About LDAP
The Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) provides centralized validation of users attempting to gain access to an NX-OS device. An LDAP daemon (service process), which typically runs on a UNIX or Windows NT workstation, maintains LDAP services in a database. To make the LDAP features on your Cisco NX-OS device available, you must access and configure an LDAP server first.
LDAP provides for separate authentication and authorization facilities. LDAP allows a single access control server (the LDAP daemon) to provide authentication and authorization for each service independently. Each service can be tied into its own database to take advantage of other services available on that server or on the network, depending on the capabilities of the daemon.
The LDAP client/server protocol uses TCP (port 389) for transport requirements. NX-OS devices provide centralized authentication using the LDAP protocol.
LDAP Authentication and Authorization
Clients establish a TCP connection and authentication session with an LDAP server through a simple bind (username and password). As part of the authorization process, the LDAP server searches its database to retrieve the user profile and other information.
You can configure the bind operation to authenticate first, then authorize, or configure the operation to search first and then bind.
When you search first and bind later, you can use the distinguished name (DN) from the search result as the user DN for binding. You avoid creating a DN by adding the username (cn attribute) to the baseDN. This is useful if the user DN differs from the username and the baseDN together. For user binding, construct the bind DN using the base DN and append-with-baseDN. By default, append-with-baseDN is cn=$userid.
 Note |
As an alternative to the bind method, you can establish LDAP authentication using the compare method, which compares the attribute values of a user entry at the server. For example, the user password attribute that can be compared for authentication. The default password attribute type is userPassword. |
LDAP operations for user logins
When you attempt to log in to an NX-OS device using Password Authentication Protocol (PAP) over LDAP, these actions occur:
-
When the NX-OS device establishes a connection, it contacts the LDAP daemon to obtain your username and password.
-
The Cisco NX-OS device receives one of these responses from the LDAP daemon:
-
ACCEPT—User authentication succeeds and service begins. If the NX-OS device requires user authorization, authorization begins.
-
REJECT—User authentication fails. The LDAP daemon either denies further access to the user or prompts the user to retry the login sequence.
-
ERROR—An error may occur in the daemon during authentication or in the network connection between the daemon and the Cisco NX-OS device. If the NX-OS device receives an ERROR response, it uses an alternative authentication method for your account.
-
-
After authentication, you also undergo an additional authorization phase if authorization is enabled on the NX-OS device. You must successfully complete LDAP authentication before proceeding to LDAP authorization.
-
If LDAP authorization is required, the NX-OS device contacts the LDAP daemon again. The daemon then returns an ACCEPT or REJECT authorization response. An ACCEPT response contains attributes that determine which services you can access. It also directs the EXEC or NETWORK session for your account. Examples of these services include:
-
Telnet, rlogin, Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP), Serial Line Internet Protocol (SLIP), and EXEC services
-
Connection parameters, including host IP addresses or a client IP address, such as IPv4 or IPv6 (Internet Protocol version 4 or 6), access lists, and user timeouts
-
 Note |
|
LDAP Server Monitoring
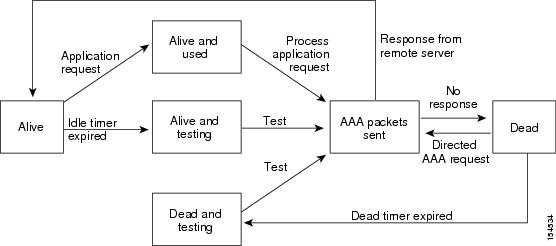
An unresponsive LDAP server can delay the processing of AAA requests. A Cisco NX-OS device can periodically monitor an LDAP server to check whether it is responding (or alive) to save time in processing AAA requests. The Cisco NX-OS device marks unresponsive LDAP servers as dead and does not send AAA requests to any dead LDAP servers. A Cisco NX-OS device periodically monitors dead LDAP servers and brings them to the alive state once they are responding. This process verifies that an LDAP server is in a working state before real AAA requests are sent its way. Whenever an LDAP server changes to the dead or alive state, a Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) trap is generated, and the Cisco NX-OS device displays an error message that a failure is taking place before it can impact performance. The following figure shows the server states for LDAP server monitoring.
 Note |
The monitoring interval for alive servers and dead servers is different and can be configured by the user. The LDAP server monitoring is performed by sending a test authentication request to the LDAP server. |
Vendor-Specific Attributes for LDAP
You can use the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) draft standard method to communicate vendor-specific attributes between your network access server and the LDAP server. Attribute 26 serves this purpose. You can use vendor-specific attributes to enable extended features that are not intended for general use.
Cisco VSA Format for LDAP
The Cisco LDAP implementation supports one vendor-specific option using the format recommended in the IETF specification. The Cisco vendor ID is 9, and the supported option is vendor type 1, which is named cisco-av-pair. The value is a string with the following format:
protocol : attribute separator value *The protocol is a Cisco attribute for a particular type of authorization, the separator is an = (equal sign) for mandatory attributes, and an * (asterisk) indicates optional attributes. When you use LDAP servers for authentication on a Cisco NX-OS device, LDAP directs the LDAP server to return user attributes, such as authorization information, along with authentication results. This authorization information is specified through VSAs. The following VSA protocol option is supported by the Cisco NX-OS software:
- Shell—Protocol used in access-accept packets to provide user profile information.
The Cisco NX-OS software supports the following attribute:
- roles—Lists all the roles to which the user belongs. The value field is a string that lists the role names delimited by white space.
Virtualization Support for LDAP
The Cisco NX-OS device uses virtual routing and forwarding instances (VRFs) to access the LDAP servers. For more information on VRFs, see the Cisco Nexus 9000 Series NX-OS Unicast Routing Configuration Guide.
 Feedback
Feedback