Provisioning mode
From UIW Release 17.16.1, IoT OD IW is changed and called as IW Service.Catalyst IW access point (AP) running in URWB mode supports configuration either from:
-
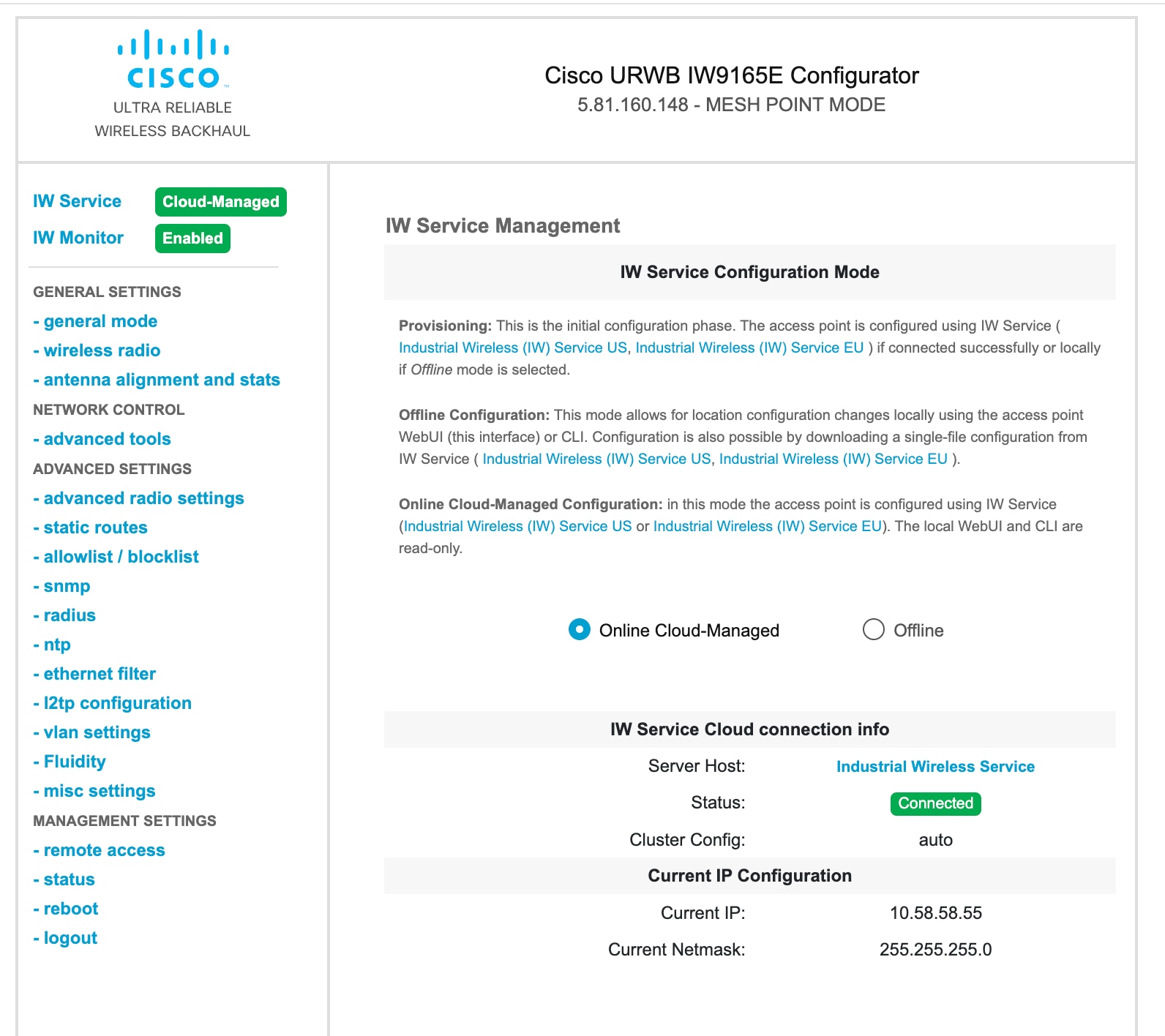
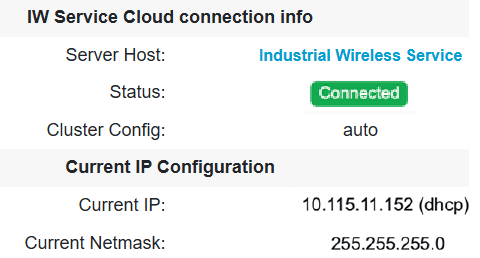
Online Cloud-Managed: configure the device using Industrial Wireless (IW) Service, or
-
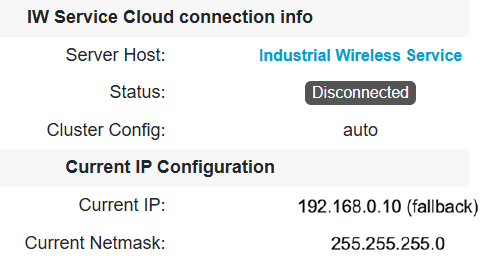
Offline: configure the device using local management interfaces (GUI or CLI).
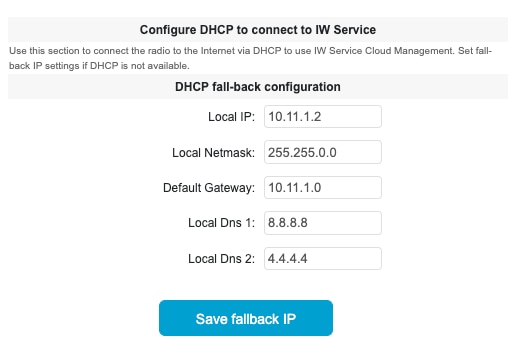
By default, an AP with no configuration starts in Provisioning mode. In this mode, the IW Service provides the initial configuration.





 Feedback
Feedback