Unleashing the Potential of Private 5G with
Non-Terrestrial Networks White Paper Enabling Seamless, Resilient, and Secure Network Solutions for Limitless Connectivity
Available Languages
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
The relentless evolution of enterprise network requirements for connectivity, security, and scalability has driven organizations to seek solutions beyond traditional terrestrial network boundaries. While private 5G networks are transforming how enterprises orchestrate secure, high-performance wireless connectivity within their premises, many operational landscapes remain out of reach due to geographic remoteness, infrastructure limitations, or disaster scenarios. Non-Terrestrial Networking (NTN) capabilities, as introduced in 3GPP Release 17, bridge this gap by integrating satellite and Low Earth Orbit (LEO)-based high-altitude platforms into the 5G ecosystem, delivering continuous, seamless coverage wherever it is needed.
This white paper presents Cisco’s unique approach, combining its Private 5G-as-a-Service (P5GaaS) and Non-Terrestrial Networking solutions with robust integration with Cisco® Identity Services Engine (ISE), in an architecture that is directly aligned with 3GPP Release 17 standards for NTN. To illustrate the effectiveness of NTN integrated into Cisco’s P5GaaS, this document will also cover the validation and testing using Telesat’s Lightspeed Emulator that simulates Telesat highly innovative global network initially comprised of 198 state-of-the-art Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellites to showcase the potential for customers.
The integration of Cisco NTN with Cisco Private 5G creates a unified network architecture that automatically transitions between terrestrial and satellite connectivity, enabling service providers to deliver seamless, secure communications with single-pane-of-glass management that helps ensure critical connectivity during emergencies while expanding coverage to remote areas and reducing operational complexity.
Cisco ISE permits only authorized users and devices to access network resources, with centralized identity management and granular policy enforcement across both terrestrial and non-terrestrial domains.
We explore how this holistic, standards-based solution empowers enterprises across diverse industries to extend secure, policy-driven, and resilient connectivity to every corner of the globe. Through detailed architectural analysis, practical deployment scenarios, and real-world examples, we demonstrate how Cisco enables the next generation of business-critical infrastructure—anywhere, anytime.
Non-terrestrial network global reach and business resilience
For modern enterprises, the capacity to sustain secure, high-quality connectivity—regardless of location—is not merely a technological advantage, but a fundamental requirement for ensuring operational continuity and overall business success. In an era where digital transformation extends to every corner of the globe, organizations can no longer afford to have their operations constrained by the reach of terrestrial networks. The advent of Non-Terrestrial Network-Enabled (NTN) private 5G fundamentally changes this dynamic, empowering businesses to transcend traditional geographic limitations and maintain seamless communications wherever their operations take them.

Non-terrestrial network Global Reach
One of the most significant benefits of NTN-enabled private 5G is the assurance of operational continuity in the most remote and challenging locations. Industries that manage extensive infrastructure—such as pipelines stretching across continents, high-voltage transmission lines traversing vast territories, offshore oil rigs isolated at sea, remote mining operations in rugged terrain, or fleets constantly on the move—can now monitor, manage, and secure their assets in real time. Even in regions where terrestrial coverage is sparse, unreliable, or nonexistent, NTN provides the connectivity backbone necessary for uninterrupted oversight and control, reducing downtime and increasing efficiency.
NTN also plays a critical role in disaster recovery and emergency response scenarios. When natural disasters strike, when power grids fail, or when cyber incidents disrupt terrestrial networks, enterprises need a resilient and independent layer of communication. NTN delivers this essential redundancy, helping ensure that emergency teams, first responders, and crisis managers remain connected and able to coordinate efforts, even in the most adverse conditions. The ability to maintain reliable communications during such events is vital for mitigating damage, accelerating recovery, and safeguarding lives.
In addition, NTN-enabled connectivity supports organizations in meeting stringent compliance and regulatory mandates. Many industries are obligated to collect, monitor, and report data from remote or distributed sites to satisfy legal, environmental, or safety requirements. Continuous data availability, made possible by NTN’s global reach, ensures that operations remain transparent, auditable, and fully compliant—eliminating gaps that could otherwise lead to regulatory breaches or costly penalties. An example of this approach is to utilize Cisco’s PCA Solution to manage NTN service links as illustrated below.
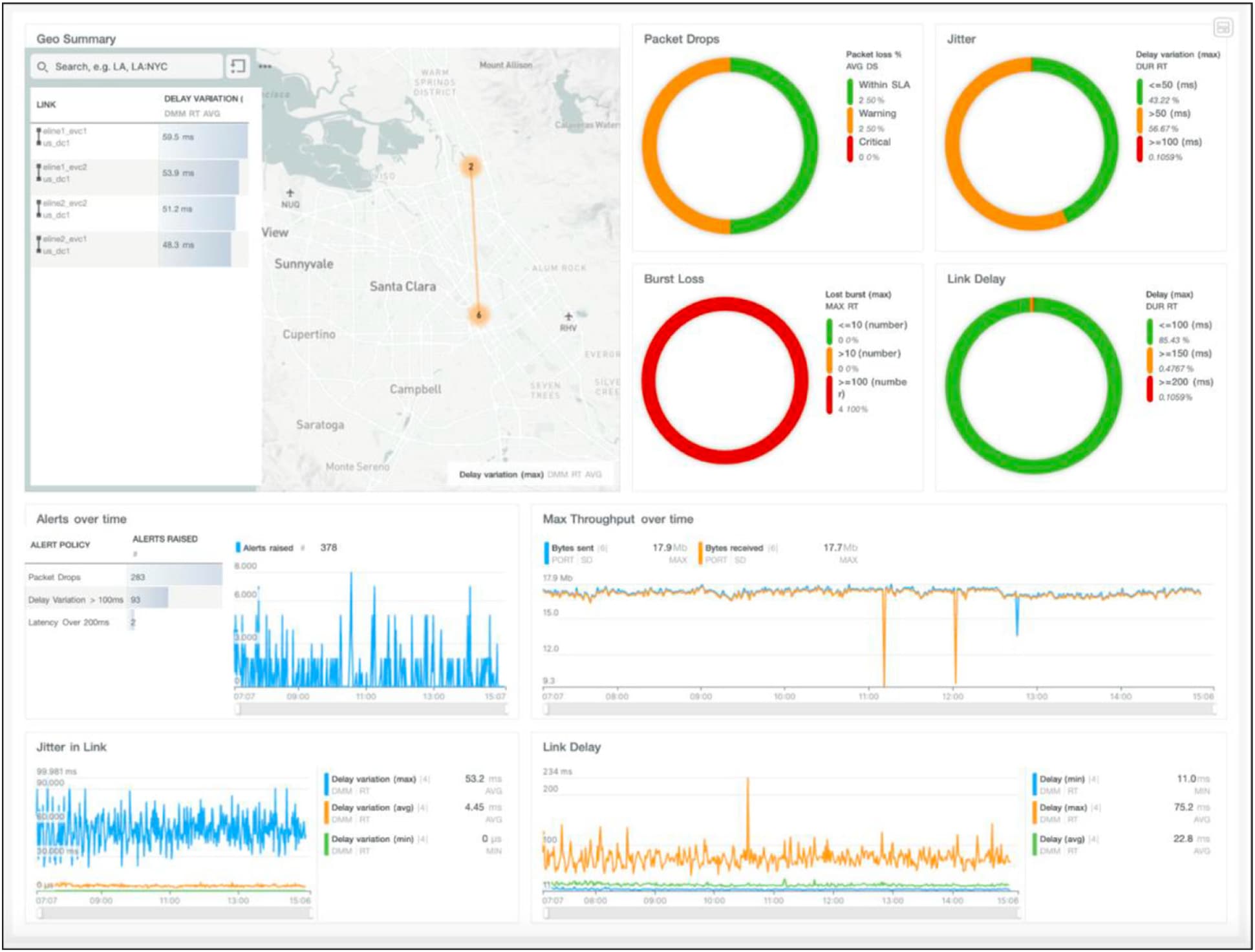
Using Cisco PCA solution’s dashboard to monitor a NTN link deployed for a Private 5G instance.
Finally, the well-being and safety of employees is paramount, particularly for those working in hazardous, isolated, or highly mobile environments. Reliable communication channels are essential for issuing real-time alerts, transmitting video feeds, and enabling voice communications, all of which contribute to a safer workplace. With NTN, organizations can respond quickly to accidents or security incidents, coordinate rescue or evacuation efforts, and maintain contact with personnel regardless of their location. This capability not only enhances worker protection but also reinforces an organization’s commitment to safety and duty of care.
It is therefore clear that NTN-enabled private 5G is a transformative solution that underpins enterprise resilience, regulatory compliance, and the safety of both assets and personnel—making it an indispensable element of modern business infrastructure.
As digital transformation accelerates, enterprises are reimagining their business models, operations, and customer experiences. This transformation relies fundamentally on the ability to connect people, devices, and applications—securely, reliably, and at scale. However, for many organizations, especially those with distributed assets, mobile operations, or critical infrastructure in remote locations, the limitations of terrestrial connectivity—such as cellular dead zones, lack of fiber, and vulnerability to physical disruption—are significant barriers.
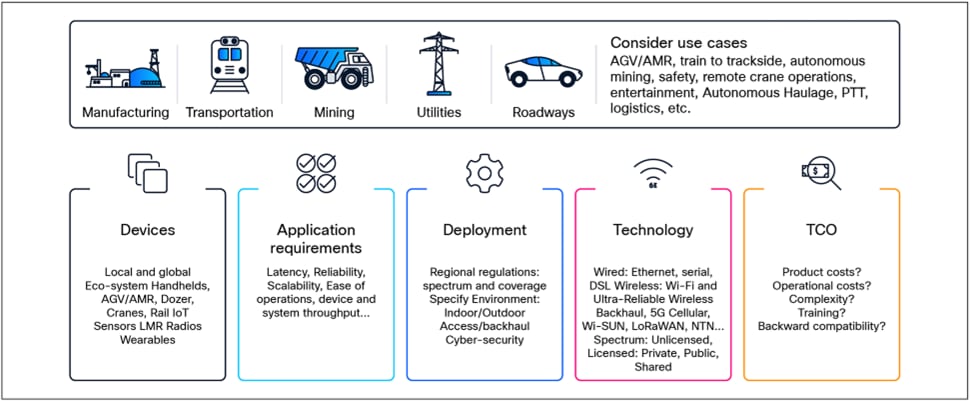
Considerations for deploying a non-terrestrial solution network.
Industries like oil and gas, mining, utilities, transportation, logistics, maritime, and public safety face daily operational challenges due to the lack of coverage in vast or transient geographies. The inability to monitor, manage, and secure remote assets in real time not only impacts productivity but also exposes organizations to safety, compliance, and reputational risks. These gaps are further exposed during natural disasters or emergencies, where terrestrial networks may become unavailable or overloaded, making rapid and coordinated response difficult.
The integration of NTN with private 5G networks is a powerful catalyst for digital transformation, enabling enterprises to pursue new strategies and unlock business value in ways that were previously out of reach. This convergence of advanced wireless technologies not only extends connectivity to the farthest edges of the globe but also empowers organizations to reimagine how they operate, deliver services, and compete in the digital era.
One of the most transformative outcomes of NTN-enabled private 5G is the ability to achieve truly global IoT and asset tracking. Enterprises can now deploy and manage thousands—or even millions—of IoT devices, including sensors, vehicles, containers, and machinery, across vast and distributed supply chains. With continuous, real-time connectivity, organizations gain unprecedented visibility into the status and location of critical assets, no matter how remote or mobile they may be. This capability supports sophisticated use cases such as predictive maintenance—where potential equipment failures can be identified and addressed before they cause disruption—as well as comprehensive asset optimization, which drives efficiency and reduces operational costs on a global scale.
Another major advantage lies in the realm of edge computing local analytics and generative AI at the edge. By integrating edge compute nodes directly into remote or hard-to-reach locations, organizations can process vast amounts of data locally, closer to where it is generated. This approach is especially valuable for latency-sensitive applications such as autonomous vehicles or industrial automation, where split-second decision making is essential. By handling analytics and processing at the edge, enterprises can minimize the need for costly and bandwidth-intensive data backhaul to centralized data centers, resulting in faster responsiveness, reduced network congestion, and significant cost savings.
NTN-enabled private 5G also paves the way for the development and deployment of highly specialized, industry-specific applications. Sectors such as agriculture, fisheries, mining, maritime, and logistics can now harness connectivity for innovative solutions uniquely tailored to their operational environments. For example, precision agriculture can leverage real-time soil and weather data for smarter planting and irrigation; smart fisheries can monitor and protect marine resources; autonomous mining vehicles can safely operate in remote quarries; and connected ships can optimize routes and cargo handling while at sea. These industry-driven innovations not only improve operational efficiency but also open entirely new business models and sources of competitive advantage.
To address these global connectivity challenges, innovation must extend beyond traditional ground-based systems. The addition of support for NTN in the 3GPP Release 17 standard introduces a paradigm shift: by integrating satellite and high-altitude platforms directly into the fabric of 5G, organizations can now achieve ubiquitous, seamless coverage, overcoming the last-mile and last-hundred-mile barriers. When paired with the flexibility, security, and control of private 5G networks, NTN enables enterprises to unify operations, safeguard assets, and unlock new digital initiatives anywhere in the world. This integration extends coverage to remote areas, enhances reliability, and boosts network capacity. The combination enables seamless connectivity and provides critical communication during emergencies, creating a more robust and comprehensive network for service providers.

NTN based architecture and deployment scenarios
Cisco’s vision for seamless global connectivity is built on delivering next-generation infrastructure that integrates Private 5G-as-a-Service (P5GaaS), advanced security and policy management via Cisco ISE, and our Non-Terrestrial Networking solution—all in full compliance with global standards—empowering customers to confidently extend critical operations into even the most remote and challenging environments. By providing a comprehensive set of solutions, Cisco can address a large set of use-cases and requirements enterprise customers need to address.

Cisco Non-Terrestrial Networking Solutions Overview
The flexibility and reach of NTN-enabled private 5G enables enterprises bolstered with the other services such as SD-WAN Managed Services, Security, Service Assurance to name a few allows for novel subscription and service models. Operators can now offer tailored and differentiated offerings—such as premium global tracking services for high-value goods, deployable mobile command centers for rapid response scenarios, or secure pop-up networks for temporary events and remote operations. These new service paradigms allow businesses to expand their portfolios, tap into new revenue streams, and better address the evolving needs of their customers and partners.
In essence, by combining the pervasive coverage of NTN with the robust, secure, and customizable capabilities of private 5G, enterprises equip themselves to drive digital transformation at an unprecedented scale and scope—no matter where their business ambitions take them.
Non-terrestrial networks represent the convergence of satellite, high-altitude platform systems (HAPS), and terrestrial 5G networks into a unified, standards-based architecture. The 3GPP Release 17 specification provides the technical foundation for integrating these diverse access domains, enabling seamless mobility, service continuity, and interoperability. 3GPP’s Release 17 marks a significant milestone in the evolution of global mobile standards, formally incorporating NTN into the 5G ecosystem. Release 17 defines the technical enablers for:
● Radio interface enhancements: Modifications to the 5G NR protocol stack support Doppler compensation, extended timing advance, and adaptive modulation schemes suitable for the long distances and variable link conditions of satellite and airborne platforms.
● Network architecture extensions: Release 17 details functional splits and interfaces for integrating NTN nodes—whether they are satellites, HAPS, or gateways—into the core 5G architecture.
● Mobility management: New procedures ensure seamless handover and session continuity as devices move between terrestrial and non-terrestrial coverage zones.
● Device and application support: Release 17 specifies the operation of both direct-to-device and relay-based NTN connections, supporting a wide range of consumer, enterprise, and industrial use cases.
● Security and quality of service: The standard addresses authentication, encryption, and differentiated service levels to match the requirements of critical and noncritical applications.
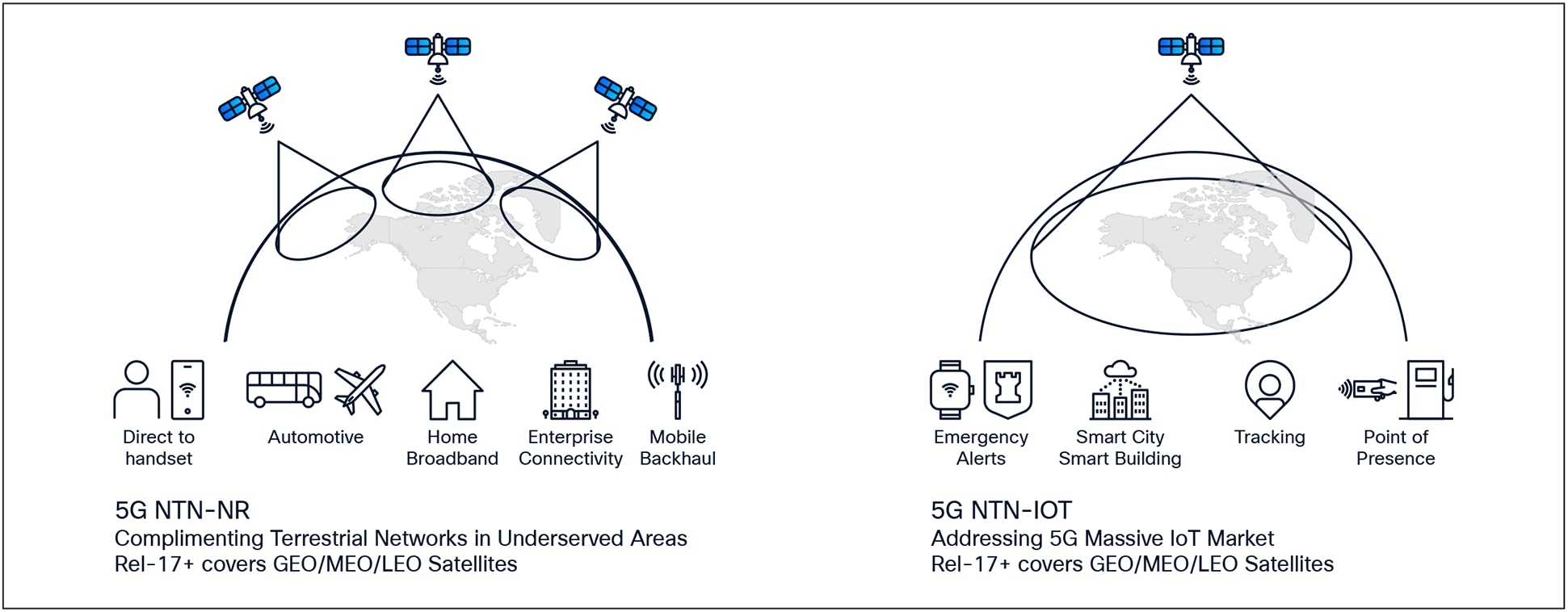
3GPP Release 17 Non-Terrestrial networking scope
3GPP Release 17 Non-Terrestrial networking covers Low, Medium and Geosynchronous Earth Orbit (LEO, MEO and GEO) assets in addition to Unmanned and High-Altitude Vehicle Systems (UAS and HAPS). Each asset covers a range of service capabilities with respect to coverage, latency, throughput, and ground system integration.
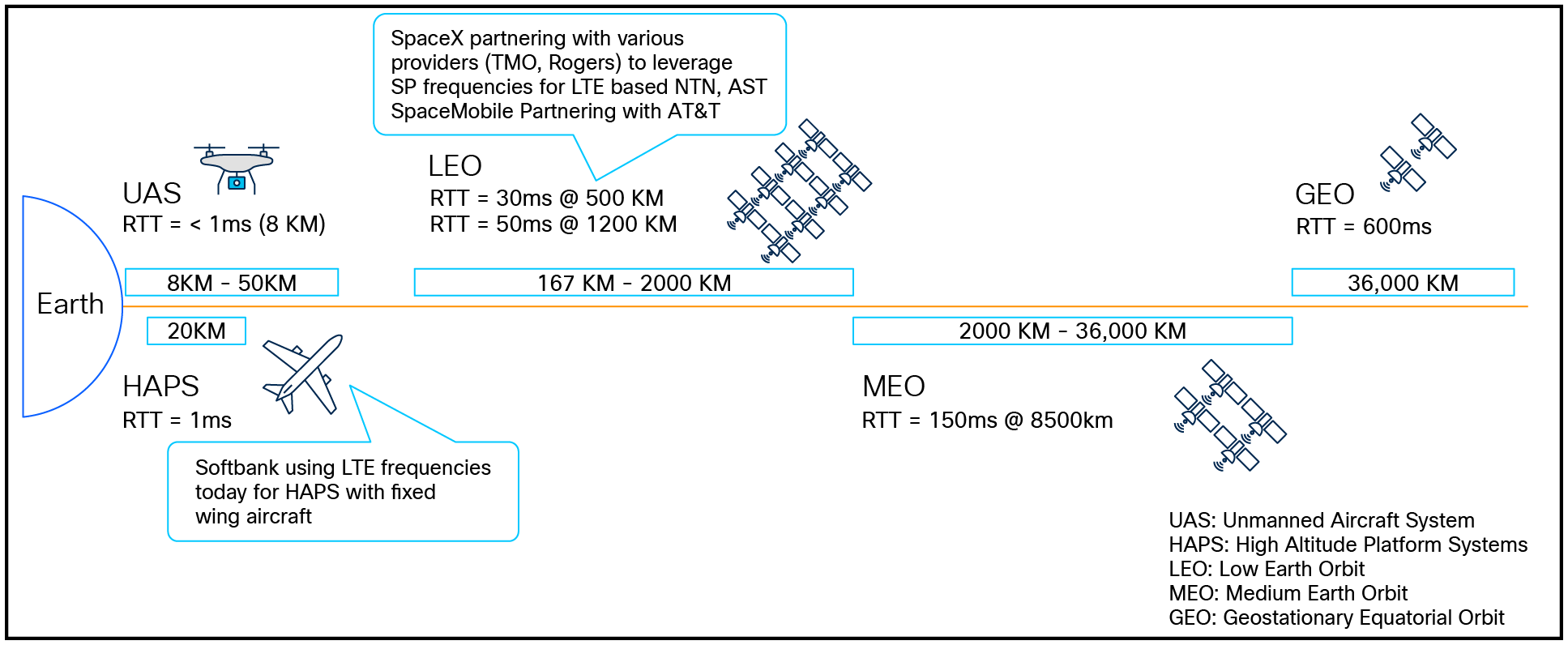
Non-Terrestrial Service Experience
At the foundation of the NTN ecosystem are the standards bodies, such as the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) and the International Telecommunication Union (ITU). These organizations play a pivotal role in shaping the technical specifications and frameworks that guide the development of NTN. Through their collaborative processes, they ensure that all aspects of non-terrestrial integration adhere to globally recognized standards. This harmonization is crucial, as it fosters compatibility across vendors, network operators, and geographic regions, thereby enabling seamless communication and interoperability worldwide.

Non-Terrestrial Network Ecosystem, Source, CCS Insight, Oct-2024
Complementing the work of these standards organizations are the industry alliances, most notably the Global System for Mobile Communications Association (GSMA), O-RAN Alliance, MEF and TM Forum (for for open standards on systems/API integration) . These groups bring together a broad spectrum of industry stakeholders to promote cooperation, drive the adoption of open architectures, and establish best practices for the deployment of NTN technologies. Their efforts are evidenced by the publication of comprehensive white papers and the development of reference implementations, which provide valuable guidance and practical blueprints for enterprises and service providers seeking to adopt NTN solutions.
The landscape is further enriched by satellite operators and HAPS providers, including established names like SES, Eutelsat OneWeb, Telesat, Viasat and Starlink, as well as new entrants developing innovative HAPS technologies. These organizations are actively expanding their service footprints and coverage areas at a rapid pace. By introducing new service offerings and increasing the availability of non-terrestrial connectivity, they are enabling a broader range of use cases and driving the overall growth of the NTN market.
In parallel, device and chipset manufacturers are playing a critical role by bringing to market modules and devices that are compliant with 3GPP Release 17. Their ongoing innovations ensure that enterprises can integrate NTN capabilities into their operations without being constrained by proprietary technologies or vendor lock-in. This growing availability of standardized, interoperable hardware is a key enabler for widespread adoption of NTN solutions.
Finally, the application development community is experiencing significant growth and diversification. Developers are creating a wide array of industry-specific solutions designed to harness the unique capabilities of NTN for sectors such as logistics, agriculture, energy, public safety, and beyond. This vibrant ecosystem of application providers is essential for realizing the full potential of NTN, as it delivers tailored tools and platforms that address the distinct requirements and challenges of each sector.
This collaborative environment helps ensure that enterprises adopting Cisco’s NTN-enabled Private 5G are not only standards-compliant but also future-ready, with access to a broad array of partner capabilities and innovations.
For Enterprise customers, non-terrestrial connectivity is used primarily as a last-mile access technology by enterprises and telecom operators. The satellite ground stations, or gateway sites are typically deployed at the terrestrial partner Point-Of-Presence (POP) site or nearby. Ground-station sites are aggregated at the POP location where satellite operators are deploying their services within a small data center fabric. Hosting services at partner POP locations help satellite operators interconnect with cloud operators, telecom operators, and large enterprises, and deploy internet peering points.
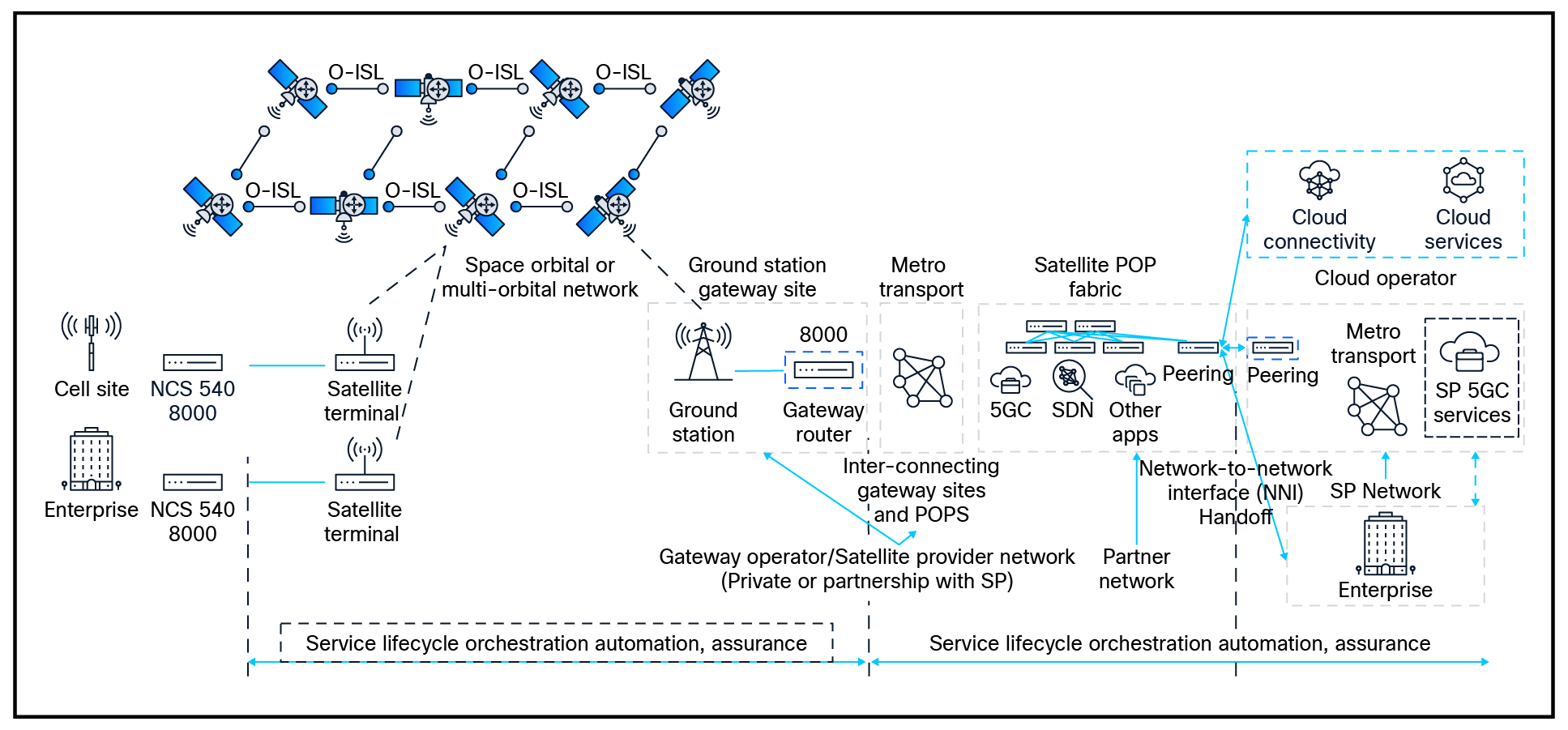
Convergence of terrestrial and non-terrestrial networks.
Key 3GPP NTN Release 17 technology attributes:
● Satellite integration: NTN leverages low Earth orbit, (LEO), medium Earth orbit (MEO), and geostationary Earth orbit (GEO) satellites to deliver wide area 5G coverage. LEO constellations in particular offer low-latency, high-throughput connectivity, supporting bandwidth-intensive and latency-sensitive applications previously limited to terrestrial domains.
● Aerial platforms: HAPS and unmanaged aerial vehicle (UAV)-based 5G base stations provide flexible, on-demand coverage for temporary events, disaster recovery, or areas where deploying terrestrial infrastructure is impractical.
● Seamless handover: Devices can transition between terrestrial and non-terrestrial coverage without service interruption. This is enabled by enhancements to the 5G New Radio (NR) protocol stack to address challenges like Doppler shift, higher propagation delay, and variable link quality inherent in satellite and airborne links.
● Direct-to-device (D2D): Standard 5G handsets, IoT sensors, and industrial devices can connect directly to NTN nodes without specialized satellite hardware, simplifying deployment and lowering costs.
● IoT and mMTC support: NTN networks extend 5G’s promise of massive machine-type communications (mMT C), enabling global-scale IoT deployments for asset tracking, monitoring, and control.
By extending coverage, NTN not only addresses connectivity “blind spots” but also enhances resilience by providing a complementary layer to terrestrial networks. It is this integration of non-terrestrial and terrestrial networking that is enabling seamless, resilient, and secure network Solutions for limitless connectivity demanded by enterprises.
Cisco Private 5G-as-a-Service (P5GaaS)
As part of Cisco’s Mobility Services Platform (MSP), the Cisco Private 5G-as-a-Service offering redefines enterprise wireless connectivity by providing a fully managed, cloud-delivered 5G solution tailored to the unique needs of each customer. P5GaaS abstracts the complexity of network deployment and operation, allowing organizations to focus on outcomes, not infrastructure
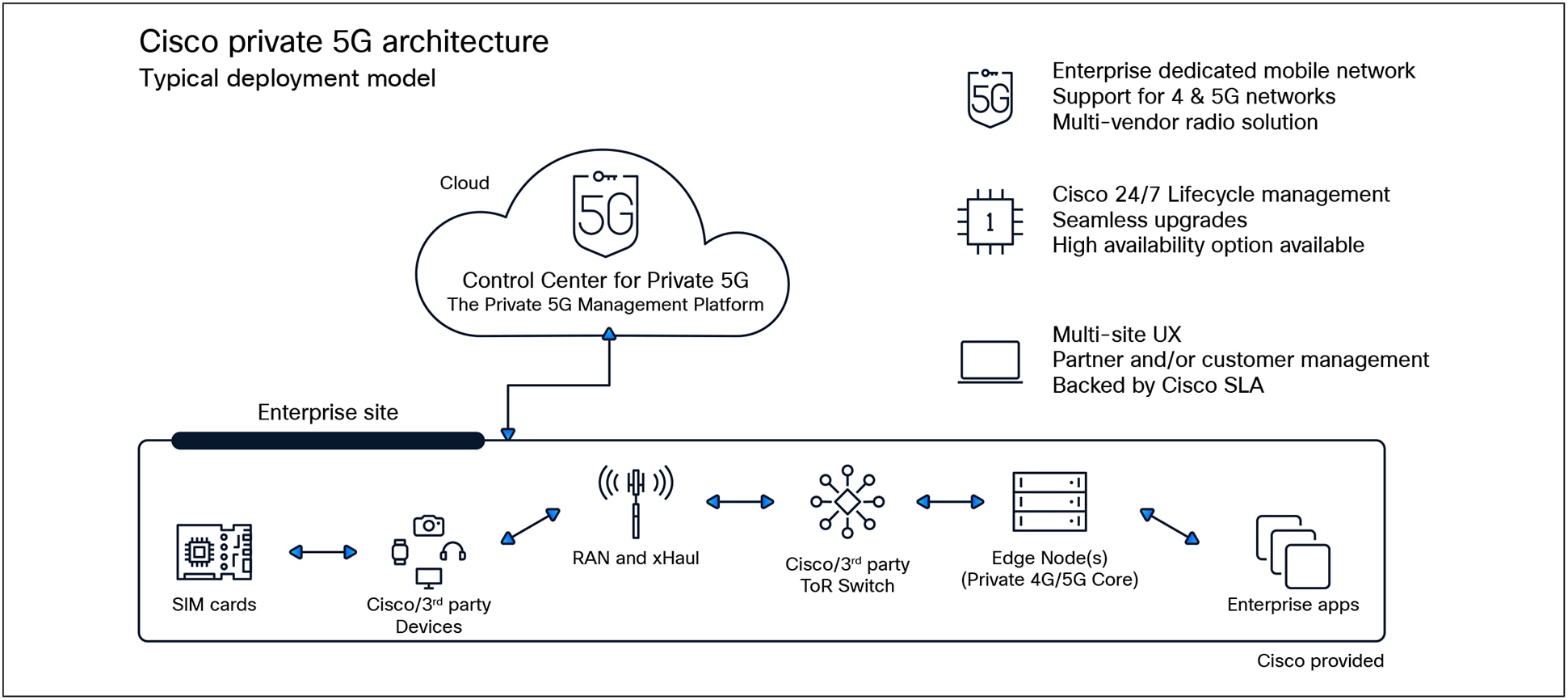
Cisco Private 5G architecture
Cisco P5GaaS solution differentiators for enterprise customers:
● Cloud-native converged 4G/5G core: Cisco’s Private 5G core is built on a cloud-native, microservices-based architecture, providing agility, scalability, and rapid service innovation. The core supports all 5G functions, including user plane, control plane, mobility management, and network slicing.
● Flexible radio access: Customers can deploy any mix of terrestrial gNBs, satellite terminals, and HAPS-based radios, all orchestrated centrally. This flexibility is essential for dynamic or geographically diverse operations.
● Automated lifecycle management: P5GaaS provides zero-touch provisioning, automated upgrades, integrated monitoring, and predictive analytics, reducing operational overhead and risk.
● API-first integration: Rich APIs facilitate seamless integration with enterprise IT/OT systems, enabling rapid onboarding of new devices, users, and applications.
● Service segregation and Quality of Service (QoS): Organizations can define Access Point Name (APN)/Downlink Data Notification (DDN) service slices tailored to specific business units, applications, or regulatory requirements, helping ensure service quality and isolation.
By leveraging Cisco P5GaaS, enterprises gain the confidence to deploy critical applications across any geography, with confidence in the performance, security, and compliance of their network.
Cisco Identity Services Engine (ISE)
A key component in the Cisco P5GaaS solution is the integration with Cisco ISE solution. For enterprise customers, security and policy management are paramount as networks expand beyond traditional boundaries. Cisco ISE serves as the nerve center for identity and access control, helping ensure that only authorized users and devices can access network resources, regardless of where or how they connect.

Cisco ISE: Foundation for Pervasive Enterprise Policy
Cisco ISE offers centralized identity management by integrating with enterprise directories, Public Key Infrastructure (PKI), and device management platforms. This integration creates a single, unified source of truth for user and device identities, spanning both terrestrial and Non-Terrestrial Network (NTN) domains. With ISE, organizations can enforce security policies at a granular level, leveraging a wide range of contextual attributes such as device type, user role, location, time, and compliance posture. This enables dynamic, risk-based access control and network segmentation.
The platform also streamlines device onboarding by supporting certificate-based, SIM-based, and multifactor authentication methods. This makes it easier to securely connect corporate assets, personal (BYOD) devices, and IoT endpoints. ISE provides robust visibility and analytics, offering real-time monitoring and historical reporting that deliver actionable insights for compliance, threat detection, and operational optimization.
As a fundamental component of Cisco’s zero-trust architecture, ISE ensures that every network connection is explicitly authenticated and authorized. It continuously assesses trust throughout the session lifecycle, helping organizations maintain strong security across diverse environments.
By integrating the Cisco ISE with Cisco P5GaaS solution, Cisco is embedding security and policy at the heart of the private wireless network. Cisco ISE helps to ensure that NTN-enabled private 5G deployments meet the highest standards for privacy, compliance, and risk management. Cisco ISE gives enterprise customers granular control on a per-device, per application flow, how NTN based services are to be consumed.
Cisco non-terrestrial networking solution
Cisco’s NTN solution, integrated with Cisco Private 5G, delivers a unified, standards-based infrastructure that extends secure, high-performance connectivity far beyond the limits of terrestrial networks. This powerful combination enables seamless mobility, intelligent policy enforcement, and resilient operations across remote, mobile, and hard-to-reach environments—empowering industries to maintain mission-critical communications anywhere on the planet.
This integration creates a powerful synergy that addresses multiple critical needs for service providers, enabling seamless connectivity and unified operations across diverse and distributed environments. It transforms separate network technologies into a unified, intelligent system that automatically adapts to provide optimal connectivity based on availability and environmental conditions.
In Figure 12, several NTN capable scenarios are available for consideration for Enterprise customers depending on their requirements and use cases. For this white paper, recent interests in the wholesale scenario, specifically the Mplify Alliance (former MEF) Carrier Ethernet based services from LEO satellite service providers have peaked interests as it underscores a unique set of value propositions that was not available before.

Use of MEF based non-terrestrial ethernet services.
LEO satellites (such as Telesat, OneWeb and SpaceX’s Starlink constellation) offer several advantages over Geostationary Earth Orbit (GEO) satellites. LEO satellites orbit the Earth at a much lower altitude, typically between 500 and 2000 kilometers. This results in much lower latency, typically around 25 to 60 milliseconds, making LEO satellites a viable transport for enterprise networking transactions and even real-time applications.
LEO satellites are designed to operate across the Ku or Ka frequency bands, and additionally Ka-band based service offers having more uplink spectrum available for efficient bandwidth deployments. Additionally, LEO satellite constellations consist of many satellites that can work together to provide a wider coverage area and more bandwidth. For satellite operators that are focused primarily on providing broadband services, the connectivity is mostly asymmetric, with the upload bandwidth typically ranging between 5 and 50 Mbps, while the download bandwidth can reach 250 Mbps or more. Newer offers, such as from Telesat Lightspeed which can deliver 1+ Gbps of download to a site, should increase range. As a result of these advantages, LEO satellites are becoming increasingly popular for a wide range of enterprise applications, including mobile broadband, IoT devices, enterprise private VPNs, 5G backhaul, and cloud computing.
For private cellular use cases, LEO based MEF connectivity services are often used to deploy remote or backhaul challenging locations, where rapid deployment is demanded but services for Internet and related Enterprise WAN are often lacking.

Cisco P5GaaS and NTN based MEF L2 for Backhaul
Typically, a L2 based Ethernet-Service is used, although for multiple remote site operations, a L3 based Etherent service is more desirable and typically provided via MNO L3 overlay. Consumed via a Mobile Operator with satellite services, the shift in the industry is clearly heading where enterprises are now directly engaging with satellite operators such as Telesat Lightspeed offer.
Case Study: Cisco P5GaaS Edge N6/SGi and Telesat Lightspeed - Carrier Ethernet Service
Cisco performed a validation and design conformance test for a standard Cisco P5GaaS 5G deployment at the Toronto Innovation Center integrated with a Telesat Lightspeed LEO network emulator service for the purpose to provide backhaul connectivity to the Internet via the P5GaaS Edge’s SGi/N6 interface. This validation step was to showcase the often-requested use-case where a complete remote private 5G deployment needs to be serviced by a Carrier Ethernet service over satellite.
The validation setup components are:
● Radio Access Network (RAN):
◦ Terrestrial 5G gNodeB’s offer local high-capacity coverage.
◦ LEO simulated Satellite terminals with a programmable coverage set of models (based on location) to simulate remote deployment location.
● Cisco Private 5G core (as-a-Service):
◦ Remote deployed cloud-native private 4G/5G core servicing mobility, and session continuity across 4G, 5G and WiFi access types.
◦ Deployed on Cisco UCS computing platform (UCS-C220-M7) which supports enterprise applications requiring ultra-low latency or local data processing.
● Cisco Identity Services Engine (ISE):
◦ Central authority for policy, identity, and access management, helping ensure consistent security across all domains.
◦ Dynamic segmentation and zero-trust enforcement.
◦ Integrated with the Cisco P5GaaS Core.
● Public Cloud based Unified management and analytics:
◦ Single-pane-of-glass dashboard offers visibility, performance analytics, and automation for the Cisco P5GaaS solution.
◦ Integration with Cisco PCA, a proactive, service-centric assurance platform designed to deliver real-time, network-wide visibility and monitoring across complex environments that span multiple vendors, domains, and network layers.
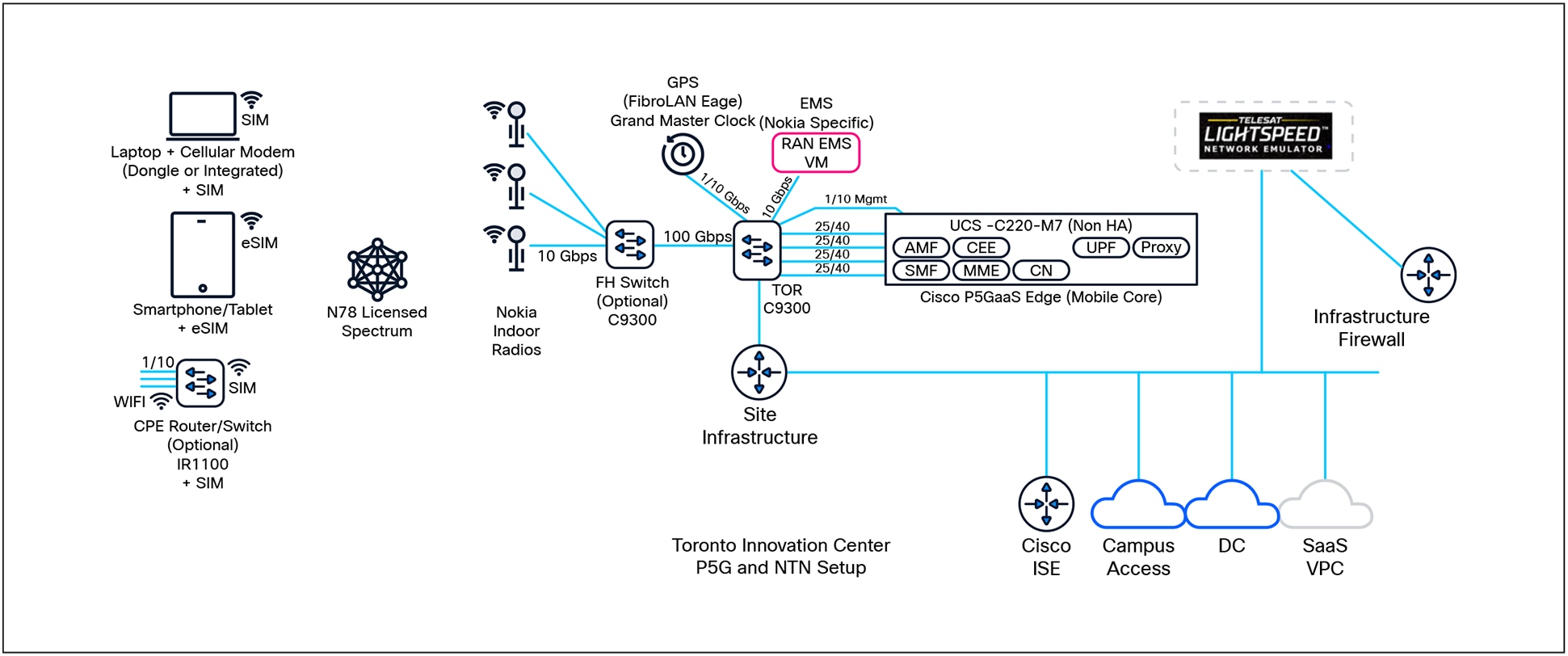
Toronto Innovation Center P5G and Telesat Lightspeed NTN Emulator Setup
The primary goal of this validation exercise is to rigorously assess the integration of the Cisco Private 5G as a Service (P5GaaS) solution with Telesat’s Lightspeed Non-Terrestrial Network (NTN) service Emulator. This deployment leverages a 5G Radio Access Network (RAN) supporting both Cisco and third-party user devices (smartphones, tablets, Cisco industrial Routers, Meraki Gateways), and utilizes Telesat’s Carrier Ethernet E-line service as the main backhaul for the cellular network to the public internet. Through this validation, we aim to demonstrate that LEO-based NTN technology is not only viable but also a high-performing and resilient solution for enterprise-grade backhaul in private 5G deployments. Additionally, Cisco’s Private 5G Control and Assurance (PCA) platform will be used to deliver end-to-end user experience monitoring and service assurance, further underscoring the robustness and transparency of the overal solution.

Telesat's LEO Emulator: Telesat Lightspeed
End-to-End Service Connectivity
A fundamental objective is to ensure seamless end-to-end connectivity for user devices—across both Cisco and diverse third-party 5G endpoints—using the Cisco P5GaaS infrastructure. This involves validating that all devices can successfully register, authenticate, and establish secure data sessions through the private 5G network, with all traffic efficiently backhauled via Telesat’s LEO-based NTN E-line service. The test plan includes scenarios where User Equipment (UE) initiates and maintains connectivity, even as it moves across different radio cells, ensuring that session continuity and service integrity are never compromised.
The setup is configured for a LEO based service between a site in the pacific northwest, and a Telesat PoP in Virginia suported by a set of Landing Stations.
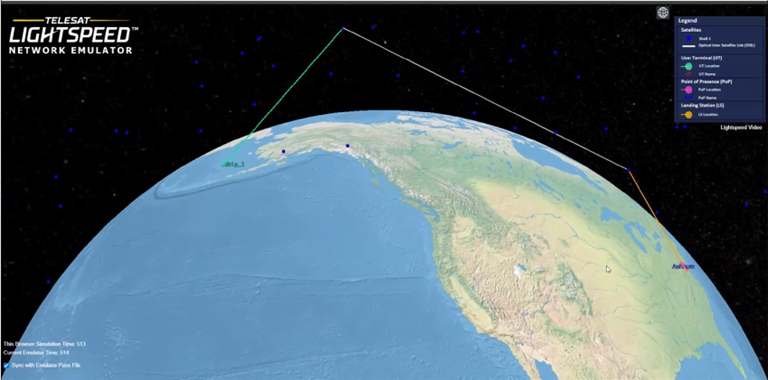
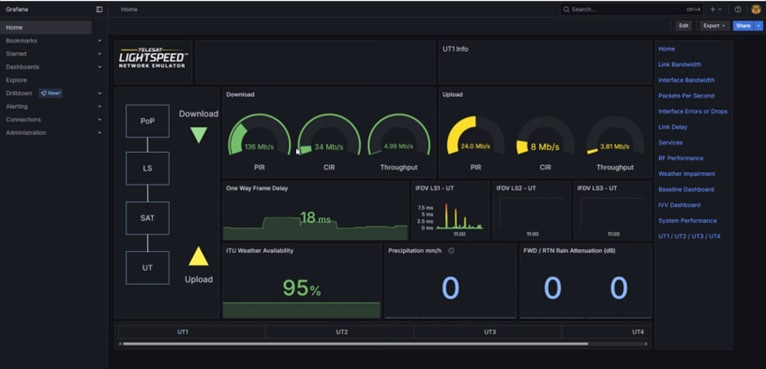
Telesat’s LEO Emulator: UT and POP Selection for Testing
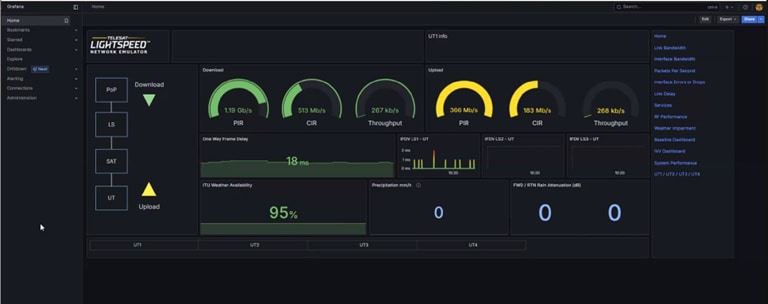
Telesat’s LEO Emulator: E-line service definition and performance profile
Telesat’s LEO Emulator: LEO intra/inter Satellite Profile
This connectivity validation extends to verifying that the Cisco P5GaaS platform can manage device provisioning, policy enforcement, and secure routing of user traffic through the LEO-based backhaul. The solution’s ability to support both static and mobile use cases—such as stationary IoT sensors or mobile enterprise endpoints—will be thoroughly assessed.
Backhaul Performance and Viability
Another crucial aspect of validation is to empirically evaluate the performance and reliability of the LEO-based NTN as the primary backhaul. This assessment will focus on key performance indicators such as throughput, latency, jitter, and packet loss, capturing metrics under typical, peak, and stress-test scenarios. The goal is to benchmark the LEO NTN service against enterprise connectivity standards and to validate its suitability for mission-critical and latency-sensitive applications.
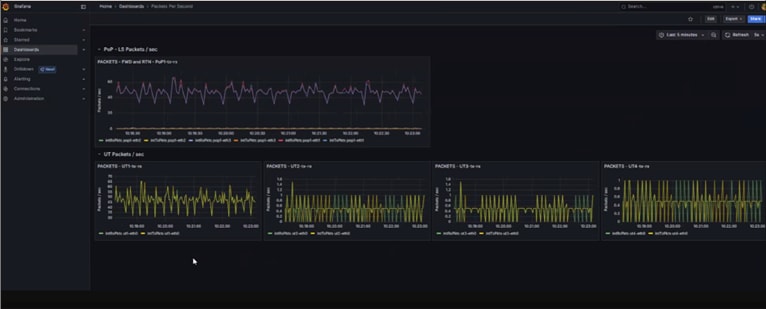
Telesat’s LEO Eimulator: LEO intra/inter Satellite Profile with live traffic
Emphasis will be placed on assessing how LEO’s unique characteristics—such as variable satellite coverage and dynamic handovers—affect overall backhaul quality. The validation will also include resilience testing, where network impairments or failover scenarios are simulated to ensure continued service delivery and rapid recovery in the face of disruptions.
MEF E-Line Service Compliance
Given the reliance on Telesat’s MEF-based E-line service as the backhaul, it is imperative to validate strict compliance with MEF standards. This includes ensuring that the E-line service delivers the expected point-to-point connectivity, bandwidth profiles, and service multiplexing as defined by MEF Carrier Ethernet specifications. Interoperability tests will be conducted to confirm seamless integration between Cisco P5GaaS, the 5G RAN, and third-party network elements, providing confidence that the solution aligns with carrier-class network requirements.
User Experience and Service Assurance with Cisco PCA
To provide both operational transparency and actionable insights, the Cisco PCA platform will be deployed as the central monitoring and assurance tool. The validation will demonstrate PCA’s ability to ingest real-time telemetry from both the RAN and the LEO-based backhaul, presenting a unified view of service health and user experience. Through PCA’s analytics dashboards, operations teams will be able to visualize per-user and per-service experience, rapidly identify issues, and correlate perceived user impact with underlying network metrics.
Proactive assurance will be validated through the triggering of automated alerts and the generation of detailed reports in response to service degradations, SLA breaches, or anomalous behavior. This objective includes validating PCA’s unique value in facilitating root cause analysis and rapid troubleshooting, supporting higher service levels and greater end-user satisfaction.
Multi-Vendor Device Support
To ensure the open ecosystem nature of the solution, validation will include extensive testing with a representative set of both Cisco and third-party 5G devices. This objective is to confirm that onboarding, provisioning, and service assurance workflows function seamlessly across heterogeneous device types, without compromising user experience or network security. Interoperability testing will cover device registration, session setup, mobility management, and consistent monitoring via PCA, providing confidence in the solution’s flexibility and scalability.
Validation scenarios and results
Throughput and Latency Test: Simulate high-bandwidth and latency-sensitive applications (e.g., video streaming, real-time control) from UEs connected through the 5G RAN and LEO NTN backhaul. Use PCA to capture and report on performance metrics in real time.

Cisco PCA Dashboard: Latency Summary for Telesat LEO E-line link

Cisco PCA Dashboard: Delay/Jitter details for Telesat LEO E-line link
Mobility and Handover Test: Move active UEs across multiple radio cells, validating uninterrupted session continuity and minimal performance degradation. PCA analytics will be used to track and visualize user experience throughout the mobility event.
Impairment and Resilience Test: Introduce controlled satellite backhaul impairments (such as increased latency or dropped packets), and verify PCA’s ability to detect, alert, and document the impact on both network and user experience. Confirm that recovery and failover mechanisms operate effectively.

Cisco PCA Dashboard: Delay details Telesat LEO E-line link during LEO handover
Case Study Summary: Technical and Performance Validation
The validation and conformance testing initiative successfully demonstrated the seamless integration of the Telesat Lightspeed NTN emulator within the Cisco P5GaaS environment. This crucial step validates the compatibility and interoperability between Telesat's emulated satellite network and Cisco's private cellular solution, laying a foundational groundwork for future developments and deployments for enterprise customers in the real-world.
Across all test scenarios, performance metrics consistently indicated stable latency and minimal packet loss, underscoring the robustness and efficiency of the integrated system. These results are highly encouraging, suggesting that the combined architecture can maintain high-quality data transmission even under simulated LEO conditions.
Under certain corner cases regarding specific UTs, obeservations regarding jitter and mis-ordered packets were also made. While overall performance was strong, specific findings related to these metrics will be detailed in the comprehensive report, providing deeper insights into the network's behavior and potential areas for optimization.
Based on the outcomes of this testing and validation phase, Cisco is embarking on completing further field testing to include exploring higher traffic loads to stress-test the system's limits, evaluating different QoS (Quality of Service) configurations, and conducting long-duration stability tests to identify any subtle performance degradations over time. These next steps will help refine the integration and ensure optimal performance for Telesat LEO Constellation's services.
Empowering Enterprise Innovation & Unlocking Ubiquity Through Converged NTN and Private 5G Networks
As enterprises accelerate their digital transformation, network boundaries are extending far beyond traditional infrastructure.
Integrating Cisco Private 5G with Cisco’s NTN solution unlocks seamless, secure, and globally available connectivity—extending enterprise-grade performance to even the most remote or mobile environments. This synergy empowers industries to maintain continuous operations across land, sea, and air, transforming the reach and resilience of modern networks.
Built on open standards and integrated with leading network, identity, and policy management, Cisco’s combined solution empowers organizations to achieve global, secure, and resilient connectivity. These converged technologies will help CSPs significantly reduce costs, generate new revenue streams, and deliver ubiquitous coverage. By bridging terrestrial and non-terrestrial domains, Cisco provides not just a network, but a foundation for innovation—enabling new business models, improving operational efficiency, and safeguarding critical assets worldwide.
● To learn more about Cisco Non-Terrestrial Networking, visit www.cisco.com/go/NTN.
● To learn more about Cisco Private 5G, visit Cisco’s P5GaaS Solution
● To learn more about Cisco’s Mobility Services Platform, visit www.cisco.com/go/mobility-services-platform.
● To schedule a demonstration of Cisco’s Private 5G and NTN solutions, contact your Cisco sales representative.
● 3GPP TS 22.261: Service requirements for the 5G system; Stage 1, www.3gpp.org.
● 3GPP TS 38.821: Solutions for NR to support non-terrestrial networks, www.3gpp.org.
● GSMA. Non-Terrestrial Networks: 5G and beyond. 2023. gsma.com
● Cisco’s P5GaaS Solution overview
● Cisco Identity Services Engine. https://www.cisco.com/site/us/en/products/security/identity-services-engine/index.html
● O-RAN Alliance: NTN White Papers, o-ran.org
● SES. Satellite-Enabled 5G Networks: Use Cases and Opportunities, ses.com
● Inmarsat: Private 5G and NTN for Industry White Paper, 2024, viasat.com
● Telesat: 5G's future is hybrid – the non-terrestrial opportunity" white paper, telesat.com