Troubleshoot DHCP in Layer 2 Only VLAN - Wireless
Available Languages
Download Options
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
Contents
Introduction
This document describes how to troubleshoot DHCP for wireless endpoints in a Layer-2 Only network in SD-Access (SDA) fabric.
Prerequisites
Requirements
Cisco recommends that you have knowledge of these topics:
- Internet Protocol (IP) Forwarding
- Locator/ID Separation Protocol (LISP)
- Protocol Independent Multicast (PIM) Sparse-Mode
- Fabric Enabled Wireless
Hardware & Software Requirements
- Catalyst 9000 series switches
- Catalyst Center Version 2.3.7.9
- Catalyst 9800 series wireless LAN controllers
- Catalyst 9100 series access points
- Cisco IOS® XE 17.12 and later
Limitations
-
Only one L2 Border can handoff a unique VLAN/VNI concurrently, unless robust loop prevention mechanisms, such as FlexLink+ or EEM scripts to disable links, are properly configured.
L2 Only Overview
Overview
In typical SD-Access deployments, the L2/L3 boundary resides at the Fabric Edge (FE), where the FE hosts the client's gateway in the form of an SVI, which is often called "Anycast Gateway". L3 VNIs (Routed) are established for inter-subnet traffic, while L2 VNIs (Switched) manage intra-subnet traffic. Consistent configuration across all FEs enables seamless client roaming. Forwarding is optimized: intra-subnet (L2) traffic is directly bridged between FEs, and inter-subnet (L3) traffic is routed either between FEs or between an FE and a Border Node.
For endpoints in SDA Fabrics that require a strict network entry point outside the fabric, the SDA Fabric must provide an L2 channel from the Edge to an external gateway.
This concept is analogous to traditional Ethernet campus deployments where a Layer 2 access network connects to a Layer 3 router. Intra-VLAN traffic remains within the L2 network, while inter-VLAN traffic is routed by the L3 device, often returns to a different VLAN on the L2 network.
Within a LISP context, the Site Control Plane primarily tracks MAC addresses and their corresponding MAC-to-IP bindings, much like traditional ARP entries. L2 VNI/L2-only pools are designed to facilitate registration, resolution, and forwarding exclusively based on these two EID types. Therefore, any LISP-based forwarding in an L2-only environment relies solely on MAC and MAC-to-IP information, it completely disregards IPv4 or IPv6 EIDs. To complement LISP EIDs, L2-only pools heavily depend on flood-and-learn mechanisms, similar to the behavior of traditional switches. Consequently, L2 Flooding becomes a critical component for handling Broadcast, Unknown Unicast, and Multicast (BUM) traffic within this solution, requires the use of Underlay Multicast. Conversely, normal unicast traffic is forwarded using standard LISP forwarding processes, primarily via Map-Caches.
Both Fabric Edges and the "L2 Border" (L2B) maintain L2 VNIs, which map to local VLANs (this mapping is locally device-significant within SDA, allowing different VLANs to map to the same L2 VNI across nodes). In this specific use case, no SVI is configured on these VLANs at these nodes, meaning there is no corresponding L3 VNI.
DHCP Behavior Change in L2 Only VLANs
In Anycast Gateway pools, DHCP presents a challenge because every Fabric Edge acts as the gateway for its directly connected endpoints, with the same gateway IP across all FEs. To properly identify the original source of a DHCP relayed packet, FEs must insert DHCP Option 82 and its sub-options, including the LISP RLOC information. This is achieved with DHCP Snooping on the client VLAN at the Fabric Edge. DHCP Snooping serves a dual purpose in this context: it facilitates the insertion of Option 82 and, crucially, prevents the flood of DHCP broadcast packets across the bridge-domain (VLAN/VNI). Even when Layer-2 Flooding is enabled for an Anycast Gateway, DHCP Snooping effectively suppresses the broadcast packet to be forwarded out of the Fabric Edge as a broadcast.
In contrast, a Layer 2 Only VLAN lacks a gateway, which simplifies DHCP source identification. Since packets are not relayed by any Fabric Edges, complex mechanisms for source identification are unnecessary. Without DHCP Snooping on the L2 Only VLAN, the flood-control mechanism for DHCP packets is effectively bypassed. This allows DHCP broadcasts to be forwarded via L2 Flooding to their final destination, which could be a DHCP server directly connected to a Fabric Node or a Layer 3 device that provides DHCP relay functionality.

Warning: The "Multiple IP to MAC" functionality within an L2 Only pool automatically activates DHCP Snooping in Bridge VM mode, which enforces DHCP flood control. Consequently, this renders the L2 VNI pool incapable to support DHCP for its endpoints.
Underlay Multicast
Given DHCP's heavy reliance on broadcast traffic, Layer 2 flooding must be leveraged to support this protocol. As with any other L2 Flooding-enabled pool, the underlay network must be configured for multicast traffic, specifically Any-Source-Multicast utilizing PIM Sparse-Mode. While underlay multicast configuration is automated via the LAN Automation workflow, if this step was omitted, additional configuration is required (manual or template).
- Enable IP Multicast Routing on all nodes (Borders, Edges, Intermediate Nodes, etc.).
- Configure PIM Sparse-Mode on the Loopback0 interface of each Border and Edge node.
- Enable PIM Sparse-Mode on each IGP (underlay routing protocol) interface.
- Configure the PIM Rendezvous Point (RP) on all nodes (Borders, Edges, Intermediate Nodes), RP placement on Borders is encouraged.
- Verify PIM Neighbors, PIM RP, and PIM Tunnel status.
Broadcast Over Access-Tunnel Interfaces
Fabric Enabled Wireless employs local switching and VTEP functionality at the AP and FE. However, an IOS-XE 16.10+ limitation prevents egress broadcast forwarding over VXLAN to APs. In L2 Only networks, this blocks DHCP Offers/ACKs from reaching wireless clients. The "flood access-tunnel" feature addresses this by enabling broadcast forwarding on Fabric Edge access tunnel interfaces.
Topology
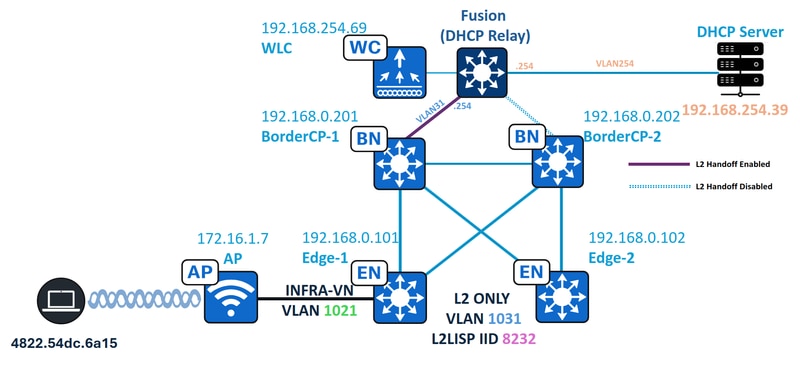 Network Topology
Network Topology
In this topology:
- 192.168.0.201 and 192.168.0.202 are Collocated Borders for the Fabric Site, BorderCP-1 is the only Border with the Layer 2 Hand-off feature enabled.
- 192.168.0.101 and 192.168.0.102 are Fabric Edge Nodes
- 172.16.1.7 is the Access Point in INFRA-VN with VLAN 1021
- 192.168.254.39 is the DHCP Server
- 192.168.254.69 is the Wireless LAN Controller
- 4822.54dc.6a15 is the DHCP-enabled endpoint
- The Fusion device acts as DHCP Relay for the fabric subnets.
L2 Only VLAN Configuration
L2 Only VLAN Deployment from Catalyst Center
Path: Catalyst Center / Provision / Fabric Site / Layer 2 Virtual Networks / Edit Layer 2 Virtual Networks
 L2VNI Configuration with Fabric-Enabled Wireless
L2VNI Configuration with Fabric-Enabled Wireless
L2 Only VLAN Configuration - Fabric Edges
Fabric Edge nodes have the VLAN configured with CTS enabled, IGMP and IPv6 MLD disabled, and the required L2 LISP configuration. This L2 Only pool is a Wireless pool; therefore, features typically found in L2 Only Wireless Pools, such as RA-Guard, DHCPGuard, and Flood Access Tunnel, are configured. ARP Flooding is not enabled on a wireless pool.
Fabric Edge (192.168.0.101) Configuration
ipv6 nd raguard policy dnac-sda-permit-nd-raguardv6device-role routeripv6 dhcp guard policy dnac-sda-permit-dhcpv6device-role servervlan configuration1031ipv6 nd raguard attach-policy dnac-sda-permit-nd-raguardv6ipv6 dhcp guard attach-policy dnac-sda-permit-dhcpv6cts role-based enforcement vlan-list 1031vlan 1031name L2_Only_Wirelessip igmp snooping querier
no ip igmp snooping vlan 1031 querierno ip igmp snooping vlan 1031no ipv6 mld snooping vlan 1031router lispinstance-id 8240remote-rloc-probe on-route-changeservice etherneteid-table vlan 1031broadcast-underlay 239.0.17.1flood unknown-unicast
flood access-tunnel 232.255.255.1 vlan 1021database-mapping mac locator-set rloc_91947dad-3621-42bd-ab6b-379ecebb5a2bexit-service-ethernet
The flood-access tunnel command is configured in it's multicast replication variation, where all BUM traffic is encapsulated to APs using the source specific multicast group (232.255.255.1) using the INFRA-VN Access Point VLAN as the VLAN that is consulted by IGMP snooping to forward the BUM traffic.
L2 Only VLAN Configuration - Wireless LAN Controller
On the WLC (Wireless LAN Controller) side, site tags associated with fabric access points must be configured with "no fabric ap-arp-caching" to disable proxy-ARP functionality. Additionally, "fabric ap-dhcp-broadcast" must be enabled, this configuration allows DHCP broadcast packets to be forwarded from the AP to wireless endpoints.
Fabric WLC (192.168.254.69) Configuration
wireless tag site RTP-Site-Tag-3description "Site Tag RTP-Site-Tag-3"no fabric ap-arp-cachingfabric ap-dhcp-broadcast

Tip: The wireless multicast group 232.255.255.1 is the default group used by all site-tags.
WLC#show wireless tag site detailed RTP-Site-Tag-3Site Tag Name : RTP-Site-Tag-3Description : Site Tag RTP-Site-Tag-3----------------------------------------AP Profile : default-ap-profileLocal-site : YesImage Download Profile: defaultFabric AP DHCP Broadcast : EnabledFabric Multicast Group IPv4 Address : 232.255.255.1RTP-Site-Tag-3 Load : 0
L2 Hand-off Configuration (Fabric Border)
From an operational perspective, the DHCP server (or Router/Relay) is allowed to be connected to any Fabric Node, including both Borders and Edges.
Using Border nodes to connect the DHCP server is the recommended approach, however, requires careful design consideration. This is because the Border must be configured for L2 Hand-Off on a per-interface basis. This allows the Fabric Pool to be handed off to either the same VLAN as within the Fabric or a different one. This flexibility in VLAN IDs between Fabric Edges and Borders is possible because both are mapped to the same L2 LISP Instance-ID. L2 Hand-off physical ports must not be simultaneously enabled with the same VLAN to prevent Layer 2 loops within the SD-Access network. For redundancy, methods such as StackWise Virtual, FlexLink+, or EEM scripts are required.
In contrast, connecting the DHCP Server or Gateway Router to a Fabric Edge requires no additional configuration.
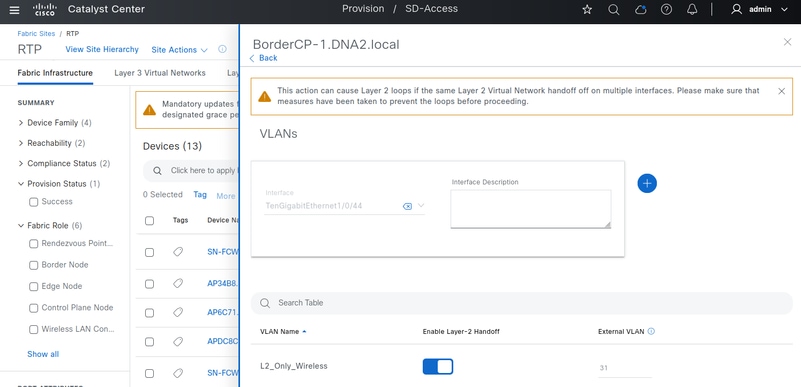 L2 Hand-off Configuration
L2 Hand-off Configuration
Fabric Border/CP (192.168.0.201) Configuration
ipv6 nd raguard policy dnac-sda-permit-nd-raguardv6device-role routeripv6 dhcp guard policy dnac-sda-permit-dhcpv6device-role servervlan configuration 31ipv6 nd raguard attach-policy dnac-sda-permit-nd-raguardv6ipv6 dhcp guard attach-policy dnac-sda-permit-dhcpv6cts role-based enforcement vlan-list 31vlan 31name L2_Only_Wirelessip igmp snooping querier
no ip igmp snooping vlan 1031 querierno ip igmp snooping vlan 1031no ipv6 mld snooping vlan 1031router lispinstance-id 8240remote-rloc-probe on-route-changeservice etherneteid-table vlan 31broadcast-underlay 239.0.17.1flood unknown-unicast
flood access-tunnel 232.255.255.1 vlan 1021database-mapping mac locator-set rloc_91947dad-3621-42bd-ab6b-379ecebb5a2bexit-service-ethernetinterface TenGigabitEthernet1/0/44switchport mode trunk<--DHCP Relay/Server interface
Wireless Multicast Enablement
Fabric Edges are configured to forward broadcast packets to access points via the flood access-tunnel mechanism. these packets are encapsulated into the 232.255.255.1 multicast group on the INFRA-VN VLAN. Access points automatically join this multicast group, as their site-tag is pre-configured to utilize it.
WLC#show ap name AP1 config general | i SiteSite Tag Name : RTP-Site-Tag-3WLC#show wireless tag site detailed RTP-Site-Tag-3Site Tag Name : RTP-Site-Tag-3Description : Site Tag RTP-Site-Tag-3----------------------------------------AP Profile : default-ap-profileLocal-site : YesImage Download Profile: defaultFabric AP DHCP Broadcast : EnabledFabric Multicast Group IPv4 Address : 232.255.255.1RTP-Site-Tag-3 Load : 0
From the access point, upon a fabric wireless endpoint's association, a VXLAN tunnel is formed (dynamic on the AP side, always-on on the Fabric Edge side). Within this tunnel, the CAPWAP fabric multicast group is verified with commands from the AP terminal.
AP1#show ip tunnel fabricFabric GWs Information:Tunnel-Id GW-IP GW-MAC Adj-Status Encap-Type Packet-In Bytes-In Packet-Out Bytes-out1 192.168.0.101 00:00:0C:9F:F2:BC Forward VXLAN 1117063026 1019814432 1116587492 980205146AP APP Fabric Information:GW_ADDR ENCAP_TYPE VNID SGT FEATURE_FLAG GW_SRC_MAC GW_DST_MACAP1#show capwap mcastIPv4 Multicast:Vlan Group IP Version Query Timer Sent QRV left Port0 232.255.255.1 2 972789.691334200 140626 2 0
From the Fabric Edge side, confirm that IGMP snooping is enabled for the INFRA-VN AP VLAN, the access points have formed an access-tunnel interface and they have joined the multicast group 232.255.255.1
Edge-1#show ip igmp snooping vlan 1021 | i IGMPGlobal IGMP Snooping configuration:IGMP snooping : EnabledIGMPv3 snooping : EnabledIGMP snooping : EnabledIGMPv2 immediate leave : DisabledCGMP interoperability mode : IGMP_ONLYEdge-1#show ip igmp snooping groups vlan 1021 232.255.255.1Vlan Group Type Version Port List-----------------------------------------------------------------------1021 232.255.255.1 igmp v2 Te1/0/12 ----- Access Point PortEdge-1#show device-tracking database interface te1/0/12 | be NetworkNetwork Layer Address Link Layer Address Interface vlan prlvl age state Time leftDH4 172.16.1.7 dc8c.3756.99bc Te1/0/12 1021 0024 1s REACHABLE 251 s(76444 s)Edge-1#show access-tunnel summaryAccess Tunnels General Statistics:Number of AccessTunnel Data Tunnels = 1Name RLOC IP(Source) AP IP(Destination) VRF ID Source Port Destination Port------ --------------- ------------------ ------ ----------- ----------------Ac2 192.168.0.101 172.16.1.7 0 N/A 4789<snip>
These verifications confirm the successful enablement of wireless multicast across the Access Point, Fabric Edge, and Wireless LAN Controller.
DHCP Traffic Flow
DHCP Discover and Request - Wireless Side
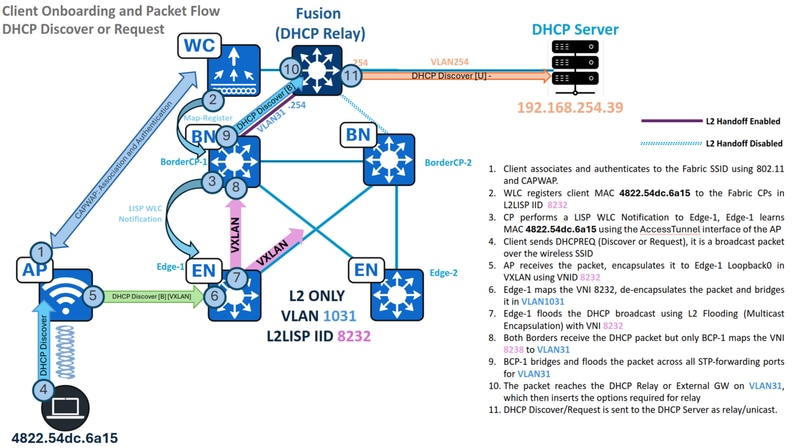 Traffic Flow - DHCP Discover and Request in L2 Only
Traffic Flow - DHCP Discover and Request in L2 Only
identify the wireless endpoint's state, its connected access point, and associated fabric properties.
WLC#show wireless client summary | i MAC|-|4822.54dc.6a15MAC Address AP Name Type ID State Protocol Method Role-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------4822.54dc.6a15 AP1 WLAN 17 Run 11n(2.4) MAB LocalWLC#show wireless client mac 4822.54dc.6a15 detail | se AP Name|Policy Profile|FabricAP Name: AP1Policy Profile : RTP_POD1_SSID_profileFabric status : EnabledRLOC : 192.168.0.101VNID : 8232SGT : 0Control plane name : default-control-plane
It is important to confirm that both central-switching and central-dhcp features are disabled on the policy profile. The commands "no central dhcp" and "no central switching" must be configured on the policy profile for the SSID.
WLC#show wireless profile policy detailed RTP_POD1_SSID_profile | i CentralFlex Central Switching : DISABLEDFlex Central Authentication : ENABLEDFlex Central DHCP : DISABLEDVLAN based Central Switching : DISABLED
These verifications confirm that the endpoint is connected to "AP1", which is associated with the Fabric Edge RLOC 192.168.0.101. Consequently, its traffic is encapsulated via VXLAN with VNID 8232 for transmission from the Access Point to the Fabric Edge.
DHCP Discover and Request - Fabric Edge
MAC Learning using WLC Notification
During endpoint onboarding, the WLC registers the wireless endpoint's MAC address with the Fabric Control Plane. Simultaneously, the Control Plane notifies the Fabric Edge node (to which the Access Point is connected) to create a special "CP_LEARN" MAC learning entry, pointing to the Access Point's access-tunnel interface.
Edge-1#show lisp sessionSessions for VRF default, total: 2, established: 2Peer State Up/Down In/Out Users192.168.0.201:4342 Up 2w2d 806/553 44192.168.0.202:4342 Up 2w2d 654/442 44Edge-1#show lisp instance-id 8232 ethernet database wlc 4822.54dc.6a15WLC clients/access-points information for LISP 0 EID-table Vlan 1031 (IID 8232)Hardware Address: 4822.54dc.6a15Type: clientSources: 2Tunnel Update: SignalledSource MS: 192.168.0.201RLOC: 192.168.0.101Up time: 1w6dMetadata length: 34Metadata (hex): 00 01 00 22 00 01 00 0C AC 10 01 07 00 00 10 0100 02 00 06 00 00 00 03 00 0C 00 00 00 00 68 996A D2Edge-1#show mac address-table address 4822.54dc.6a15Mac Address Table-------------------------------------------Vlan Mac Address Type Ports---- ----------- -------- -----1031 4822.54dc.6a15 CP_LEARN Ac2
If the endpoint's MAC address is correctly learned via the access-tunnel interface corresponding to its connected access point, this stage is considered complete.
DHCP Broadcast Bridged in L2 Flooding
When DHCP Snooping is disabled, DHCP Broadcasts are not blocked; instead, they are encapsulated in multicast for Layer 2 Flooding. Conversely, enabling DHCP Snooping prevents the flooding of these broadcast packets.
Edge-1#show ip dhcp snoopingSwitch DHCP snooping isenabledSwitch DHCP gleaning is disabledDHCP snooping is configured on following VLANs:12-13,50,52-53,333,1021-1026DHCP snooping isoperationalon following VLANs:12-13,50,52-53,333,1021-1026<--VLAN1031 should not be listed, as DHCP snooping must be disabled in L2 Only pools.Proxy bridge is configured on following VLANs:1024Proxy bridge is operational on following VLANs:1024<snip>
Since DHCP Snooping is disabled, the DHCP Discover/Request utilizes the L2LISP0 interface, bridging traffic via L2 Flooding. Depending on the Catalyst Center version and applied Fabric Banners, the L2LISP0 interface may have access-lists configured in both directions; therefore, ensure DHCP traffic (UDP ports 67 and 68) is not explicitly denied by any Access Control Entries (ACEs).
interface L2LISP0
ip access-group SDA-FABRIC-LISP in
ip access-group SDA-FABRIC-LISP out
Edge-1#show access-list SDA-FABRIC-LISP
Extended IP access list SDA-FABRIC-LISP
10 deny ip any host 224.0.0.22
20 deny ip any host 224.0.0.13
30 deny ip any host 224.0.0.1
40 permit ip any any
Utilize the configured broadcast-underlay group for the L2LISP instance and the Fabric Edge's Loopback0 IP address to verify the L2 Flooding (S,G) entry that bridges this packet to other Fabric Nodes. Consult the mroute and mfib tables to validate parameters such as the incoming interface, outgoing interface list, and forwarding counters.
Edge-1#show ip interface loopback 0 | i Internet
Internet address is 192.168.0.101/32
Edge-1#show running-config | se 8232
interface L2LISP0.8232
instance-id 8232
remote-rloc-probe on-route-change
service ethernet
eid-table vlan 1031
broadcast-underlay 239.0.17.1
Edge-1#show ip mroute 239.0.17.1 192.168.0.101 | be \(
(192.168.0.101, 239.0.17.1), 00:00:19/00:03:17, flags: FT
Incoming interface: Null0, RPF nbr 0.0.0.0 <-- Local S,G IIF must be Null0
Outgoing interface list:
TenGigabitEthernet1/1/2, Forward/Sparse, 00:00:19/00:03:10, flags: <-- 1st OIF = Te1/1/2 = Border2 Uplink
TenGigabitEthernet1/1/1, Forward/Sparse, 00:00:19/00:03:13, flags: <-- 2nd OIF = Te1/1/1 = Border1 Uplink
Edge-1#show ip mfib 239.0.17.1 192.168.0.101 count
Forwarding Counts: Pkt Count/Pkts per second/Avg Pkt Size/Kilobits per second
Other counts: Total/RPF failed/Other drops(OIF-null, rate-limit etc)
Default
13 routes, 6 (*,G)s, 3 (*,G/m)s
Group: 239.0.17.1
Source: 192.168.0.101,
SW Forwarding: 1/0/392/0, Other: 1/1/0
HW Forwarding: 7/0/231/0, Other: 0/0/0 <-- HW Forwarding counters (First counter = Pkt Count) must increase
Totals - Source count: 1, Packet count: 8

Tip: Tip: If an (S,G) entry is not found or the Outgoing Interface List (OIL) contains no Outgoing Interfaces (OIFs), it indicates an issue with the underlay multicast configuration or operation.
Packet Captures
Configure a simultaneous embedded packet capture on the switch to record both the ingress DHCP packet from the AP and the corresponding egress packet for L2 Flooding.
Fabric Edge (192.168.0.101) packet catpures
monitor capture cap interface TenGigabitEthernet1/0/12 IN <-- Access Point Portmonitor capture cap interface TenGigabitEthernet1/1/1 OUT <-- Multicast Route (L2 Flooding) OIFmonitor capture cap match anymonitor capture cap buffer size 100monitor capture cap limit pps 1000monitor capture cap startmonitor capture cap stop
Upon packet capture, three distinct packets must be observed:
- DHCP Discover - VXLAN - AP to Edge
- DHCP Discover - CAPWAP - AP to WLC
- DHCP Discover - VXLAN - Edge to Multicast Group
Edge-1#show monitor capture cap buffer display-filter "bootp and dhcp.hw.mac_addr==4822.54dc.6a15"<-- 4822.54dc.6a15 is the endpoint MACStarting the packet display ........ Press Ctrl + Shift + 6 to exit129 4.865410 0.0.0.0 -> 255.255.255.255 DHCP 394 DHCP Discover - Transaction ID 0x824bdf45 <-- From AP to Edge130 4.865439 0.0.0.0 -> 255.255.255.255 DHCP 420 DHCP Discover - Transaction ID 0x824bdf45 <-- From AP to WLC131 4.865459 0.0.0.0 -> 255.255.255.255 DHCP 394 DHCP Discover - Transaction ID 0x824bdf45 <-- From Edge to L2 Flooding GroupEdge-1#show monitor capture cap buffer display-filter "bootp and dhcp.hw.mac_addr==4822.54dc.6a15 and vxlan"Starting the packet display ........ Press Ctrl + Shift + 6 to exit129 4.865410 0.0.0.0 -> 255.255.255.255 DHCP 394 DHCP Discover - Transaction ID 0x824bdf45131 4.865459 0.0.0.0 -> 255.255.255.255 DHCP 394 DHCP Discover - Transaction ID 0x824bdf45Edge-1#show monitor capture cap buffer display-filter "bootp and dhcp.hw.mac_addr==4822.54dc.6a15 and udp.port==5247"Starting the packet display ........ Press Ctrl + Shift + 6 to exit130 4.865439 0.0.0.0 -> 255.255.255.255 DHCP 420 DHCP Discover - Transaction ID 0x824bdf45Edge-1#show monitor capture cap buffer display-filter "bootp and dhcp.hw.mac_addr==4822.54dc.6a15 and vxlan"detail| i InternetInternet Protocol Version 4, Src: 172.16.1.7, Dst: 192.168.0.101 <-- From AP to EdgeInternet Protocol Version 4, Src: 0.0.0.0, Dst: 255.255.255.255Internet Protocol Version 4, Src: 192.168.0.101, Dst: 239.0.17.1 <-- From Edge to Upstream (Layer 2 Flooding)Internet Protocol Version 4, Src: 0.0.0.0, Dst: 255.255.255.255

Tip: On Fabric Enabled Wireless, VXLAN encapsulated packets deliver DHCP traffic to clients or servers. CAPWAP DATA (UDP 5247) encapsulated packets, however, transmit to the WLC solely for tracking purposes, such as IP Learn state or Wireless Device-Tracking.
DHCP Discover and Request - L2 Border
After the Edge sends the DHCP Discover and Request packets via Layer 2 Flooding, encapsulated with the Broadcast-Underlay group 239.0.17.1, these packets are received by the L2 Hand-Off Border, specifically Border/CP-1 in this scenario.
For this to occur, Border/CP-1 must possess a multicast route with the (S,G) of the Edge, and its outgoing interface list must include the L2LISP instance of the L2 Handoff VLAN. It's important to note that L2 Hand-Off Borders share the same L2LISP Instance-ID, even if they utilize different VLANs for the Hand-Off.
BorderCP-1#show vlan id 31VLAN Name Status Ports---- -------------------------------- --------- -------------------------------31 L2_Only_Wireless active L2LI0:8232, Te1/0/44BorderCP-1#show ip mroute 239.0.17.1 192.168.0.101 | be \((192.168.0.101, 239.0.17.1), 00:03:20/00:00:48, flags: MTAIncoming interface: TenGigabitEthernet1/0/42, RPF nbr 192.168.98.3 <-- IIF Te1/0/42 is the RPF interface for 192.168.0.101 (Edge RLOC)Outgoing interface list:TenGigabitEthernet1/0/26, Forward/Sparse, 00:03:20/00:03:24, flags:L2LISP0.8232, Forward/Sparse-Dense, 00:03:20/00:02:39, flags:BorderCP-1#show ip mfib 239.0.17.1 192.168.0.101 countForwarding Counts: Pkt Count/Pkts per second/Avg Pkt Size/Kilobits per secondOther counts: Total/RPF failed/Other drops(OIF-null, rate-limit etc)Default13 routes, 6 (*,G)s, 3 (*,G/m)sGroup: 239.0.17.1Source: 192.168.0.101,SW Forwarding: 1/0/392/0, Other: 0/0/0HW Forwarding: 3/0/317/0, Other: 0/0/0 <-- HW Forwarding counters (First counter = Pkt Count) must increaseTotals - Source count: 1, Packet count: 4

Tip: If an (S,G) entry is not found, it indicates an issue with the underlay multicast configuration or operation. If the L2LISP for the requried instance is not present as OIF, it indicates an issue with the operation UP/DOWN status of the L2LISP sub-interface or the IGMP enablement status of the L2LISP interface.
Similar to the Fabric Edge node, ensure no Access Control Entry denies the ingress DHCP packet on the L2LISP0 interface.
BorderCP-1#show ip access-lists SDA-FABRIC-LISPExtended IP access list SDA-FABRIC-LISP10 deny ip any host 224.0.0.2220 deny ip any host 224.0.0.1330 deny ip any host 224.0.0.140 permit ip any any
After the packet is de-encapsulated and placed on the VLAN matching VNI 8240, its broadcast nature dictates that it is flooded out all Spanning Tree Protocol forwarding ports for hand-off VLAN 141.
BorderCP-1#show spanning-tree vlan 31 | be InterfaceInterface Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type------------------- ---- --- --------- -------- --------------------------------Te1/0/44 Desg FWD 2000 128.56 P2p
The Device-Tracking table confirms that interface Te1/0/44, which connects to the Gateway/DHCP Relay, must be an STP-forwarding port.
BorderCP-1#show device-tracking database address 172.16.141.254 | be NetworkNetwork Layer Address Link Layer Address Interface vlan prlvl age state Time leftARP 172.16.131.254 f87b.2003.7fd5 Te1/0/44 31 0005 34s REACHABLE 112 s try 0
Packet Captures
Configure a simultaneous embedded packet capture on the switch to record both the incoming DHCP packet from L2 Flooding (S,G incoming interface) and the corresponding egress packet to the DHCP Relay. Upon packet capture, two distinct packets should be observed: the VXLAN encapsulated packet from Edge-1, and the de-encapsulated packet that goes to the DHCP Relay.
Fabric Border/CP (192.168.0.201) packet catpures
monitor capture cap interface TenGigabitEthernet1/0/42 IN<--Ingress interface for Edge's S,G Mroute (192.168.0.101, 239.0.17.1)monitor capture cap interface TenGigabitEthernet1/0/44 OUT <-- Interface that connects to the DHCP Relaymonitor capture cap match any
monitor capture cap buffer size 100monitor capture cap startmonitor capture cap stopBorderCP-1#show monitor capture cap buffer display-filter "bootp and dhcp.hw.mac_addr==4822.54dc.6a15"Starting the packet display ........ Press Ctrl + Shift + 6 to exit324 16.695022 0.0.0.0 -> 255.255.255.255 DHCP 394 DHCP Discover - Transaction ID 0x824bdf45 <-- 394 is the Lenght of the VXLAN encapsulated packet325 10.834141 0.0.0.0 -> 255.255.255.255 DHCP 420 DHCP Discover - Transaction ID 0x168bd882 <-- 420 is the Lenght of the CAPWAP encapsulated packet326 16.695053 0.0.0.0 -> 255.255.255.255 DHCP 352 DHCP Discover - Transaction ID 0x824bdf45 <-- 352 is the Lenght of the VXLAN encapsulated packetPacket 324: VXLAN EncapsulatedBorderCP-1#show monitor capture cap buffer display-filter "frame.number==324" detail | i InternetInternet Protocol Version 4, Src: 192.168.0.101, Dst: 239.0.17.1Internet Protocol Version 4, Src: 0.0.0.0, Dst: 255.255.255.255Packet 326: Plain (dot1Q cannot be captured at egress due to EPC limitations)BorderCP-1#show monitor capture cap buffer display-filter "frame.number==326" detailed | i InternetInternet Protocol Version 4, Src: 0.0.0.0, Dst: 255.255.255.255
At this point, the Discover/Request packet has exited the SD-Access fabric, concluding this section. However, before proceeding, a crucial parameter—the DHCP Broadcast Flag, determined by the endpoint itself—will dictate the forwarding scenario for subsequent Offer or ACK packets. We can examine one of our Discover packets to inspect this flag.
BorderCP-1#show monitor capture cap buffer display-filter "bootp.type==1 and dhcp.hw.mac_addr==4822.54dc.6a15" detailed | sect DynamicDynamic Host Configuration Protocol (Discover)Message type: Boot Request (1)Hardware type: Ethernet (0x01)Hardware address length: 6Hops: 0Transaction ID: 0x00002030Seconds elapsed: 3Bootp flags: 0x8000, Broadcast flag (Broadcast)1... .... .... .... = Broadcast flag: Broadcast <-- Broadcast Flag set by the Endpoint.000 0000 0000 0000 = Reserved flags: 0x0000

Tip: The bootp.type==1 can be used to filter only Discover and Request packets.
DHCP Offer and ACK - Broadcast - L2 Border
 Traffic Flow - Broadcast DHCP Offer and ACK in L2 Only
Traffic Flow - Broadcast DHCP Offer and ACK in L2 Only
Now that the DHCP Discover has exited the SD-Access fabric, the DHCP relay will insert traditional DHCP Relay Options (e.g., GiAddr/GatewayIPAddress) and forward the packet as a unicast transmission to the DHCP Server. In this flow, the SD-Access fabric does not append any special DHCP options.
Upon the arrival of a DHCP Discover/Request to the server, the server honors the embedded Broadcast or Unicast flag. This flag dictates whether the DHCP Relay Agent forwards the DHCP Offer to the downstream device (our Borders) as a broadcast or unicast frame. For this demonstration, a broadcast scenario is assumed.
MAC Learning and Gateway Registration
When the DHCP relay sends a DHCP Offer or ACK, the L2BN node must learn the gateway's MAC address, add it to its MAC address table, then to the L2/MAC SISF table, and finally to the L2LISP Database for VLAN 141, mapped to L2LISP Instance 8232.
BorderCP-1#show mac address-table interface te1/0/44Mac Address Table-------------------------------------------Vlan Mac Address Type Ports---- ----------- -------- -----31 f87b.2003.7fd5 DYNAMIC Te1/0/44BorderCP-1#show vlan id 31VLAN Name Status Ports---- -------------------------------- --------- -------------------------------31 L2_Only_Wireless active L2LI0:8232, Te1/0/44BorderCP-1#show device-tracking database mac | i 7fd5|vlanMAC Interface vlan prlvl state Time left Policy Input_indexf87b.2003.7fd5 Te1/0/44 31 NO TRUST MAC-REACHABLE 61 s LISP-DT-GLEAN-VLAN 64BorderCP-1#show lisp ins 8232 dynamic-eid summary | i Name|f87b.2003.7fd5Dyn-EID Name Dynamic-EID Interface Uptime Last PendingAuto-L2-group-8232 f87b.2003.7fd5 N/A 6d06h never 0BorderCP-1#show lisp instance-id 8232 ethernet databasef87b.2003.7fd5LISP ETR MAC Mapping Database for LISP 0 EID-table Vlan 31 (IID 8232), LSBs: 0x1Entries total 1, no-route 0, inactive 0, do-not-register 0f87b.2003.7fd5/48, dynamic-eid Auto-L2-group-8240, inherited from default locator-set rloc_0f43c5d8-f48d-48a5-a5a8-094b87f3a5f7, auto-discover-rlocsUptime: 6d06h, Last-change: 6d06hDomain-ID: localService-Insertion: N/ALocator Pri/Wgt Source State192.168.0.201 10/10 cfg-intf site-self, reachableMap-server Uptime ACK Domain-ID192.168.0.201 6d06h Yes 0192.168.0.202 6d06h Yes 0
If the MAC address of the gateway is correctly learned and the ACK flag has been marked as "Yes" for the Fabric Control planes, this stage is considered completed.
DHCP Broadcast Bridged in L2 Flooding
Without DHCP Snooping enabled, DHCP Broadcasts are not blocked and are encapsulated in multicast for Layer 2 Flooding. Conversely, if DHCP Snooping is enabled, the flood of DHCP Broadcast packets is prevented.
BorderCP-1#show ip dhcp snoopingSwitch DHCP snooping is enabledSwitch DHCP gleaning is disabledDHCP snooping is configured on following VLANs:1001DHCP snooping is operational on following VLANs:1001 <-- VLAN31 should not be listed, as DHCP snooping must be disabled in L2 Only pools.Proxy bridge is configured on following VLANs:noneProxy bridge is operational on following VLANs:none
<snip>
Because DHCP Snooping is not enabled in the L2Border, DHCP Snooping Trust configuration is not needed.
At this stage, L2LISP ACL validation is already done in both devices.
Utilize the configured broadcast-underlay group for the L2LISP instance and the L2Border Loopback0 IP address to verify the L2 Flooding (S,G) entry that will bridge this packet to other Fabric Nodes. Consult the mroute and mfib tables to validate parameters such as the incoming interface, outgoing interface list, and forwarding counters.
BorderCP-1#show ip int loopback 0 | i InternetInternet address is 192.168.0.201/32BorderCP-1#show run | se 8232interface L2LISP0.8232instance-id 8232remote-rloc-probe on-route-changeservice etherneteid-table vlan 1031broadcast-underlay 239.0.17.1BorderCP-1#show ip mroute 239.0.17.1 192.168.0.201 | be \((192.168.0.201, 239.0.17.1), 1w5d/00:02:52, flags: FTAIncoming interface: Null0, RPF nbr 0.0.0.0 <-- Local S,G IIF must be Null0Outgoing interface list:TenGigabitEthernet1/0/42, Forward/Sparse, 1w3d/00:02:52, flags: <-- Edge1 Downlink
TenGigabitEthernet1/0/43, Forward/Sparse, 1w3d/00:02:52, flags: <-- Edge2 DownlinkBorderCP-1#show ip mfib 239.0.17.1 192.168.0.201 countForwarding Counts: Pkt Count/Pkts per second/Avg Pkt Size/Kilobits per secondOther counts: Total/RPF failed/Other drops(OIF-null, rate-limit etc)Default13 routes, 6 (*,G)s, 3 (*,G/m)sGroup: 239.0.17.1Source: 192.168.0.201,SW Forwarding: 1/0/392/0, Other: 1/1/0HW Forwarding: 92071/0/102/0, Other: 0/0/0 <-- HW Forwarding counters (First counter = Pkt Count) must increaseTotals - Source count: 1, Packet count: 92071

Tip: If an (S,G) entry is not found or the Outgoing Interface List (OIL) contains no Outgoing Interfaces (OIFs), it indicates an issue with the underlay multicast configuration or operation.
With these validations, along packet captures similar to the previous steps, we conclude this section, as the DHCP Offer will be forwaded as a broadcast to all Fabric Edges using the outgoing interface list contents, in this case, out of interface TenGig1/0/42 and TenGig1/0/43.
DHCP Offer and ACK - Broadcast - Edge
Exactly as the previous flow, we now check the L2Border S,G in the Fabric Edge, where the incoming interface points towards the L2BN and the OIL contains the L2LISP instance mapped to VLAN 1031.
Edge-1#show vlan id 1031VLAN Name Status Ports---- -------------------------------- --------- -------------------------------1031 L2_Only_Wireless active L2LI0:8232, Te1/0/2, Te1/0/17, Te1/0/18, Te1/0/19, Te1/0/20, Ac2, Po1Edge-1#show ip mroute 239.0.17.1 192.168.0.201 | be \((192.168.0.201, 239.0.17.1), 1w3d/00:01:52, flags: JTIncoming interface: TenGigabitEthernet1/1/2, RPF nbr 192.168.98.2 <-- IIF Te1/1/2 is the RPF interface for 192.168.0.201 (L2BN RLOC)aOutgoing interface list:L2LISP0.8232, Forward/Sparse-Dense, 1w3d/00:02:23, flags:Edge-1#show ip mfib 239.0.17.1 192.168.0.201 countForwarding Counts: Pkt Count/Pkts per second/Avg Pkt Size/Kilobits per secondOther counts: Total/RPF failed/Other drops(OIF-null, rate-limit etc)Default13 routes, 6 (*,G)s, 3 (*,G/m)sGroup: 239.0.17.1Source: 192.168.0.201,SW Forwarding: 1/0/96/0, Other: 0/0/0HW Forwarding: 76236/0/114/0, Other: 0/0/0<-- HW Forwarding counters (First counter = Pkt Count) must increaseTotals - Source count: 1, Packet count: 4

Tip: If an (S,G) entry is not found, it indicates an issue with the underlay multicast configuration or operation. If the L2LISP for the requried instance is not present as OIF, it indicates an issue with the operation UP/DOWN status of the L2LISP sub-interface or the IGMP enablement status of the L2LISP interface.
L2LISP ACL validation is already done in both devices.
After the packet is de-encapsulated and placed on the VLAN matching VNI 8232, its broadcast nature dictates that it is flooded out all wired Spanning Tree Protocol forwarding ports for VLAN1031.
Edge-1#show spanning-tree vlan 1041 | be InterfaceInterface Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type------------------- ---- --- --------- -------- --------------------------------Te1/0/2 Desg FWD 20000 128.2 P2p EdgeTe1/0/17 Desg FWD 2000 128.17 P2pTe1/0/18 Back BLK 2000 128.18 P2pTe1/0/19 Desg FWD 2000 128.19 P2pTe1/0/20 Back BLK 2000 128.20 P2p
However, the interface we are looking for to broadcast the DHCP Offer is the Access-Tunnel interface associated with the Access-Point. This is only possible because "flood access-tunnel" is enabled on the L2LISP IID 8232, otherwise this packet is blocked to be forwarded to the AccessTunnel interface.
Edge-1#show lisp instance-id 8232 ethernet | se Multicast FloodMulticast Flood Access-Tunnel: enabledMulticast Address: 232.255.255.1Vlan ID: 1021Edge-1#show ip igmp snooping groups vlan1021 232.255.255.1Vlan Group Type Version Port List-----------------------------------------------------------------------1021 232.255.255.1 igmp v2 Te1/0/12 <-- AP1 Port
With the IGMP snooping entry for the multicast flooding group, DHCP Offers and ACKs are forwarded to the AP's physical port.
The DHCP Offer and ACK process remains consistent. Without DHCP Snooping enabled, no entries are created in the DHCP Snooping table. Consequently, the Device-Tracking entry for the DHCP-enabled endpoint are generated by gleaned ARP packets. It is also expected that commands like "show platform dhcpsnooping client stats" display no data, as DHCP snooping is disabled.
Edge-1#show device-tracking database interface Ac2 | be NetworkNetwork Layer Address Link Layer Address Interface vlan prlvl age state Time leftARP 172.16.131.4 4822.54dc.6a15 Ac2 1031 0005 45s REACHABLE 207 s try 0Edge-1#show ip dhcp snooping binding vlan 1041MacAddress IpAddress Lease(sec) Type VLAN Interface------------------ --------------- ---------- ------------- ---- --------------------Total number of bindings: 0
DHCP Offer and ACK - Unicast - L2 Border
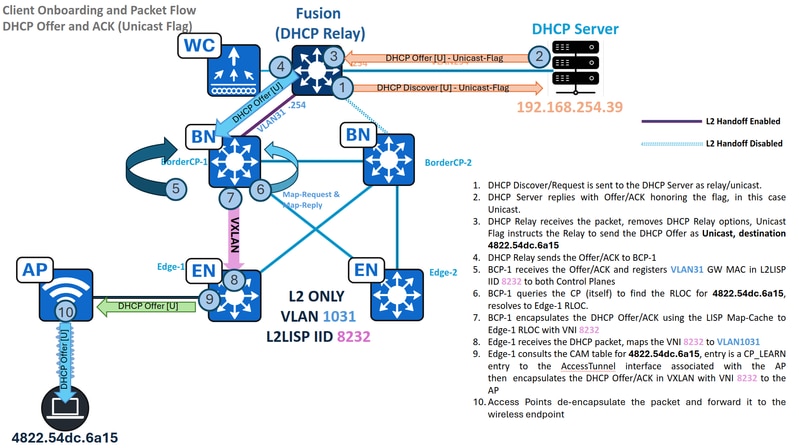 Traffic Flow - Unicast DHCP Offer and ACK in L2 Only
Traffic Flow - Unicast DHCP Offer and ACK in L2 Only
Here the scenario is a bit different, the endpoint sets the DHCP Broadcast Flag as unset or "0".
The DHCP Relay does not send the DHCP Offer/ACK as Broadcast, but as a unicast packet instead, with a destination MAC address derived from the client hardware address inside the DHCP payload. This drastically modifies the way the packet is handled by the SD-Access fabric, it uses the L2LISP Map-Cache to forward the traffic, not the Layer 2 Flooding multicast encapsulation method.
Fabric Border/CP (192.168.0.201) packet catpure: Ingress DHCP Offer
BorderCP-1#show monitor capture cap buffer display-filter "bootp.type==1 and dhcp.hw.mac_addr==4822.54dc.6a15" detailed | sect DynamicDynamic Host Configuration Protocol (Discover)Message type: Boot Request (1)Hardware type: Ethernet (0x01)Hardware address length: 6Hops: 0Transaction ID: 0x00002030Seconds elapsed: 0Bootp flags: 0x0000, Broadcast flag (Unicast)0... .... .... .... = Broadcast flag: Unicast.000 0000 0000 0000 = Reserved flags: 0x0000Client IP address: 0.0.0.0Your (client) IP address: 0.0.0.0Next server IP address: 0.0.0.0Relay agent IP address: 0.0.0.0Client MAC address: 48:22:54:dc:6a:15 (48:22:54:dc:6a:15)
In this scenario, L2 Flooding is exclusively used for Discover/Requests, while Offers/ACKs are forwarded via L2LISP Map-Caches, simplifying the overall operation. Adhering to unicast forwarding principles, the L2 Border queries the Control Plane for the destination MAC address. Assuming successful "MAC Learning and WLC Notification" on the Fabric Edge, the Control Plane has have this Endpoint ID (EID) registered.
BorderCP-1#show lisp instance-id 8232 ethernet server 4822.54dc.6a15LISP Site Registration InformationSite name: site_uciDescription: map-server configured from Catalyst CenterAllowed configured locators: anyRequested EID-prefix:EID-prefix: 4822.54dc.6a15/48 instance-id 8232First registered: 00:53:30Last registered: 00:53:30Routing table tag: 0Origin: Dynamic, more specific of any-macMerge active: NoProxy reply: YesSkip Publication: NoForce Withdraw: NoTTL: 1d00hState: completeExtranet IID: UnspecifiedRegistration errors:Authentication failures: 0Allowed locators mismatch: 0ETR 192.168.0.101:51328, last registered 00:53:30, proxy-reply, map-notifyTTL 1d00h, no merge, hash-function sha1state complete, no security-capabilitynonce 0xBB7A4AC0-0x46676094xTR-ID 0xDEF44F0B-0xA801409E-0x29F87978-0xB865BF0Dsite-ID unspecifiedDomain-ID 1712573701Multihoming-ID unspecifiedsourced by reliable transportLocator Local State Pri/Wgt Scope192.168.0.101 yes up 10/10 IPv4 noneETR 192.168.254.69:58507, last registered 00:53:30, no proxy-reply, no map-notify <-- Registered by the Wireless LAN ControllerTTL 1d00h, no merge, hash-function sha2state complete, no security-capabilitynonce 0x00000000-0x00000000xTR-ID N/Asite-ID N/Asourced by reliable transportAffinity-id: 0 , 0WLC AP bit: ClearLocator Local State Pri/Wgt Scope192.168.0.101 yes up 0/0 IPv4 none <-- RLOC of Fabric Edge with the Access Point where the endpoint is connected
After the Border's query to the Control Plane (local or remote), the LISP resolution establishes a Map-Cache entry for the endpoint's MAC address.
BorderCP-1#show lisp instance-id 8232 ethernet map-cache 4822.54dc.6a15LISP MAC Mapping Cache for LISP 0 EID-table Vlan 31 (IID 8232), 1 entries4822.54dc.6a15/48, uptime: 4d07h, expires: 16:33:09, via map-reply, complete, local-to-siteSources: map-replyState: complete, last modified: 4d07h, map-source: 192.168.0.206Idle, Packets out: 46(0 bytes), counters are not accurate (~ 00:13:12 ago)Encapsulating dynamic-EID trafficLocator Uptime State Pri/Wgt Encap-IID192.168.0.101 4d07h up 10/10 -<snip>
With the RLOC resolved, the DHCP Offer is encapsulated in unicast and sent directly to Edge-1 at 192.168.0.101, with VNI 8240.
BorderCP-1#show mac address-table address aaaa.dddd.bbbbMac Address Table-------------------------------------------Vlan Mac Address Type Ports---- ----------- -------- -----31 4822.54dc.6a15 CP_LEARN L2LI0BorderCP-1#show platform software fed switch active matm macTable vlan 141 mac aaaa.dddd.bbbbVLAN MAC Type Seq# EC_Bi Flags machandle siHandle riHandle diHandle *a_time *e_time ports Con
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------31 4822.54dc.6a15 0x1000001 0 0 64 0x718eb52c48e8 0x718eb52c8b68 0x718eb44c6c18 0x0 0 1064 RLOC 192.168.0.101 adj_id 1044 NoBorderCP-1#show ip route 192.168.0.101Routing entry for 192.168.0.101/32Known via "isis", distance 115, metric 20, type level-2Redistributing via isis, bgp 65001TAdvertised by bgp 65001 level-2 route-map FABRIC_RLOCLast update from 192.168.98.3 on TenGigabitEthernet1/0/42, 1w3d agoRouting Descriptor Blocks:* 192.168.98.3, from 192.168.0.101, 1w3d ago, via TenGigabitEthernet1/0/42Route metric is 20, traffic share count is 1
With the same methodology as in previous sections, capture traffic both ingress from the DHCP Relay and to the RLOC egress interface to observe the VXLAN encapsulation in unicast to the Edge RLOC.
DHCP Offer and ACK - Unicast - Edge
The Edge receives the unicast DHCP Offer/ACK from the Border, de-encapsulates the traffic and consult its MAC address table to determine the correct egress port. Unlike broadcast Offer/ACKs, the Edge node will then forward the packet only to the specific Access-Tunnel where the endpoint is connected, rather than flood it to all ports.
The MAC address table identifies port AccessTunnel2 as our virtual port associated to AP1.
Edge-1#show mac address-table address 4822.54dc.6a15Mac Address Table-------------------------------------------Vlan Mac Address Type Ports---- ----------- -------- -----1031 4822.54dc.6a15 CP_LEARN Ac2Edge-1#show interfaces accessTunnel 2 descriptionInterface Status Protocol DescriptionAc2 up up Radio MAC: dc8c.37ce.58a0, IP: 172.16.1.7Edge-1#show device-tracking database address 172.16.1.7 | be NetworkNetwork Layer Address Link Layer Address Interface vlan prlvl age state Time leftDH4 172.16.1.7 dc8c.3756.99bc Te1/0/12 1021 0024 6s REACHABLE 241 s try 0(86353 s)Edge-1#show cdp neighbors tenGigabitEthernet 1/0/12 | be DeviceDevice ID Local Intrfce Holdtme Capability Platform Port IDAP1 Ten 1/0/12 119 R T AIR-AP480 Gig 0
The DHCP Offer and ACK process remains consistent. Without DHCP Snooping enabled, no entriess are created in the DHCP Snooping table. Consequently, the Device-Tracking entry for the DHCP-enabled endpoint are generated by gleaned ARP packets, not DHCP. It is also expected that commands like "show platform dhcpsnooping client stats" will display no data, as DHCP snooping is disabled.
Edge-1#show device-tracking database interface te1/0/2 | be NetworkNetwork Layer Address Link Layer Address Interface vlan prlvl age state Time leftARP 172.16.141.1 aaaa.dddd.bbbb Te1/0/2 1041 0005 45s REACHABLE 207 s try 0Edge-1#show ip dhcp snooping binding vlan 1041MacAddress IpAddress Lease(sec) Type VLAN Interface------------------ --------------- ---------- ------------- ---- --------------------Total number of bindings: 0
It is crucial to note that the SD-Access fabric does not influence the use of the Unicast or Broadcast flag, as this is solely an endpoint behavior. While this functionality might be overridden by the DHCP Relay or the DHCP Server itself, both mechanisms are essential for seamless DHCP operation in an L2 Only environment: L2 Flooding with Underlay Multicast for Broadcast Offers/ACKs, and proper Endpoint registration in the Control Plane for Unicast Offer/ACKs.
DHCP Transaction - Wireless Verification
From the WLC, the DHCP transaction is monitored through RA-Traces.
WLC#debug wireless mac 48:22:54:DC:6A:15 to-file bootflash:client6a15RA tracing start event,conditioned on MAC address: 48:22:54:dc:6a:15Trace condition will be automatically stopped in 1800 seconds.Execute 'no debug wireless mac 48:22:54:dc:6a:15' to manually stop RA tracing on this condition.WLC#no debug wireless mac 48:22:54:dc:6a:15
RA tracing stop event,
conditioned on MAC address: 48:22:54:dc:6a:15WLC#more flash:client6a15 | i DHCP2025/08/11 06:13:48.600929726 {wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [sisf-packet] [15981]: (info): RX: DHCPv4 from interface capwap_90000006 on vlan 1 Src MAC: 4822.54dc.6a15 Dst MAC: ffff.ffff.ffff src_ip: 0.0.0.0, dst_ip: 255.255.255.255, BOOTPREQUEST, SISF_DHCPDISCOVER, giaddr: 0.0.0.0, yiaddr: 0.0.0.0, CMAC: 4822.54dc.6a152025/08/11 06:13:50.606037404 {wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [sisf-packet] [15981]: (info): RX: DHCPv4 from interface capwap_90000006 on vlan 1 Src MAC: f87b.2003.7fd5 Dst MAC: 4822.54dc.6a15 src_ip: 172.16.131.254, dst_ip: 172.16.131.4, BOOTPREPLY, SISF_DHCPOFFER, giaddr: 172.16.131.254, yiaddr: 172.16.131.4, CMAC: 4822.54dc.6a152025/08/11 06:13:50.609855406 {wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [sisf-packet] [15981]: (info): RX: DHCPv4 from interface capwap_90000006 on vlan 1 Src MAC: 4822.54dc.6a15 Dst MAC: ffff.ffff.ffff src_ip: 0.0.0.0, dst_ip: 255.255.255.255, BOOTPREQUEST, SISF_DHCPREQUEST, giaddr: 0.0.0.0, yiaddr: 0.0.0.0, CMAC: 4822.54dc.6a152025/08/11 06:13:50.613054692 {wncd_x_R0-0}{1}: [sisf-packet] [15981]: (info): RX: DHCPv4 from interface capwap_90000006 on vlan 1 Src MAC: f87b.2003.7fd5 Dst MAC: 4822.54dc.6a15 src_ip: 172.16.131.254, dst_ip: 172.16.131.4, BOOTPREPLY, SISF_DHCPACK, giaddr: 172.16.131.254, yiaddr: 172.16.131.4, CMAC: 4822.54dc.6a15
At the end of the transaction, the endpoint is added to the Device-Tracking database on the Wireless LAN Controller.
WLC#show wireless device-tracking database mac 4822.54dc.6a15MAC VLAN IF-HDL IP ZONE-ID/VRF-NAME--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------4822.54dc.6a15 1 0x90000006 172.16.131.4 0x00000000fe80::b070:b7e1:cc52:69ed 0x80000001
The entire DHCP transaction is debugged on the Access Point itself.
AP1#debug client 48:22:54:DC:6A:15AP1#term monAP1#
Aug 11 05:37:47 AP1 kernel: [*08/11/2025 05:37:47.3530] [1754890667:353058] [AP1] [48:22:54:dc:6a:15] < wifi0> [U:W] DHCP_DISCOVER : TransId 0x76281006Aug 11 05:37:47 AP1 kernel: [*08/11/2025 05:37:47.3531] chatter: dhcp_req_local_sw_nonat: 1754890667.353086: 0.0.0.0.68 > 255.255.255.255.67: udp 310Aug 11 05:37:47 AP1 kernel: [*08/11/2025 05:37:47.3533] chatter: dhcp_from_inet: 1754890667.353287600: 0.0.0.0.68 > 255.255.255.255.67: udp 310Aug 11 05:37:47 AP1 kernel: [*08/11/2025 05:37:47.3533] chatter: dhcp_reply_nonat: 1754890667.353287600: 0.0.0.0.68 > 255.255.255.255.67: udp 310Aug 11 05:37:49 AP1 kernel: [*08/11/2025 05:37:49.3587] chatter: dhcp_from_inet: 1754890669.358709760: 172.16.131.254.67 > 172.16.131.4.68: udp 309Aug 11 05:37:49 AP1 kernel: [*08/11/2025 05:37:49.3588] chatter: dhcp_reply_nonat: 1754890669.358709760: 172.16.131.254.67 > 172.16.131.4.68: udp 309Aug 11 05:37:49 AP1 kernel: [*08/11/2025 05:37:49.3589] [1754890669:358910] [AP1] [48:22:54:dc:6a:15] <apr0v2> [D:W] DHCP_OFFER : TransId 0x76281006 tag:534Aug 11 05:37:49 AP1 kernel: [*08/11/2025 05:37:49.3671] [1754890669:367110] [AP1] [48:22:54:dc:6a:15] < wifi0> [U:W] DHCP_REQUEST : TransId 0x76281006Aug 11 05:37:49 AP1 kernel: [*08/11/2025 05:37:49.3671] chatter: dhcp_req_local_sw_nonat: 1754890669.367134760: 0.0.0.0.68 > 255.255.255.255.67: udp 336Aug 11 05:37:49 AP1 kernel: [*08/11/2025 05:37:49.3709] [1754890669:370945] [AP1] [48:22:54:dc:6a:15] <apr0v2> [D:W] DHCP_ACK : TransId 0x76281006 tag:536Aug 11 05:37:49 AP1 kernel: [*08/11/2025 05:37:49.3733] [1754890669:373312] [AP1] [48:22:54:dc:6a:15] < wifi0> [D:A] DHCP_OFFER : TransId 0x76281006 [Tx Success] tag:534Aug 11 05:37:49 AP1 kernel: [*08/11/2025 05:37:49.3983] [1754890669:398318] [AP1] [48:22:54:dc:6a:15] < wifi0> [D:A] DHCP_ACK : TransId 0x76281006 [Tx Success] tag:53* U:W = Uplink Packet from Client to Wireless Driver
* D:W = Downlink Packet from Client to Click Module
* D:A = Downlink Packet from Client sent over the air
Revision History
| Revision | Publish Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
19-Aug-2025
|
Initial Release |
Contributed by Cisco Engineers
- Alejandro JonCustomer Delivery Engineering Technical Leader
- Bheem NegiEngineering Technical Leader
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)
 Feedback
Feedback