
Agent has stopped checking to the cluster services. This can happen due to several reasons:
-
The host might have been down
-
The network connectivity has been broken or blocked by firewall rules
-
The agent service has been stopped
Verify the folloiwng on all platforms:
-
Verify the host is active and healthy
-
Verify the agent service is up and running
-
Verify the network connectivity to the cluster is working
Upgrade Failure
Agent upgrade has failed. This can be triggered by few cases such as:
-
Not finding the package when the check in script attempts to download it - the upgrade package cannot be unpacked or the installer from the package cannot be verified.
-
Installation process failing from an OS issue or dependency.
Windows
-
Missing CA root certificate: Certificate Issues
-
If agent was originally installed manually with a MSI install package, check if the Windows edition matches list of supported platforms in user guide: Check If Platform Is Currently Supported
-
Check to make sure OS is configured correctly for Windows Installer operation: Windows Installer Issues
-
Make sure there is enough free disk space on host
Linux
-
If the host OS has been upgraded since the last agent installation, verify the current release matches list of supported platforms in user guide: Check If Platform Is Currently Supported
-
Make sure there have been no changes to the required dependencies since the last installation. You can run the agent installer script with –no-install option to re-verify these dependencies.
-
Make sure there is enough free disk space on host
AIX
-
Make sure there have been no changes to the required dependencies since the last installation. You can run the agent installer script with –no-install option to re-verify these dependencies.
-
Make sure there is enough free disk space on host
Convert Failed
The current agent type mismatches desired agent type and the convert attempt has timed out. This issue can be caused by a communication issue when an agent does check_in to download the package, or wss service failed to push convert_commnad to the agent.
For all platforms, verify the current release and agent type matches list of supported platforms in user guide: Check If Platform Is Currently Supported
Convert Capability
The ability to convert the agent from one type (such as deep visibility) to another type (such as enforcement) is not available by all agents. If an agent that is not capable to do the conversion is required to convert, the anomaly will be reported.
Policy Out of Sync
The current policy (NPC) version last reported by the agent does not match the current version generated on the cluster. This can be caused by a communications error between the agent and the cluster, the agent failing to enforce the policy with the local firewall, or the agent enforcement service not running.
Windows
-
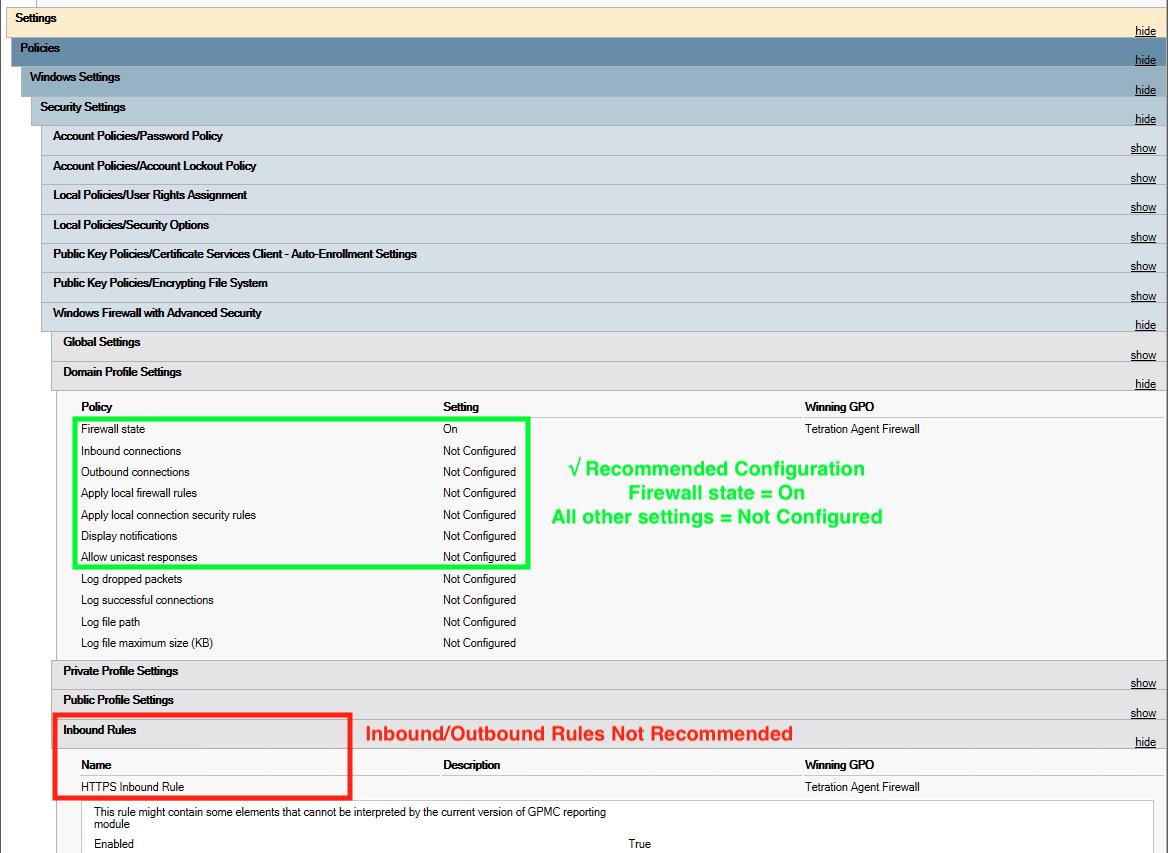
If enforcement mode is WAF, verify there are no GPOs present on the host that would prevent the Firewall from being enabled, adding rules (with Preserve Rules Off) or setting default actions: GPO Configurations
-
Verify there is connectivity between the host and the cluster: SSL Troubleshooting
-
Verify the generated rule count is less than 2000
-
Verify the WindowsAgentEngine service is running: sc query windowsagentengine
-
Verify there are available system resources
Linux
-
Verify iptables and ipset is present with the iptables and ipset command
-
Verify there is connectivity between the host and the cluster: SSL Troubleshooting
-
Verify the tet-enforcer process is running: ps -ef | grep tet-enforcer
AIX
-
Verify ipfilter is installed and running with the ipf -V command
-
Verify there is connectivity between the host and the cluster: SSL Troubleshooting
-
Verify the tet-enforcer process is running: ps -ef | grep tet-enforcer
Flow Export
Pcap Open
If the Secure Workload Agent cannot open the pcap device to capture flows, you see errors in the Agent logs. A successfully opened Pcap device will report as follows:
I0609 15:25:52.354 24248 Started capture thread for device <device_name>
I0609 15:25:52.354 71912 Opening device {<device_id>}I0610 03:24:22.354 16614 Opening device <device_name>
[2020/06/10 03:24:23:3524] NOTICE: lws_client_connect_2: <device_id>: address 172.29.
˓→136.139
HTTPS Connectivity
Connectivity between the agent and the cluster is externally blocked therefore preventing flows and other system information from being delivered. This is caused by one or more configuration issues with network firewalls, SSL decryption services, or third party security agents on the host.
-
If there are known firewalls or SSL decryption security devices between the agent and the cluster, make sure that communications to all Secure Workload collector and VIPs IP addresses are being permitted. For on-prem clusters, the list of collectors will be listed under in the navigation bar at the left side of the Secure Workload web interface. Look for collectorDatamover-*. For Secure Workload cloud, all the IP addresses that need to be permitted will be listed in your Portal.
-
To help identify if there is SSL decryption, openssl s_client can be used to make a connection and display the returned certificate. Any additional certificate added to the chain will be rejected by the Agent’s local CA. SSL Troubleshooting

Note
Typically, the service to update "flow export anomaly status” runs every 5 minutes. This duration may vary because the agents' status updates are being executed in small batches of 5000. Thus, when there are fewer agents in the cluster, the updates are faster. When there are larger number of agents, the updates can take a maximum of 70 minutes.
After the initial sorting of agents records in the database, the cluster and agents become stable, and eventually, the update interval becomes lesser and more consistent.
Windows Certificate Issues
Certificate Issues for MSI installer
MSI installer is signed using code signing certificate:
For MSI Installer, version 3.6.x onwards and 3.5.1.31 onwards
-
Leaf Certificate: Cisco Systems, Inc
-
Intermediate Certificate: DigiCert Trusted G4 Code Signing RSA4096 SHA384 2021 CA1
-
Root Certificate: DigiCert Trusted Root G4
For MSI Installer, earlier versions
-
Leaf Certificate: Cisco Systems, Inc
-
Intermediate Certificate: Symantec Class 3 SHA256 Code Signing CA
-
Root Certificate: VeriSign Class 3 Public Primary Certification Authority - G5
It uses timestamp certificate:
For MSI Installer, version 3.6.x onwards and 3.5.1.31 onwards
-
Leaf Certificate: Symantec SHA256 TimeStamping Signer - G3
-
Intermediate Certificate: Symantec SHA256 TimeStamping CA
-
Root Certificate: VeriSign Universal Root Certification Authority
For MSI Installer, earlier versions
-
Leaf Certificate: Symantec SHA256 Timestamping Signer - G2
-
Intermediate Certificate: Symantec SHA256 Timestamping CA
-
Root Certificate: VeriSign Universal Root Certification Authority
Windows Sensor Installation or upgrade will fail if digital signature of MSI installer is invalid. Digital signature is invalid if
-
MSI Installer Signing Root Certificate or MSI Installer timestamp Root Certificate is not in a “Trusted Root Certification Authority” store
-
MSI Installer Signing Root Certificate or MSI Installer timestamp Root Certificate is expired or revoked.
|
Issue |
Resolution |
|---|---|
|
Installation of agent might fail with below error in the TetUpdate.exe.log “Msi signature is not trusted. 0x800b0109" |
|
|
Windows Sensor upgrade fails with the following error in TetUpdate.exe.log “Msi signature is not trusted. 0x800B010C" A certificate was explicitly revoked by its issuer. |
|
|
Windows Sensor upgrade fails with the following in TetUpdate.exe.log “Msi signature is not trusted. 0x80096005" |
If it the certificate is missing, import it from other machine. To import the certificate, follow below steps: First export the certificate VeriSign Universal Root Certification Authority from one of Working server. Follow below steps:
To import the certificate, follow below steps: First export the certificate VeriSign Universal Root Certification Authority from one of Working server. Follow below steps:
|
Applicable to Windows 2012 , Windows 2012 R2, Windows 8, Windows 8.1
Issue 1
CheckServiceStatus : Exception System.InvalidOperationException: Service npcap was not found on computer
‘.’. —> System.ComponentModel.Win32Exception: The specified service does not exist as an installed serviceResolution
-
Run the command certmgr from command prompt
-
Check “DigiCert High Assurance EV Root CA” in “Trusted Root Certification Authority” store.
-
If it the certificate is missing, import it from other machine.
To import the certificate, follow below steps:
First export the certificate “DigiCert High Assurance EV Root CA” from one of Working server. Follow below steps:
-
Run the command certmgr from command prompt
-
Right click on the certificate “DigiCert High Assurance EV Root CA” under “Trusted Root Certification Authorities” and go to All tasksExport.
-
Copy the exported certificate to the Non-working server and then import the certificate.
To import the certificate, follow below steps:
-
Run the command certmgr from command prompt
-
Right click on the certificates tab under Trusted Root Certification Authorities and go to All tasksImport.
-
Select the Root certificate that you copied and add it in the store.
Applicable to Windows 2008 R2
Issue 1
CheckServiceStatus : Exception System.InvalidOperationException: Service npcap was not found on
computer ‘.’. —> System.ComponentModel.Win32Exception: The specified service does not exist as an
installed serviceResolution
-
Run the command certmgr from command prompt
-
Check DigiCert High Assurance EV Root CA in Trusted Root Certification Authority store.
-
If it the certificate is missing, import it from other machine.
To import the certificate, follow below steps:
First export the certificate “DigiCert High Assurance EV Root CA” from one of Working server. Follow below steps:
-
Run the command certmgr from command prompt
-
Right click on the certificate “DigiCert High Assurance EV Root CA” under “Trusted Root Certification Authorities” and go to All tasksExport.
-
Copy the exported certificate to the Non-working server and then import the certificate.
To import the certificate, follow below steps:
-
Run the command certmgr from command prompt
-
Right click on the certificates tab under Trusted Root Certification Authorities and go to All tasksImport.
-
Select the Root certificate that you copied and add it in the store.
Windows Host Rename
Scenario 1: Not able to see IP Addresses and VRF info after renaming the Windows Host Steps to fix the issue:
-
Remove the entry(with new Hostname that is missing IP Addresses and VRF info) from the TaaS UI.
-
Uninstall ‘Cisco Secure Workload Agent’ from the Windows Host and delete the ‘Cisco Tetration’ directory (typically the path for this will be : ‘C:Program FilesCisco Tetration’).
-
Install ‘Cisco Secure Workload Agent’ on the Windows Host.
Following the above steps should register the Agent on the TaaS UI successfully with the IP Addresses and VRF info.
Scenario 2: Planned Windows Host rename (in advance) Steps to follow:
-
Uninstall ‘Cisco Secure Workload Agent’ from the Windows Host and delete the ‘Cisco Tetration’ directory (typically the path for this will be : ‘C:Program FilesCisco Tetration’).
-
Rename the Windows Host and Reboot.
-
Install ‘Cisco Secure Workload Agent’ on the Windows Host(with new Hostname).
Following the above steps for planned Host rename should register the Agent on the TaaS UI with new Hostname.
Check If Platform is Currently Supported
Windows
-
Run the command winver.exe
-
Compare this release to what is listed here: Supported Platforms and Requirements
Linux
-
Run cat /etc/os-release
-
Compare this release to what is listed here: Supported Platforms and Requirements
AIX
-
Run the command uname -a
-
Note: The major and minor versions are reversed
p7-ops2> # uname -a AIX p7-ops2 1 7 00F8AF944C00 -
In this example, the first number after the host name is the minor and the second number is the major version, so AIX version 7.1. Compare this release to what is listed here: Supported Platforms and Requirements
Windows Installer Issues
-
Make sure there is a C:\Windows\Installer directory. This is not visible in File Explorer, easiest way to verify is in a CMD session and running: dir C:\Windows\Installer
-
Check if the Windows Installer service is not disabled. It must be set to Manual
-
Check to see if there are no other errors being reported by Windows Installer. Check Windows System Event logs under
Required Windows Services
Below is a list of services, that when disabled, have been linked to installation issues of the agent. It is recommended these services are running during the initial installation and any upgrade of the Deep Visibility and Enforcement agents.
|
Service |
Purpose for installation |
|---|---|
|
Device Setup Manager |
Device driver management for the installation of the Npcap filter driver. |
|
Device Install Service |
Also used for the installation of the Npcap filter driver. |
|
Windows Installer |
Required for the installation of agent MSI package. |
|
Windows Firewall |
Required for WAF enforcement mode. |
|
Application Experience |
Used to determine capatibility executables on the system. |
 Note |
Application Experience service only applies to Windows Server 2008, 2008R2, 2012, 2012R2 and Win- dows 7. If disabled, a file lock may occur during Npcap installation causing it to fail. |

 Feedback
Feedback