VMware ESXi Support Information
This chapter contains information about VMware tools/software and the VM requirements for Cisco CSR 1000v / Cisco IOS XE software.
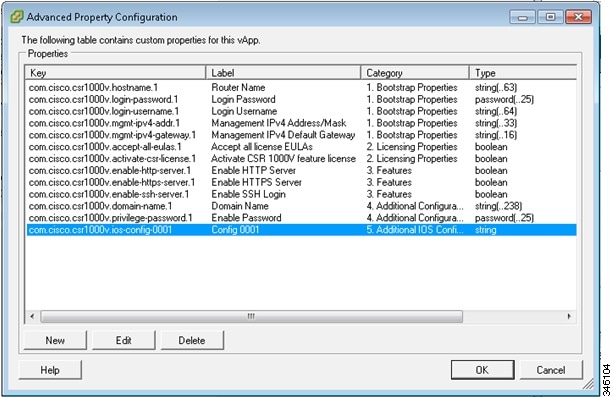
The Cisco CSR 1000v can run on the VMware ESXi hypervisor. VMware ESXi runs on PCs with x86-based CPUs. You can use the same hypervisor to run several VMs.
VMware vSphere Web Client is a web application that runs on a PC and accesses VMware vCenter Server. You can use VMware vSphere Web Client software to create, configure, and manage VMs on the vCenter Server and to start/stop the Cisco CSR 1000v. The Cisco CSR 1000v boots from a virtual disk located on the data store.
 Note |
If you upgrade VMware ESXi, and ESXi contains an existing Cisco CSR 1000v, the interfaces of the CSR 1000v may be renamed. For example, GigabitEthernet1 may appear as GigabitEthernet4. To recover the original interface names, perform the following two Cisco IOS XE configuration commands from the console or terminal of the CSR 1000v, immediately after upgrading the VMware ESXi hypervisor: clear platform software vnic nvtable reload |
 Caution |
Oversubscription of host resources can lead to a reduction of performance and your instance could become instable. We recommend that you follow the guidelines and the best practices for your host hypervisor |
 Note |
Only ESXi hypervisor supports the FIPS mode. Ensure that you have configured the virtual machine properly to allow entropy gathering when in FIPS mode. Failing to configure ESXi properly or using another hypervisor results in the device crashing. This is applicable only for CSR 1000v release 16.9.x. The 16.10 image and later allows entropy when you use any supported hypervisor. |
To find out more about installing VMware vSphere products, see VMware product documentation .


 Feedback
Feedback