- Overview of the Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway
- IP Sessions Over Gigabit EtherChannel
- Multiple-Flow Tunnel
- Service Provider WiFi: Support for Integrated Ethernet Over GRE
- GTPv2 Support in the iWAG
- iWAG SSO Support for GTP
- Configuring ISG Policy Templates
- Cisco ISG Accounting Accuracy for LNS Sessions
- Call Admission Control
- iWAG Dual-Stack IPoE Session
- Flow-Based Redirect
- Web Authentication Support for iWAG-GTP
- QoS on Ethernet over GRE Tunnels
- PMIP MAG SSO
- iWAG-GTP: S2a Interface Support and High Availability Enhancements
- DHCP Option 82 Remote ID Format
- VLAN ID Based Policy Control
- EoGRE iWAG Subscriber Roaming
- EoGRE: Inter-chassis HA
- Call Flows for Simple IP Users
- Call Flows for 3G and 4G Mobile IP Users
- iWAG Scalability and Performance
- Finding Feature Information
- Information About Ethernet Over GRE
- Restrictions for Configuring Ethernet Over GRE
- Prerequisites for Configuring Ethernet Over GRE
- Information About Configuring Ethernet Over GRE
- Supported Features
- How to Configure the EoGRE Feature
- Example: Configuring the EoGRE Feature
- Additional References
- Feature Information for Configuring Ethernet Over GRE
Service Provider WiFi: Support for Integrated Ethernet Over GRE
Generic Routing Encapsulation (GRE) is a tunneling protocol that encapsulates a wide variety of network layer protocols inside virtual point-to-point links over a Layer 3 IPv4 or Layer 3 IPv6 access network.
- Finding Feature Information
- Information About Ethernet Over GRE
- Restrictions for Configuring Ethernet Over GRE
- Prerequisites for Configuring Ethernet Over GRE
- Information About Configuring Ethernet Over GRE
- Supported Features
- How to Configure the EoGRE Feature
- Example: Configuring the EoGRE Feature
- Additional References
- Feature Information for Configuring Ethernet Over GRE
Finding Feature Information
Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest caveats and feature information, see Bug Search Tool and the release notes for your platform and software release. To find information about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each feature is supported, see the feature information table at the end of this module.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Information About Ethernet Over GRE
Ethernet over GRE (EoGRE) is a new aggregation solution for aggregating WiFi traffic from hotspots. This solution enables customer premises equipment (CPE) devices to bridge the Ethernet traffic coming from an end host, and encapsulate the traffic in Ethernet packets over an IP GRE tunnel. When the IP GRE tunnels are terminated on a service provider broadband network gateway, the end host’s traffic is terminated and subscriber sessions are initiated for the end host.
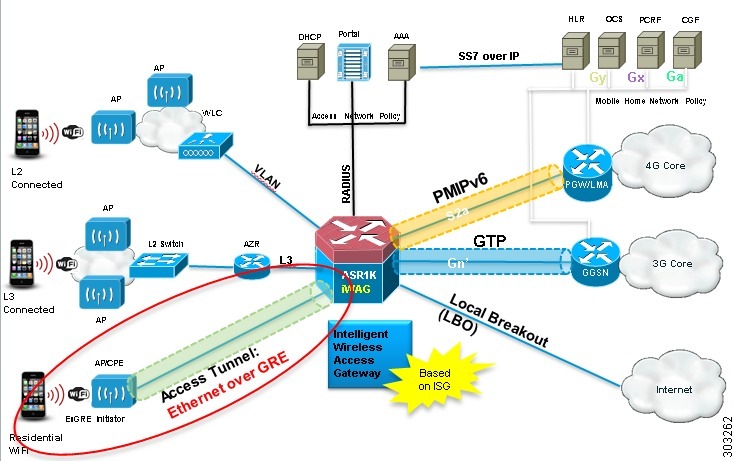
The following figure shows the structure of the Ethernet over GRE.
Restrictions for Configuring Ethernet Over GRE
The following features are not supported on the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers:
- IPsec tunnel between the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers and the CPE devices
- Native multicast coexistence for subscribers
- Per-CPE QoS
- IPv6 subscriber
- The Cisco Intelligent Services Gateway (ISG) RADIUS proxy initiator
- QinQ tag for the inner L2 frame
- High Availability is not supported if ISG is not configured.
- If the VLAN priority tag inside the EoGRE packet is set to a nonzero value, iWAG ignores the packet
Prerequisites for Configuring Ethernet Over GRE
Before you configure the Ethernet over GRE feature on the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers, ensure that the following prerequisites are met:
Information About Configuring Ethernet Over GRE
The Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers serve as a service provider broadband network gateway that:
The EoGRE feature works with legacy residential gateways and CPE devices to terminate the Ethernet L2 traffic in the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers. When configured as an intelligent Wireless Access Gateway (iWAG) with EoGRE access tunneling support, the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers can extend mobility and the ISG services in support of these legacy devices.
The following figure shows the structure of the EoGRE feature with PMIP/GTP integrated for mobility service.

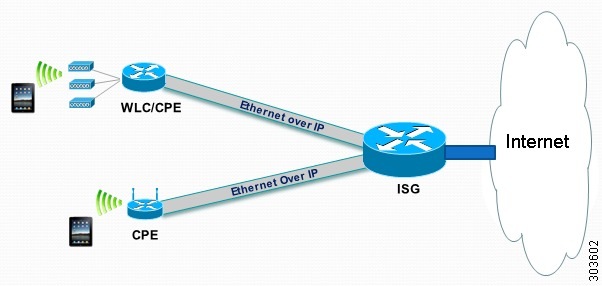
The following figure shows the structure of the EoGRE feature for simple IP service.

The EoGRE feature supports the following deployments:
- EoGRE Deployment with PMIPv6 Integrated for Mobility Service
- EoGRE Deployment with GTP Integrated for Mobility Service
- EoGRE Deployment with ISG Integrated for Simple IP Service
EoGRE Deployment with PMIPv6 Integrated for Mobility Service
Proxy Mobile IPv6 (PMIPv6) provides mobility service to the mobile nodes that are connected to the Mobile Access Gateway (MAG) via an EoGRE tunnel. The following figure shows the structure of the EoGRE deployment with PMIPv6 integrated for mobility service.

Mobile nodes access the mobile internet service over Wi-Fi access points. The access points are either autonomous access points or are connected to the Cisco Wireless LAN Controller (WLC). These access points and WLCs are used as residential gateways or CPE devices. CPEs are preconfigured with a point-to-multipoint GRE IP tunnel to the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers as the MAG. The tunnel from the CPE device can be configured with a static GRE key. The CPEs are provisioned to forward the Ethernet traffic from both public and private customers to the GRE tunnel, and to add a VLAN tag on the Ethernet frame before forwarding the traffic.
As with regular PMIPv6 deployments, the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers can create IP sessions on EoGRE access tunnels similar to the regular IP sessions on the physical Ethernet interfaces, and allocate IP addresses for mobile nodes, either locally or in the proxy mode. Mobility service is provided to the mobile nodes and the tunneled Ethernet traffic is forwarded via IP tunnels to the Local Mobility Anchor (LMA).
 Note | When you ping a mobile node from the MAG with a packet size that is larger than that of the path maximum transmission unit (PMTU) that is configured with the DF bit set, the packet will be dropped. However, you will not get the return type as M.M.M (could not fragment). This is reflected in the log messages or error messages. |
For more information about PMIPv6 and the ISG configurations for the iWAG, see the Intelligent Wireless Gateway Configuration Guide.
EoGRE Deployment with GTP Integrated for Mobility Service
GPRS Tunneling Protocol (GTP) provides mobility service to the mobile nodes that are connected to the iWAG via an EoGRE tunnel, as shown in the following figure.

For more information about the GTP and ISG configurations for the iWAG, see the Intelligent Wireless Gateway Configuration Guide.
EoGRE Deployment with ISG Integrated for Simple IP Service
The ISG provides simple IP service to mobile nodes that are connected to ISG via the EoGRE tunnel, as shown in the following figure. The Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers use the ISG framework to allocate IP sessions for authenticated subscribers. Simple IP subscribers are provided ISG services, including Internet access, but are not provided access to mobility services via GTP or PMIPv6.
Supported Features
The following features are supported as part of the EoGRE feature on the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers:
How to Configure the EoGRE Feature
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
interface interface-name
4.
ip unnumbered loopback
interface-name or
ip address ip-address
5.
tunnel source
interface-type interface-number
6. (For simple IP mode) mac-address H.H.H
7. tunnel mode ethernet gre ipv4 or tunnel mode ethernet gre ipv6
8. (Optional) tunnel vlan vlan-id
9. end
DETAILED STEPS
Example: Configuring the EoGRE Feature
aaa new-model ! aaa group server radius AAA_SERVER_CAR server-private 5.3.1.76 auth-port 2145 acct-port 2146 key cisco ! aaa authentication login default none aaa authentication login ISG_PROXY_LIST group AAA_SERVER_CAR aaa authorization network ISG_PROXY_LIST group AAA_SERVER_CAR aaa authorization subscriber-service default local group AAA_SERVER_CAR aaa accounting network PROXY_TO_CAR action-type start-stop group AAA_SERVER_CAR ! aaa accounting network ISG_PROXY_LIST start-stop group AAA_SERVER_CAR ! aaa server radius dynamic-author client 5.3.1.76 server-key cisco auth-type any ignore server-key ! ! ip dhcp excluded-address 172.16.254.254 ! ip dhcp pool ISG_SIMPLE_IP network 172.16.0.0 255.255.0.0 default-router 172.16.254.254 domain-name cisco.com ! policy-map type control EOGRE_L2_ISG class type control always event session-start 2 authorize aaa list ISG_PROXY_LIST password cisco identifier mac-address 4 set-timer IP_UNAUTH_TIMER 5 ! class type control always event service-start 1 service-policy type service identifier service-name 2 collect identifier nas-port ! ! interface Loopback0 ip address 9.9.9.9 255.255.255.255 interface GigabitEthernet1/0/0 ip address 192.168.0.9 255.255.255.0 negotiation auto ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/0.778 description "to ASR5K GGSN" encapsulation dot1Q 778 ip address 172.16.199.9 255.255.255.0 ! interface Tunnel10 description "EoGRE Tunnel for Simple IP subscribers" mac-address 0000.5e00.5213 ip address 172.16.254.254 255.255.0.0 no ip redirects tunnel source 172.16.199.9 tunnel mode ethernet gre ipv4 service-policy type control EOGRE_L2_ISG ip subscriber l2-connected initiator unclassified mac-address initiator dhcp interface Tunnel100 description "IPv4 EoGRE Tunnel for PMIP/GTP subscribers" ip unnumbered Loopback0 tunnel source GigabitEthernet1/0/0 tunnel mode ethernet gre ipv4 tunnel vlan 100 service-policy type control EOGRE_L2_ISG ip subscriber l2-connected initiator unclassified mac-address initiator dhcp ! interface Tunnel200 description "IPv6 EoGRE Tunnel for PMIP/GTP subscribers" ip unnumbered Loopback0 tunnel source 2001:161::9 tunnel mode ethernet gre ipv6 tunnel vlan 200 service-policy type control EOGRE_L2_ISG ip subscriber l2-connected initiator unclassified mac-address initiator dhcp ! mcsa enable sessionmgr ! ipv6 mobile pmipv6-domain D1 replay-protection timestamp window 255 lma LMA_5K ipv4-address 192.168.199.1 ! ipv6 mobile pmipv6-mag M1 domain D1 sessionmgr role 3GPP address ipv4 9.9.9.9 interface Tunnel100 interface Tunnel200 lma LMA_5K D1 ipv4-address 192.168.199.1 encap gre-ipv4 ! ntp master ! gtp information-element rat-type wlan interface local GigabitEthernet1/0/0.778 apn 1 apn-name gtp.com ip address ggsn 172.16.199.1 fixed link-layer address 00ab.00cd.00ef default-gw 20.100.254.254 prefix-len 16 dns-server 20.100.254.254 dhcp-server 20.100.254.254 ! end
show ip dhcp sip statistics show subscriber statistics show subscriber session show ipv6 mobile pmipv6 mag binding show gtp pdp-context all show interface tunnel-name
Additional References
Related Documents
|
Related Topic |
Document Title |
|---|---|
|
Cisco IOS commands |
|
|
iWAG commands |
Cisco IOS Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Command Reference |
MIBs
|
MIB |
MIBs Link |
|---|---|
|
No new or modified MIBs are supported by this feature. |
To locate and download MIBs for selected platforms, Cisco software releases, and feature sets, use Cisco MIB Locator found at the following URL: |
Technical Assistance
|
Description |
Link |
|---|---|
|
The Cisco Support website provides extensive online resources, including documentation and tools for troubleshooting and resolving technical issues with Cisco products and technologies. To receive security and technical information about your products, you can subscribe to various services, such as the Product Alert Tool (accessed from Field Notices), the Cisco Technical Services Newsletter, and Really Simple Syndication (RSS) Feeds. Access to most tools on the Cisco Support website requires a Cisco.com user ID and password. |
Feature Information for Configuring Ethernet Over GRE
The following table provides release information about the feature or features described in this module. This table lists only the software release that introduced support for a given feature in a given software release train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that software release train also support that feature.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.| Feature Name | Releases | Feature Information |
|---|---|---|
|
Service Provider WiFi: Integrated Ethernet Over GRE |
3.9.1S |
This feature enables the Ethernet over Generic Routing Encapsulation (EoGRE) tunnel to be used as a service provider WiFi access interface from CPE devices. A Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Router is used as an L2 aggregator to terminate L2 traffic at the GRE tunnel interface and provide L3 services. In Cisco IOS XE Release 3.9.1S, this feature is implemented on the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers. The following sections provide information about this feature: |
 Feedback
Feedback