Cisco Adaptive Security Virtual Appliance (ASAv) Quick Start Guide, 9.4
偏向のない言語
この製品のドキュメントセットは、偏向のない言語を使用するように配慮されています。このドキュメントセットでの偏向のない言語とは、年齢、障害、性別、人種的アイデンティティ、民族的アイデンティティ、性的指向、社会経済的地位、およびインターセクショナリティに基づく差別を意味しない言語として定義されています。製品ソフトウェアのユーザインターフェイスにハードコードされている言語、RFP のドキュメントに基づいて使用されている言語、または参照されているサードパーティ製品で使用されている言語によりドキュメントに例外が存在する場合があります。シスコのインクルーシブ ランゲージの取り組みの詳細は、こちらをご覧ください。
翻訳について
このドキュメントは、米国シスコ発行ドキュメントの参考和訳です。リンク情報につきましては、日本語版掲載時点で、英語版にアップデートがあり、リンク先のページが移動/変更されている場合がありますことをご了承ください。あくまでも参考和訳となりますので、正式な内容については米国サイトのドキュメントを参照ください。
- Updated:
- 2015年5月12日火曜日
章のタイトル: AWS クラウドへの ASAv の導入
Deploy the ASAv On the AWS Cloud
You can deploy the ASAv on the Amazon Web Sources (AWS) cloud.
- About ASAv Deployment On the AWS Cloud
- Prerequisites for the ASAv and AWS
- Guidelines and Limitations for the ASAv and AWS
- Sample Network Topology for ASAv on AWS
- Deploy the ASAv on AWS
About ASAv Deployment On the AWS Cloud
AWS is a public cloud environment that uses a private Xen Hypervisor. The ASAv runs as a guest in the AWS environment of the Xen Hypervisor. ASAv on AWS supports the following instance types:
Note: Both the ASAv10 and ASAv30 are supported on c3.large, but we do not recommend the ASAv30 on c3.large due to resource under-provisioning.
Note: Only the ASAv30 is supported on c3.xlarge.
Note: The ASAv does not support the Xen Hypervisor outside of the AWS environment.
You create an account on AWS, set up the ASAv using the AWS Wizard, and chose an Amazon Machine Image (AMI). The AMI is a template that contains the software configuration needed to launch your instance.
Note: The AMI images are not available for download outside of the AWS environment.
Prerequisites for the ASAv and AWS
- Create an account on aws.amazon.com.
- License the ASAv. Until you license the ASAv, it will run in degraded mode, which allows only 100 connections and throughput of 100 Kbps. See Smart Software Licensing for the ASAv.
- Interface requirements:
–![]() Inside and outside interfaces
Inside and outside interfaces
–![]() (Optional) Additional subnet (DMZ)
(Optional) Additional subnet (DMZ)
–![]() Management interface—Used to connect the ASAv to the ASDM; can’t be used for through traffic.
Management interface—Used to connect the ASAv to the ASDM; can’t be used for through traffic.
–![]() Inside interface (required)—Used to connect the ASAv to inside hosts.
Inside interface (required)—Used to connect the ASAv to inside hosts.
–![]() Outside interface (required)—Used to connect the ASAv to the public network.
Outside interface (required)—Used to connect the ASAv to the public network.
–![]() DMZ interface (optional)—Used to connect the ASAv to the DMZ network when using the c3.xlarge interface.
DMZ interface (optional)—Used to connect the ASAv to the DMZ network when using the c3.xlarge interface.
- For ASAv system requirements, see Cisco ASA Compatibility.
Guidelines and Limitations for the ASAv and AWS
The ASAv on AWS supports the following features:
- Deployment in the Virtual Private Cloud (VPC)
- Enhanced networking (SR-IOV) where available
- Deployment from Amazon Marketplace
- Maximum of four vCPUs per instance
- User deployment of L3 networks
- Routed mode (default)
The ASAv on AWS does not support the following:
- Console access (management is performed using SSH or ASDM over network interfaces)
- IPv6
- VLAN
- Promiscuous mode (no sniffing or transparent mode firewall support)
- Multi-context mode
- Clustering
- ASAv native HA
- EtherChannel is only supported on direct physical interfaces
- VM import/export
- Amazon Cloudwatch
- Hypervisor agnostic packaging
- VMware ESXi
- Broadcast/multicast messages
These messages are not propagated within AWS so routing protocols that require broadcast/multicast do not function as expected in AWS. VXLAN can operate only with static peers.
These ARPS are not accepted within AWS so NAT configurations that require gratuitous ARPs or unsolicited ARPs do not function as expected.
Sample Network Topology for ASAv on AWS
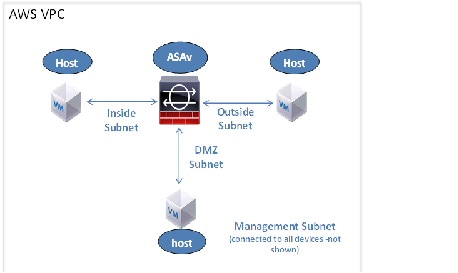
Figure 1 shows the recommended topology for the ASAv in Routed Firewall Mode with four subnets configured in AWS for the ASAv (management, inside, outside, and DMZ).
Figure 1 Sample ASAv on AWS Deployment
Deploy the ASAv on AWS
The following procedure is a top-level list of steps to set up AWS on the ASAv. For detailed steps for setup, see Getting Started with AWS.
1.![]() Log into aws.amazon.com and choose your region.
Log into aws.amazon.com and choose your region.
AWS is divided into multiple regions that are isolated from each other. The region is displayed in the upper right corner of your screen. Resources in one region do not appear in another region. Check periodically to make sure you are in the intended region.
2.![]() Click My Account > AWS Management Console, and under Networking, click VPC > Start VPC Wizard, and create your VPC by choosing a single public subnet, and set up the following (you can use the default settings unless otherwise noted):
Click My Account > AWS Management Console, and under Networking, click VPC > Start VPC Wizard, and create your VPC by choosing a single public subnet, and set up the following (you can use the default settings unless otherwise noted):
–![]() Inside and outside subnet—Enter a name for the VPC and the subnets.
Inside and outside subnet—Enter a name for the VPC and the subnets.
–![]() Internet Gateway—Enables direct connectivity over the Internet (enter the name of the Internet gateway).
Internet Gateway—Enables direct connectivity over the Internet (enter the name of the Internet gateway).
–![]() outside table—Add entry to enable outbound traffic to the Internet (add 0.0.0.0/0 to Internet Gateway).
outside table—Add entry to enable outbound traffic to the Internet (add 0.0.0.0/0 to Internet Gateway).
3.![]() Click My Account > AWS Management Console > EC2, and then click Create an Instance.
Click My Account > AWS Management Console > EC2, and then click Create an Instance.
–![]() Select your AMI (for example Ubuntu Server 14.04 LTS).
Select your AMI (for example Ubuntu Server 14.04 LTS).
Use the AMI identified in the your image delivery notification.
–![]() Choose the instance type supported by the ASAv (for example, c3.large).
Choose the instance type supported by the ASAv (for example, c3.large).
–![]() Configure the instance (CPUs and memory are fixed).
Configure the instance (CPUs and memory are fixed).
–![]() Under Advanced Details, add the Day 0 Configuration if desired. For more information on how to configure the Day 0 configuration with more information, such as Smart Licensing, see Prepare the Day 0 Configuration File.
Under Advanced Details, add the Day 0 Configuration if desired. For more information on how to configure the Day 0 configuration with more information, such as Smart Licensing, see Prepare the Day 0 Configuration File.
–![]() Storage (accept the defaults).
Storage (accept the defaults).
–![]() Tag Instance—You can create a lot of tags to classify your devices. Give it a name you can use to find it easily.
Tag Instance—You can create a lot of tags to classify your devices. Give it a name you can use to find it easily.
–![]() Security Group—Create a security group and name it. The security group is a virtual firewall for an instance to control inbound and outbound traffic.
Security Group—Create a security group and name it. The security group is a virtual firewall for an instance to control inbound and outbound traffic.
By default the Security Group is open to all addresses. Change the rules to only allow SSH in from addresses you will be using to access your ASAv.
–![]() Review your configuration and then click Launch.
Review your configuration and then click Launch.
Give the key pair a name you will recognize and download the key to a safe place; the key can never be downloaded again. If you lose the key pair, you must destroy your instances and redeploy them again.
5.![]() Click Launch Instance to deploy your ASAv.
Click Launch Instance to deploy your ASAv.
6.![]() Click My Account > AWS Management Console > EC2 > Launch an Instance > My AMIs.
Click My Account > AWS Management Console > EC2 > Launch an Instance > My AMIs.
7.![]() Make sure that the Source/Destination Check is disabled per interface for the ASAv.
Make sure that the Source/Destination Check is disabled per interface for the ASAv.
AWS default settings only allow an instance to receive traffic for its IP address and only allow an instance to send traffic from its own IP address. To enable the ASAv to act as a routed hop, you must disable the Source/Destination Check on each of the ASAv's traffic interfaces (inside, outside, and DMZ).
 フィードバック
フィードバック