Introduction
This document describes a new feature introduced in ACI software version 6.1(3f) that simplifies the configuration of an AAEP.
Prerequisites
Requirements
Each Endpoint Group (EPG) has to be explicitly associated with a Physical Domain before it can be deployed on physical ports. Without this association, the EPG could not consume any physical infrastructure, even if the underlying access policies were correctly configured.

Note: The Attachable Access Entity Profile (AAEP) must still be properly configured with domain and VLAN pool associations to avoid Fault F0467 and ensure successful VLAN provisioning at the physical switch interfaces.
Components Used
To utilize this feature, your Cisco ACI software must be running version 6.1(3f) or later.
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, ensure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Benefits
The AAEP direct to EPG association simplifies deployment by allowing an application EPG to be applied to all ports linked to an AAEP in a single configuration step. This approach streamlines policy application across multiple interfaces, which is especially beneficial in large environments with numerous servers or clusters, enhancing operational efficiency and consistency across the fabric.
AAEP automates Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) assignment by linking VLAN pools to the AAEP, ensuring consistent VLAN usage across all associated ports and reducing manual errors.
Configuration Options
EPG to Associated Static AAEP
In the APIC GUI, this setting is found under:
Tenant > tenant_name > Application Profiles > [EPG_Name] > Static AAEP
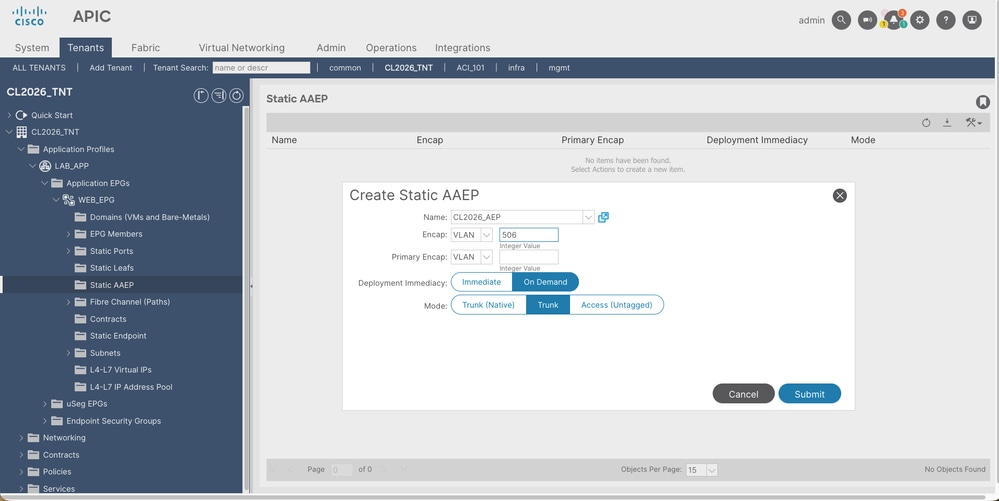
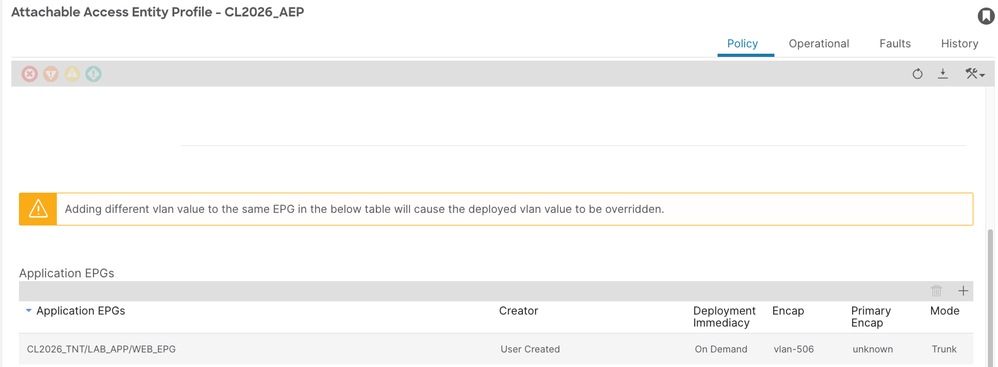
When configuring the policy directly from the EPG, a new instance of the fvRsAepAtt class is created at the APIC level. This object is a direct child of the EPG and establishes a direct reference back to the AAEP.
moquery Output for fvRsAepAtt (EPG-Initiated Association):
Site1-apic1# moquery -c fvRsAepAtt
dn : uni/tn-CL2026_TNT/ap-LAB_APP/epg-WEB_EPG/rsaepAtt-CL2026_AEP
encap : vlan-506
primaryEncap : unknown
When this association is made from the EPG, the corresponding infraRsFuncToEpg object (which represents the relationship from the Attachable Entity Profile to the EPG) this has its creator attribute set to SYSTEM. This indicates that the system automatically created this relationship based on the EPG configuration.
In the APIC GUI, this setting is found under:
Fabric > Access Policies > Policies > Global > Attachable Access Entity Profiles > [AAEP_Name] > Application EPGs
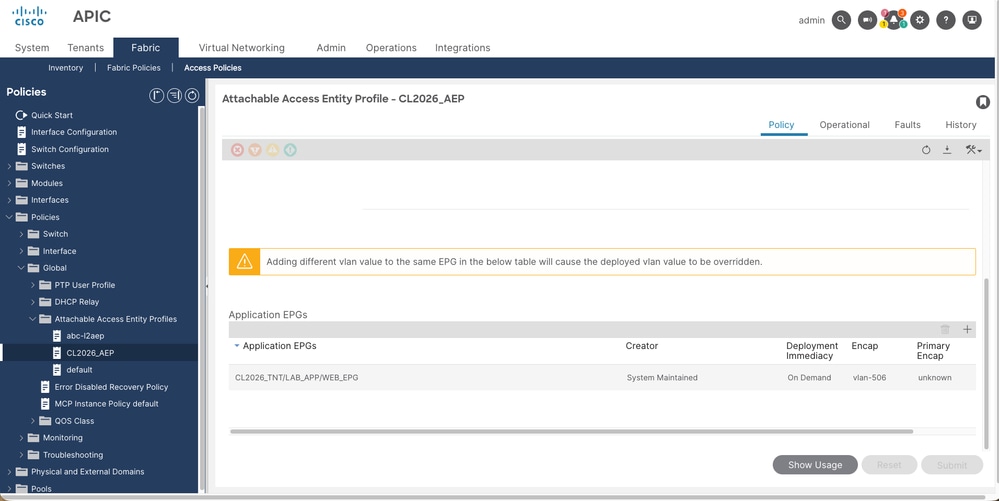
moquery Output for infraRsFuncToEpg (System Maintained):
Site1-Leaf106# moquery -c infraRsFuncToEpg
creator : SYSTEM
dn : uni/infra/attentp-CL2026_AEP/gen-default/rsfuncToEpg-[uni/tn-CL2026_TNT/ap-LAB_APP/epg-WEB_EPG]
encap : vlan-506
primaryEncap : unknown
Relationship between Cisco ACI Classes infraRsFuncToEpg and fvRsAepAtt to fvAEPg:
+----------------------+ +---------------------+
| infraRsFuncToEpg | | fvRsAepAtt |
| (Relation from | | (Relation from |
| Attachable Entity | | EPG to Attachable |
| Profile to EPG) | | Entity Profile) |
+-----------+----------+ +----------+----------+
| |
| |
+-----------+ +---------------+
| |
v v
+---------------------+
| EPG (fvAEPg) |
+---------------------+
A key characteristic of EPG-initiated associations is that the infraRsFuncToEpg object, while referencing the AAEP, cannot be directly deleted from the AAEP configuration. Attempting to do so is expected to result in a validation error:
"Failed to delete object. Validation failed: Can not modify system created mo Dn0=uni/infra/attentp-AAEP/gen-default/rsfuncToEpg-[uni/tn-CL2026_TNT/ap-LAB_APP/epg-WEB_EPG]"
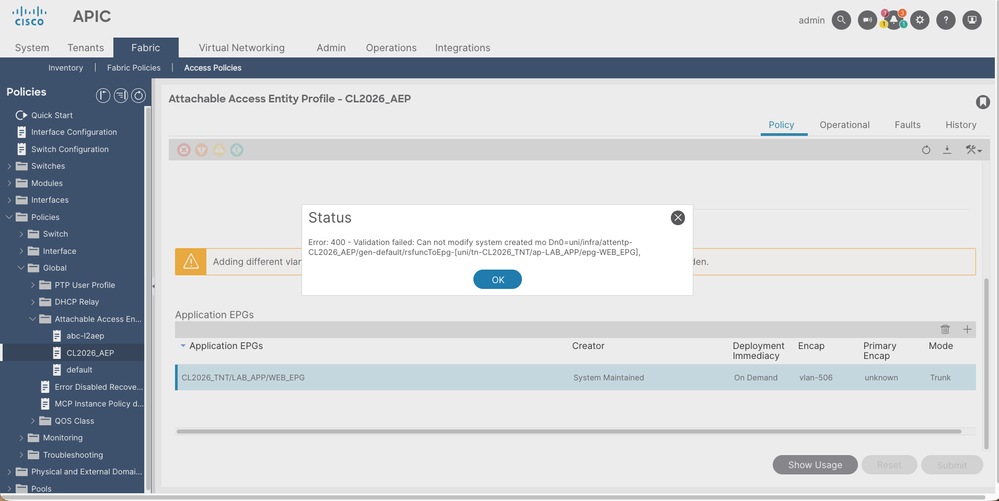
This behavior ensures that the association remains consistent with the EPG configuration. For both configuration options (EPG-initiated or AAEP-initiated), modifications can only be made at the point of initial configuration.
AAEP to Associate EPG
It is important to note that this EPG association capability through AAEP has existed in ACI for multiple releases and is not a newly introduced feature. However, many customers and administrators are not leveraging this functionality because most getting-started guides and training materials focus on the traditional EPG-to-domain association method, making the AAEP-based approach less visible.
In this scenario, the infraRsFuncToEpg object creator attribute is set to USER, indicating that this association was explicitly configured by a user at the AAEP level.
In the APIC GUI, this setting is found under:
Fabric > Access Policies > Policies > Global > Attachable Access Entity Profiles > [AAEP_Name] > Application EPGs
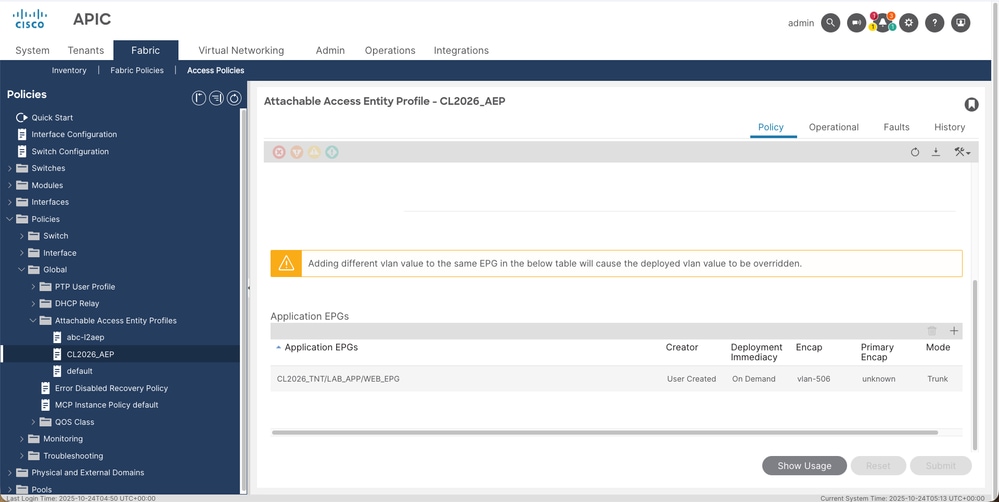
moquery Output for infraRsFuncToEpg (User Created):
Site1-Leaf106# moquery -c infraRsFuncToEpg
creator : USER
dn : uni/infra/attentp-CL2026_AEP/gen-default/rsfuncToEpg-[uni/tn-CL2026_TNT/ap-LAB_APP/epg-WEB_EPG]
encap : vlan-506
primaryEncap : unknown
A notable difference with this configuration option is that the EPG static AAEP configuration does not reflect the policy configured at the AAEP level. This means that while the infraRsFuncToEpg class is created with the creator attribute set to USER, a corresponding fvRsAepAtt object is not automatically generated at the EPG level to visually represent this association to the user.
+----------------------+
| infraRsFuncToEpg |
| (Relation from |
| Attachable Entity |
| Profile to EPG) |
+----------+-----------+
|
|
v
+---------------------+
| EPG (fvAEPg) |
+---------------------+
Verify
At the APIC level:
Site1-apic1# moquery -c vlanCktEp -x 'query-target-filter=wcard(vlanCktEp.encap,"vlan-506")' | egrep "dn|epgDn|name"
dn : topology/pod-1/node-106/sys/ctx-[vxlan-2392066]/bd-[vxlan-16121790]/vlan-[vlan-506]
epgDn : uni/tn-CL2026_TNT/ap-LAB_APP/epg-WEB_EPG
name : CL2026_TNT:LAB_APP:WEB_EPG
At the leaf level:
Site1-Leaf106# show vlan encap-id 506
VLAN Name Status Ports
---- -------------------------------- --------- --------
14 CL2026_TNT:LAB_APP:WEB_EPG active Eth1/20
Troubleshoot
Access Policy Misconfiguration
If the VLAN encapsulation used by an EPG was not properly associated with the domain in the AAEP, Fault F0467 would be raised, preventing VLAN deployment at the switch level. This requires careful coordination between the tenant configuration (EPG/Domain) and the fabric access policies (AAEP/VLAN Pool).
Configuring the EPG to AAEP static association and missing the respective domain association to complete the access policies mapping.
This causes an invalid path association identified by a F0467 fault at the APIC that depending on the Enforce Domain Validation configuration is likely to cause a outage.
Site1-apic1# moquery -c faultInst -f 'fault.Inst.code=="F0467"'
code : F0467
changeSet : configQual:invalid-path, configSt:failed-to-apply, debugMessage:invalid-path: vlan-506 :There is no domain, associated with both EPG and Port, that has required VLAN;, temporaryError:no
descr : Configuration failed for node 106 due to Invalid Path Configuration, debug message: invalid-path: vlan-506 :There is no domain, associated with both EPG and Port, that has required VLAN;
dn : topology/pod-1/node-106/local/svc-policyelem-id-0/uni/epp/fv-[uni/tn-CL2026_TNT/ap-LAB_APP/epg-WEB_EPG]/node-106/attEntitypathatt-[CL2026_AEP]/rsstPathAtt-[sys/conng/path-[eth1/20]]/nwissues/fault-F0467
lastTransition : 2025-10-21T05:33:12.868+00:00
severity : critical
VLAN Override
Related Information
Deploying an EPG through an AEP to Multiple Interfaces Using the APIC GUI
Cisco Application Centric Infrastructure (ACI) Design Guide
Cisco On Demand Library - ACI Objects: How to Avoid Getting Your Configuration Wires Crossed - BRKDCN-2647
Understand ACI Enforce Domain Validation









 Feedback
Feedback