Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine 3.0 EFT Release Notes
This document provides an overview of Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine, new features, and any limitations for this release.
 Note |
This is an EFT document. The documented content, features, and support are still a work in progress. |
Overview of Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine
Network operators are facing challenges to support the exponential growth of network traffic while addressing the pressure to efficiently run network operations. Providing quick service and network resolutions is vital for the business to remain viable. Network operators need a toolset to help automate bandwidth optimization and efficiently steer traffic with little operator intervention. Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine fulfills this need by providing real-time network optimization capabilities that allow operators to effectively maximize network utility as well as increase service velocity.
In a typical lifecycle, there is always a feedback loop that traditionally is done manually through human intervention. With network automation, the objective is to automate the feedback loop to enable quicker reaction to network events and faster determination on actions to perform on the network. Looking at the following figure, Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine is built to fulfill the need for a closed-loop optimization loop as described under “Near Real-Time Feedback Loop”. Through Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine, the operator would be able to define the optimization intent, implement the intent, and continuously monitor, track, and react to maintain the original intent.
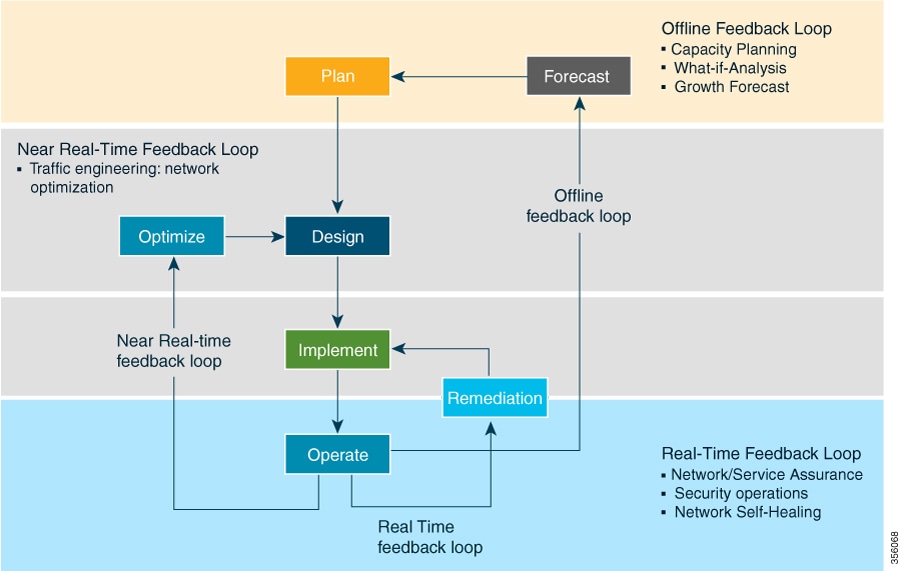
Real-time Visibility
End-to-end visibility is important to any network operator to run their network effectively. Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine not only provides this visibility, but also the ability to visualize the network across different layers (optical to IP) and the relationship between each layer. Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine leverages IETF-standard BGP-LS protocol to discover IP network automatically, including the following features:
-
Real-time visibility: Provides the network operator with a true representation of the actual topology
-
Hierarchical topology view: Enables operators to define the different levels of granularity in the topology visualization
Simplified SR-TE Policy and RSVP-TE Tunnel Lifecycle Management
Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine also provides an easy to use UI and API to manage and monitor the TE tunnel lifecycle. The UI and API enables the network operator to perform the following tasks:
-
Visualize SR-TE (SR-MPLS and SRv6) policies and RSVP-TE tunnels.
-
Create, modify, and remove SR-MPLS policies and RSVP-TE tunnels using an intuitive workflow
-
Continuously track SR-MPLS policies and RSVP-TE tunnels dynamic path computations to maintain SLA objectives
-
Preview an SR-MPLS policy or RSVP-TE tunnel before deploying it to the network
Extensibility through Function Packs
Crosswork Optimization Engine feature packs (available with correct licensing) provide congestion mitigation and closed loop bandwidth optimization. A user defines the optimization intent and the tools implement the intent, and continuously monitor, track, and react to maintain the original intent.
Due to licensing or the configuration of the role associated with your user account, you may not be able to access all of the features and functions. For licensing and ordering information, see the Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine Ordering Guide (accessible to Cisco Partners)or contact your Cisco Sales representative.
What's New in Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine 3.0
This section lists new features and changes delivered in Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine 3.0. For compatibility information, see the Cisco Crosswork Infrastructure 4.1 and Applications Installation Guide.
|
Feature |
What's New? |
|---|---|
|
Segment Routing Over IPv6 (SRv6) Visualization |
SRv6 visualization supports the following:
In addition to previously supported IPv4 policy data, the following SRv6 policy data is also supported:
Starting with this release, SR-TE policies are now separated into either SRv6 or SR-MPLS policies. SRv6 and SR-MPLS policies (including link details) are shown separately in the UI. |
|
Flexible Algorithm Visualization |
The ability to view up to 2 Flexible Algorithm IDs in your network can be enabled in the Traffic Engineering topology view
(Traffic Engineering >
For more information, see Visualize Flexible Algorithms. |
|
Maximum SID Depth (MSD) Enforcement |
Bandwidth on Demand (BWoD) can restrict solution policies to the number of SIDs the headend hardware is capable of supporting. This feature is enabled via the BWoD advanced configuration when the Strict Network option is selected under Policy Violations. |
|
Local Congestion Mitigation (LCM) |
This feature is only available as part of the Advanced RTM license package. For licensing and ordering information, see the Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine Ordering Guide (accessible to Cisco Partners) or contact your Cisco Sales representative. |
|
Topology Map |
|
|
Binding SID (B-SID) Policy Visualization |
Visualize underlying paths of a defined B-SID hop that you have manually configured on a device. For more information, see Visualize Underlying Paths Associated with a Defined Binding-Segment ID (B-SID) Label. |
|
Multiple Path Candidate (MCP) Visualization |
MCP visualization for SR-MPLS and SRv6 policies supports the following:
For more information, see Find Multiple Candidate Paths. |
|
Native Segment Routing Path Over Inter-AS Option C Visualization |
Visualize the actual physical paths (native SR LSPs) which carry traffic on the topology map. |
|
APIs |
For more information, see the Cisco Crosswork Network Automation API Documentation on Cisco DevNet. For licensing and ordering information, see the Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine (accessible to Cisco Partners) or contact your Cisco Sales representative. |
Cisco IOS Software Version Support-TBD
Information has not been vetted.
The following tables list what Cisco IOS software versions Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine supports:|
SR-PCE Software Version1 |
PCC Software Version (Headend Routers) |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Cisco ASR 9000 (32 bit) |
Cisco ASR 9000 (64 bit) |
Cisco XRv 90002 |
Cisco NCS 5500 series 3 |
Cisco NCS 540 series 4 |
Cisco NCS 560 series |
|
|
6.6.3 + SMU |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.1.2 |
||||||
|
7.31 |
||||||
|
7.3.2 |
||||||
 Note |
|
|
SR-PCE Software Version |
PCC Software Version (Headend Routers) |
|
|---|---|---|
|
Cisco ASR 902 RSP 2 |
Cisco ASR 903 RSP 3 |
|
|
6.6.3 + SMU |
|
|
|
7.1.2 |
||
|
7.31 |
||
Compatibility Information-TBD
This section is a work in progress.
The following table lists software versions that have been tested and are known to be compatible with Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine. For complete installation requirements, see the Cisco Crosswork Infrastructure 4.0 and Applications Installation Guide.
| Hardware/Software | Supported Version |
|---|---|
|
Cisco Network Services Orchestrator (Cisco NSO) |
|
|
Cisco Network Element Driver (NED)
|
|
|
Function Packs |
|
|
Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway |
Version 2.0 |
|
Browsers |
|
Scale Support
Information has not been vetted.
The following number of devices, and SR-TE policies (SR-MPLS and SRv6) and RSVP-TE tunnels are supported.
 Note |
These scale numbers have been qualified on a 3 node cluster system setup with 4 CDG VMs (each with 2.5 K) and 3 SR-PCE pairs (6 SR-PCEs total). |
|
Feature |
Scale Support |
|---|---|
|
Devices |
10,000 |
|
Total Interfaces (including IGP) |
650,000 |
|
Provision of SR-TE policies and RSVP-TE tunnel (PCE initiated) |
60,000 |
|
Visualization of IGP links |
TBD |
Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine Documentation
The following table lists the guides that Cisco provides for Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine. You can access all Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine end user documentation at https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/cloud-systems-management/crosswork-optimization-engine/model.html.
 Note |
We sometimes update the documentation after original publication. Therefore, you should always review the documentation on Cisco.com for any updates. |
|
Documentation Title |
What is Included |
|---|---|
|
Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine 3.0 Release Notes |
This document |
|
Infrastructure 4.1 and Applications Installation Guide |
Shared installation guide for all the Cisco Crosswork applications and their common infrastructure. Covers:
|
|
Cisco Crosswork Infrastructure 4.0 and Applications Administrator Guide |
Shared administration guide for all the Cisco Crosswork applications and their common infrastructure. Covers:
|
|
Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine 3.0 User Guide |
|
|
Open Source Used in Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine |
Lists of licenses and notices for open source software used in Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine 3.0. |
Additional Related Documentation
This section needs updated links to the latest documents.
This section provides links to documentation for products related to Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine:
-
Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway 4.0.x
-
Cisco Network Services Orchestrator 5.4.x
You can access documentation for all Cisco Crosswork products at https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/cloud-systems-management/crosswork-network-automation/tsd-products-support-series-home.html
Cisco Crosswork Network Automation API Documentation
Advanced users can integrate other Crosswork applications and third-party applications with Crosswork Optimization Engine functions by using application programming interfaces (APIs) delivering new capabilities into their network operations.
For more information, see the Cisco Crosswork Network Automation API Documentation on Cisco DevNet.
Open Bugs in Cisco Crosswork
If you encounter problems while working with Cisco Crosswork, please check this list of open bugs. Each bug ID in the list links to a more detailed description and workaround.
You can use the Cisco Bug Search Tool to search for a specific bug or to search for all bugs in a release.
-
Go to the Cisco Bug Search Tool.
-
Enter your registered Cisco.com username and password, and click Log In.
The Bug Search page opens.

Note -
Use any of these options to search for bugs, and then press Enter (Return) to initiate the search:
— To search for a specific bug, enter the bug ID in the Search For field.
— To search for bugs based on specific criteria, enter search criteria, such as a problem description, a feature, or a product name, in the Search For field.
— To search for bugs based on products, enter or choose the product from the Product list.
— To search for bugs based on releases, in the Releases list choose whether to search for bugs affecting a specific release, bugs that were fixed in a specific release, or both. Then enter one or more release numbers in the Releases field.
-
When the search results are displayed, use the filter tools to narrow down the results. You can filter the bugs by status, severity, and so on.
 Tip |
To export the results to a spreadsheet, click Export Results to Excel. |
Accessibility Features
For a list of accessibility features in Cisco Crosswork Optimization Engine, visit https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/about/accessibility/voluntary-product-accessibility-templates.html (VPAT) website, or contact accessibility@cisco.com.
All product documents except for some images, graphics, and charts are accessible. If you would like to receive the product documentation in audio format, braille, or large print, contact accessibility@cisco.com.
 Feedback
Feedback