- Overview of the Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway
- IP Sessions Over Gigabit EtherChannel
- Multiple-Flow Tunnel
- Service Provider WiFi: Support for Integrated Ethernet Over GRE
- GTPv2 Support in the iWAG
- iWAG SSO Support for GTP
- Configuring ISG Policy Templates
- Cisco ISG Accounting Accuracy for LNS Sessions
- Call Admission Control
- iWAG Dual-Stack IPoE Session
- Flow-Based Redirect
- Web Authentication Support for iWAG-GTP
- QoS on Ethernet over GRE Tunnels
- PMIP MAG SSO
- iWAG-GTP: S2a Interface Support and High Availability Enhancements
- DHCP Option 82 Remote ID Format
- VLAN ID Based Policy Control
- EoGRE iWAG Subscriber Roaming
- EoGRE: Inter-chassis HA
- Call Flows for Simple IP Users
- Call Flows for 3G and 4G Mobile IP Users
- iWAG Scalability and Performance
Call Flows for Simple IP Users
This chapter provides various call flows for simple IP users.
- Finding Feature Information
- Simple IP Unclassified MAC Authentication (MAC TAL and Web Login) Call Flows
Finding Feature Information
Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest caveats and feature information, see Bug Search Tool and the release notes for your platform and software release. To find information about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each feature is supported, see the feature information table at the end of this module.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Simple IP Unclassified MAC Authentication (MAC TAL and Web Login) Call Flows
The MAC Transparent Auto Login (TAL) authentication method is associated with the web authentication method and is prevalent in public access control as used in public wireless LAN (PWLAN) applications or in limited usage as in broadband residential access. Here, many sessions are aggregated on a single VLAN or interface at the broadband remote access server (BRAS), and individual sessions are identified based on the source MAC address for the Layer 2 access subscriber.
MAC TAL enables the iWAG to authorize a subscriber on the basis of the subscriber’s source MAC address. After authentication, the iWAG applies the auto-login services on the session and the subscriber will be able to access the service. If the initial authorization based on the MAC address fails, then the iWAG subscriber is redirected to the ISP’s web portal, where the subscriber enters the ISP-assigned credentials (username and password) to complete the authentication in order to avail the ISP’s services. The iWAG then applies the services that the subscriber selected from the portal, and provides the subscriber full access to those services.
This use case covers the following:
iWAG session creation
User authorization based on MAC address
Default service activation (Internet)
Auto-login service activation and access
User redirection to the portal (on user authorization failure only)
User authentication at the RADIUS server
Profile download and auto-login service activation
Access to features such as change of authorization (CoA), account logout, account stop, account ping
- Simple IP Unclassified MAC with MAC TAL Authentication Call Flow
- Simple IP Unclassified MAC with Web Login Authentication Call Flow
- Simple IP Unclassified MAC Authentication Call Flow Configuration
- Additional References
- Feature Information for Call Flows for Simple IP Users
Simple IP Unclassified MAC with MAC TAL Authentication Call Flow
The following figure illustrates the unclassified MAC with MAC TAL authentication call flow for a simple IP user.
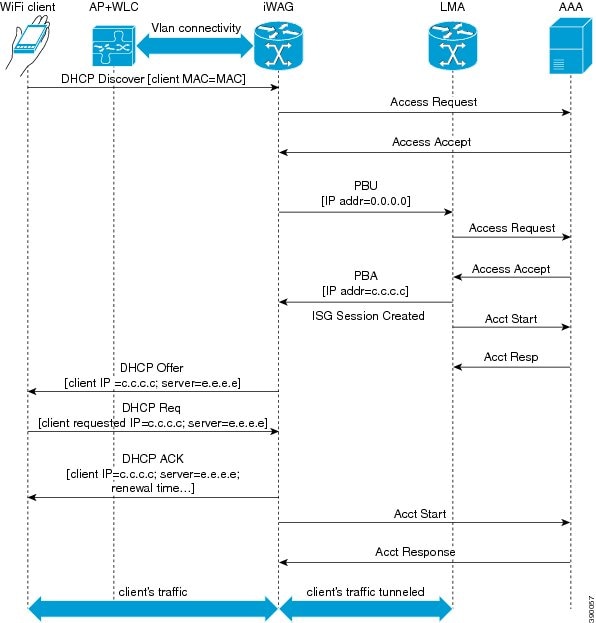
The following steps describe the call flow for a successful MAC TAL Web authorization for a simple IP subscriber:
The subscriber initiates IP traffic to get connected to the Internet service. ISG notices a new subscriber address and creates an unauthenticated subscriber session.
ISG then sends an authorization request to the RADIUS server with the subscriber’s MAC address as the username.
If the authorization is successful, the default Internet services are applied to the subscriber for the session.
The defined services are applied to the subscriber’s session and the subscriber can start accessing the Internet.
The subscriber now has full access to the network.
An Accounting Start message is sent to the application provider to indicate the start of the subscriber’s service. The subscriber can now access the Internet services applicable as part of the subscription.
Simple IP Unclassified MAC with Web Login Authentication Call Flow
The following figure illustrates the unclassified MAC with web login authentication MAC TAL call flow for a simple IP user.
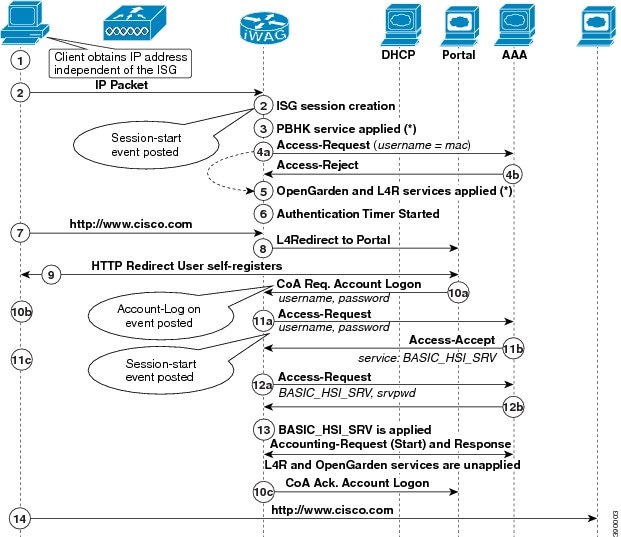
The following steps describe the call flow for a successful MAC TAL Web authorization for a simple IP subscriber:
The subscriber initiates IP traffic to get connected to the Internet service. ISG notices a new subscriber address and creates an unauthenticated subscriber session.
ISG then sends an authorization request to the RADIUS server with the subscriber’s MAC address as the username.
If the authorization fails, services such as OpenGarden and Layer 4 Redirect (L4R) are applied to the subscriber for a temporary period of time.
ISG then redirects the subscriber to the portal where the subscriber enters the username and password. The subscriber’s credentials are then sent to the ISG through the account login message.
ISG now authenticates the subscriber on the AAA server and retrieves the subscriber’s profile, which may contain a few preconfigured auto-login services.
On successful authentication, ISG enables the user’s auto-login services (Internet).
Assuming that the services for accessing the Internet are not cached on ISG prior to this session, ISG sends an access request to the corresponding service provider’s AAA server to download the service definition.
The AAA server responds with the service definition.
The defined service is applied to the subscriber’s session and the subscriber can start accessing the Internet. The subscriber now has full access to the network.
On successful account login, the L4R feature is unapplied for the subscriber in ISG to prevent subscriber traffic redirection to the ISP’s web portal.
An Accounting Start message is sent to the application provider to indicate the start of the subscriber’s service. Now, the subscriber is connected to the Internet.
Simple IP Unclassified MAC Authentication Call Flow Configuration
The following configuration is an example of a simple IP unclassified MAC call flow. This is applicable to both the MAC TAL and web logon authentication scenarios:
#---------------------------------------------- # AAA and RADIUS #---------------------------------------------- aaa new-model ! aaa server radius dynamic-author client 5.5.5.1 server-key cisco ! aaa group server radius SERVER_GROUP1 server name RAD1 ! aaa authentication login AUTHEN_LIST group SERVER_GROUP1 aaa authorization network default group SERVER_GROUP1 local aaa authorization network AUTHOR_LIST group SERVER_GROUP1 local aaa authorization subscriber-service default local group SERVER_GROUP1 aaa accounting network List1 start-stop group SERVER_GROUP1 aaa accounting system default start-stop group radius ! radius-server key cisco ! radius server RAD1 address ipv4 4.4.4.1 auth-port 1645 acct-port 1646 #---------------------------------------------- # Interface #---------------------------------------------- interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2.10 #Connected to the client, access interface. encapsulation dot1Q 10 ip address 11.11.11.1 255.255.255.0 service-policy type control TAL ip subscriber l2-connected initiator unclassified mac-address ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0/3 #Connected to the RADIUS server ip address 4.4.4.2 255.255.255.0 ip portbundle outside ! interface GigabitEthernet 0/0/4 #Connected to the Web portal ip address 5.5.5.2 255.255.255.0 ip portbundle outside ! interface Loopback0 #Loopback interface for PBHK service ip address 15.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 ! #---------------------------------------------- # Port Bundle Configurations #---------------------------------------------- ! ip portbundle length 5 source Loopback0 #---------------------------------------------- # Service Definitions #---------------------------------------------- policy-map type service OPENGARDEN_SERVICE 20 class type traffic ISG_OPENGARDEN ! policy-map type service L4REDIRECT_SERVICE 10 class type traffic L4REDIRECT redirect to group ISG_GROUP accounting aaa list IP_SESSION ! class type traffic default input drop policy-map type service PBHK_SERVICE ip portbundle ! #---------------------------------------------- # Traffic Class Definitions #---------------------------------------------- class-map type traffic match-any ISG_OPENGARDEN match access-group output name ACL_OUT_OPENGARDEN match access-group input name ACL_IN_OPENGARDEN class-map type traffic match-any L4REDIRECT match access-group input name ACL_IN_L4REDIRECT class-map type control match-all IP_UNAUTH_COND match timer IP_UNAUTH_TIMER match authen-status unauthenticated #---------------------------------------------- # Redirect Group Definition #---------------------------------------------- redirect server-group ISG_GROUP server ip 10.10.33.166 port 80 #---------------------------------------------- # Policy Map #---------------------------------------------- policy-map type control TAL class type control always event session-start 10 service-policy type service name PBHK_SERVICE 20 authorize aaa list AUTHOR_LIST password cisco123 identifier mac-address 30 service-policy type service name L4REDIRECT_SERVICE 40 service-policy type service name OPENGARDEN_SERVICE 50 set-timer IP_UNAUTH_TIMER 10 ! class type control always event account-logon 10 authenticate aaa list IP_AUTHEN_LIST 20 service-policy type service unapply name OPENGARDEN_SERVICE 30 service-policy type service unapply name L4REDIRECT_SERVICE ! class type control UNAUTHEN_COND event timed-policy-expiry 10 service disconnect ! #---------------------------------------------- # ACL #---------------------------------------------- ip access-list extended ACL_IN_OPENGARDEN … permit ip any host 10.10.33.166 … ip access-list extended ACL_OUT_OPENGARDEN … permit ip host 10.10.33.166 any …. ip access-list extended ACL_IN_L4REDIRECT … deny tcp any host 10.10.33.166 permit tcp any any eq www permit tcp any any eq 443 ….
Additional References
Related Documents
|
Related Topic |
Document Title |
|---|---|
|
Cisco IOS commands |
|
|
iWAG commands |
Cisco IOS Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Command Reference |
MIBs
|
MIB |
MIBs Link |
|---|---|
|
No new or modified MIBs are supported by this feature. |
To locate and download MIBs for selected platforms, Cisco software releases, and feature sets, use Cisco MIB Locator found at the following URL: |
Technical Assistance
|
Description |
Link |
|---|---|
|
The Cisco Support website provides extensive online resources, including documentation and tools for troubleshooting and resolving technical issues with Cisco products and technologies. To receive security and technical information about your products, you can subscribe to various services, such as the Product Alert Tool (accessed from Field Notices), the Cisco Technical Services Newsletter, and Really Simple Syndication (RSS) Feeds. Access to most tools on the Cisco Support website requires a Cisco.com user ID and password. |
Feature Information for Call Flows for Simple IP Users
The following table provides release information about the feature or features described in this module. This table lists only the software release that introduced support for a given feature in a given software release train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that software release train also support that feature.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.|
Feature Name |
Releases |
Feature Information |
|---|---|---|
|
Call Flows for Simple IP Users |
Cisco IOS XE Release 3.11 |
In Cisco IOS XE Release 3.11S, this feature was implemented on the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers. |
 Feedback
Feedback