Overview
Workflow Adapters are tools that allow a workflow to interact with systems outside the CWM. You can see them as agents and intermediaries between the CWM platform and any external services. Their role is to cause an action in an outside system that's part of a workflow stream, or to retrieve data required by a workflow to progress.
Every adapter is developed for communicating with an intended target service. Target services can be generic, such as REST APIs over HTTP, or specific, such as vendor products (Cisco's Network Services Orchestrator, for example).
If a workflow needs to access one or more external services, you can develop custom adapters for each of them using the [Adapter SDK] and [XDK]. You may also want to use five pre-built adapters which are available as part of the CWM package. These ready-made solutions include: the Cisco Network Services Orchestrator adapter, generic Database adapter, generic Email adapter, generic CLI adapter, and a generic REST API adapter.
What's in an adapter
An adapter is developed using the Workflow Adapter SDK which uses Golang for defining adapter logic and leverages Protocol Buffers for representing adapter interfaces.
Modules, packages, activities
Every adapter is a go module that represents a product by a vendor. The go module in turn is a collection of product features organized into go packages. Inside the packages you define adapter activities, which are particular actions that the adapter can trigger within a given external system. You can have multiple features inside one adapter by bundling related activities into separate packages. [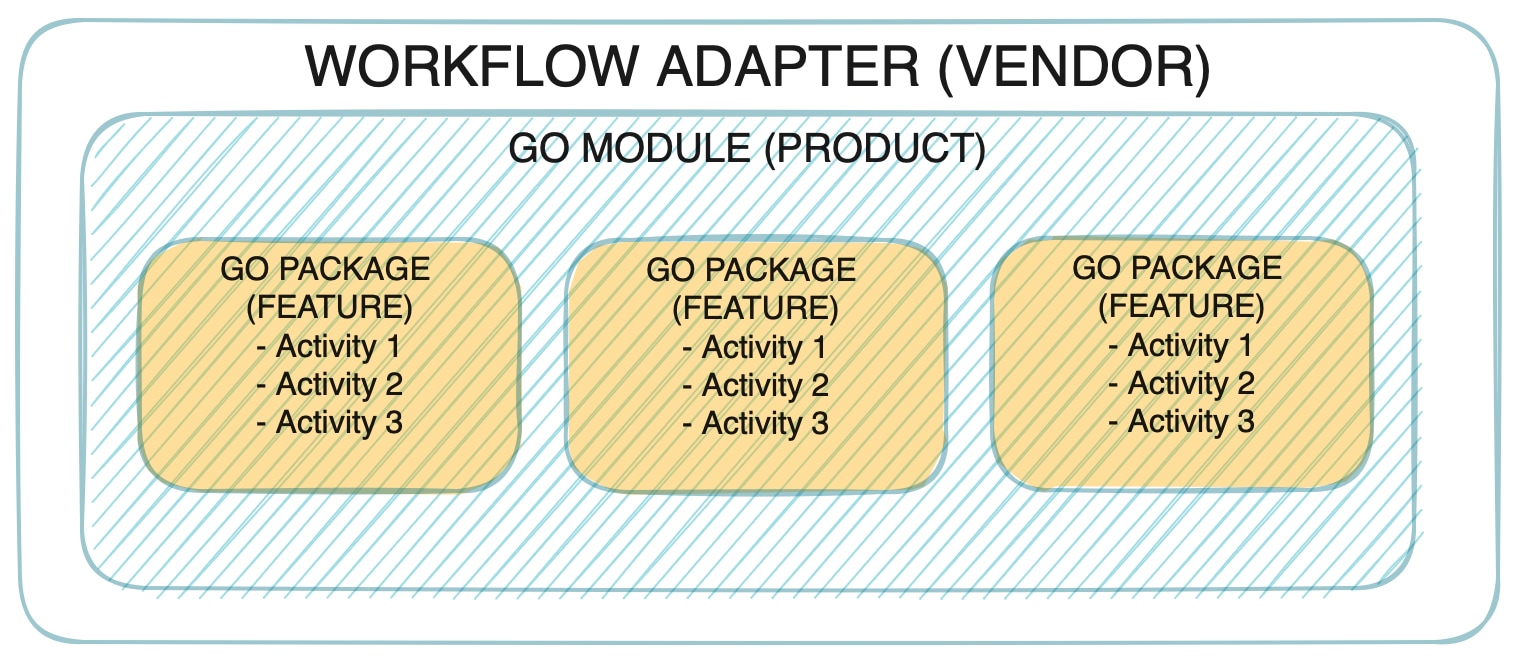 ]
]
As shown in the picture, every adapter follows the vendor, product and feature naming convention which corresponds to a standard go project layout with modules and packages as described above.
Interfaces
Each product feature is represented by a protobuf file located in the proto folder. The Adapter SDK provides command arguments to create the adapter structure and files.
As mentioned before, the naming convention for the adapter features is <vendor>.<product>.<feature>, for example, cisco.nso.restconf.
When you create an adapter, the Adapter SDK generates a .proto file for each interface (feature) you specified:
syntax = "proto3";
package <vendor>.<product>.<feature>;
option go_package = "<module>/<feature>";
The interface is defined as a list of RPCs in the service named 'Activities':
service Activities {
rpc <ActOne> (<ActOne>Request) returns (<ActOne>Response);
rpc <ActTwo> (<ActTwo>Request) returns (<ActTwo>Response);
}
Lastly, the input and output of each activity are defined as protobuf messages:
message <ActOne>Request {
...
}
message <ActOne>Response {
...
}
...
common.adapter.proto
Besides the .proto files representing the adapter interface, there is one additional file: <vendor>.<product>.common.adapter.proto.
The common .proto file is used to define additional configuration required by the adapter as well as information allowing the adapter to connect to a target system. The file is generated automatically by the Adapter SDK, but the developer can do any manual updates required.

Note The common
The common .proto file must define certain messages to enable the CWM Resource Manager to handle this data correctly. This can be done directly inside the file (default) or by importing another .proto.
// Can be defined anywhere and imported to common .proto file.
message Resource {
...
}
message Secret {
...
}
// Must be defined in common .proto file.
message Config {
Resource resource = 1;
Secret secret = 2;
}
Activities
The Adapter SDK generates activities to be implemented in Golang. Each activity is represented as a method with the receiver being a pointer to an adapter struct. Each method definition is based on the activity RPC defined in proto.
func (adp *Adapter) <ActivityName>(
ctx context.Context,
req *<ActivityName>Request,
cfg *common.Config) (*<ActivityName>Response, error) {
/* Activity implementation */
}

Note There are no restrictions on how to implement an activity. The developer is free to import any available go packages. One suggestion is to avoid panics by having robust error handling with the activity returning a meaningful error code.
There are no restrictions on how to implement an activity. The developer is free to import any available go packages. One suggestion is to avoid panics by having robust error handling with the activity returning a meaningful error code.
Resource structure (SDK v2.1.0)
For the cwm-sdk version 2.1.0, the resource message structure has been refactored to clearly separate the adapter connection layer from protocol-specific configuration.
Resource structure before SDK v2.1.0:
message Resource {
optional string scheme = 1;
string host = 2;
optional int32 port = 3;
optional int32 timeout = 4;
optional bool allowInsecure = 5;
}
Resource structure SDK v2.1.0:
message Connection {
optional string protocol = 1;
string host = 2;
optional int32 port = 3;
optional int32 timeout = 4;
optional bool allowInsecure = 5;
}
message Config {
oneof protocol {
HttpConfig http = 1;
SshConfig ssh = 2;
TelnetConfig telnet = 3;
}
}
message Resource {
Connection connection = 1;
optional Config config = 2;
}
Key changes:
- Connection-related fields (host, port, timeout, allowInsecure) are now grouped under connection
- The former scheme field has been replaced by connection.protocol
- Protocol-specific settings have been moved to config, using a
oneoffor HTTP, SSH, and Telnet - The config field is optional, allowing pure connection-level resources when applicable
Properties
Each adapter has a .properties file which serves as the source of basic data about the adapter for CWM. Mandatory properties are described below with examples:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| author=cisco | Name of adapter developer |
| vendor=cisco | Name of target system vendor |
| product=nso | Name of target system |
| module=cisco.com/cwm/adapters/cisco/adapter_name | Name of adapter module |
| version=1.0.0 | Adapter version |
| sdk.version=2.1.0 | Version of SDK used for developing the adapter |
| target.id=cwm | Name of the target platform |
| target.version=2.1.0 | Compatible target platform version |
| description=none | Adapter description |
| resourcetype=cisco.adapter.resource.v1.0.0 | Compatible resource type stored by the CWM Resource Manager |
| secret.type=default |
 Feedback
Feedback