Introduction
This document describes how to collect detailed ZTA troubleshooting logs, when to enable and step by step.
Background Information
As organizations increasingly adopt Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) to secure users, devices, and applications, troubleshooting connectivity and policy enforcement issues has become more complex. Unlike traditional perimeter-based models, ZTA relies on multiple real-time decisions across identity, device posture, network context, and cloud-based policy engines. When issues arise, high-level logs are often insufficient to pinpoint the root cause.
Collecting detailed ZTA level tracing plays a critical role in gaining deep visibility into client behavior, policy evaluation, traffic interception, and cloud service interactions. These traces enable engineers to move beyond symptom based troubleshooting and analyze the exact sequence of events leading to access failures, performance degradation, or unexpected policy outcomes.
Collecting Logs
Pre-Checks Before Opening a TAC Case
These pre-checks will help the TAC team identify the issue more efficiently. Providing this information to the engineers will assist them in resolving your problem as quickly as possible:
-
What is the issue, and how many users are affected?
-
Which OS and versions are impacted?
-
Is the issue consistent or intermittent? If intermittent, is it user-specific or widespread?
-
Did the issue start after a change, or has it been present since deployment?
-
Are there any known triggers?
-
Is there a workaround available?
Logs to Collect
-
DART bundle
- ZTNA Debug Trace mode logs
-
Wireshark capture (all interfaces, including loopback)
-
Error messages observed
-
Timestamps of the issue
-
CSC ZTA module status screenshot
-
Username of the affected user
The next sections explain how to enable and collect each of these logs in detail.
Enable ZTNA Debug Trace Mode
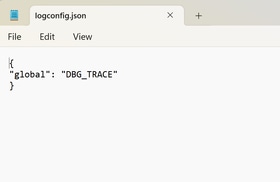
Create a file named logconfig.json with the details below:
{ "global": "DBG_TRACE" }

Warning: Be sure your file is saved with the name logconfig.json.
After creating the file, place it in the appropriate location based on the operating system:


Note: Once you have created the specified file, you must restart the Zero Trust Access Agent service (Please check step Restarting ZTA service ). If restarting the service is not possible, please restart the computer.
Increase ZTA log size in Event Viewer
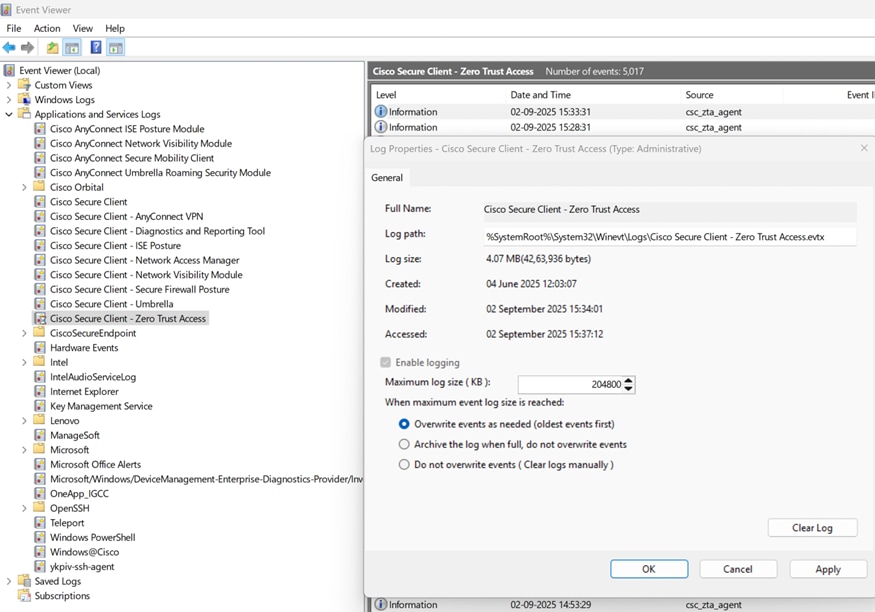
On Windows PCs, after enabling trace-level logging, you must manually increase the ZTA log file size.
- Open
Event Viewer.
- In the left pane, expand
Applications and Services Logs.
- Right click
Cisco Secure Client – Zero Trust Access and select Properties.
- Under
Maximum log size (KB), set the value to 204800 (equivalent to 200 MB).
To finalize click on Apply and then OK.
Restarting ZTA service
Windows
- Use
Windows + R to open the Run Search write services.msc and press enter
- Locate the service
Cisco Secure Client - Zero trust Access Agent and click on Restart. Once its done , verify the CSC ZTA module status to confirm it is active
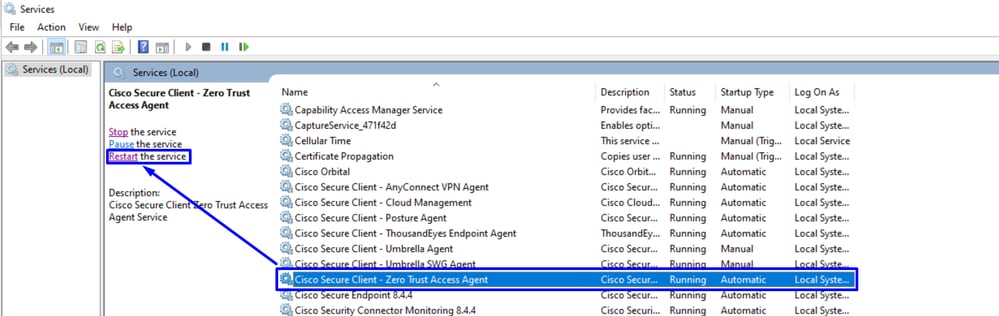

Note: If ZTA service cannot be restarted due to lack of administrative access, a full system reboot it is your next option.
MacOS
Stop Service
sudo "/opt/cisco/secureclient/zta/bin/Cisco Secure Client - Zero Trust Access.app/Contents/MacOS/Cisco Secure Client - Zero Trust Access" uninstall
Start Service
open -a "/opt/cisco/secureclient/zta/bin/Cisco Secure Client - Zero Trust Access.app"

Note: If commands cannot be executed or the ZTA service cannot be restarted due to lack of administrative access, a full system reboot it is your next option.
Enable KDF Logging, Packet Capture, Duo Debug Mode and Dart Bundle
Windows
Open a CMD with admin privileges and run the next command:
"%ProgramFiles(x86)%\Cisco\Cisco Secure Client\acsocktool.exe" -sdf 0x400080152
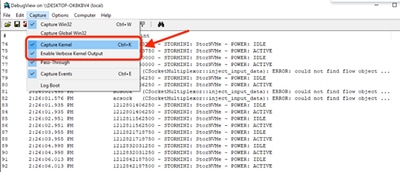
- Download DebugView from SysInternal to capture the KDF log
- Run
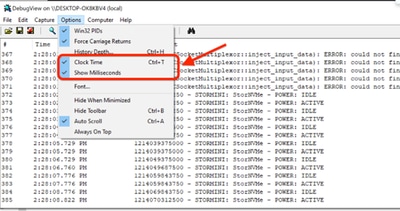
DebugViewas administratorand enable the next menu options:
- Click on Capture
- Checkmark
Capture Kernel
- Checkmark
Enable Verbose Kernel Output
- Options
- Checkmark
Clock Time
- Checkmark
Show Milliseconds
net stop csc_vpnagent && net start csc_vpnagent
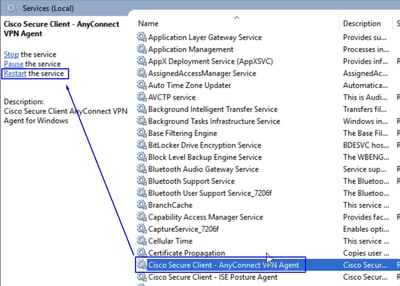
- If
net stop csc_vpnagent && net start csc_vpnagentdoes not work, restart Cisco Secure Clientservice from services.msc
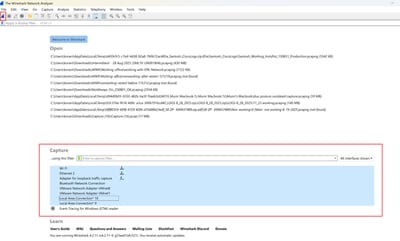
- Reproduce the issue, and save
KDF LogsandWireshark Capture, then follow the steps to capture DART Bundle
- Open the
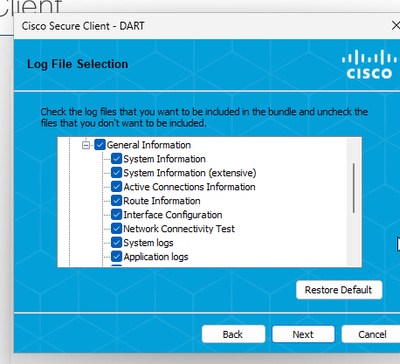
Cisco Secure Client Diagnostics & Reporting Tool (DART)with administrator privileges
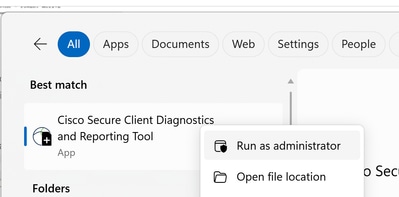
- Click on
Custom
- Include
System Information Extensiveand Network Connectivity Test
- To stop the KDF logging on Windows use the next command:
"%ProgramFiles(x86)%\Cisco\Cisco Secure Client\acsocktool.exe" -cdf

Note: Collect all the logs, KDF Logs, Wireshark Capture and DART Bundle to the TAC Case.
MacOS
Open terminal and follow the next command chain to enable KDF Logging on MacOS:
sudo "/opt/cisco/secureclient/bin/Cisco Secure Client - AnyConnect VPN Service.app/Contents/MacOS/Cisco Secure Client - AnyConnect VPN Service" uninstall
echo debug=0x400080152 | sudo tee /opt/cisco/secureclient/kdf/acsock.cfg
open -a "/opt/cisco/secureclient/bin/Cisco Secure Client - AnyConnect VPN Service.app"
- Reproduce the issue, and save
KDF LogsandWireshark Capture, then follow the steps to capture DART Bundle
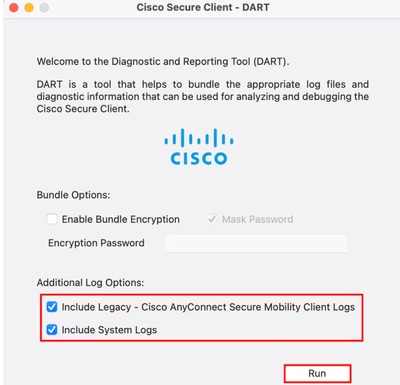
- Open the
Cisco Secure Client - DART

- Checkmark the next options:
Include Legacy - Cisco AnyConnect Secure Mobility Client LogsInclude System Logs
- Click
Run

Note: Collect all the logs, KDF Logs, Wireshark Capture and DART Bundle to the TAC Case.
Related Information
















 Feedback
Feedback