- Overview of the Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway
- IP Sessions Over Gigabit EtherChannel
- Multiple-Flow Tunnel
- Service Provider WiFi: Support for Integrated Ethernet Over GRE
- GTPv2 Support in the iWAG
- iWAG SSO Support for GTP
- Configuring ISG Policy Templates
- Cisco ISG Accounting Accuracy for LNS Sessions
- Call Admission Control
- iWAG Dual-Stack IPoE Session
- Flow-Based Redirect
- Web Authentication Support for iWAG-GTP
- QoS on Ethernet over GRE Tunnels
- PMIP MAG SSO
- iWAG-GTP: S2a Interface Support and High Availability Enhancements
- DHCP Option 82 Remote ID Format
- VLAN ID Based Policy Control
- EoGRE iWAG Subscriber Roaming
- EoGRE: Inter-chassis HA
- Call Flows for Simple IP Users
- Call Flows for 3G and 4G Mobile IP Users
- iWAG Scalability and Performance
- Finding Feature Information
- Restrictions for the iWAG Dual-Stack IPoE Session
- IPoE Dual-Stack Features
- Information About Dual Stack Support for Simple IP Subscriber Sessions
- Dual-Stack Support for Simple IP Subscriber Sessions
- Dual-Stack Simple IPoE Session with MAC TAL Call Flow
- Dual-Stack Simple IPoE Session with Web Logon Call Flow
- How to Configure Dual-Stack Support for Simple IP Subscriber Sessions
- Configuration Examples for Dual-Stack Support for Simple IP Subscriber Sessions
iWAG Dual-Stack
IPoE Session
Effective from Cisco IOS XE Release 3.11S, the Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway (iWAG) supports dual-stack session for Proxy Mobile IPv6 (PMIPv6), GPRS Tunneling Protocol (GTP) and Intelligent Services Gateway (ISG). With dual-stack, both IPv4 and IPv6 are simultaneously supported within a single IPoE session. For a dual-stack client device connecting to the iWAG over layer 2 network, a MAC-based session is established on receiving any FSOL. Based on the subscriber profile, IPv4 and IPv6 services are provisioned and activated when respective FSOL is received.
The following figure shows a deployment model of the iWAG Dual-Stack on a Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Router.
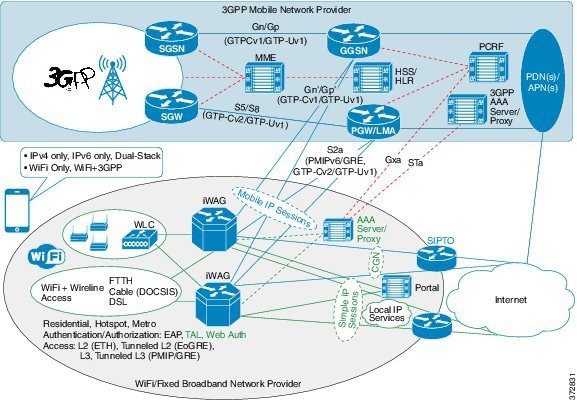
A session can be simple IPoE or mobile IPoE but the iWAG is the first-hop gateway/router for both IPv4 and IPv6.
For simple IPoE session, the iWAG provides the network connectivity and traffic is routed directly. IPv4 address and IPv6 /64 prefix are allocated locally by the iWAG and assigned to the client through DHCPv4 and IPv6 SLAAC. All the IPv4 and IPv6 features and services for simple IPoE session are handled by the iWAG.
For mobile IPoE session, mobile packet core provides the network connectivity over a tunnel established between the iWAG and the respective mobile packet core gateway. The tunnel is established between the iWAG and the packet core gateway when the session is established, and both IPv4 and IPv6 traffic is routed through the tunnel.
Mobility protocol used for establishing the tunnel and the tunnel type depends on the packet core gateway. The following mobility protocols and tunnel types are available:
-
PMIPv6 for GRE tunnel between iWAG and LMA
-
GTPv1 for GTP-U tunnel between iWAG and GGSN
-
GTPv2 for GTP-U tunnel between iWAG and PGW
The IPv4 address and IPv6/64 prefix for the session are allocated by mobile packet core and passed to the iWAG through mobility protocol, which in turn assigns to client through DHCPv4 and IPv6 Stateless Address Auto Configuration (SLAAC). Only applicable IPv4 and IPv6 features and services for mobile IPoE session are handled by iWAG and the rest by mobile packet core gateway.
This chapter contains the following sections:
- Finding Feature Information
- Restrictions for the iWAG Dual-Stack IPoE Session
- IPoE Dual-Stack Features
- Information About Dual Stack Support for Simple IP Subscriber Sessions
- Information About Dual-Stack Support for PMIPv6
- Information About Dual-Stack Support for GTP
- AAA Attributes for Dual Stack
- Additional References
- Feature Information for iWAG Dual-Stack IPoE Session
Finding Feature Information
Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest caveats and feature information, see Bug Search Tool and the release notes for your platform and software release. To find information about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each feature is supported, see the feature information table at the end of this module.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Restrictions for the iWAG Dual-Stack IPoE Session
Dual Stack is not supported on EoGRE and L3 initiated sessions.
IPoE Dual-Stack Features
The following table provides the IPoE Dual-Stack features that are supported for Simple IP and Mobile IP sessions.
| Features | Simple IP | Mobile IP (PMIPv6) | Mobile IP (GTP) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Authentication and Authorization |
MAC TAL • Web Logon |
MAC TAL |
MAC TAL |
Web logon can happen through IPv4 or IPv6
and Web Server and Portal Server should be dual stack. |
|
Session Initiators (FSOLs) |
DHCPv4, IPv6 ND (RS/NS/ NA), and Unclassified MAC Packet | DHCPv4, IPv6 ND (RS/NS/NA), Unclassified MAC Packet | DHCPv4, IPv6 ND (RS/NS/NA), Unclassified MAC Packet |
First Sign of Life (FSOL) can be IPv4 or IPv6, for initiating a session and IPv4 address assignment (through DHCPv4) or IPv6 (/64) prefix assignment (through SLAAC with unicast RA) can happen first. In case of mobile IP, address and prefix allocation happens from LMA or GGSN or PGW. |
| Address Allocation | DHCPv4, IPv6 SLAAC | DHCPv4, IPv6 SLAAC | DHCPv4, IPv6 SLAAC | |
| Layer 4 Redirect (L4R) | Supported | Not Applicable | Not Applicable | L4R is a TC feature and separate TCs
are required for IPv4 and IPv6. |
| Flow Based Redirect | Supported | Not Supported | Not Supported | Flow Based Redirect is a TC feature
and separate TCs are required for IPv4 and IPv6. |
| Flow Based Redirect-SIPTO | Not Supported | Not Supported | Supported | |
| VRF Mapping | Supported | Not Applicable | Both IPv4 and IPv6 traffic are mapped to the same VRF. | |
| PBHK | IPv4 only | Not Supported | Not Supported | PBHK is not supported for IPv6. |
| Session LI (SNMP /RADIUS ) | Supported | Supported | ||
| Mobility Protocols | Not Applicable |
PMIPv6 (MAG - S2a) |
GTP v1 (Gn) GTPv2 (S2a) |
Partial compliance to 3GPP standards with basic features/functionality and mandatory IEs. |
|
RADIUS CoA |
||||
|
Account logon and logoff |
Supported | Not Applicable | Not Applicable |
Session identifier in CoA can be any of following: |
|
Service activation and deactivation |
Supported | Supported | ||
|
Timeout Features |
||||
|
Absolute |
Supported | Supported | Supported | Absolute and Idle timeout features are supported at session level as well as Traffic Class - Service and Flow level. |
|
Idle |
Supported | Supported | Supported | |
|
QoS |
||||
|
Data Rate Limiting (DRL) |
Supported | Supported | Supported | DRL feature is supported at session level as well as TC level. |
|
Shaping |
Supported | Supported | Supported |
Shaping feature is supported only at session level. |
|
Accounting |
||||
|
Post Paid |
Supported | Supported | Supported | Post-paid accounting feature is supported at session level as well as TC level. |
|
Prepaid |
Supported | Not Applicable | Not Applicable | Prepaid is a service and applicable only for TCs. Separate TCs are required for IPv4 and IPv6. iWAG prepaid authorization and re-authorization is separate for IPv4 and IPv6. The back-end system (prepaid server) can manage quota either separately for IPv4 and IPv6 TCs, or combined. Prepaid for mobile IP is done at MPC/EPC (GGSN/PGW, LMA) side. |
Information About Dual Stack Support for Simple IP Subscriber Sessions
Dual-Stack Support for Simple IP Subscriber Sessions
The Dual-Stack Support for Simple IP Subscriber Sessions feature enables L2-connected, dual-stack IP over Ethernet (IPoE) sessions to be provisioned on the Cisco Intelligent Services Gateway (ISG). This module describes how to configure ISG to support IPv6 L2-connected sessions and dual-stack IP sessions.
Prerequisites for Dual-Stack Support for Simple IP Subscriber Sessions
-
The subscriber must be Layer 2-connected.
-
The web or portal server should be a dual-stack host.
-
The ipv6 unicast-routing command needs to be enabled on the ISG to enable dual-stack sessions.
-
Either the IPv6 pool has to be configured in the ISG or the framed IPv6 prefix needs to be downloaded from RADIUS.
-
The ISG has to be configured with the respective TCs or services to ensure proper web or portal access.
-
You should be familiar with the concepts and tasks described in the “Configuring ISG Control Policies” module.
Dual-Stack Simple IPoE Session with MAC TAL Call Flow
The following figure illustrates the call flow for a dual-stack simple IPoE session with MAC TAL.
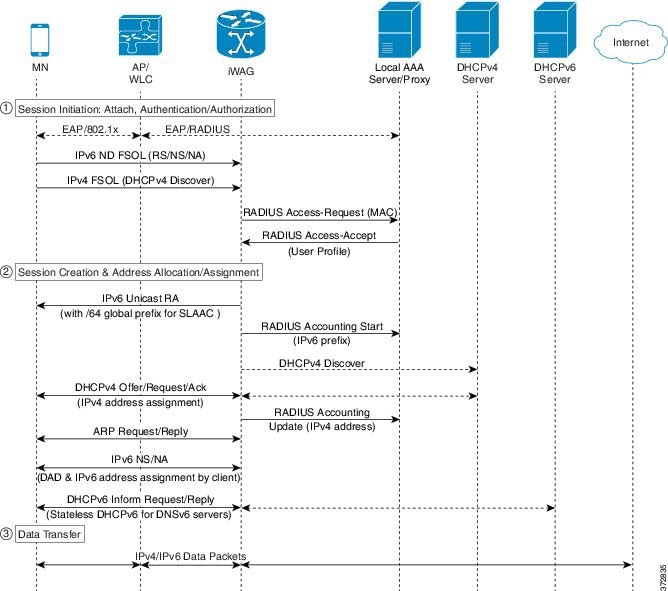
-
A mobile device is automatically associated to the service set identifier (SSID) broadcast by the access points to establish and maintain wireless connectivity.
-
The access point (AP) or Wireless LAN controller (WLC) starts the authentication process using Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) by sending an EAP Request ID to the mobile device.
-
The mobile device sends a response for the EAP Request ID back to the AP or WLC.
-
Upon successful authentication, the mobile device sends a DHCPv4 Discover message to the iWAG.
-
The iWAG sends a RADIUS Access Request to the AAA server asking it to authenticate the subscriber.
-
The iWAG creates a MAC-based ISG session, initiates MAC TAL and pulls the subscriber profile from the AAA server. If the profile has the AAA attribute value as "Cisco-AVPair=mn-service=dual", then the subscriber is authorized for both IPv4 and IPv6 data transfer. Similarly, the AAA attribute value of "Cisco-AVPair=mn-service=ipv4" or "Cisco-AVPair=mn-service=ipv6" represents the IPv4 or IPv6 protocol, using which the subscriber is authorized to send data.
-
The mobile device sends an IPv6 FSOL that could be router solicit, neighbor solicit, or neighbor advertisement, to the iWAG.
-
The iWAG checks whether the ISG session for the MAC address is initiated or created. IWAG waits for verifying the subscriber profile from AAA server.
-
The AAA server sends the RADIUS Access Accept message to the iWAG.
-
In response to the IPv6 (RS) FSOL sent, the iWAG sends a router advertisement (RA) packet using SLAAC that includes the IPv6 prefix, to the mobile device. The mobile device appends the IPv6 prefix to it's 64-bit (EUI or MAC address appended with FFFE) to form a unique 128 bit address.
-
The iWAG sends the IPv4 address through a DHCP Offer message to the mobile device. The iWAG provisions the IPv4 stack.
-
An Accounting Start message is sent to the application provider to indicate the start of the subscriber's service. Now, the subscriber is connected to the Internet.
Dual-Stack Simple IPoE Session with Web Logon Call Flow
The following figure illustrates the call flow for a dual-stack simple IPoE session with Web Logon.
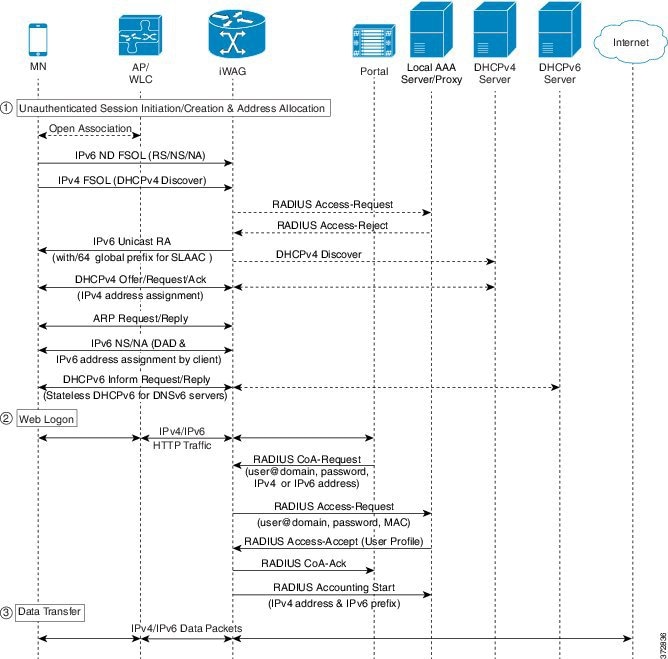
-
A mobile device is automatically associated to the service set identifier (SSID) broadcast by the access points to establish and maintain wireless connectivity.
-
The access point (AP) or Wireless LAN controller (WLC) starts the authentication process using Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) by sending an EAP Request ID to the mobile device.
-
The mobile device sends a response for the EAP Request ID back to the AP or WLC.
-
Upon successful authentication, the mobile device sends an IPv6 FSOL that could be router solicit, neighbor solicit, or neighbor advertisement, to the iWAG.
-
The iWAG creates a MAC-based ISG session and pulls the subscriber profile from the AAA server. If the profile has the AAA attribute value as "Cisco-AVPair=mn-service=dual", then the subscriber is authorized for both IPv4 and IPv6 data transfer. Similarly, the AAA attribute value of "Cisco-AVPair=mn-service=ipv4" or "Cisco-AVPair=mn-service=ipv6" represents the IPv4 or IPv6 protocol, using which the subscriber is authorized to send data.
-
The iWAG sends a RADIUS Access Request to the AAA server asking it to authenticate the subscriber.
-
The mobile device sends a DHCPv4 Discover message to the iWAG.
-
The iWAG checks whether the ISG session for the MAC address is initiated or created.
-
The AAA server sends the RADIUS Access Accept message to the iWAG.
-
In response to the IPv6 (RS) FSOL sent, the iWAG sends a router advertisement (RA) packet using SLAAC that includes the IPv6 prefix, to the mobile device. The mobile device appends the IPv6 prefix to it's 64-bit (EUI or MAC address appended with FFFE) to form a unique 128 bit address.
-
The iWAG sends the IPv4 address through a DHCP Offer message to the mobile device. The iWAG provisions the IPv4 stack.
-
An Accounting Start message is sent to the application provider to indicate the start of the subscriber's service. Now, the subscriber is connected to the Internet.
How to Configure Dual-Stack Support for Simple IP Subscriber Sessions
Configuring Dual Stack Support on ISG
Dual stack can be configured in ISG for both MAC TAL and WebAuth subscribers.
To configure dual stack for MAC TAL users, perform the following actions:
To configure dual stack for WebAuth users, perform the following actions:
Verifying Dual Stack Support on ISG
To verify the dual stack configuration on an ISG device, use any of the following show commands, in any order, in privileged EXEC mode.
1.
show subscriber session detail
2.
show ip subscriber detail
DETAILED STEPS
Configuration Examples for Dual-Stack Support for Simple IP Subscriber Sessions
Example: Configuring Simple IP Dual Stack with MAC TAL
#----------------------------- # Configure the IPv6 pool #----------------------------- ! access-list 101 permit ip host 22.22.22.1 any access-list 101 permit icmp host 22.22.22.1 any ipv6 route 2001:420:54FF:4::400:0/119 2001:420:54FF:4::400:1 ipv6 local pool FIRST 9999::/48 64 ---> To support ipv6 on the existing v4 box ipv6 local pool RED 6868::/48 64 ! ! ! #----------------------------- # Enable IPv6 on the interface #----------------------------- ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0 #Configuring the core interface ip address 9.27.52.4 255.255.0.0 ip portbundle outside negotiation auto ipv6 enable ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 #Configuring the access interface ip unnumbered Loopback68 negotiation auto ipv6 enable service-policy type control START_WEB ip subscriber l2-connected initiator unclassified mac-address initiator dhcp !
Example: Configuring Simple IP Dual Stack with Web Auth
#----------------------------- # Configure the IPv6 pool #----------------------------- ! access-list 101 permit ip host 22.22.22.1 any access-list 101 permit icmp host 22.22.22.1 any ipv6 route 2001:420:54FF:4::400:0/119 2001:420:54FF:4::400:1 ipv6 local pool FIRST 9999::/48 64 ---> To support ipv6 on the existing v4 box ipv6 local pool RED 6868::/48 64 ! ! ! #----------------------------- # Enable IPv6 on the interface #----------------------------- ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0 #Configuring the core interface ip address 9.27.52.4 255.255.0.0 ip portbundle outside negotiation auto ipv6 enable ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 #Configuring the access interface ip unnumbered Loopback68 negotiation auto ipv6 enable service-policy type control START_WEB ip subscriber l2-connected initiator unclassified mac-address initiator dhcp ! #----------------------------- # Configure policy #----------------------------- ! ipv6 access-list TCPv6 #Configuring IPv6 ACL permit tcp any any ! ipv6 access-list TCPv6_ALL permit tcp any any ! class-map type traffic match-any TCPv6 #Configuring the class map for IPv6 traffic match access-group input name TCPv6 match access-group output name TCPv6 ! class-map type traffic match-any TCPv4 match access-group input name TCPv4 match access-group output name TCPv4 ! policy-map type service L4Rv4 class type traffic TCPv4 redirect to ip 18.18.18.18 port 8080 ! ! policy-map type service L4Rv6 #Service definition for IPv6 class type traffic TCPv6 redirect to ip 1818::1818 port 80 ! ! policy-map type control START_WEB class type control UNAUTH_COND event timed-policy-expiry 10 service disconnect ! class type control always event session-start 8 service-policy type service name PBHK 9 authorize identifier mac-address 11 service-policy type service name L4Rv6 #Associating the service to the control policy 12 service-policy type service name L4Rv4 15 set-timer UNAUTH_TIMER 10 ! class type control always event session-restart 8 service-policy type service name PBHK 9 authorize identifier mac-address 11 service-policy type service name L4Rv6 12 service-policy type service name L4Rv4 15 set-timer UNAUTH_TIMER 10 ! class type control always event account-logon 2 authenticate aaa list List1 14 service-policy type service unapply name L4Rv6 15 service-policy type service unapply name L4Rv4 ! !
Information About Dual-Stack Support for PMIPv6
The Dual Stack Support for PMIPv6 feature allows both IPv4 and IPv6 traffic streams to flow through a single PMIPv6 session. The IPv4 and IPv6 traffic streams from a subscriber are identified using the Subscriber MAC address. The iWAG supports following functionalities:
Dual-Stack Mobile IPoE Session PMIPv6 Call Flow
The following figure and steps describe the call flow pertaining to a Dual-Stack Mobile IP over Ethernet (IPoE) session as first sign of life (FSOL) for PMIPv6.
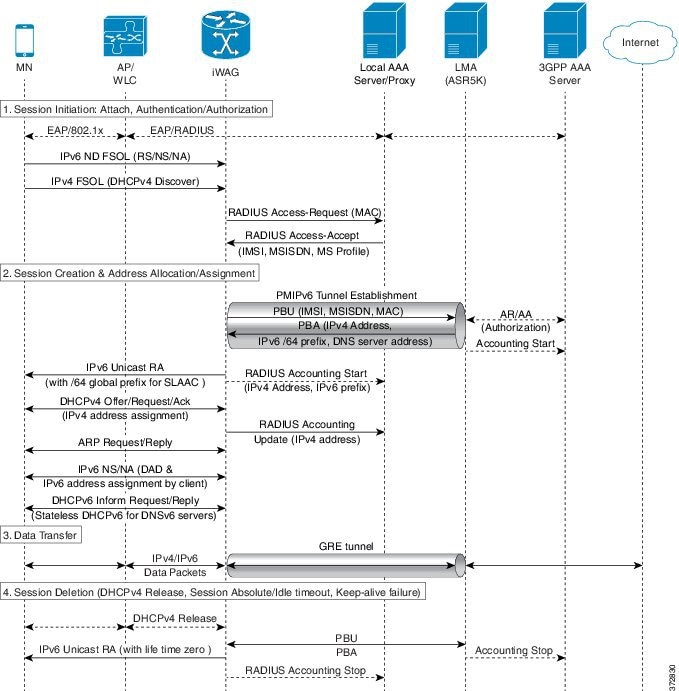
- iWAG initiates the session with the subscriber by enabling AAA.
- The first FSOL packet from the mobile subscriber is either IPv6 ND packet or DHCP Discover. When iWAG receives any FSOL, MAC TAL is initiated for authorization. The mobile subscriber profile obtained from AAA server contains both IPv4 and IPv6 features and services.
- Upon successful subscriber authorization, the session is created and the address is allocated and assigned.
- The IPv6 prefix received from the LMA is assigned to the subscriber through stateless address auto-configuration (SLAAC) (unicast RA). Based on the received mobile subscriber Profile and the local configuration, IPv6 features and services for the session are activated.
- The IPv4 address received from the LMA is assigned to the mobile subscriber through DHCPv4. Based on the received mobile subscriber profile and local configuration, the IPv4 features and services for the session are activated.
- After the tunnel has been established, the data flows bidirectionally.
Configuration Examples for Dual-Stack PMIPv6
Example: Dual Stack Mobile IPoE Session for PMIPv6
#----------------------------------------------
# Configuring AAA and RADIUS
#----------------------------------------------
aaa new-model
!
aaa server radius dynamic-author
client 10.5.5.1 server-key cisco1
!
aaa group server radius SERVER_GROUP1
server name RAD1
!
aaa authentication login AUTHEN_LIST group SERVER_GROUP1
aaa authorization network default group SERVER_GROUP1 local
aaa authorization network AUTHOR_LIST group SERVER_GROUP1 local
aaa authorization subscriber-service default local group SERVER_GROUP1
aaa accounting network List1 start-stop group SERVER_GROUP1
aaa accounting system default start-stop group radius
!
radius-server key cisco1
!
radius server RAD1
address ipv4 192.0.2.1 auth-port 1645 acct-port 1646
#----------------------------------------------------
#Configuring an Access Interface for Dual-Stack PMIPv6
#-----------------------------------------------------
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2
description user1 connected to MN1
ip address 192.0.2.20 255.255.255.0
negotiation auto
ipv6 address FE80::260:3EFF:FE11:6770 link-local
service-policy type control PMIP_DUAL_STACK #subscriber services are applied based on
the control policy definition
ip subscriber l2-connected #invokes iWAG functionality
initiator unclassified mac-address #unclassified MAC address with IPv4
and IPv6 packets,are treated
as FSOL to create a dual stack session
initiator dhcp #DHCP control packets are used as FSOL
to create DHCPv4 only session
end
#--------------------------------------------------------
#Configuring Mobile Access Gateways for Dual-Stack PMIPv6
#--------------------------------------------------------
ipv6 mobile pmipv6-domain D1 #domain with name D1 configuration
replay-protection timestamp window 255
mn-profile-load-aaa #subscriber service profile downloaded from AAA server
lma lma1 #associating LMA with name lma1 to domain D1
ipv6-address 2001:DB8::1
ipv4-address 10.1.1.2
mag M1 #associating MAG with name M1 to domain D1
ipv6-address 2001:DB8:0:ABCD::1
ipv4-address 10.1.1.1
nai MN1@example.com #local subscriber NAI definition for authotrization,
where service for this particular NAI is defined
apn example.com
lma lma1
service dual #dual stack is enabled for MN1@example.com client
int att ETHERNET l2-addr 0000.1111.2222
!
ipv6 mobile pmipv6-mag M1 domain D1
no discover-mn-detach
sessionmgr
apn example.com
address ipv6 2001:DB8:0:ABCD::1
address ipv4 10.1.1.1
binding maximum 40000
replay-protection timestamp window 255
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2
enable pmipv6 default MN1@example.com
lma lma1 D1
ipv6-address 2001:DB8::1
ipv4-address 10.1.1.2
encap gre-ipv4
#-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
#Configuring an Access List Traffic Classmap for Dual-Stack PMIPv6
#-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
ip access-list extended ACL_OUT_INTERNET
permit ip any any
ip access-list extended ACL_OUT_INTERNET2
permit ip any any
ip access-list extended ACL_OUT_OPENGARDEN
permit ip any any
permit udp any any
ip access-list extended ACL_IN_INTERNET
permit ip any any
ip access-list extended ACL_IN_INTERNET2
permit ip any any
ip access-list extended ACL_IN_OPENGARDEN
permit ip any any
permit udp any any
ipv6 access-list IPV6_ACL_INTERNET
permit ipv6 any any
ipv6 access-list IPV6_ACL_INTERNET2
permit ipv6 any any
ipv6 access-list IPV6_ACL_OPENGARDEN
permit ipv6 any any
#-------------------------------------------------------------
#Configuring a Classmap for Dual-Stack PMIPv6
#-------------------------------------------------------------
class-map type traffic match-any TC_OPENGARDEN #defines the traffic rule used
in the service using ACL.
match access-group output name ACL_OUT_OPENGARDEN
match access-group input name ACL_IN_OPENGARDEN
!
class-map type traffic match-any TC_INTERNET2
match access-group output name ACL_OUT_INTERNET2
match access-group input name ACL_IN_INTERNET2
!
class-map type traffic match-any TC_INTERNET
match access-group output name ACL_OUT_INTERNET
match access-group input name ACL_IN_INTERNET
class-map type traffic match-any TC_INTERNET_IPV6
match access-group output name IPV6_ACL_INTERNET
match access-group input name IPV6_ACL_INTERNET
class-map type traffic match-any TC_INTERNET_IPV6_2
match access-group output name IPV6_ACL_INTERNET2
match access-group input name IPV6_ACL_INTERNET2
class-map type traffic match-any TC_OPENGARDEN_IPV6
match access-group output name IPV6_ACL_OPENGARDEN
match access-group input name IPV6_ACL_OPENGARDEN
#-------------------------------------------------------------
# Configuring a Policymap for Dual-Stack PMIPv6
#-------------------------------------------------------------
policy-map type service DRL_V4 #provides service definition for services
applied during session start and restart
20 class type traffic TC_INTERNET
police input 512000 512000 10000
police output 1280000 560000 20000
!
policy-map type service ACC_V4
20 class type traffic TC_INTERNET2
accounting aaa list default
!
policy-map type service TO_V4
20 class type traffic TC_OPENGARDEN
timeout idle 60
!
policy-map type service DRL_V6
20 class type traffic TC_INTERNET_IPV6
police input 512000 512000 10000
police output 1280000 560000 20000
!
policy-map type service ACC_V6
20 class type traffic TC_INTERNET_IPV6_2
accounting aaa list default
!
policy-map type service TO_V6
20 class type traffic TC_OPENGARDEN_IPV6
timeout idle 60
!
#-------------------------------------------------------------
#Configuring a Control Policy for Dual-Stack PMIPv6
#-------------------------------------------------------------
policy-map type control PMIP_DUAL_STACK
class type control always event session-start
10 service-policy type service name DRL_V4 #applying services during dual stack
11 service-policy type service name DRL_V6 #applying services during dual stack
15 service-policy type service name ACC_V4 #applying services during dual stack
16 service-policy type service name ACC_V6 #applying services during dual stack
20 service-policy type service name TO_V4 #applying services during dual stack
21 service-policy type service name TO_V6 #applying services during dual stack
25 service-policy type service name SESSION_TIMEOUT_SERVICE #applying services
during dual stack
30 authorize aaa list default identifier mac-address #performs MAC TAL authorization
class type control always event session-restart
10 service-policy type service name DRL_V4 #applying services during dual stack
11 service-policy type service name DRL_V6 #applying services during dual stack
15 service-policy type service name ACC_V4 #applying services during dual stack
16 service-policy type service name ACC_V6 #applying services during dual stack
20 service-policy type service name TO_V4 #applying services during dual stack
21 service-policy type service name TO_V6 #applying services during dual stack
25 service-policy type service name SESSION_TIMEOUT_SERVICE #applying services during
dual stack
30 authorize aaa list default identifier mac-address #performs MAC TAL authorization
#-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
#Configuring the Local Mobility Anchor for Cisco ASR 5000 Routers
#-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
context pgw
ip pool PMIP_POOL 192.168.1.0 255.255.0.0 public 0 subscriber-gw-address 192.168.2.0
ip pool v4_staticpool 192.168.255.255 255.255.0.0 static
ipv6 pool v6_pool prefix eeee::1/48 public 0 policy allow-static-allocation
router rip
network ip 192.168.1.0/16
network name lma2
redistribute connected
version 2
exit
interface lma2
ipv6 address 2001:DB8:2222:7272::72/64
ip address 192.0.2.201 255.255.255.0 secondary
exit
subscriber default
exit
apn example.com
pdp-type ipv4 ipv6 #enables dual-stack address assignment under ASR 5K LMA
selection-mode sent-by-ms
accounting-mode none
ip context-name pgw
exit
aaa group default
exit
gtpp group default
exit
lma-service lma2
no aaa accounting
reg-lifetime 40000
timestamp-replay-protection tolerance 0
mobility-option-type-value standard
revocation enable
bind address 2001:DB8:2222:7272::72
exit
pgw-service pgw1
plmn id mcc 100 mnc 200
associate lma-service lma2
exit
ipv6 route 2001:DB8::/64 next-hop 2001:DB8:0:0:E000::F interface lma2
ip igmp profile default
exit
exit
port ethernet 17/1
boxertap ethernet 4
no shutdown
bind interface lma2 pgw
exit
port ethernet 17/3
vlan 200
no shutdown
exit
exit
port ethernet 17/4
no shutdown
exit
end
Information About Dual-Stack Support for GTP
The Dual Stack Support for GTP feature allows both IPv4 and IPv6 traffic streams to flow through a single GTP session. The IPv4 and IPv6 traffic streams from a subscriber are identified using the Subscriber MAC address. This feature enables the assignment of both an IPv4 address and an IPv6 address to a client. Therefore, the overall number of supported subscribers on the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers are not affected by a mix of IPv4 and IPv6 traffic.
 Note | Prior to the introduction of the Dual-Stack feature, GTP supported only IPv4 sessions. |
Dual-Stack GTP sessions support the following session initiators:
- Dual-Stack Mobile IPoE Session for GTPv1 Call Flow
- Dual-Stack Mobile IPoE Session for GTPv2 Call Flow
- Configuration Examples for Dual-Stack GTP
Dual-Stack Mobile IPoE Session for GTPv1 Call Flow
The following figure and steps describe the call flow pertaining to a Dual-Stack Mobile IP over Ethernet (IPoE) session for GTPv1.
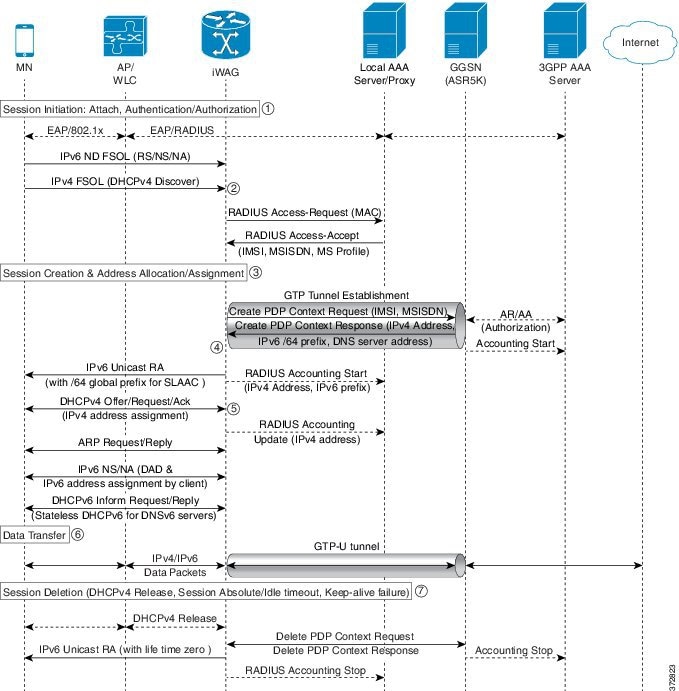
-
The iWAG initiates the session with the subscriber by enabling AAA.
-
The first FSOL packet from the mobile subscriber is either IPv6 ND packet or DHCP Discover. When iWAG receives any FSOL, MAC TAL is initiated for authorization.
The mobile subscriber profile obtained from AAA server contains both IPv4 and IPv6 features and services.
-
Upon successful subscriber authorization, the session is created and the address is allocated and assigned.
-
The IPv6 prefix received from the GGSN is assigned to the mobile subscriber through stateless address auto configuration (SLAAC) (unicast RA). Based on the received mobile subscriber profile and the local configuration, IPv6 features and services for the session are activated.
-
The IPv4 address received from the GGSN is assigned to the mobile subscriber through DHCPv4. Based on the received mobile subscriber profile and local configuration, IPv4 features and services for the session are activated.
-
After the tunnel has been established, the data can flow bi-directionally.
Dual-Stack Mobile IPoE Session for GTPv2 Call Flow
The following figure and steps describe the call flow pertaining to a Dual-Stack Mobile IP over Ethernet (IPoE) session for GTPv2.
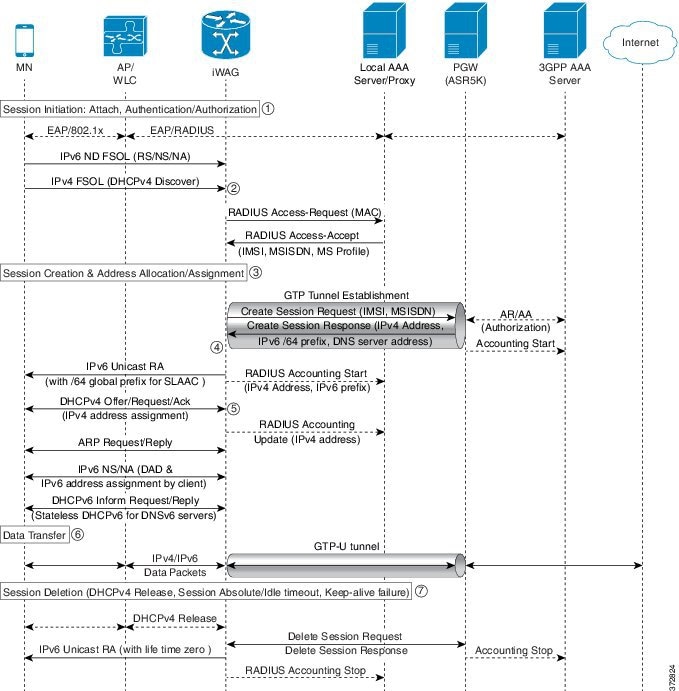
-
The iWAG initiates the session with the subscriber by enabling AAA.
-
The first FSOL packet from the mobile subscriber is either IPv6 ND packet or DHCP Discover. When iWAG receives any FSOL, MAC TAL is initiated for authorization.
The mobile subscriber profile obtained from AAA server contains both IPv4 and IPv6 features and services.
-
Upon successful subscriber authorization, the session is created and the address is allocated and assigned.
-
The IPv6 prefix received from the PGW is assigned to the mobile subscriber through stateless address auto configuration (SLAAC) (unicast RA). Based on the received mobile subscriber profile and the local configuration, IPv6 features and services for the session are activated.
-
The IPv4 address received from the PGW is assigned to the mobile subscriber through DHCPv4. Based on the received mobile subscriber profile and local configuration, IPv4 features and services for the session are activated.
-
After the tunnel has been established, the data can flow bi-directionally.
Configuration Examples for Dual-Stack GTP
Example: Configuring Dual-Stack Sessions for GTP
gtp information-element rat-type wlan interface local GigabitEthernet0/1/3 apn 1 apn-name example1.com ip address ggsn 10.201.31.2 default-gw 30.1.0.1 prefix-len 16 dns-server 192.165.1.1 dhcp-lease 1801 apn 2 apn-name example2.com ip address ggsn 10.201.31.4 default-gw 30.2.0.1 prefix-len 16 dns-server 192.165.1.1 dhcp-lease 1801
Example: Configuring an Interface to PGW or GGSN
interface GigabitEthernet0/1/3 description SGSN to GGSN port ip address 10.201.31.1 255.255.255.0 negotiation auto ipv6 address 2007::2/64 end
Example: Configuring a Control Policy for Dual-Stack GTP
policy-map type control BB_PMAP class type control always event session-start 10 authorize aaa list BB_1 password cisco identifier mac-address
Example: Configuring an Access Interface for Dual-Stack GTP
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/3 ip address 21.0.0.1 255.255.0.0 ipv6 address 8001::1/16 ipv6 enable ipv6 nd ra interval 600 service-policy type control BB_PMAP ip subscriber l2-connected initiator unclassified mac-address initiator dhcp end
Example: Enabling IPv6 Routing
ipv6 unicast-routing
AAA Attributes for Dual Stack
After the AAA server authenticates a subscriber, an AAA attribute is returned in the Access Accept message sent to the iWAG to indicate the session type.
The AAA attribute for the Dual Stack configuration can have the following value:
"cisco-AVPair=mn-service=dual"
(The iWAG retrieves both the IPv4 and IPv6 addresses, but will assign the IPv4 or IPv6 address to the subscriber based on the FSOL.)
Additional References
Related Documents
|
Related Topic |
Document Title |
|---|---|
|
Cisco IOS commands |
|
|
iWAG commands |
Cisco IOS Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Command Reference |
MIBs
|
MIB |
MIBs Link |
|---|---|
|
No new or modified MIBs are supported by this feature. |
To locate and download MIBs for selected platforms, Cisco software releases, and feature sets, use Cisco MIB Locator found at the following URL: |
Technical Assistance
|
Description |
Link |
|---|---|
|
The Cisco Support website provides extensive online resources, including documentation and tools for troubleshooting and resolving technical issues with Cisco products and technologies. To receive security and technical information about your products, you can subscribe to various services, such as the Product Alert Tool (accessed from Field Notices), the Cisco Technical Services Newsletter, and Really Simple Syndication (RSS) Feeds. Access to most tools on the Cisco Support website requires a Cisco.com user ID and password. |
Feature Information for iWAG Dual-Stack IPoE Session
The following table provides release information about the feature or features described in this module. This table lists only the software release that introduced support for a given feature in a given software release train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that software release train also support that feature.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.|
Feature Name |
Releases |
Feature Information |
|---|---|---|
|
iWAG Dual-Stack IPoE Session |
Cisco IOS XE Release 3.11 |
The iWAG Dual-Stack IPoE Session feature allows both IPv4 and IPv6 traffic streams to flow through a single PMIPv6 or GTP or ISG session. In Cisco IOS XE Release 3.11S, this feature was implemented on the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers. |
 Feedback
Feedback