Auto Scale Solution for the Threat Defense Virtual on Azure
Overview
The auto scale solution enables allocation of resources to match performance requirements and reduce costs. If the demand for resources increases, the system ensures that resources are allocated as required. If the demand for resources decreases, resources are deallocated to reduce costs.
The Firewall Threat Defense Virtual auto scale for Azure is a complete serverless implementation which makes use of serverless infrastructure provided by Azure (Logic App, Azure Functions, Load Balancers, Security Groups, Virtual Machine Scale Set, etc.).
Some of the key features of the Firewall Threat Defense Virtual auto scale for Azure implementation include:
-
Azure Resource Manager (ARM) template-based deployment.
-
Support for scaling metrics based on CPU and memory (RAM).

Note
See Auto Scale Logic for more information.
-
Support for Firewall Threat Defense Virtual deployment and multi-availability zones.
-
Completely automated Firewall Threat Defense Virtual instance registration and de-registration with the Firewall Management Center.
-
NAT policy, Access Policy, and Routes automatically applied to scaled-out Firewall Threat Defense Virtual instances.
-
Support for Load Balancers and multi-availability zones.
-
Support for enabling and disabling the auto scale feature.
-
Works only with the Firewall Management Center; the Firewall Device Manager is not supported.
-
Support to deploy the Firewall Threat Defense Virtual with PAYG or BYOL licensing mode. PAYG is applicable only for Firewall Threat Defense Virtual software version 6.5 and onwards. See Supported Software Platforms.
-
Cisco provides an auto scale for Azure deployment package to facilitate the deployment.
The Firewall Threat Defense Virtual auto scale solution on Azure supports two types of use cases configured using different topologies:
-
Auto scale using Sandwich Topology – The Firewall Threat Defense Virtual scale set is sandwiched between an Azure Internal load balancer (ILB) and an Azure External load balancer (ELB).
-
Auto scale with Azure Gateway load balancer (GWLB) – The Azure GWLB is integrated with Secure Firewall, public load balancer, and internal servers - to simplify deployment, management, and scaling of firewalls.
Supported Software Platforms
The Firewall Threat Defense Virtual auto scale solution is applicable to the Firewall Threat Defense Virtual managed by the Firewall Management Center, and is software version agnostic. The Cisco Secure Firewall Threat Defense Compatibility Guide provides software and hardware compatibility, including operating system and hosting environment requirements.
-
The Firewall Management Centers: Virtual table lists compatibility and virtual hosting environment requirements for the Firewall Management Center Virtual.
-
The Firewall Threat Defense Virtual Compatibility table lists compatibility and virtual hosting environment requirements for the Firewall Threat Defense Virtual on Azure.
 Note |
For purposes of deploying the Azure auto scale solution, the minimum supported version for the Firewall Threat Defense Virtual on Azure is Version 6.4. |
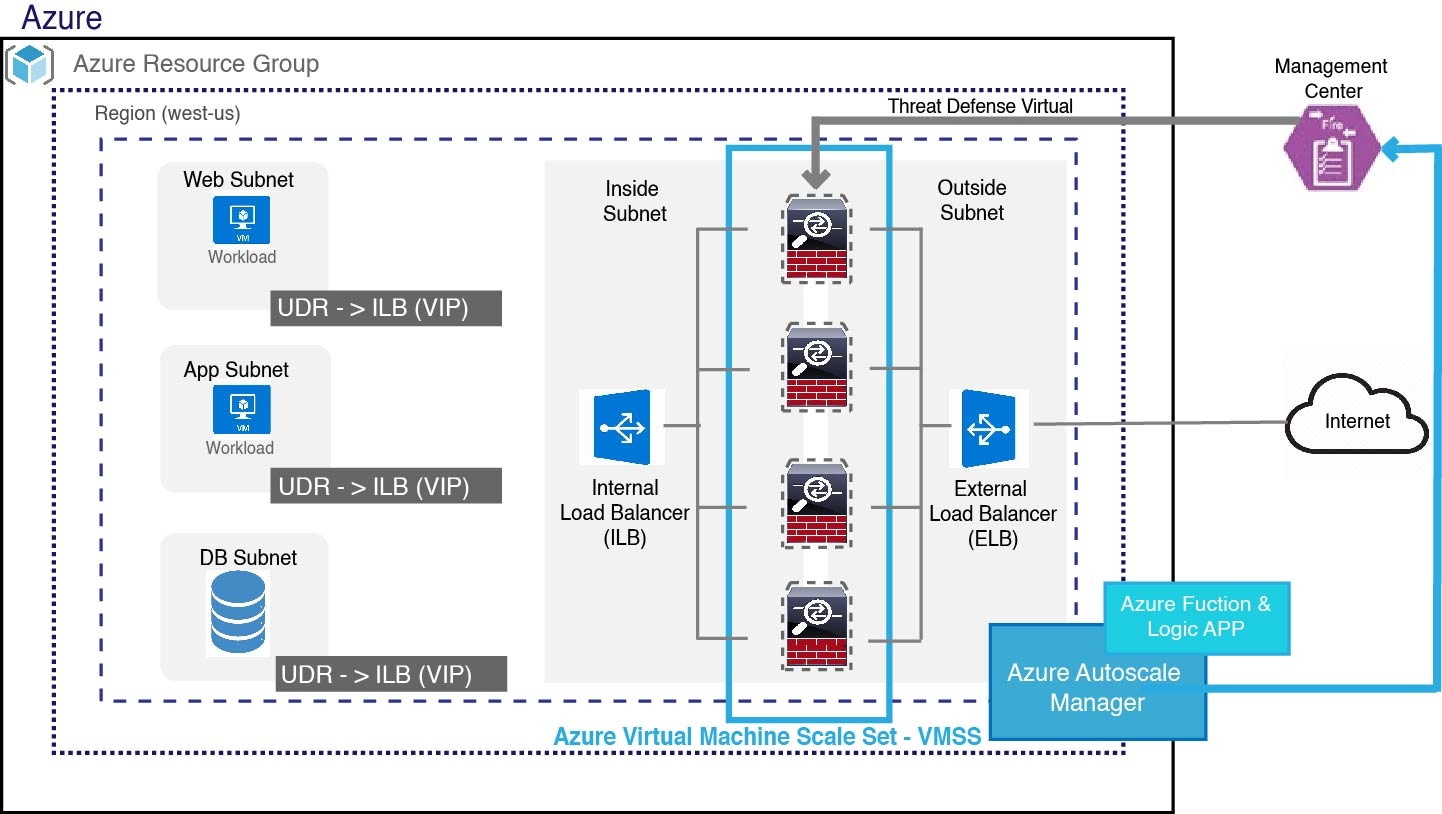
Auto Scale using Sandwich Topology Use Case
The Firewall Threat Defense Virtual auto scale for Azure is an automated horizontal scaling solution that positions the Firewall Threat Defense Virtual scale set sandwiched between an Azure Internal load balancer (ILB) and an Azure External load balancer (ELB).
-
The ELB distributes traffic from the Internet to Firewall Threat Defense Virtual instances in the scale set; the firewall then forwards traffic to application.
-
The ILB distributes outbound Internet traffic from an application to Firewall Threat Defense Virtual instances in the scale set; the firewall then forwards traffic to Internet.
-
A network packet will never pass through both (internal & external) load balancers in a single connection.
-
The number of Firewall Threat Defense Virtual instances in the scale set will be scaled and configured automatically based on load conditions.
Auto Scale with Azure Gateway Load Balancer Use Case
The Azure Gateway Load Balancer (GWLB) ensures that internet traffic to and from an Azure VM, such as an application server, is inspected by Secure Firewall without requiring any routing changes. This integration of the Azure GWLB with Secure Firewall simplifies deployment, management, and scaling of firewalls. This integration also reduces operational complexity and provides a single entry and exit point for traffic at the firewall. The applications and infrastructure can maintain visibility of source IP address, which is critical in some environments.
In the Azure GWLB Auto Scale use case, the Firewall Threat Defense Virtual uses only two interfaces: Management and one data interface.
 Note |
|
Licensing
Both PAYG and BYOL are supported.
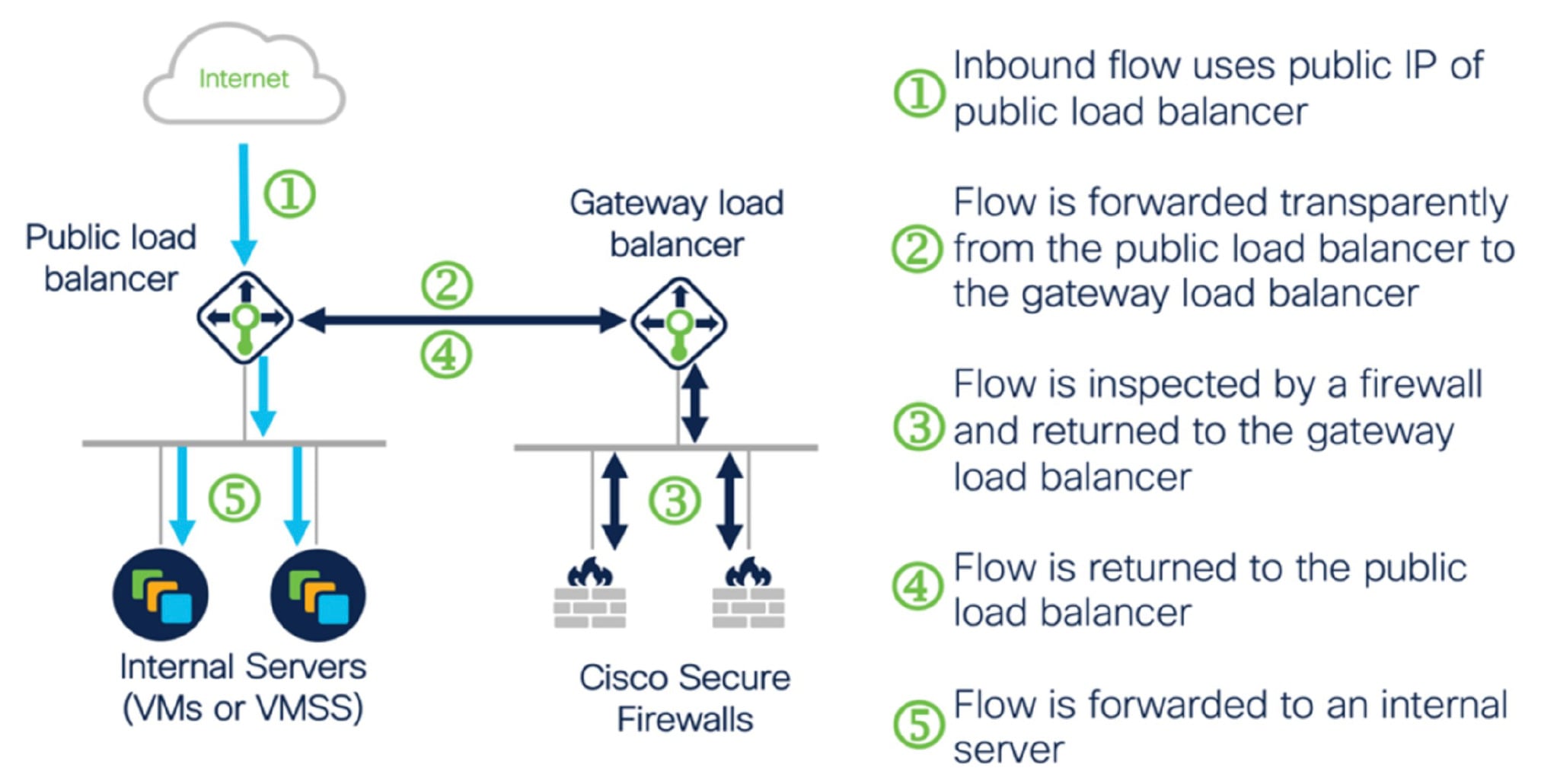
Inbound Traffic Use Case and Topology
The following diagram displays the traffic flow for inbound traffic.
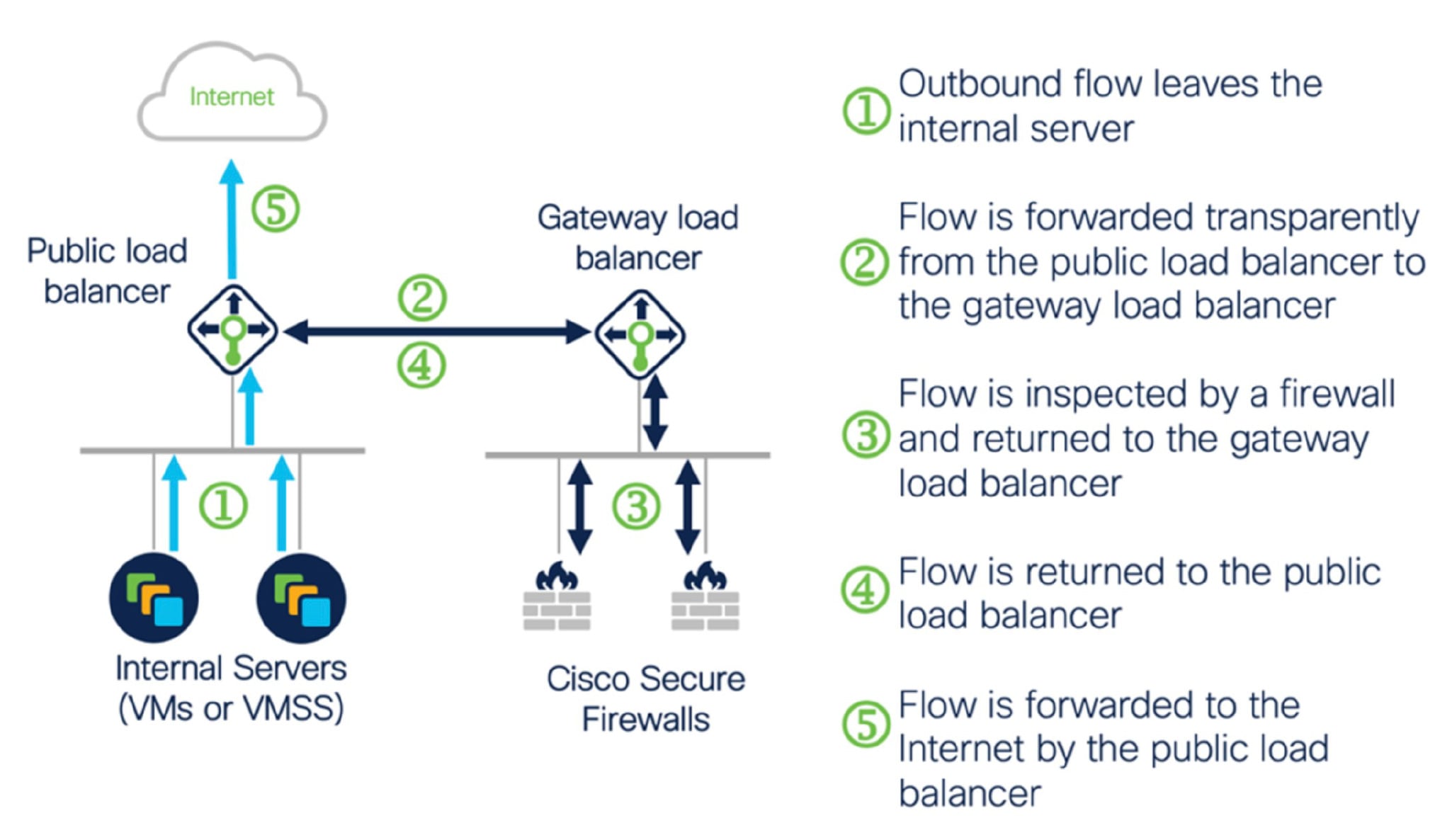
Outbound Traffic Use Case and Topology
The following diagram displays the traffic flow for outbound traffic.
 Note |
To deploy and configure the management center, see the procedures in the Cisco Secure Firewall Management Center Device Configuration Guide. Use the deployed management center to manage the threat defense virtual instances. |
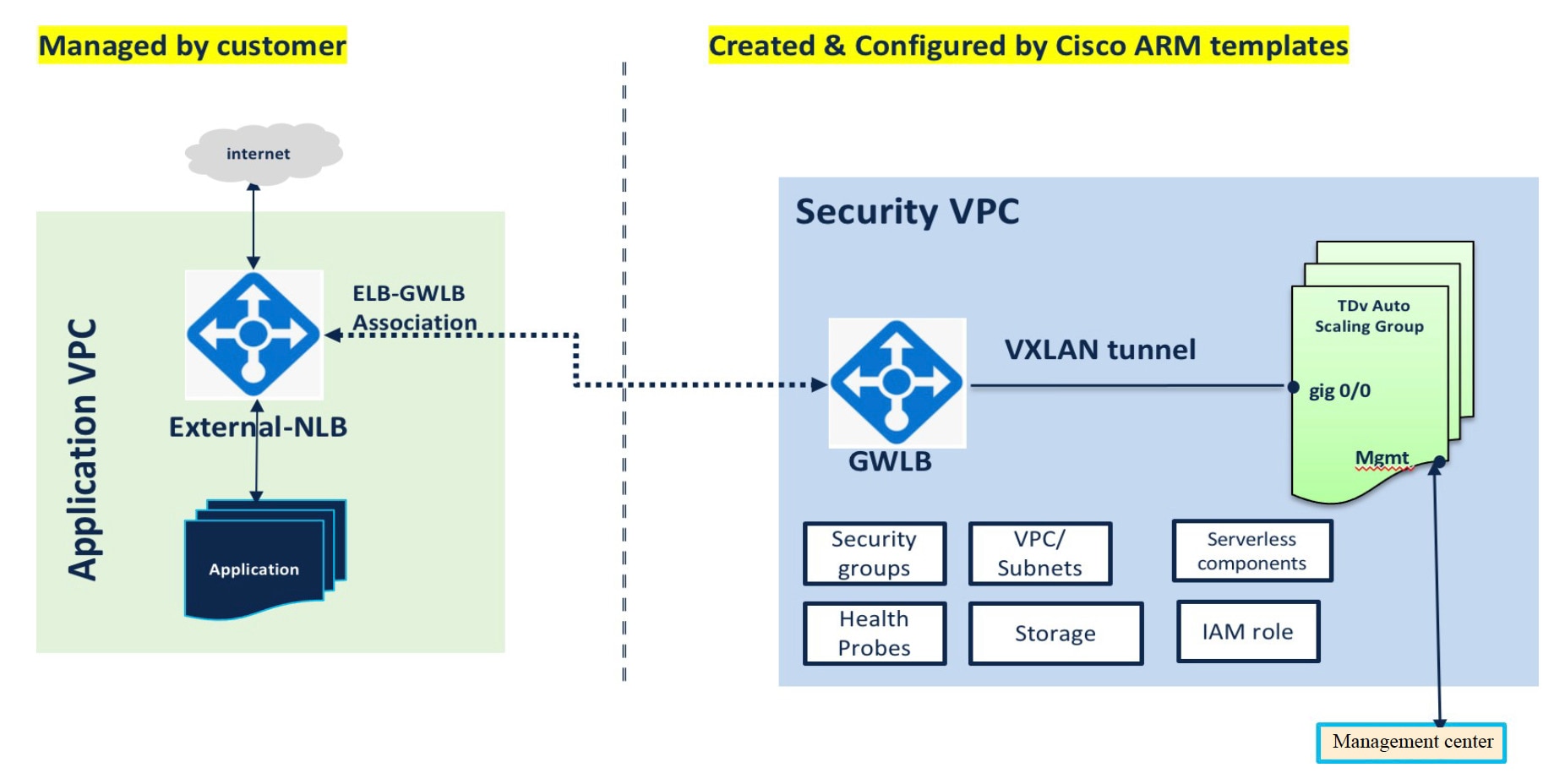
Traffic Flow between the Application VNet and Security VNet
In the diagram shown below, traffic is redirected from the existing topology to the firewalls for inspection by the external load balancer. The traffic is then routed to the newly created GWLB. Any traffic that is routed to the ELB is forwarded to the GWLB.
The GWLB then forwards the VXLAN-encapsulated traffic to a Firewall Threat Defense Virtual instance. You have to create two Firewall Threat Defense Virtual associations as the GWLB uses two separate VXLAN tunnels for ingress and egress traffic. The Firewall Threat Defense Virtual decapsulates the VXLAN-encapsulated traffic, inspects it, and routes the traffic to the GWLB. The GWLB then forwards the traffic to the ELB.
Scope
This document covers the detailed procedures to deploy the serverless components for the Firewall Threat Defense Virtual auto scale for Azure solution and the auto scale with Azure GWLB solution.
 Important |
|
Download the Deployment Package
The Firewall Threat Defense Virtual auto scale for Azure solution using sandwich topology is an Azure Resource Manager (ARM) template-based deployment which makes use of the serverless infrastructure provided by Azure (Logic App, Azure Functions, Load Balancers, Virtual Machine Scale Set, and so on).
The Firewall Threat Defense Virtual auto scale with Azure GWLB solution is an ARM template-based deployment that creates the GWLB, networking infrastructure, threat defense virtual auto scaling group, serverless components, and other required resources.
The deployment procedure for both the solutions are similar.
Download the files required to launch the Firewall Threat Defense Virtual auto scale for Azure solution. Deployment scripts and templates for your version are available in the GitHub repository.
 Attention |
Note that Cisco-provided deployment scripts and templates for auto scale are provided as open source examples, and are not covered within the regular Cisco TAC support scope. Check GitHub regularly for updates and ReadMe instructions. See Build Azure Functions from Source Code for instructions on how to build the ASM_Function.zip package. |
Auto Scale Solution Components
The following components make up the Firewall Threat Defense Virtual auto scale for Azure solution.
Azure Functions (Function App)
The Function App is a set of Azure functions. The basic functionality includes:
-
Communicate/Probe Azure metrics periodically.
-
Monitor the Firewall Threat Defense Virtual load and trigger Scale In/Scale Out operations.
-
Register a new Firewall Threat Defense Virtual with the Firewall Management Center.
-
Configure a new Firewall Threat Defense Virtual via Firewall Management Center.
-
Unregister (remove) a scaled-in Firewall Threat Defense Virtual from the Firewall Management Center.
These functions are delivered in the form of compressed Zip package (see Build the Azure Function App Package). The functions are as discrete as possible to carry out specific tasks, and can be upgraded as needed for enhancements and new release support.
Orchestrator (Logic App)
The Auto Scale Logic App is a workflow, i.e. a collection of steps in a sequence. Azure functions are independent entities and cannot communicate with each other. This orchestrator sequences the execution of these functions and exchanges information between them.
-
The Logic App is used to orchestrate and pass information between the auto scale Azure functions.
-
Each step represents an auto scale Azure function or built-in standard logic.
-
The Logic App is delivered as a JSON file.
-
The Logic App can be customized via the GUI or JSON file.
Virtual Machine Scale Set (VMSS)
The VMSS is a collection of homogeneous virtual machines, such as Firewall Threat Defense Virtual devices.
-
The VMSS is capable of adding new identical VMs to the set.
-
New VMs added to the VMSS are automatically attached with Load Balancers, Security Groups, and network interfaces.
-
The VMSS has a built–in auto scale feature which is disabled for Firewall Threat Defense Virtual for Azure.
-
You should not add or delete Firewall Threat Defense Virtual instances in the VMSS manually.
Azure Resource Manager (ARM) Template
ARM templates are used to deploy the resources required by the Firewall Threat Defense Virtual auto scale for Azure solution.
Threat defense virtual auto scale for Azure - The ARM template azure_ftdv_autoscale.json provides input for the Auto Scale Manager components including:
-
Azure Function App
-
Azure Logic App
-
The Virtual Machine Scale Set (VMSS)
-
Internal/External load balancers.
-
Security Groups and other miscellaneous components needed for deployment.
Threat defense virtual auto scale with Azure GWLB - The ARM template azure_ftdv_autoscale_with_GWLB.json provides input for the Auto Scale Manager components including:
-
Azure Function App
-
Azure Logic App
-
Virtual Machine (VM) or Virtual Machine Scale Set (VMSS)
-
Networking Infrastructure
-
Gateway load balancer
-
Security Groups and other miscellaneous components needed for deployment
 Important |
The ARM template has limitations with respect to validating user input, hence it is your responsibility to validate input during deployment. |
Prerequisites
-
Ensure that you have Owner role in the Azure subscription.
-
Create the Azure Resource Group. Ensure that the Azure Virtual Network along with the necessary subnets are created.
-
Interfaces for NLB-based cluster : Management, Diagnostic, Inside, Outside, CCL and the function app.
-
Interfaces for GWLB-based cluster : Management, Diagnostic, Data, CCL and the function app.
-
-
On the Management Center:
-
Ensure that Management Center Virtual is licensed correctly.
-
Create the access control policy.
-
Create the Security Zone (SZ) object for the interfaces. For NLB based cluster, create the SZ for inside and outside interfaces. For GWLB-based cluster, create the SZ for the data interface.
-
Create a separate user name and password for the azure function to add the Threat Defense Virtual instances to the Management Center Virtual and configure the instances.
-
-
Install the Azure CLI on your local system.
-
Download the Azure Clustering Autoscale repository from GitHub to your local computer and run the command python3 make.py build to create the Azure functions zip file.
Azure Resources
Resource Group
An existing or newly created Resource Group is required to deploy all the components of this solution.
 Note |
Record the Resource Group name, the Region in which it is created, and the Azure Subscription ID for later use. |
Networking
Make sure a virtual network is available or created. An auto scale deployment with sandwich topology does not create, alter, or manage any networking resources. However, note that auto scale deployment with the Azure GWLB creates networking infrastructure.
The Firewall Threat Defense Virtual requires four network interfaces, thus your virtual network requires four subnets for:
-
Management traffic
-
Diagnostic traffic
-
Inside traffic
-
Outside traffic
The following ports should be open in the Network Security Group to which the subnets are connected:
-
SSH(TCP/22)
Required for the Health probe between the Load Balancer and Firewall Threat Defense Virtual.
Required for communication between the Serverless functions and Firewall Threat Defense Virtual.
-
TCP/8305
Required for communication between Firewall Threat Defense Virtual and the Firewall Management Center.
-
HTTPS(TCP/443)
Required for communication between the Serverless components and the Firewall Management Center.
-
Application-specific protocol/ports
Required for any user applications (for example, TCP/80, etc.).
 Note |
Record the virtual network name, the virtual network CIDR, the names of the 4 subnets, and the Gateway IP addresses of the outside and inside subnets. |
Build the Azure Function App Package
The Firewall Threat Defense Virtual auto scale solution requires that you build an archive file: ASM_Function.zip. which delivers a set of discrete Azure functions in the form of a compressed ZIP package.
See Build Azure Functions from Source Code for instructions on how to build the ASM_Function.zip package.
These functions are as discrete as possible to carry out specific tasks, and can be upgraded as needed for enhancements and new release support.
Prepare the Firewall Management Center
You manage the Firewall Threat Defense Virtual using the Firewall Management Center, a full-featured, multidevice manager. The Firewall Threat Defense Virtual registers and communicates with the Firewall Management Center on the Management interface that you allocated to the Firewall Threat Defense Virtual machine.
Create all the objects needed for the Firewall Threat Defense Virtual configuration and management, including a device group, so you can easily deploy policies and install updates on multiple devices. All the configurations applied on the device group will be pushed to the Firewall Threat Defense Virtual instances.
The following sections provide a brief overview of basic steps to prepare the Firewall Management Center. You should consult the full Secure Firewall Management Center Configuration Guide for complete information. When you prepare the Firewall Management Center, make sure you record the following information:
-
The Firewall Management Center public IP address.
-
The Firewall Management Center username/password.
-
The security policy name.
-
The inside and outside security zone object names.
-
The device group name.
Create a New Firewall Management Center User
Create a new user in the Firewall Management Center with Admin privileges to be used only by AutoScale Manager.
 Important |
It's important to have the Firewall Management Center user account dedicated to the Firewall Threat Defense Virtual auto scale solution to prevent conflicts with other Firewall Management Center sessions. |
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Create new user in the Firewall Management Center with Admin privileges. Choose and click Create User. The username must be Linux-valid:
|
|
Step 2 |
Complete user options as required for your environment. See the Cisco Secure Firewall Management Center Administration Guide for complete information. |
Configure Access Control
Configure access control to allow traffic from inside to outside. Within an access control policy, access control rules provide a granular method of handling network traffic across multiple managed devices. Properly configuring and ordering rules is essential to building an effective deployment. See "Best Practices for Access Control" in the Cisco Secure Firewall Management Center Device Configuration Guide.
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Choose . |
|
Step 2 |
Click New Policy. |
|
Step 3 |
Enter a unique Name and, optionally, a Description. |
|
Step 4 |
See the Cisco Secure Firewall Management Center Device Configuration Guide to configure security settings and rules for your deployment. |
Configure Licensing
All licenses are supplied to the Firewall Threat Defense by the Firewall Management Center. You can optionally purchase the following feature licenses:
-
Secure Firewall Threat Defense IPS—Security Intelligence and Cisco Secure IPS
-
Secure Firewall Threat Defense Malware Defense—Malware Defense
-
Secure Firewall Threat Defense URL Filtering—URL Filtering
-
RA VPN—AnyConnect Plus, AnyConnect Apex, or AnyConnect VPN Only.
 Note |
When you buy a IPS , malware defense, or URL filtering license, you also need a matching subscription license to access updates for 1, 3, or 5 years. |
Before you begin
-
Have a master account on the Cisco Smart Software Manager.
If you do not yet have an account, click the link to set up a new account. The Smart Software Manager lets you create a master account for your organization.
-
Your Cisco Smart Software Licensing account must qualify for the Strong Encryption (3DES/AES) license to use some features (enabled using the export-compliance flag).
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Make sure your Smart Licensing account contains the available licenses you need. When you bought your device from Cisco or a reseller, your licenses should have been linked to your Smart Software License account. However, if you need to add licenses yourself, use the Find Products and Solutions search field on the Cisco Commerce Workspace. Search for the following license PIDs: 
|
||
|
Step 2 |
If you have not already done so, register the Firewall Management Center with the Smart Licensing server. Registering requires you to generate a registration token in the Smart Software Manager. See the Cisco Secure Firewall Management Center Administration Guide for detailed instructions. |
Create Security Zone Objects
Create inside and outside security zone objects for your deployment.
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Choose . |
|
Step 2 |
Choose Interface from the list of object types. |
|
Step 3 |
Click . |
|
Step 4 |
Enter a Name (for example inside, outside). |
|
Step 5 |
Choose Routed as the Interface Type. |
|
Step 6 |
Click Save. |
Create a Device Group
Device groups enable you to easily assign policies and install updates on multiple devices.
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Choose . 
|
|
Step 2 |
From the Add drop-down menu, choose Add Group. |
|
Step 3 |
Enter a Name. For example, AutoScaleGroup. 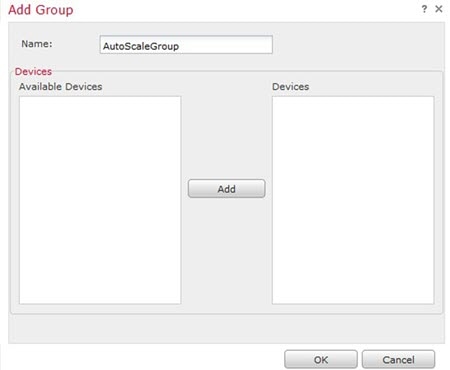
|
|
Step 4 |
Click OK to add the device group. 
|
Configure Secure Shell Access
Platform settings for Firewall Threat Defense devices configure a range of unrelated features whose values you might want to share among several devices. Firewall Threat Defense Virtual Auto Scale for Azure requires a Firewall Threat Defense Platform Settings Policy to allow SSH on the Inside/Outside zones and the device group created for the auto scale Group. This is required so that the Firewall Threat Defense Virtual’s data interfaces can respond to Health Probes from Load Balancers.
Before you begin
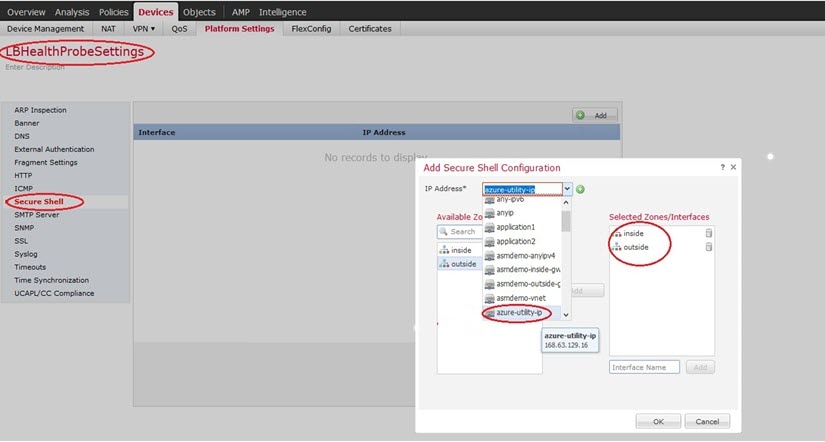
You need network objects that define the hosts or networks you will allow to make SSH connections to the device. You can add objects as part of the procedure, but if you want to use object groups to identify a group of IP addresses, ensure that the groups needed in the rules already exist. Select to configure objects. For example, see the azure-utility-ip (168.63.129.16) object in the following procedure.
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Select and create or edit a Firewall Threat Defense policy, for example LBHealthProbeSettings. 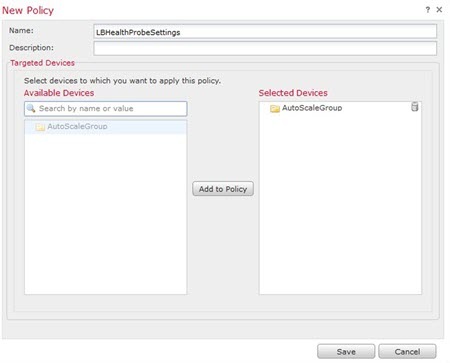
|
||
|
Step 2 |
Select Secure Shell. |
||
|
Step 3 |
Identify the interfaces and IP addresses that allow SSH connections. |
||
|
Step 4 |
Click Save. You can now go to and deploy the policy to assigned devices. The changes are not active until you deploy them.
|
Configure NAT
Create a NAT policy and create the necessary NAT rules to forward traffic from the outside interface to your application, and attach this policy to the device group you created for auto scale.
 Note |
You have to configure NAT only if you are configuring auto scale using a sandwich topology. |
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Choose . |
||
|
Step 2 |
From the New Policy drop-down list, choose Threat Defense NAT. |
||
|
Step 3 |
Enter a unique Name. |
||
|
Step 4 |
Optionally, enter a Description. |
||
|
Step 5 |
Configure your NAT rules. See the procedure "Configure NAT for Threat Defense" in the Cisco Secure Firewall Management Center Device Configuration Guide for guidelines on how to create NAT rules and apply NAT policies. The following figure shows a basic approach. 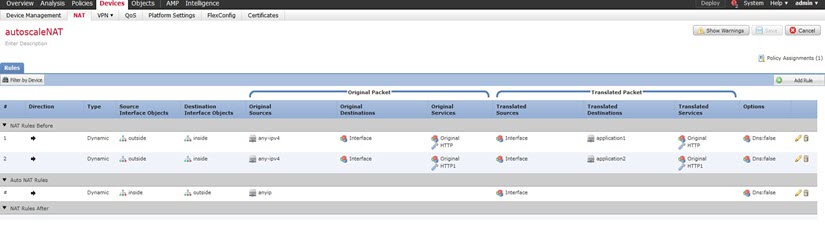
|
||
|
Step 6 |
Click Save. |
Input Parameters
The following table defines the template parameters and provides an example. Once you decide on these values, you can use these parameters to create the Firewall Threat Defense Virtual device when you deploy the ARM template into your Azure subscription. See Deploy the Auto Scale ARM Template.In the Auto scale with Azure GWLB solution, networking infrastructure is also created due to which additional input parameters have to be configured in the template. The parameter descriptions are self-explanatory.
|
Parameter Name |
Allowed Values/Type |
Description |
Resource Creation Type |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
resourceNamePrefix |
String* (3-10 characters) |
All the resources are created with name containing this prefix. Note: Use only lowercase letters. Example: ftdv |
New |
||||
|
virtualNetworkRg |
String |
The virtual network resource group name. Example: cisco-virtualnet-rg |
Existing |
||||
|
virtualNetworkName |
String |
The virtual network name (already created). Example: cisco-virtualnet |
Existing |
||||
|
virtualNetworkCidr |
CIDR format x.x.x.x/y |
CIDR of Virtual Network (already created) |
Existing |
||||
|
mgmtSubnet |
String |
The management subnet name (already created). Example: cisco-mgmt-subnet |
Existing |
||||
|
diagSubnet |
String |
The diagnostic subnet name (already created). Example: cisco-diag-subnet |
Existing |
||||
|
insideSubnet |
String |
The inside Subnet name (already created). Example: cisco-inside-subnet |
Existing |
||||
|
internalLbIp |
String |
The internal load balancer IP address for the inside subnet (already created). Example: 1.2.3.4 |
Existing |
||||
|
insideNetworkGatewayIp |
String |
The inside subnet gateway IP address (already created). |
Existing |
||||
|
outsideSubnet |
String |
The outside subnet name (already created). Example: cisco-outside-subnet |
Existing |
||||
|
outsideNetworkGatewayIp |
String |
The outside subnet gateway IP (already created). |
Existing |
||||
|
deviceGroupName |
String |
Device group in Firewall Management Center (already created) |
Existing |
||||
|
insideZoneName |
String |
Inside Zone name in the Firewall Management Center (already created) |
Existing |
||||
|
outsideZoneName |
String |
Outside Zone name in the Firewall Management Center (already created) |
Existing |
||||
|
softwareVersion |
String |
The Firewall Threat Defense Virtual Version (selected from drop-down during deployment). |
Existing |
||||
|
vmSize |
String |
Size of Firewall Threat Defense Virtual instance (selected from drop-down during deployment). |
N/A |
||||
|
ftdLicensingSku |
String |
Firewall Threat Defense Virtual Licensing Mode (PAYG/BYOL) Note: PAYG is supported in Version 6.5+. |
N/A |
||||
|
licenseCapability |
Comma-separated string |
BASE, MALWARE, URLFilter, THREAT |
N/A |
||||
|
ftdVmManagementUserName |
String* |
The Firewall Threat Defense Virtual VM management administrator user name. This cannot be ‘admin’. See Azure for VM administrator user name guidelines. |
New |
||||
|
ftdVmManagementUserPassword |
String* |
Password for the Firewall Threat Defense Virtual VM management administrator user. Passwords must be 12 to 72 characters long, and must have: lowercase, uppercase, numbers, and special characters; and must have no more than 2 repeating characters.
|
New |
||||
|
fmcIpAddress |
String x.x.x.x |
The public IP address of the Firewall Management Center (already created) |
Existing |
||||
|
fmcUserName |
String |
Firewall Management Center user name, with administrative privileges (already created) |
Existing |
||||
|
fmcPassword |
String |
Firewall Management Center password for above Firewall Management Center user name (already created) |
Existing |
||||
|
policyName |
String |
Security Policy created in the Firewall Management Center (already created) |
Existing |
||||
|
scalingPolicy |
POLICY-1 / POLICY-2 |
POLICY-1: Scale-Out will be triggered when the average load of any Firewall Threat Defense Virtual goes beyond the Scale Out threshold for the configured duration. POLICY-2: Scale-Out will be triggered when average load of all the Firewall Threat Defense Virtual devices in the auto scale group goes beyond the Scale Out threshold for the configured duration. In both cases Scale-In logic remains the same: Scale-In will be triggered when average load of all the Firewall Threat Defense Virtual devices comes below the Scale In threshold for the configured duration. |
N/A |
||||
|
scalingMetricsList |
String |
Metrics used in making the scaling decision. Allowed: CPU CPU, MEMORY Default: CPU |
N/A |
||||
|
cpuScaleInThreshold |
String |
The Scale-In threshold in percent for CPU metrics. Default: 10 When the Firewall Threat Defense Virtual metric goes below this value the Scale-In will be triggered. See Auto Scale Logic. |
N/A |
||||
|
cpuScaleOutThreshold |
String |
The Scale-Out threshold in percent for CPU metrics. Default: 80 When the Firewall Threat Defense Virtual metric goes above this value, the Scale-Out will be triggered. The ‘cpuScaleOutThreshold’ should always be greater than the ‘cpuScaleInThreshold’. See Auto Scale Logic. |
N/A |
||||
|
memoryScaleInThreshold |
String |
The Scale-In threshold in percent for memory metrics. Default: 0 When the Firewall Threat Defense Virtual metric goes below this value the Scale-In will be triggered. See Auto Scale Logic. |
N/A |
||||
|
memoryScaleOutThreshold |
String |
The Scale-Out threshold in percent for memory metrics. Default: 0 When the Firewall Threat Defense Virtual metric goes above this value, the Scale-Out will be triggered. The ‘memoryScaleOutThreshold´ should always be greater than the ‘memoryScaleInThreshold’. See Auto Scale Logic. |
N/A |
||||
| minFtdCount |
Integer |
The minimum Firewall Threat Defense Virtual instances available in the scale set at any given time. Example: 2 |
N/A |
||||
|
maxFtdCount |
Integer |
The maximum Firewall Threat Defense Virtual instances allowed in the Scale set. Example: 10
|
N/A |
||||
|
metricsAverageDuration |
Integer |
Select from the drop-down. This number represents the time (in minutes) over which the metrics are averaged out. If the value of this variable is 5 (i.e. 5min), when the Auto Scale Manager is scheduled it will check the past 5 minutes average of metrics and based on this it will make a scaling decision.
|
N/A |
||||
|
initDeploymentMode |
BULK / STEP |
Primarily applicable for the first deployment, or when the Scale Set does not contain any Firewall Threat Defense Virtual instances. BULK: The Auto Scale Manager will try to deploy 'minFtdCount' number of Firewall Threat Defense Virtual instances in parallel at one time.
STEP: The Auto Scale Manager will deploy the 'minFtdCount' number of Firewall Threat Defense Virtual devices one by one at each scheduled interval.
|
|||||
|
*Azure has restrictions on the naming convention for new resources. Review the limitations or simply use all lowercase. Do not use spaces or any other special characters. |
|||||||
Deploy the Auto Scale Solution
Download the Deployment Package
The Firewall Threat Defense Virtual auto scale for Azure solution using sandwich topology is an Azure Resource Manager (ARM) template-based deployment which makes use of the serverless infrastructure provided by Azure (Logic App, Azure Functions, Load Balancers, Virtual Machine Scale Set, and so on).
The Firewall Threat Defense Virtual auto scale with Azure GWLB solution is an ARM template-based deployment that creates the GWLB, networking infrastructure, threat defense virtual auto scaling group, serverless components, and other required resources.
The deployment procedure for both the solutions are similar.
Download the files required to launch the Firewall Threat Defense Virtual auto scale for Azure solution. Deployment scripts and templates for your version are available in the GitHub repository.
 Attention |
Note that Cisco-provided deployment scripts and templates for auto scale are provided as open source examples, and are not covered within the regular Cisco TAC support scope. Check GitHub regularly for updates and ReadMe instructions. See Build Azure Functions from Source Code for instructions on how to build the ASM_Function.zip package. |
Deploy the Auto Scale ARM Template
Threat defense virtual auto scale for Azure using Sandwich Topology - Use the ARM template azure_ftdv_autoscale.json to deploy the resources required by the Firewall Threat Defense Virtual auto scale for Azure. Within a given resource group, the ARM template deployment creates the following:
-
Virtual Machine Scale Set (VMSS)
-
External Load Balancer
-
Internal Load Balancer
-
Azure Function App
-
Logic App
-
Security groups (For Data and Management interfaces)
Threat defense virtual auto scale with Azure GWLB - Use the ARM template azure_ftdv_autoscale_with_GWLB.json to deploy the resources required by the Firewall Threat Defense Virtual auto scale with Azure GWLB solution. Within a given resource group, the ARM template deployment creates the following:
-
Virtual Machine (VM) or Virtual Machine Scale Set (VMSS)
-
Gateway Load Balancer
-
Azure Function App
-
Logic App
-
Networking Infrastructure
-
Security Groups and other miscellaneous components needed for deployment
Before you begin
-
Download the ARM templates from the GitHub repository (https://github.com/CiscoDevNet/cisco-ftdv/tree/master/autoscale/azure).
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
If you need to deploy the Firewall Threat Defense Virtual instances in multiple Azure zones, edit the ARM template based on the zones available in the Deployment region. Example:This example shows the “Central US” region which has 3 zones. |
||
|
Step 2 |
Edit the traffic rules required in External Load Balancer. You can add any number of rules by extending this ‘json’ array. This is valid for the Auto Scale using Sandwich Topology use case. Example:
|
||
|
Step 3 |
Log in to the Microsoft Azure portal using your Microsoft account username and password. |
||
|
Step 4 |
Click Resource groups from the menu of services to access the Resource Groups blade. You will see all the resource groups in your subscription listed in the blade. Create a new resource group or select an existing, empty resource group; for example, Firewall Threat Defense Virtual_AutoScale. 
|
||
|
Step 5 |
Click Create a resource (+) to create a new resource for template deployment. The Create Resource Group blade appears. |
||
|
Step 6 |
In Search the Marketplace, type Template deployment (deploy using custom templates), and then press Enter. 
|
||
|
Step 7 |
Click Create. |
||
|
Step 8 |
There are several options for creating a template. Choose Build your own template in editor. 
|
||
|
Step 9 |
In the Edit template window, delete all the default content and copy the contents from the updated azure_ftdv_autoscale.json and click Save. 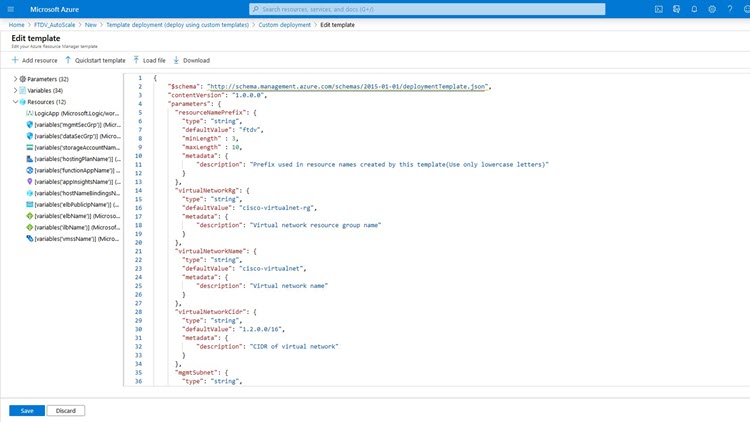
|
||
|
Step 10 |
In next section, fill all the parameters. Refer to Input Parameters for details about each parameter, then click Purchase. 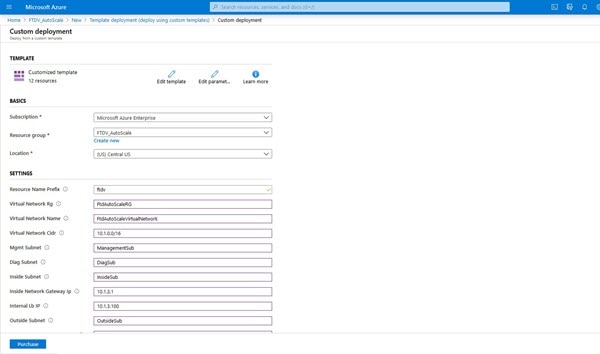
|
||
|
Step 11 |
When a template deployment is successful, it creates all the required resources for the Firewall Threat Defense Virtual auto scale for Azure solution. See the resouses in the following figure. The Type column describes each resource, including the Logic App, VMSS, Load Balancers, Public IP address, etc. 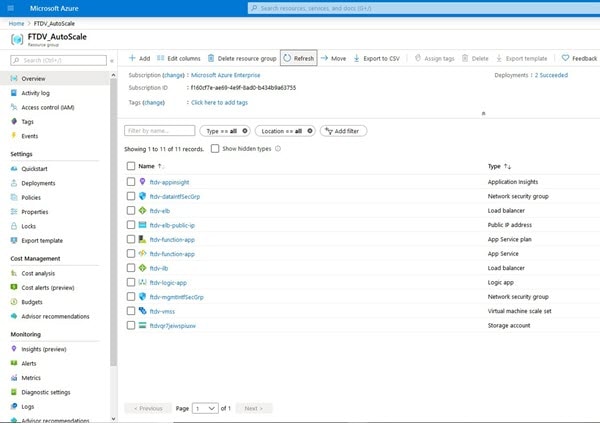
|
Deploy the Azure Function App
When you deploy the ARM template, Azure creates a skeleton Function App, which you then need to update and configure manually with the functions required for the Auto Scale Manager logic.
Before you begin
-
Build the ASM_Function.zip package. See Build Azure Functions from Source Code.
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Go to the Function App you created when you deployed the ARM template, and verify that no functions are present. In a browser go to this URL: https://<Function App Name>.scm.azurewebsites.net/DebugConsole For the example in Deploy the Auto Scale ARM Template: |
|
Step 2 |
In the file explorer navigate to site/wwwroot. |
|
Step 3 |
Drag-and-drop the ASM_Function.zip to the right side corner of the file explorer. 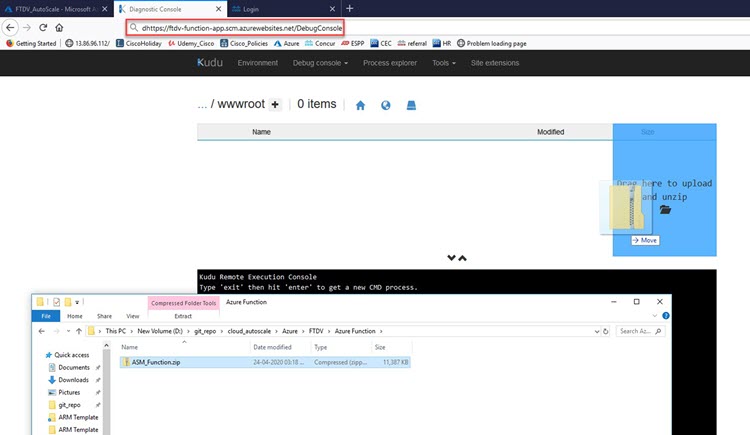
|
|
Step 4 |
Once the upload is successful, all of the serverless functions should appear. 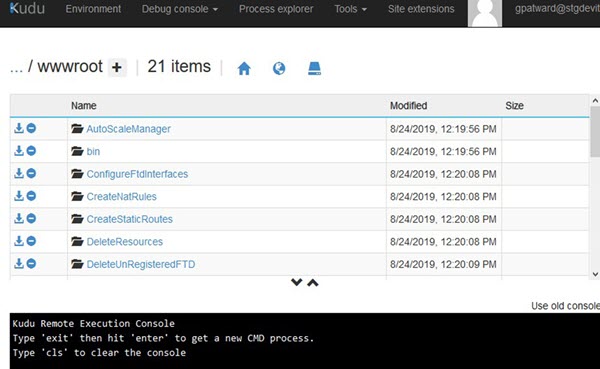
|
|
Step 5 |
Download the PuTTY SSH client. Azure functions need to access the Firewall Threat Defense Virtual via an SSH connection. However, the opensource libraries used in the serverless code do not support the SSH key exchange algorithms used by the Firewall Threat Defense Virtual. Hence you need to download a pre-built SSH client. Download the PuTTY command-line interface to the PuTTY back end (plink.exe) from www.putty.org. 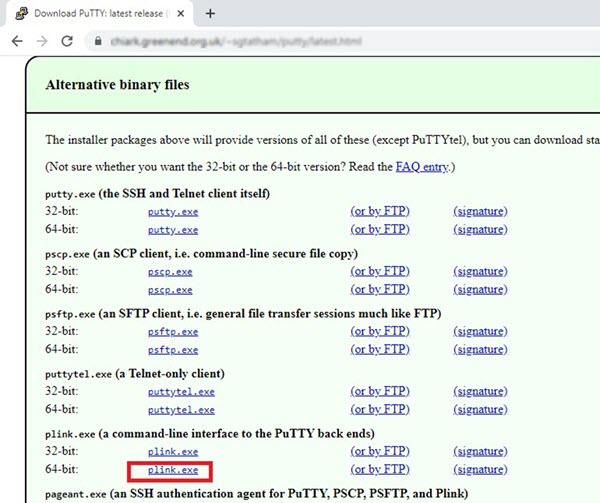
|
|
Step 6 |
Rename the SSH client executable file plink.exe to ftdssh.exe. |
|
Step 7 |
Drag-and-drop the ftdssh.exe to the right side corner of the file explorer, to the location where ASM_Function.zip was uploaded in the previous step. |
|
Step 8 |
Verify the SSH client is present with the function application. Refresh the page if necessary. |
Fine Tune the Configuration
There are a few configurations available to fine tune the Auto Scale Manager or to use in debugging. These options are not exposed in the ARM template, but you can edit them under the Function App.
Before you begin
 Note |
This can be edited at any time. Follow this sequence to edit the configurations.
|
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
In the Azure portal, search for and select the Firewall Threat Defense Virtual function application. 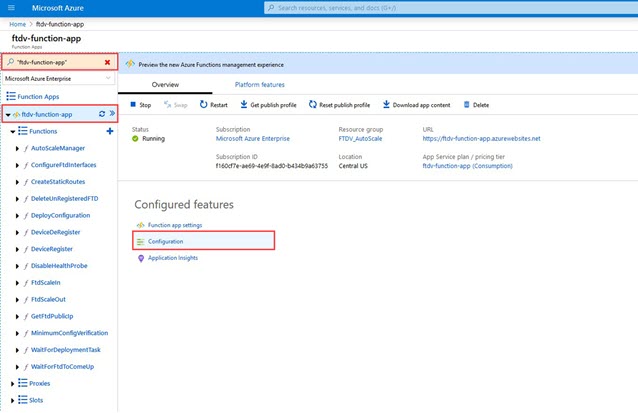
|
||
|
Step 2 |
Configurations passed via the ARM template can also be edited here. Variable names may appear different from the ARM template, but you can easily identify the purpose of these variables from their name. 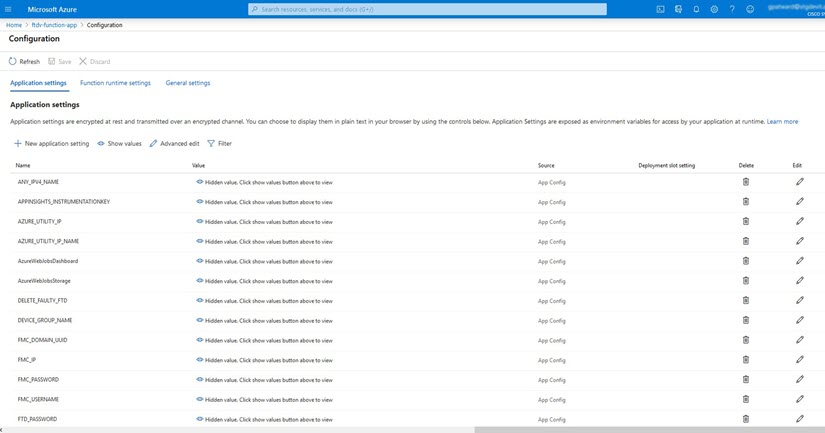
Most of the options are self-explanatory from the name. For example:
|
Configure the IAM Role in the Virtual Machine Scale Set
Azure Identity and Access Management (IAM) is used as a part of Azure Security and Access Control to manage and control a user’s identity. Managed identities for Azure resources provides Azure services with an automatically managed identity in Azure Active Directory.
This allows the Function App to control the Virtual Machine Scale Sets (VMSS) without explicit authentication credentials.
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
In the Azure portal, go to the VMSS. |
||
|
Step 2 |
Click Access control (IAM). |
||
|
Step 3 |
Click Add to add a role assignment |
||
|
Step 4 |
From the Add role assignment drop-down, choose Contributor. |
||
|
Step 5 |
From the Assign access to drop-down, choose Function App. |
||
|
Step 6 |
Select the Firewall Threat Defense Virtual function application. 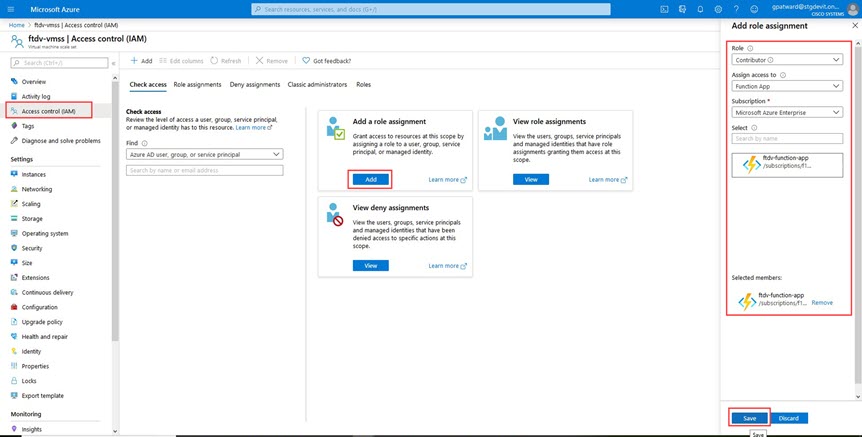
|
||
|
Step 7 |
Click Save.
|
Update Security Groups
The ARM template creates two security groups, one for the Management interface, and one for data interfaces. The Management security group will allow only traffic required for Firewall Threat Defense Virtual management activities. However, the data interface security group will allow all traffic.
Procedure
|
Fine tune the security group rules based on the topology and application needs of your deployments.
|
Update the Azure Logic App
The Logic App acts as the orchestrator for the Autoscale functionality. The ARM template creates a skeleton Logic App, which you then need to update manually to provide the information necessary to function as the auto scale orchestrator.
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
From the repository, retrieve the file LogicApp.txt to the local system and edit as shown below.
|
||||
|
Step 2 |
Go to the Logic App code view, delete the default contents and paste the contents from the edited LogicApp.txt file, and click Save. 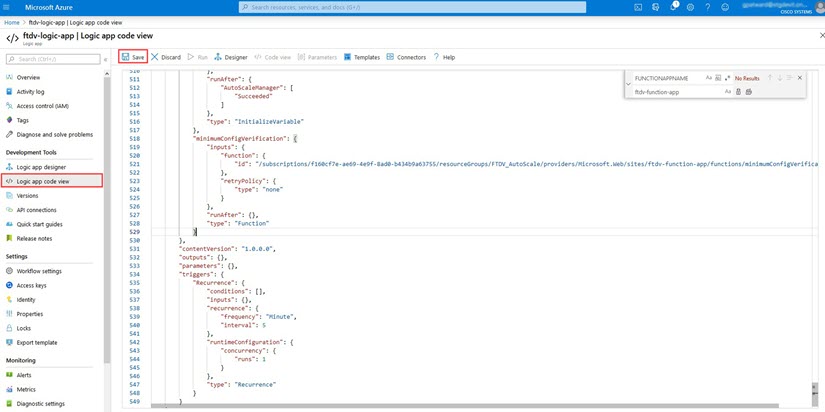
|
||||
|
Step 3 |
When you save the Logic App, it is in a 'Disabled' state. Click Enable when you want to start the Auto Scale Manager. 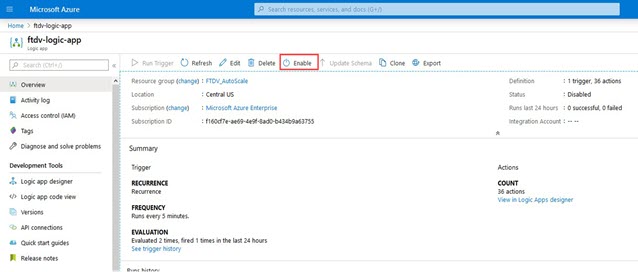
|
||||
|
Step 4 |
Once enabled, the tasks start running. Click the 'Running' status to see the activity. 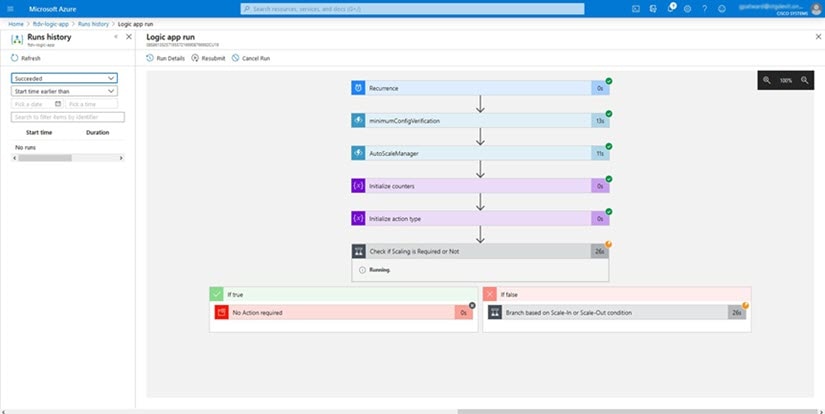
|
||||
|
Step 5 |
Once the Logic App starts, all the deployment-related steps are complete. |
||||
|
Step 6 |
Verify in the VMSS that Firewall Threat Defense Virtual instances are being created. 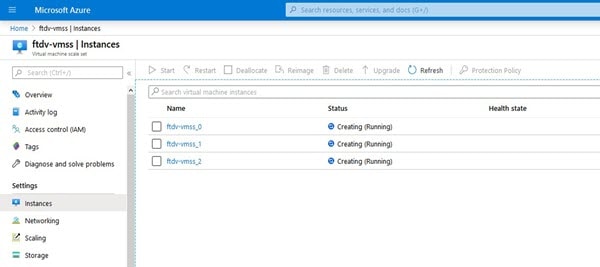
In this example, three Firewall Threat Defense Virtual instances are launched because 'minFtdCount' was set to '3' and 'initDeploymentMode' was set to 'BULK' in the ARM template deployment. |
Upgrade the Firewall Threat Defense Virtual
The Firewall Threat Defense Virtual upgrade is supported only in the form of an image upgrade of virtual machine scale set (VMSS). Hence, you upgrade the Firewall Threat Defense Virtual through the Azure REST API interface.
 Note |
You can use any REST client to upgrade the Firewall Threat Defense Virtual. |
Before you begin
-
Obtain the new Firewall Threat Defense Virtual image version available in market place (example: 650.32.0).
-
Obtain the SKU used to deploy original scale set (example: ftdv-azure-byol ).
-
Obtain the Resource Group and the virtual machine scale set name.
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
In a browser go to the following URL: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/rest/api/compute/virtualmachinescalesets/update#code-try-0 |
|
Step 2 |
Enter the details in the Parameters section. 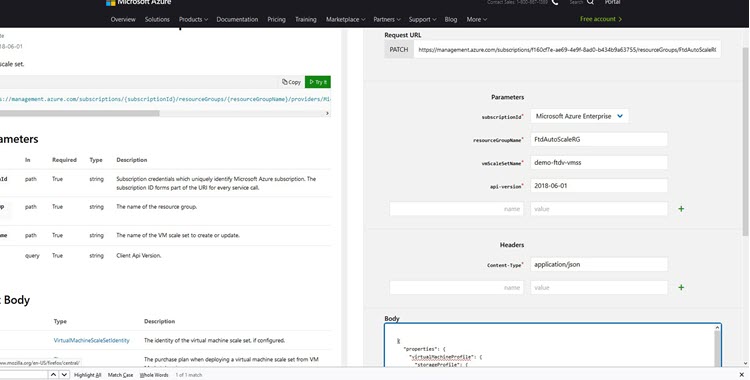
|
|
Step 3 |
Enter the JSON input containing the new Firewall Threat Defense Virtual image version, SKU, and trigger RUN in the Body section. |
|
Step 4 |
A successful response from Azure means that the VMSS has accepted the change. The new image will be used in the new Firewall Threat Defense Virtual instances which will get launched as part of Scale-Out operation.
|
Auto Scale Logic
Scaling Metrics
You use the ARM template to deploy the resources required by the Firewall Threat Defense Virtualauto scale solution. During ARM template deployment, you have the following options for scaling metrics:
-
CPU
-
CPU, Memory (Version 6.7+).

Note
CPU metrics are collected from Azure; memory metrics are collected from the Firewall Management Center.
Scale-Out Logic
-
POLICY-1: Scale-Out will be triggered when the average load of any Firewall Threat Defense Virtual goes beyond the Scale-Out threshold for the configured duration. When using the ‘CPU,MEMORY’ scaling metric, the Scale-Out threshold is the average CPU or memory utilization of any Firewall Threat Defense Virtual in the scale set.
-
POLICY-2: Scale-Out will be triggered when average load of all of the Firewall Threat Defense Virtual devices go beyond Scale-Out threshold for the configured duration. When using the ‘CPU,MEMORY’ scaling metric, the Scale-Out threshold is the average CPU or Memory utilization of all Firewall Threat Defense Virtual devices in the scale set.
Scale-In Logic
-
If the CPU utilization of all of the Firewall Threat Defense Virtual devices goes below the configured Scale-In threshold for the configured duration. When using the ‘CPU,MEMORY’ scaling metric, if the CPU and memory utilization of all Firewall Threat Defense Virtual devices in the scale set goes below the configured Scale-In threshold for the configured duration, the Firewall Threat Defense Virtual with the least loaded CPU will be selected for termination
Notes
-
Scale-In/Scale-Out occurs in steps of 1 (i.e. only 1 Firewall Threat Defense Virtual will be scaled in/out at a time).
-
The memory consumption metric received from the Firewall Management Center is not an average value calculated over time, but rather an instantaneous snapshot/sample value. Therefore, the memory metric alone cannot be considered in making scaling decisions. You do not have the option to use a memory-only metric during deployment.
Auto Scale Logging and Debugging
Each component of the serverless code has its own logging mechanism. In addition, logs are published to application insight.
-
Logs of individual Azure functions can be viewed.
Figure 26. Azure Function Logs 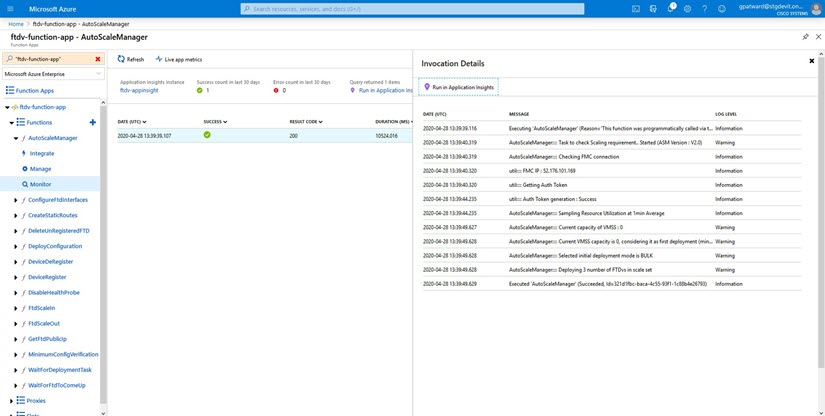
-
Similar logs for each run of the Logic App and its individual components can be viewed.
Figure 27. Logic App Run Logs 
-
If needed, any running task in the Logic App can be stopped/terminated at any time. However, currently running Firewall Threat Defense Virtual devices getting launched/terminated will be in an inconsistent state.
-
The time taken for each run/individual task can be seen in the Logic App.
-
The Function App can be upgraded at any time by uploading a new zip. Stop the Logic App and wait for all tasks to complete before upgrading the Function App.
Auto Scale Guidelines and Limitations
Be aware of the following guidelines and limitations when deploying the Firewall Threat Defense Virtual auto scale for Azure:
-
(Version 6.6 and earlier) Scaling decisions are based on CPU utilization.
-
(Version 6.7+) Scaling decisions can use either CPU-only utilization, or CPU and memory utilization.
-
Firewall Management Center management is required. Firewall Device Manager is not supported.
-
The Firewall Management Center should have a public IP address.
-
The Firewall Threat Defense Virtual Management interface is configured to have public IP address.
-
Only IPv4 is supported.
-
Firewall Threat Defense Virtual auto scale for Azure only supports configurations such as Access policies, NAT policies, Platform Settings, etc. which are applied the Device Group and propagated to scaled-out Firewall Threat Defense Virtual instances. You can only modify Device Group configurations using the Firewall Management Center. Device-specific configurations are not supported.
-
The ARM template has limited input validation capabilities, hence it is your responsibility to provide the correct input validation.
-
The Azure administrator can see sensitive data (such as admin login credentials and passwords) in plain text format inside Function App environment. You can use the Azure Key Vault service to secure sensitive data.
-
Any changes in configuration won’t be automatically reflected on already running instances. Changes will be reflected on upcoming devices only. Any such changes should be manually pushed to already existing devices.
-
If you are facing issues while manually updating the configuration on existing instances, we recommend removing these instances from the Scaling Group and replacing them with new instances.
Troubleshooting
The following are common error scenarios and debugging tips for the Firewall Threat Defense Virtual auto scale for Azure:
-
Connection to the Firewall Management Center failed: Check the Firewall Management Center IP / Credentials; check if the Firewall Management Center is faulty / unreachable.
-
Unable to SSH into the Firewall Threat Defense Virtual: Check if a complex password is passed to the Firewall Threat Defense Virtual via the template; check if Security Groups allow SSH connections.
-
Load Balancer Health check failure: Check if the Firewall Threat Defense Virtual responds to SSH on data interfaces; check Security Group settings.
-
Traffic issues: Check Load Balancer rules, NAT rules / Static routes configured in Firewall Threat Defense Virtual; check Azure virtual network / subnets / gateway details provided in the template and Security Group rules.
-
The Firewall Threat Defense Virtual failed to register with the Firewall Management Center: Check the Firewall Management Center capacity to accommodate new Firewall Threat Defense Virtual devices; check Licensing; check the Firewall Threat Defense Virtual version compatibility.
-
Logic App failed to access VMSS: Check if the IAM role configuration in VMSS is correct.
-
Logic App runs for very long time: Check SSH access on scaled-out Firewall Threat Defense Virtual devices; check any device registration issues in Firewall Management Center; check the state of the Firewall Threat Defense Virtual devices in Azure VMSS.
-
Azure Function throwing error related to subscription ID : Verify that you have a default subscription selected in your account.
-
Failure of Scale-In operation: Sometimes, Azure takes a considerably long time to delete an instance in such situations, Scale-in operation may time out and report an error; but eventually the instance, will get deleted.
-
Before doing any configuration change, make sure to disable the logic application and wait for all the running tasks to complete.
The following are troubleshooting tips if you encounter any issues during Firewall Threat Defense Virtual auto scale with Azure GWLB deployment:
-
Check the ELB-GWLB association.
-
Check the health probe status in the GWLB.
-
Check VXLAN configuration by verifying the traffic flow at the physical and logical interfaces of the Firewall Threat Defense Virtual.
-
Check security group rules.
Build Azure Functions from Source Code
System Requirements
-
Microsoft Windows desktop/laptop.
-
Visual Studio (tested with Visual studio 2019 version 16.1.3)

Note
Azure functions are written using C#.
-
The "Azure Development" workload needs to be installed in Visual Studio.
Build with Visual Studio
-
Download the 'code' folder to the local machine.
-
Navigate to the folder 'FTDAutoScaleManager'.
-
Open the project file 'FTDAutoScaleManager.csproj' in Visual Studio.
-
Use Visual Studio standard procedure to Clean and Build.
Figure 28. Visual Studio Build 
-
Once the build is compiled successfully, navigate to the \bin\Release\netcoreapp2.1 folder.
-
Select all the contents, click , and save the ZIP file as ASM_Function.zip.
Figure 29. Build ASM_Function.zip 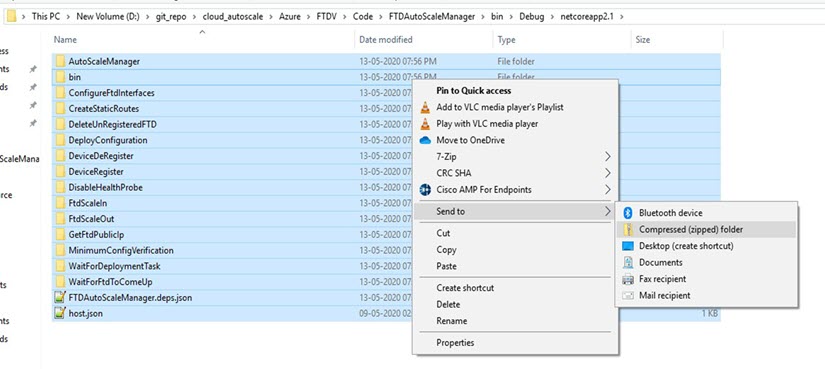
 Feedback
Feedback