Configuration of History and History Table in Remote Network Monitoring (RMON) on Sx500 Series Stackable Switches
Available Languages
Objective
Remote Network Monitoring (RMON) was developed by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) to support monitoring and protocol analysis of LANs. It is a standard monitoring specification which enables different network monitors and console systems to exchange their network-monitoring data with each other. RMON facilitates network administrators to choose among the network-monitoring probes and consoles with features that meet their particular networking needs. RMON specifically defines the information that any network monitoring system should be able to provide. The ten groups in RMON are: statistics, events, history, alarms, hosts, hosts top N, matrix, filter, capture, and token ring. History group in RMON is used to collect the history of port statistics so that the data traffic trends or patterns in the device can be observed.
This document explains how to configure history and the history table in RMON on Sx500 Series Stackable Switches.
Applicable Devices
• Sx500 Series Stackable Switches
Software Version
• 1.3.0.62
Configuration of History in RMON
Step 1. Log in to the web configuration utility and choose Status and Statistics > RMON > History. The History page opens:
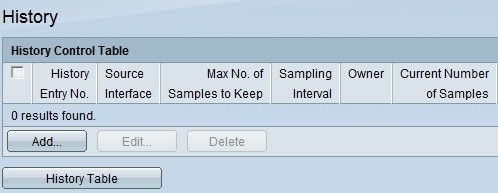
Step 2. Click Add to add a new history entry, which has a specific defined number samples and intervals and their details. The Add RMON History page opens:
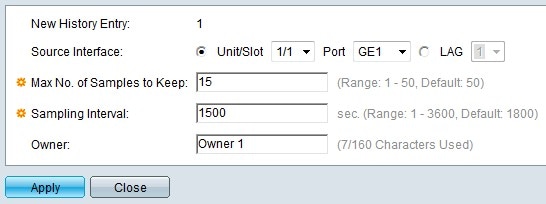
Note: The New History Entry field displays the event entry index number for the new entry.
Step 3. Choose the Source Interface on which the history samples are to be taken, from the Unit/Slot drop-down list and then choose the port from the Port drop-down list. If you configured the LAG then you choose the desired LAG from the LAG drop-down list.
Note: To configure Link Aggregation Group (LAG) refer to the article Link Aggregation Group (LAG) Management and Settings on Sx500 Series Stackable Switches.
Step 4. Enter the number of samples to store in the Max No. of Samples to Keep field. By default it will be 50 samples.
Step 5. Enter the sampling interval in seconds in the Sampling Interval field. This is the amount of time that elapses between the collection of samples. By default it will be 1800 seconds (30 minutes).
Step 6. Enter the RMON station device user that requests the RMON information in the Owner field.
Step 7. Click Apply to save. The entry is added to the History Control Table and the running configuration file is updated.
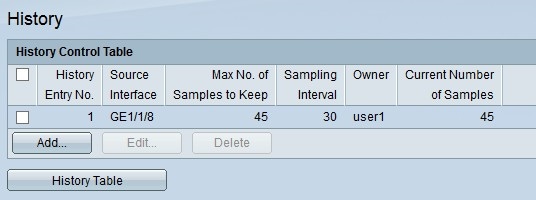
Step 8. Click History Table to view the statistics. The History Control Table page opens:
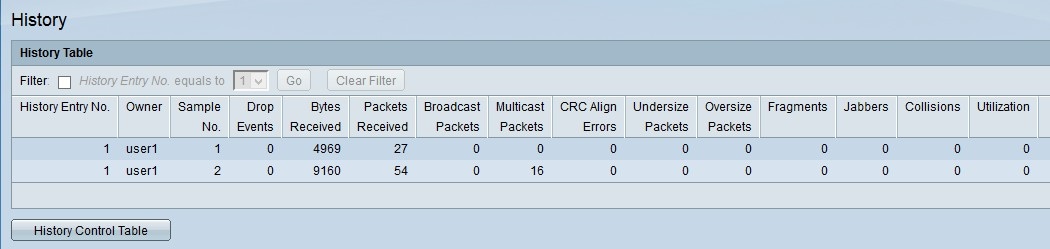
The above fields are explained as follows:
• Owner — Displays history table entry owner.
• Sample No. — Displays the sample number from which the statics were considered.
• Drop Events — Displays the number of dropped packets. These could happen due to many reasons, one of the reasons being due to the failure of network resources during the sampling interval.
• Bytes Received — Displays the number of octets of bytes received on the chosen interface. This includes error packets and FCS octets. FCS (Frame Check Sequence) is a 4-octet CRC to detect the corrupted data in the frames.
• Packets Received — Displays the number of packets received on the chosen interfaces. It includes error packets, multicast packets, and broadcast packets.
• Broadcast Packets — Displays the number of broadcast packets received on the chosen interface. This number does not include Multicast packets.
• Multicast Received — Displays the number of multicast packets received on the chosen interface. This number does not include Broadcast packets.
• CRC Align Errors — Displays the number of CRC (Cyclic Redundancy Check) Align errors that have occurred. The frames that do not end with an even number of octets or have a bad CRC are considered CRC Align errors.
• Undersize Packets — Displays the number of undersized packets received. Undersized packets are the packets whose size is less than 64 octets.
• Oversize Packets — Displays the number of oversize packets received. Oversize packets are the packets whose size is more than 2000 octets.
• Fragments — Displays the number of fragments received. Fragments are the packets with less than 64 octets, excluding framing bits, and includes FCS octets.
• Jabbers — Displays the number of received packets whose size was longer than 2000 octets, excluding frame bits, and includes FCS octets that had either a FCS error or alignment error.
• Collisions — Displays the number of collisions detected.
• Utilization — Displays the percentage of current traffic that is used by the interface compared to maximum traffic that the interface can handle.
Step 9. Click History Control Table to return to the history control page.
 Feedback
Feedback