Congestion Avoidance
Congestion avoidance is a traffic management technique that
-
helps prevent buffer overflows in network queues by managing packet drops before queues reach full capacity
-
monitors queue thresholds, and
-
triggers early drops of lower-priority packets to maintain the availability of buffer memory.
Queueing for congestion avoidance
Queuing for congestion avoidance manages queue buffers to prevent memory overflow in the ASIC or NPU. When queues fill beyond set thresholds, low-priority packets are dropped early to preserve memory for critical traffic and maintain overall system performance.
Shaping and scheduling context
-
Shaping buffers packets within a queue to smooth bursty traffic and control the transmission rate.
-
Scheduling moves packets out of queues based on priority and available bandwidth, ensuring traffic flow continuity.
|
Feature Name |
Release Information |
Feature Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Queueing for Congestion Avoidance |
Release 25.1.1 |
Introduced in this release on: Fixed Systems (8010 [ASIC: A100])(select variants only*) *This feature is now supported on Cisco 8011-4G24Y4H-I routers. |
|
Queueing for Congestion Avoidance |
Release 24.4.1 |
Introduced in this release on: Fixed Systems (8700) (select variants only*) You can shape traffic to control the traffic flow from queues and also configure queues to ensure certain traffic classes get a guaranteed amount of bandwidth. *This functionality is now supported on Cisco 8712-MOD-M routers. |
|
Queueing for Congestion Avoidance |
Release 24.3.1 |
Introduced in this release on: Modular Systems (8800 [LC ASIC: P100]) (select variants only*), Fixed Systems (8200) (select variants only*), Fixed Systems (8700 (P100, K100)) (select variants only*) , You can shape traffic to control the traffic flow from queues and also configure queues to ensure certain traffic classes get a guaranteed amount of bandwidth. *This feature is supported on:
|
|
Queueing for Congestion Avoidance |
Release 24.2.11 |
Introduced in this release on: Modular Systems (8800 [LC ASIC: P100]) (select variants only*) By placing packets in different queues based on priority, queueing helps prevent traffic congestion and ensures that high-priority traffic is transmitted with minimal delay. You can shape traffic to control the traffic flow from queues and also configure queues to ensure certain traffic classes get a guaranteed amount of bandwidth. Queueing provides buffers to temporarily store packets during bursts of traffic and also supports strategies that enable dropping lower-priority packets when congestion builds up. *This feature is supported on 88-LC1-36EH. |

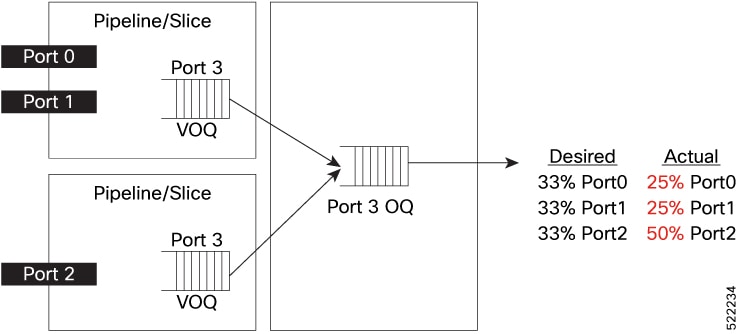
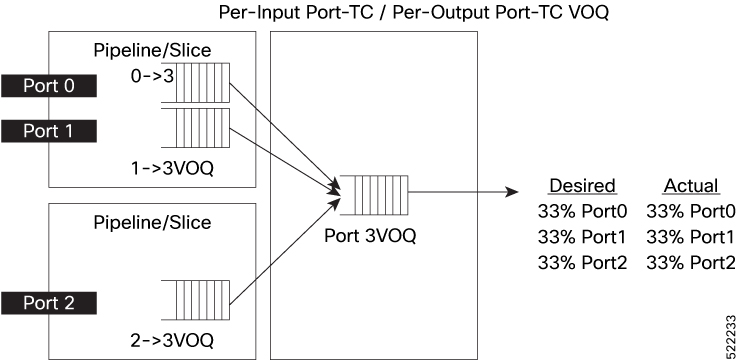
 Feedback
Feedback